Brain Research 887 (2000) 465–468
www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Short communication
Expression of 5-HT
1Areceptor mRNA in rat nucleus raphe magnus
neurons after peripheral inflammation
a,b a a a a ,
*
Yu-Qiu Zhang
, Xiu Gao , Zhi-Lan Yang , Ya-Lin Huang , Gen-Cheng Wu
a
State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, Department of Neurobiology, Medical Center of Fudan University, 138 Yi Xue Yuan Road,
Shanghai200032, China
b
Key Laboratory of Neurobiology, Shanghai Institute of Physiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 320 Yue Yang Road, Shanghai 200031, China
Accepted 19 September 2000
Abstract
The present study demonstrated that 5-HT1Areceptor mRNA was expressed with moderate level in the NRM neurons. Most of 5-HT1A
receptor mRNA positive cells were 5-HT neurons, suggesting the majority of 5-HT1Areceptor in the NRM might be autoreceptors. Eight hours after carrageenan inflammation, the expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the NRM neurons, especially in the 5-HT neurons, was significantly increased. These results suggest that synthesis of 5-HT1A receptors, including 5-HT1Aautoreceptors, is increased in the NRM during peripheral inflammation. 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Theme: Neurotransmitters, modulators, transporters and receptors
Topic: Topic: serotonin receptor
Keywords: 5-HT1A receptor mRNA; Carrageenan inflammation; In situ hybridization; Fluorescent in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry; Nucleus raphe magnus
NRM is thought to be a major source of the descending inflammation (unpublished results), suggesting that the 5-HT fibers terminating in the spinal cord. It contains a lot expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in spinal cord is of 5-HT neurons and 5-HT receptors, especially 5-HT1A related to inflammatory process. It is not known whether receptor [2,14]. It has been reported that iontophoresis of the expression of 5-HT1A receptor in brain, especially in 5-HT1A agonist reduced the spontaneous firing of most of the 5-HT neurons of the NRM, will changes with peripher-the NRM neurons (87%) [7]. Intracellular recording has al inflammation. The aim of the present study is to also shown that 5-HT hyperpolarized 5-HT neurons in the examine the expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the NRM, and the hyperpolarization could be mimicked by the NRM, especially in the 5-HT neurons following car-5-HT receptor agonist 5-CT and car-5-HT1 1A receptor agonist rageenan inflammation.
8-OH-DPAT or antagonized by the 5-HT1A receptor Male Sprague–Dawley rats (220–250 g) were used in antagonists NAN-190 and spiperone [1,4,9,10]. Generally, this study. The peripheral inflammation was induced by the 5-HT1A receptor-mediated the synaptic inhibition, at intraplantar injection of carrageenan [l-carrageenan, least in part, may act through dendritic autoreceptors Sigma, 3 mg / 150ml of normal saline (0.9% NaCl, NS)] in
[5,13]. the right hindpaw. Rats were perfused at 1, 3, 8 or 24 h
Several lines of evidence have implicated that the raphe- after intraplantar injection of carrageenan. Vehicle-injected spinal 5-HT system is involved in modulating nociception. control rats received an intraplantar injection of 150ml NS Recent studies from our laboratory have shown that the and were perfused at 8 h after NS injection. Non-stimu-expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in ipsilateral spinal lated control rats were kept free movement in their home dorsal horn were markedly increased following peripheral cages before perfusing. All animals were given an over-dose of Urethane (1.5 g / kg, i.p.) and perfused transcardial-ly with 200 ml NS followed by 300 ml 4%
paraformal-*Corresponding author. Tel.:186-21-6404-1900, ext. 2397; fax:1
86-dehyde in 0.1 M phosphate-buffer (PB, PH 7.4). The brain
21-6417-4579.
