© 2007 by Prentice Hall
1
4
Chapter
IT Infrastructure:
Hardware and Software IT Infrastructure:
Hardware and Software
Presented by
Dr. Yeffry Handoko Putra, S.T., M.T, CISA Magister Sistem Informasi
Universitas Komputer Indonesia
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
3
http://www.ubibusiness.com/assets/Uploads/_resampled/ResizedImage600390-Master-Plan-for-Acceleration.png
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
4
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
5
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
7
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indonesianictsectormarket-151130164810-lva1-app6891/95/indonesian-ict-sector-market-6-638.jpg?cb=1448902199
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
8
Defining IT Infastructure
• as technology
a set of physical devices and software applications that are required to operate the entire enterprise.
• as services clusters
a set of firmwide services budgeted by management and comprising
both human and technical
capabilities (Weill et al., 2002)
As service Platform
❖ Computing platforms used to provide computing services that connect employees customers, and suppliers into a coherent digital environment, including large mainframes, desktop and laptop computers, and personal digital assistants (PDAs) and Internet appliances
❖ Telecommunications services that provide data, voice, and video connectivity to employees, customers, and suppliers.
❖ Data management services that store and manage corporate data and provide capabilities for analyzing the data.
❖ Application software services that provide enterprise-wide capabilities such as enterprise resource planning, customer relationship management, supply chain management, and
knowledge management systems that are shared by all business units.
As service Platform
❖ Physical facilities management services that develop and
manage the physical installations required for computing, telecommunications, and data management services.
❖ IT management services that plan and develop the
infrastructure, coordinate with the business units for IT
services, manage accounting for the IT expenditure, and provide project management services.
❖ IT standards services that provide the firm and its business
units with policies that determine which information
technology will be used, when, and how.
❖ IT education services that provide training in system use to
employees and offer managers training in how to plan for and manage IT investments.
❖ IT research and development services that provide the firm
with research on potential future IT projects and investments that could help the firm differentiate itself in the
marketplace.
Level of IT Infrastructure
INFRASTRUCTURE COMPONENTS
❖ Computer Hardware Platforms
❖ Operating System Platforms
❖ Enterprise Software Applications
❖ Data Management and Storage
❖ Networking/Telecommunications Platforms
❖ Internet Platforms
❖ Consulting and System Integration
Services
The IT infrastructure ecosystem
Infrastructure as A part of IT Portfolio
Enterprise Portfolio Management
Mission
Vision
Strategy
Enterprise Portfolio Management
Enterprise Architecture Operational Deployment
IT Portfolio Management Investment
Management
Asset Management
Risk Management
Environ- mental Management
Basic Portfolio Template
Application Portfolio Example (individual case)
Portfolio Management
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
19
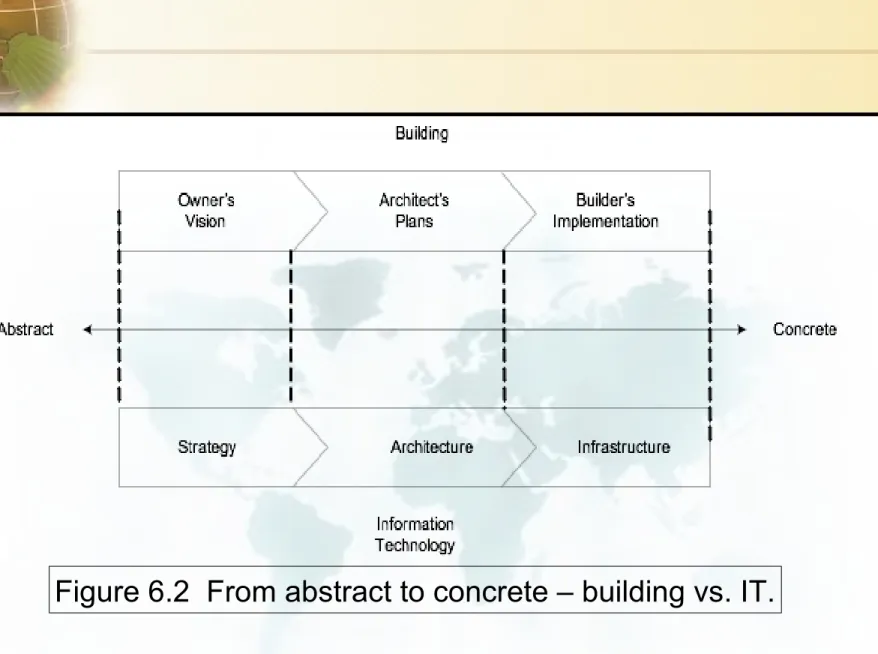
Figure 6.2 From abstract to concrete – building vs. IT.
