Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Meilani
- Pengajar:
- Prof. Dra, Hj. Suwarsih Madya, M.A., Ph.D
- Sekolah: Yogyakarta State University
- Mata Pelajaran: English Language Education
- Topik: Improving Students’ Speaking Skills through Pre-Communicative and Communicative Activities in Class X IS II of SMAN 1 Godean
- Tipe: Thesis
- Tahun: 2016
- Kota: Yogyakarta
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
This chapter sets the stage for the research by outlining the background of the problem, identifying specific issues related to English speaking skills in Class X IS II of SMAN 1 Godean during the 2015-2016 academic year, defining the scope of the research, stating its objectives, and explaining its significance. The background highlights the global importance of English as a lingua franca and the challenges faced in teaching it as a foreign language, particularly in Indonesia. The problem identification section pinpoints shortcomings in teaching methodologies, student confidence, and learning materials. The limitations of the study are clearly defined, focusing on improving speaking skills through pre-communicative and communicative activities. Finally, the objectives and significance sections detail the research's goals and its potential contributions to both theory and practice in English language teaching.
1.1 Background of the Problems
This section establishes the context of the study by discussing the global significance of English and the challenges involved in teaching it in Indonesia's educational system. It highlights the disparity between the importance of English proficiency and the actual skill level of Indonesian students, particularly in speaking. The section uses data from existing literature and the researcher's observations to highlight the need for improved teaching strategies. It cites the Indonesian curriculum and its challenges, the limited teaching time allocated to English, and the generally low English proficiency levels among graduating students. The section also describes the specific situation at SMAN 1 Godean, highlighting the issues of student passivity, the predominance of presentation activities, and the students' lack of confidence in speaking English.
1.2 Problem Identification
This section details the problems identified within the SMAN 1 Godean context, categorized by the teacher's role, students' characteristics and challenges, learning activities employed, learning materials used, and available learning media. The analysis focuses on the teacher's limited time for preparation due to administrative burdens, leading to a lack of activity variation. It then addresses student issues including low confidence, fear of making mistakes, and a lack of meaningful interaction in class. Problems with learning activities are discussed, specifically the lack of variety, the minimal information gap in activities, and the absence of opportunities for genuine communicative interaction. The section also examines the learning materials and media, finding shortcomings in the materials’ suitability for developing speaking skills and the underutilization of the school’s language laboratory.
1.3 Limitation of the Problem
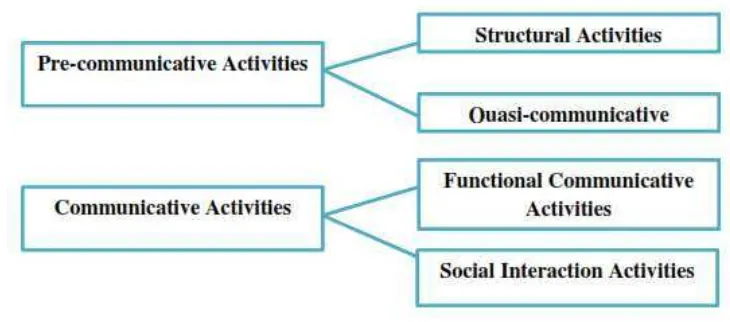
This section outlines the specific focus of the research, narrowing down the broad range of identified problems. The research is limited to improving the speaking skills of Class X IS II students through pre-communicative and communicative activities within the framework of communicative language teaching (CLT). This narrowing of focus allows for a more manageable and in-depth investigation. The decision to focus on speaking skills is justified by their importance, the students' expressed need for improvement, and the suitability of CLT principles for fostering communicative competence. This section emphasizes the intention to create activities that increase student confidence, participation, and interaction.
1.4 Formulation of the Problem
This section presents the central research question: How can the speaking skills of students in Class X IS II of SMAN 1 Godean be improved through pre-communicative and communicative activities? This question guides the research process and forms the basis for the subsequent analysis of findings.
1.5 Objectives of the Research
This section clearly states the research objective: to observe and describe the processes, changes, and results of implementing pre-communicative and communicative activities to enhance the students’ speaking skills. This concisely summarizes the research's aim.
1.6 Significance of the Research Study
This section outlines the potential theoretical and practical contributions of the research. Theoretically, the study strengthens existing learning theories and provides new perspectives on research methodologies in the field of English language teaching. Practically, it benefits students by improving their English speaking skills and building confidence. It also provides valuable insights for teachers, aiding in their professional development and offering a model for improving classroom practice. Furthermore, the study's contribution extends to the school and wider research community, potentially influencing curriculum design and future research initiatives.
II. Literature Review and Conceptual Framework
This chapter provides the theoretical underpinnings of the study. The literature review examines relevant theories and concepts related to English language teaching, communicative language teaching, speaking skills development, and classroom dynamics. It also explores the Indonesian national curriculum standards and their implications for English language instruction. The section on relevant studies reviews previous research findings to contextualize the current study and identify existing knowledge gaps. Finally, the conceptual framework presents a visual representation of the research's key variables and their relationships, guiding the research design and data analysis.