E-mail address: [email protected] (G.-C. Wu). were removed and post-fixed in the same fixative solution
466 Y.-Q. Zhang et al. / Brain Research 887 (2000) 465 –468
for 4 h at 48C, and immersed in 30% sucrose in PB for probe, overdose unlabeled probe or omitting probe in 24–48 h at 48C for cryoprotection. Thirty micrometer-thick hybridization solution as well as RNAase pretreatment. coronal frozen sections were cut and collected in cryop- The specificity of the antibody was verified by both rotectant solution (0.05 M PB, 30% sucrose, 30% ethylene omitting the primary antibody during the overnight incuba-glycol) and then stored at 2208C until use. tion and by the preabsorption experiments.
A 48 mer oligonucleotide probe for rat 5-HT1A receptor 5-TH1A receptor mRNA positive cells, 5-HT positive mRNA (nt 687–734) [8] was synthesized and purified by somata as well as 5-HT1A receptor mRNA and 5-HT-Beijing Bioneer Corporation. The probe was 39 end- immunoreactive (5-HT-IR) double labeled cells were labeled with DIG-11-UTP by using oligonucleotide-tailing counted using a computerized image analysis system kit (Boehringer Mannheim Biochemica, Germany). (Leica Q 500 IW, Germany). The number of positive cells In situ hybridization (ISH) as well as fluorescent ISH was evaluated in six sections through the NRM (10.3–11.3 and fluorescent immunohistochemistry (FIH) double stain- mm caudal to bregma) for each animal. Results were ing were performed as previously described [11,16]. FISH expressed as mean number of positive cells / section6SEM. and FIH double staining sections were observed with Statistical analysis was carried out by ANOVA followed by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) (Leica TCS- the Newman–Keuls post-hoc test. P,0.05 was considered NT, Germany) by using laser beams of 488 and 543 nm statistically significant.
with an appropriate emission filters for FITC (510–525 In non-stimulated and vehicle-injected control rats, nm) and Rhodamine (590–610 nm). An adjacent series of moderate expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA was sections to hybridization were stained with Cresyl Violet to observed in bilateral the NRM (Fig. 1A, B). The number
aid in anatomic localization. of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA positive cells were 39.5862.47
The specificity of DIG-labeled antisense oligonucleotide and 38.7562.41 per section in the contralateral NRM of probe was examined by hybridizing with labeled sense non-stimulated and vehicle-injected rats, respectively.
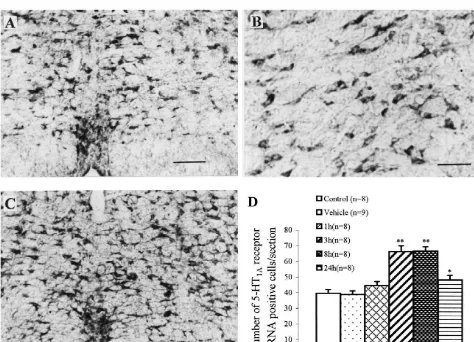
Fig. 1. (A–C) Photomicrographs showing the expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the NRM. (A and B) Vehicle-injected control (at 8 h after intraplantar injection or NS), (C) at 8 h after intraplantar injection of carrageenan. Calibration: A and C: 200mm. B: 80mm. (D) Time-course of 5-HT1A
Y.-Q. Zhang et al. / Brain Research 887 (2000) 465 –468 467
There were not significant differences between either the a clear decrease, but still a substantial number of labeled two control groups (Fig. 1D) or both sides of the NRM cells (Fig. 1D).