The connection between the firm, IT infrastructure, and
business capabilities
Four Portfolio Categories (McFarlan)
Warren McFarlan, “IT Changes the Way You Compete,” Harvard Business Review,
May–June, 1984, pp. 98–103.
Evolution of IT Infrastructure: 1950–2008
Cloud Computing (off premise) to hybrid
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
24
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing
❖ ELECTRONIC ACCOUNTING MACHINE ERA: 1930–1950
❖ GENERAL-PURPOSE MAINFRAME AND MINICOMPUTER ERA: 1959 TO PRESENT
❖ PERSONAL COMPUTER ERA: (1981 TO PRESENT)
❖ CLIENT/SERVER ERA (1983 TO PRESENT)
❖ ENTERPRISE INTERNET COMPUTING ERA (1992 TO
PRESENT)
A multitiered client/server network (N-tier)
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
31
IT INFRASTRUCTURE
Technology Drivers of Infrastructure Evolution
Moore’s Law The law of mass
digital storage Metcalfe’s law
Declining
communications costs
and the Internet
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
35
Infrastructure
• Currently Involved Processes
– Capacity Management – Availability Management – IT Service Continuity
Management
– Configuration Management – Incident Management
– Problem Management – Change Management – Release Management
• Benefits
– Better understanding of the big picture
– Clearer understanding of the tasks
– More efficient interfaces with other team
– Leverage best practices
to provide better services
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
36
ARE THERE ANY QUESTION?
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
37
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
• IT infrastructure: Provides platform for supporting all information systems in the business
• Computer hardware
• Computer software
• Data management technology
• Organizes, manages, and processes business data concerned with inventory, customers, and vendors
• Networking and telecommunications technology
• Technology services
• E.g. consultants for systems integration with legacy systems
Infrastructure Components
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
38
IT Infrastructure Components
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-1
A firm’s IT infrastructure is composed of hardware, software, data management technology, networking technology, and technology services.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
39
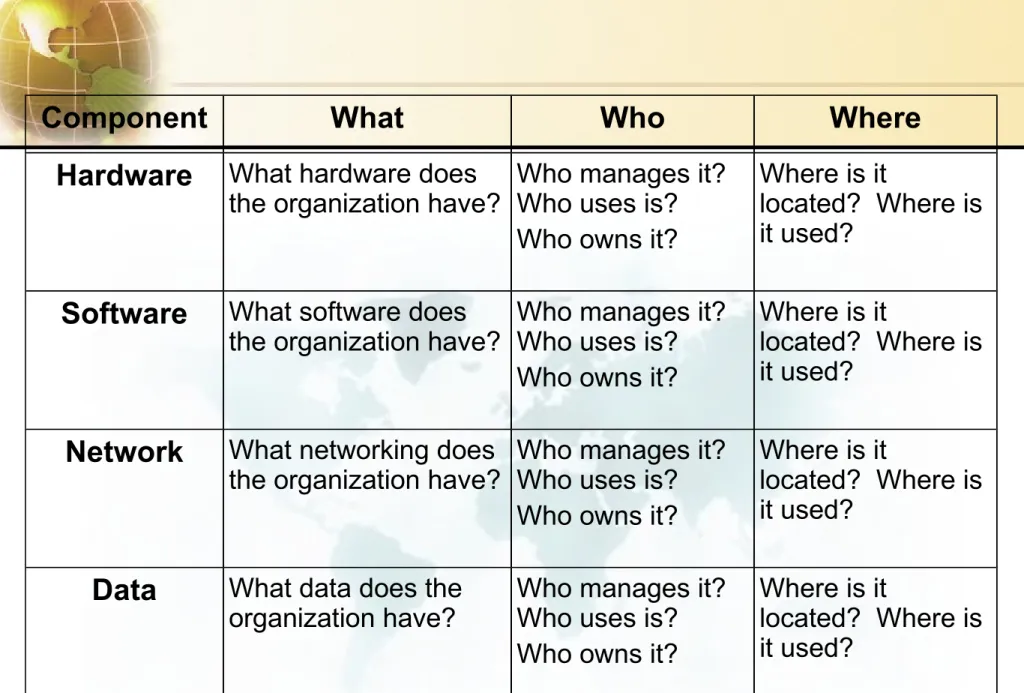
Component What Who Where
Hardware What hardware does
the organization have? Who manages it?
Who uses is?
Who owns it?
Where is it
located? Where is it used?
Software What software does
the organization have? Who manages it?
Who uses is?
Who owns it?
Where is it
located? Where is it used?
Network What networking does
the organization have? Who manages it?
Who uses is?
Who owns it?
Where is it
located? Where is it used?
Data What data does the
organization have? Who manages it?
Who uses is?
Who owns it?
Where is it
located? Where is it used?