2.1 Theoretical Review
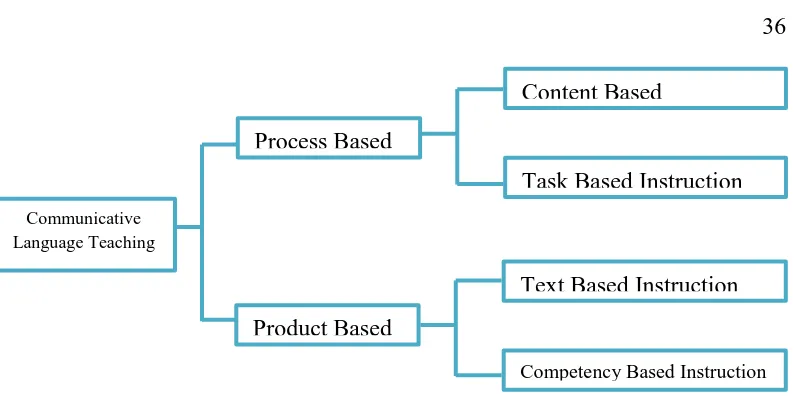
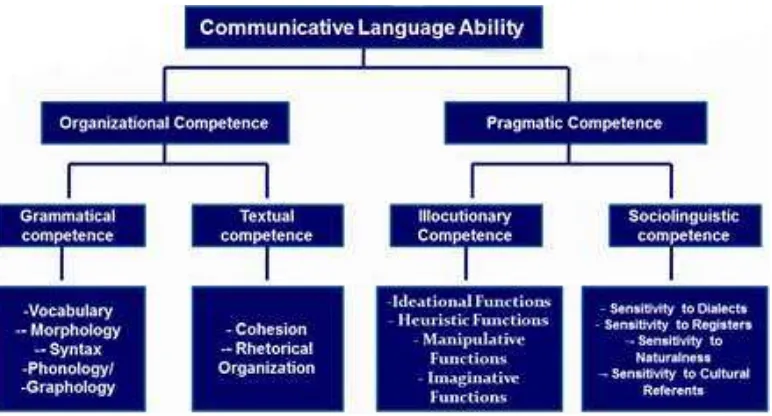
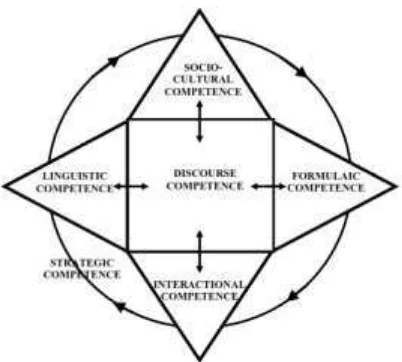
This section delves into the theoretical foundations of the research, starting with the legal basis of English teaching in Indonesian senior high schools. It explores the relevant government regulations and curriculum standards, emphasizing the mandated scientific approach to teaching and the distinction between compulsory and elective English courses. The section then examines various theoretical perspectives on speaking and teaching speaking, encompassing the nature of speaking as oral communication, the different types of speaking activities, and the common difficulties faced by non-native English speakers. Key theories and models in communicative language teaching (CLT) are explored, emphasizing the principles of information gap, choice, and feedback, crucial to creating engaging communicative activities.
2.2 Relevant Studies
This section reviews previous research related to improving students’ speaking skills, communicative language teaching, and action research methodologies. It summarizes key findings from existing studies, highlighting similarities and differences with the current research, and identifies gaps in the literature that the current study aims to address. This section provides a critical review of the existing body of knowledge, positioning the current research within the broader field of ELT research.
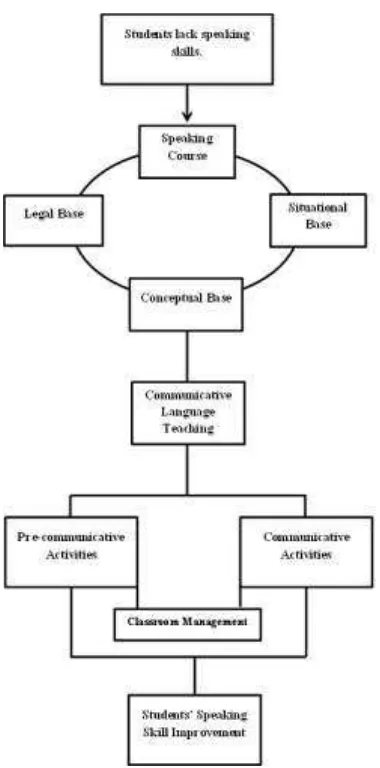
2.3 Conceptual Framework
This section presents the conceptual framework of the study, which illustrates the relationships between the key variables being investigated. It visually depicts the connections between the independent variables (pre-communicative and communicative activities), the mediating variables (student participation, confidence, and motivation), and the dependent variable (improvement in speaking skills). This framework provides a roadmap for the research, clarifying the anticipated causal links between the interventions and the observed outcomes. It helps to ensure a systematic approach to data collection and analysis.