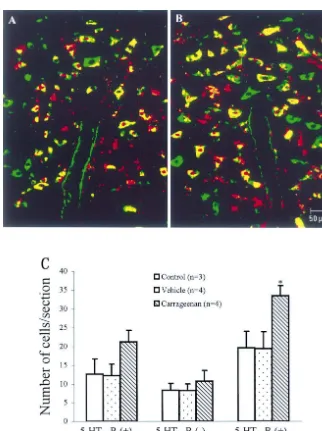
(data not shown). One hour after carrageenan injection, the In non-stimulated and vehicle-injected control groups, expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA had a little increase, about 60% of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA positive cells were but the increase was not statistically significant (ANOVA, 5-HT neurons in the NRM and a few 5-HT-IR cells (about F51.360, P50.278, n58). A maximal number of 5-HT1A 30%) lacked 5-HT1A receptor mRNA (Fig. 2A). Eight receptor mRNA positive cells was observed at 3 and 8 h hours after carrageenan injection, 5-HT1A receptor mRNA after carrageenan injection (Fig. 1C, D) (3 h: 66.1963.77 and 5-HT-IR double labeled cells were significantly in-per section, 8 h: 66.6962.74 per section for contralateral, creased as compared with non-stimulated or vehicle-in-P,0.001, compared with non-stimulated or vehicle-in- jected control rats (Fig. 2B, P,0.05, 33.562.72 per jected rats). Twenty-four hours after carrageenan injection, section vs. 19.6364.41 per section or 19.5064.44 per the expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the NRM had section). 5-HT1A receptor mRNA or 5-HT-IR single
Fig. 2. (A and B) Confocal photomicrographs showing the co-localization of 5-HT1Areceptor mRNA and 5-HT immunoreactivity in the NRM. 5-HT1A
468 Y.-Q. Zhang et al. / Brain Research 887 (2000) 465 –468
labeled cells had a little increase, but no significant for Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 9835) and differences were found between the controls and car- the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (24th). rageenan rats (Fig. 2C).
The present study revealed that 5-HT1A receptor mRNA was expressed with moderate level in the NRM, which
References consisted with the previous immunohistochemical, in situ
hybridization, binding and autoradiographic studies
[1] D.H. Bobker, J.T. Williams, Ion conductance affected by 5-HT
[2,3,15]. FISH with IFH double staining results showed receptor subtypes in mammalian neurons, Trends Neurosci. 13 that most of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA positive cells in the (1990) 169–173.
NRM are 5-HT-IR cells. This supports the result from [2] D.T. Chalmers, S.J. Watson, Comparative anatomical distribution of 5-HT receptor mRNA and 5-HT binding in rat brain-a
com-Sotelo et al. [12] that most 5-HT1A receptor-IR cells in the 1A 1A
bined in situ hybridization / in vitro receptor autoradiographic study,
NRM are 5-HT-IR cells. These data indicate that 5-HT1A Brain Res. 561 (1991) 51–60.
receptors in the NRM were autoreceptors, as expected [3] S. EI Mestikawy, M. Riad, A.M. Laporte, D. Verge, G. Daval, H.´ from previous electrophysiological studies. Golzan, M. Hamon, Production of specific anti-rat 5-HT receptor
1A
The present study demonstrated for the first time that the antibodies in rabbits injected with a synthetic peptide, Neurosci. Lett. 118 (1990) 189–192.
expression of 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the NRM,
[4] R.A. Glennon, N.A. Naiman, M.E. Pierson, M. Titeler, R.A. Lyon,
especially in the 5-HT neurons was markedly increased in
E. Weisberg, NAN-190: an arylpiperazine analog that antagonizes
carrageenan inflammatory rats. It suggests that the syn- the stimulus effects of the 5-HT agonist
8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-pro-1A
thesis of 5-HT1A receptor is increased following car- pyllamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), Eur. J. Pharmacol. 15 (1988)
rageenan inflammation. The peak occurred 3–8 h and then 339–341.
[5] J. Goldfarb, Electrophysiologic studies of serotonin receptor
activa-returned to the baseline at 24 h. This time sale of
tion: answered and unanswered questions,
Neuropsychophamacolo-development corresponds to the time-course of
hy-gy 3 (1990) 435–446.
peralgesia as shown by behavioral study [6], suggesting [6] K. Hargreaves, R. Dubner, F. Brown, C. Flores, J. Joris, A new and that 5-HT1A receptors including 5-HT1A autoreceptors and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous
non-autoreceptors may be involved in inflammatory pro- hyperalgesia, Pain 32 (1988) 77–88.