Figure 6.6a Information systems analysis framework.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
40
• Computers come in different sizes with varying capabilities for processing information
• FLOPS (Floating point operations per second)
• Smartphones, handheld mobile devices
• PCs
• Workstation
• More powerful mathematical and graphics-processing capabilities than a PC
Types of Computers
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
41
• Servers
• Type of midrange computer
• Support computer network, sharing files and resources
• Provide hardware platform for e-commerce
• Mainframes
• Large-capacity, high-performance computer that can process large amounts of data very rapidly
• E.g. used by airlines for thousands of reservations per second
Types of Computers
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
42
• Supercomputer
• More sophisticated computer used for tasks requiring extremely rapid and complex calculations with thousands of variables,
millions of measurements
• Used in engineering, scientific simulations, military/weapons research, weather forecasting
• Grid computing
• Power of geographically remote computers connected into single network to act as “virtual supercomputer”
Types of Computers
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
43
• Client/server computing
• Form of distributed computing
• Splits processing between “clients” and “servers”
• Clients: User point of entry
• Servers: Store and process shared data and perform network management activities
Types of Computers
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
44
• Client/server computing (cont.)
• Two-tiered client/server architecture
• Uses two types of machines
• Multitiered client/server architecture (N-tier)
• Balances load of network over several levels of servers
• E.g. Web servers and application servers
Types of Computers
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
45
Client/Server Computing
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-2
In client/server computing, computer processing is split between client machines and server machines linked by a network. Users interface with the client machines.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
46
A Multitiered Client/Server Network (N-Tier)
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-3
In a multitiered client/server network, client requests for service are handled by different levels of servers.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
47
Storage, Input, and Output Technology
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Primary secondary storage technologies
• Magnetic disk:
• Hard drives, USB flash drives
• RAID: Can package hundreds of drives for massage storage requirements (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
• Optical disks
• CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD
• Magnetic tape
• Storage networking: SANs
• Connect multiple storage devices on a separate high-speed
network dedicated to storage
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
48
A Storage Area Network (SAN)
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-4
A typical SAN consists of a server, storage devices, and networking devices, and is used strictly for storage. The SAN stores data on many different types of storage devices, providing data to the enterprise.
The SAN supports
communication between any server and the storage unit as well as between different storage devices in the network.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
49
Storage, Input, and Output Technology
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Input devices:
• Gather data and convert them into electronic form
• Keyboard
• Computer mouse
• Touch screen
• Optical character recognition
• Magnetic ink character recognition
• Pen-based input
• Digital scanner
• Audio input
• Sensors
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
50
Storage, Input, and Output Technology
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Output devices:
• Display data after they have been processed
• Monitor
• Printer
• Audio output
• Information systems collect and process information in one of two ways
• Batch processing: Transactions stored for predefined amount of time, then processed as group
• Online processing: Transactions processed immediately
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
51
Contemporary Hardware Trends
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Integration of computing and telecommunications platforms
• Cell phones merging with handhelds
• Growth of Internet telephony
• Nanotechnology
• Creating computer chips and other devices thousands of times
smaller through manipulating individual atoms, molecules
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
52
Examples of Nanotubes
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-5
Nanotubes are tiny tubes about 10,000 times thinner than a human hair. They consist of rolled up sheets of carbon hexagons, have potential uses as minuscule wires or in ultrasmall electronic devices, and are very powerful
conductors of electrical current.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
53
Contemporary Hardware Trends
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Edge computing
• Multitier, load-balancing scheme for Web-based applications
• Significant parts of Web site content, logic, and processing performed by smaller, less expensive servers located nearby the user
• Increases response time and resilience and lowers technology costs.
• Autonomic computing
• Development of systems that can configure themselves, heal
themselves; e.g. self-updating antivirus software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
54
Edge Computing Platform
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-6
Edge computing involves the use of the Internet to balance the processing load of enterprise platforms across the client and edge computing platform.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
55
Contemporary Hardware Trends
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Virtualization
• Process of presenting a set of computing
resources so they can be accessed in ways that are unrestricted by physical configuration or
geographic location
• Server virtualization: Running more than one
operating system at the same time on single
machine.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
56
Contemporary Hardware Trends
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Multicore processors
• Integrated circuit with two or more processors
• Enhanced performance, reduced power
consumption and more efficient simultaneous
processing of multiple tasks
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
57
• Read the Interactive Session and then discuss the following questions:
• What business and social problems does data center power consumption cause?
• What solutions are available for these problems? Which are the most environment-friendly?
• What are the business benefits and costs of these solutions?
• Should all firms move toward green computing? Why or why not?
Interactive Session: Technology Computing Goes Green
IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
58
• The software that manages and controls the computer’s activities
• PC operating systems and graphical user interfaces
• GUIs
• Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2003
• UNIX
• Linux
• Open-source software
Operating System Software
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
59
The Major Types of Software
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-7
The relationship among the system software, application software, and users can be illustrated by a series of nested boxes. System software—
consisting of operating systems, language translators, and utility programs—controls access to the hardware. Application software, including programming languages and “fourth- generation” languages, must work through the system software to operate. The user interacts primarily with the application software.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
60
Application Software and Desktop Productivity Tools
• Application programming languages for business
• COBOL
• C, C++
• Visual Basic: Visual programming language
• Fourth-generation languages
• Software tools that enable end-users to develop software applications
• Tend to be nonprocedural, may use natural languages
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
61
Categories of Fourth-Generation Languages
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Tool Description Example
PC software tools General-purpose software packages for PCs
WordPerfect Microsoft Access Query language Languages for retrieving data stored in
databases or files
SQL
Report generator Specialized tools for creating highly
customized reports Crystal Reports
Graphics language Display data from databases in graphic
format SAS Graph
Systat Application generator Preprogrammed modules to generate
entire applications FOCUS
Microsoft FrontPage Application software
package
Software programs that eliminate need for custom, in-house software
Oracle PeopleSoft HCM mySAP ERP
Very high-level
programming language
Generate program code with fewer
instructions than conventional languages
APL Nomad2
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
62
Application Software and Desktop Productivity Tools
• Software packages and desktop productivity tools
• Word processing software
• Spreadsheet software
• Data management software
• Presentation graphics
• Software suites
• Web browsers
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
63
Spreadsheet Software
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-8
Spreadsheet software organizes data into columns and rows for analysis and manipulation.
Contemporary spreadsheet software provides graphing abilities for a clear, visual
representation of the data in the spreadsheets.
This sample break-even analysis is represented as numbers in a spreadsheet as well as a line graph for easy interpretation.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
64
• Java
• Operating system-independent, processor-
independent, object-oriented programming language
• AJAX
• Allows a client and server to exchange data behind the scenes to avoid reloading a Web page after each change
• Hypertext markup language (HTML)
• Page description language for specifying how
elements are placed on a Web page and for creating links to other pages and objects
Software for the Web: Java, AJAX, and HTML
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
65
Interactive Session: Organizations Will Google Take Over the Desktop?
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Read the Interactive Session and then discuss the following questions:
• What are the benefits of using Google Apps? What kinds of businesses are most likely to benefit? What kinds are least likely to benefit?
• What reasons might a business have to continue using Microsoft Office for desktop productivity?
• Search the Web for an article titled Microsoft Office Live Vs.
Google Apps For Your Domain by Preston Gralla from September 2006. Do you agree with the author’s
conclusion?
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
66
• Web services:
• Software components that exchange information with each other using universal Web
communication standards and languages
• XML (extensible markup language)
• SOAP (simple object access protocol)
• WSDL (web services description language)
• UDDI (universal description, discovery, and integration)
• Service oriented architecture (SOA) Web Services
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
67
How Dollar Rent-a-Car Uses Web Services
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
Figure 4-9
Dollar Rent-A-Car uses Web services to provide a standard intermediate layer of software to “talk” to other companies’
information systems. Dollar Rent-A-Car can use this set of Web services to link to other companies’ information systems without having to build a separate link to each firm’s systems.
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
68
• Open Source Software
• Ubuntu
• Cloud Computing
• Google Apps, Windows Live
• Mashups
• ChicagoCrime.org
• Widgets
• Apple Dashboard
Software Trends
IT Infrastructure: Computer Software
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
69
Managing Hardware and Software Technology
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Capacity planning
• Process of predicting when hardware system becomes saturated
• Ensuring firm has enough computing power for current and future needs
• Factors include:
• Maximum number of users
• Impact of current, future software
• Performance measures
• Scalability: Ability of system to expand to serve large
number of users without breaking down
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
70
Managing Hardware and Software Technology
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) model
• Used to analyze direct and indirect costs to help determine the actual cost of owning a specific technology
• Direct costs: Hardware, software purchase costs
• Indirect costs: Ongoing administration costs, upgrades, maintenance, technical support, training, utility and real estate costs
• Hidden costs: Support staff, downtime, additional network management
• TCO can be reduced through increased centralization,
standardization of hardware and software resources
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
71
Managing Hardware and Software Technology
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Using technology service providers
• Outsourcing
• Using external provider to:
• Run networks
• Host, manage Web site(s)
• Develop software (offshore software outsourcing)
• Manage IT infrastructures
• Requires Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
72
Managing Hardware and Software Technology
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
• Using technology service providers
• On-demand computing (utility computing)
• Firms off-loading peak demand for computing power to remote, large-scale data processing centers
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Firms rent software functions from Web-based services, with users paying either on a subscription or per-
transaction basis
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
73
Managing Hardware and Software Technology
Essentials of Business Information Systems
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software