[7] I.D. Hentall, M.J. Andresen, K. Taguchi, Serotonergic, cholinergic
cess. Together with the findings that the activity of 5-HT1A
and nociceptive inhibition or excitation of raphe magnus neurons in
receptor in the NRM inhibits neuronal activity [1,4,7,9,10],
barbiturate-anesthetized rats, Neuroscience 52 (1993) 303–310.
it is reasonable to assume that the increased expression of [8] C.G. Nebigil, M.N. Garmpvskay, R.F. Spurney, J.R. Raymond, 5-HT1A receptor mRNA in the 5-HT neurons of the NRM Identification of a rat glomerular mesangial cell mitogenic 5-HT2A
might contribute to enhancing the feedback regulation on receptor, Am. J. Phys. 268 (1995) F122–F127.
[9] Z.Z. Pan, M.W. Wessendorf, J.T. Williams, Modulation by serotonin
the activity of central 5-HT neurons. Recent studies in our
of the neurons in rat nucleus raphe magnus in vitro, Neuroscience 54
laboratory (unpublished results) revealed that following
(1993) 421–429.
carrageenan-induced inflammation, the frequency of
back-[10] S.J. Peroutka, 5-HT receptor subtypes: molecular biochemical and
ground activity and nociceptive responses of spinal dorsal physiological characterization, Trends Neurosci. 11 (1988) 496– horn wide dynamic range (WDR) neurons were signifi- 500.
[11] C. Pesold, M.G. Pisu, F. Impagnatiello, D.P. Uzunov, H.J. Caruncho,
cantly increased, and the nociceptive responses threshold
Simultaneous detection of glutamic acid decarboxylase and reelin
obviously decreased. These suggest that the excitability
mRNA in adult rat neurons using in situ hybridization and
immuno-and sensitivity of dorsal horn WDR neurons increase
fluorescence, Brain Res. Protocols 3 (1998) 155–160.
during carrageenan inflammation. Simultaneously, the [12] C. Sotelo, B. Cholley, S. EI Mestikawy, H. Gozian, M. Hamon, extracellular concentrations of 5-HT and 5-HIAA in Direct immunohistochemical evidence of the existence of 5-HT1A
autoreceptors on serotoninergic neurons in the midbrain raphe
lumbar spinal dorsal horn, PAG and NRM were all
nuclei, Eur. J. Neurosci. 2 (1990) 1144–1154.
increased following carrageenan inflammation, suggesting
[13] J.S. Sprouse, G.K. Aghajanian, Electrophysiological responses of
that continuous noxious input causes an increase in 5-HT
serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1Aand 5-HT1Bagonists,
release and turnover during inflammation [17]. The physio- Synapse 1 (1987) 3–9.
logical significance of increased 5-HT1A receptor in the [14] H.W.M. Steinbusch, Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat. Cell bodies and terminals,
NRM may lie in to dampen or prevent excessive neuronal
Neuroscience 6 (1981) 557–618.
activation in response to continuously increasing excitatory
´
[15] D. Verge, G. Daval, A. Patey, H. Gozlan, S. El Mestikawy, M.
input after carrageenan injection. Thus a new balance and
Hamon, Presynaptic 5-HT autoreceptors on serotoninergic cell
stability of 5-HT neuronal activity was formed in in- bodies and / or dendrites but not terminals are of the 5-HT subtype,
1A
flammatory status. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 113 (1985) 463–464.
[16] Y.Q. Zhang, X. Gao, Y.L. Huang, G.C. Wu, Expression of 5-HT1A
receptor mRNA in rat dorsal raphe nucleus and ventrolateral periaqueductal gray neurons after peripheral inflammation,
Neuro-Acknowledgements
Report 11 (2000) (in press).
[17] Y.Q. Zhang, X. Gao, L.M. Zhang, G.C. Wu, The release of serotonin
This project was supported by the National Natural in rat spinal dorsal horn and periaqueductal gray following