Gupta, Associate Professor, Division of Educational Research, National Council of Educational Research and Training, New Delhi. Srivastava, Professor and Head, Division of Educational Research, National Council of Educational Research and Training, New Delhi (e-mail:ashokksrivastava@ . yahoo.com) Reviewer.
Concept and Meaning of Education
As a student of the education course and, as a future teacher, it is essential that you understand the meaning of education, its conceptual features and the different perspectives that have shaped its meaning from time to time. Understanding the concept of education and its dynamic features will help you develop knowledge about the purpose of becoming a teacher and assist you in educating your students.
The term “education” is a common and popular word uttered by many of us, but understood in its proper perspective by very few. The different educational processes and understanding the role and need of institutions in educating individuals are also explored by highlighting their relevance to the school context.
According to him, "Education is the manifestation of the divine perfection, which already exists in man". According to him, education should aim at developing the active tendencies of the child.
It is also stated that the curriculum should emerge from the needs and interests of the child and not from the demands of the teacher. Krishnamurthi, Rousseau, Froebel and Montessori considered the education of the child in the natural environment, where the child explores and learns through his/her experiences.
W hEThER E dUCaTIon IS I nTEnTIonal oR U nInTEnTIonal ?
The individual is a means to an end – the end of the continuation of the social order in the socialization process and the individual is an end by himself/herself in the education process. There may be certain aims of education which have the intention of initiating every man and woman in the kind of educational activities which will allow them to take their proper place in society; to develop vocational skills, so that they become independent, while there may be certain objectives to develop a thirst for knowledge for its own sake and to develop aesthetic sense in the individuals.
W haT d oES E dUCaTIon C omPRISE of ?
Let us examine these characteristics to understand what education is in the total sense. This does not mean that a teacher should passively let children sit in the classroom and provide instruction.
It is also limited to a specific period of human life, that is, from childhood until one leaves school, while the educational process continues throughout life. The educational processes in these institutions are purposefully planned with a continuous effort to impart certain types of knowledge, skills or attitudes.
Goals of Education
Examine the rationale of educational objectives articulated in the reports of various Commissions and policy documents. Formulate desired goals of education in India for the second decade of the 21st century.
The aspirations of contemporary Indian society are discussed in detail elsewhere in this chapter. In a religious society, a person who believes in the existence of a supreme power and sees human beings as a reflection of the supreme is considered an educated person.
Some of the goals in both categories are universal, that is, these goals are shared across cultures and nations. Since the world in the 21st century will be different from the world of the 20th century in several ways, it will also have different educational goals.
G oalS of E dUCaTIon In I ndIa
In the previous part, we discussed the aspirations of modern Indian society and also its vision of an educated person. The National Commission on Teachers, also known as the Chattopadhyay Commission, in its report titled "Teacher and Society" declared four national goals. It is necessary to find a balance between the development of the individual and society.
Learning to live together' is one of the four pillars of education emphasized by the Delors Commission. How would you justify the adoption of 'Self-Knowledge' as one of the educational objectives and also as a curriculum area in all stages of education. Learn the treasure within; Report of the UNESCO Commission on Education in the 21st Century, Paris.
Processes and Modes of Education
In this chapter we will discuss whether education is an activity or a process and how education is passed from one generation to another. We discussed that education is an activity that is organized to achieve desired goals. So, you might be tempted to conclude from the ongoing debates that education is both an activity and a process.
P RoCESSES of E dUCaTIon
Analyze different understandings of education from the point of view of it being an activity or a process. All these educational processes can form an activity in itself or can be a group of different activities in the same process. Details of all these processes will be shown to you in the basis of education courses such as psychology and sociology of education.
M odES of E dUCaTIon
This is considered to be the most effective form of education as there is more scope for a student to communicate with the teacher and the teacher can also explain as per the student's need and requirements. The face-to-face mode can be organized full-time or part-time depending on the student's need and the time spent on the goal. In this mode, except for the longer duration of the course, everything else remains the same as in the full-time face-to-face mode.
Schools can meet both the demand and the need for education according to individual and societal needs. Why education in the form of schooling should be made available to all citizens. Also available at Archives of Informal Learning: http://www.infed.org/archives/e-texts/colley_informal_learning.htm].
Knowledge: Meaning and Facets
Therefore, this chapter focuses on understanding the nature of knowledge and knowledge, in general, and its manifestation in the school context, in particular. The problem of definition of knowledge is ongoing and is a never-ending debate among philosophers. Forms of knowledge; since knowledge is the sum of human understanding, there should be different forms of understanding or types of knowledge; and.
K nowIng and K nowlEdgE
Therefore, instead of trying to understand or define knowledge in the form of its product, it may be appropriate to focus on cognition - the process, which explains and explains and, to a large extent, determines meaning and also the nature of knowledge. Will Durant (1966), making a journey into antiquity, highlights the irrefutable role of sensibility in establishing not only knowledge, but also in its validation (i.e. establishing truth). In the first stage, our knowledge merely expresses "the particular aspects of things, the external relations between such things."
K nowIng and K nowlEdgE : ThE I ndIan w ay
The stages of cognitive development observed by Piaget are not necessarily 'natural' for all children because, to some extent, they reflect the expectations and activities of children's culture. Lev Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development suggests that our cognition is a function of social and cultural forces.
F oRmS oF K nowlEdgE
Intuitive knowledge is the knowledge acquired without inference and/or the use of reason. In the beginning we saw that Knowledge is always knowledge of a phenomenon/thing/object. Knowledge is not the handiwork of an isolated individual mind; it is the result of the collective pursuit of society.
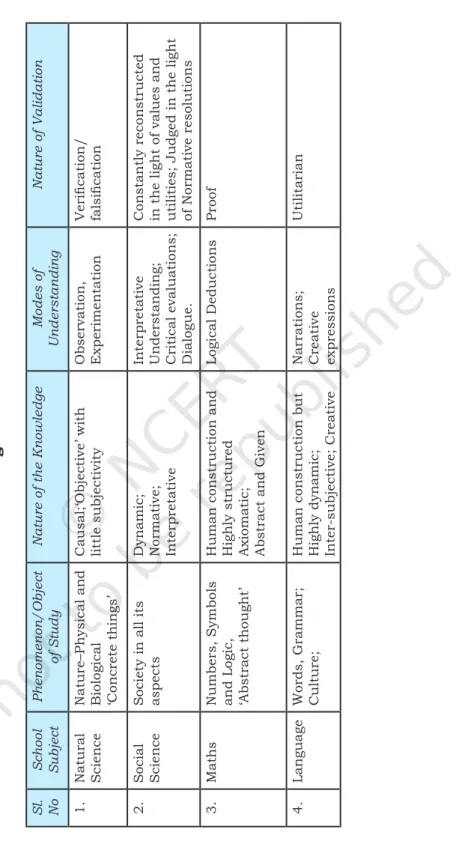
F aCETS oF K nowlEdgE
The only absolute distinction that can be made between the abstract and the concrete is the distinction between the concreteness of the phenomenon and the abstractness of its reflection in consciousness. You will read further that sensation, perception and concept formation are the essential processes of knowledge acquisition. The characteristics of knowledge include its abstract nature, its social embeddedness, its accumulation, its perspective and its limited and boundless nature.
Process of Knowing
P RoCESS of K nowIng
Any theory that attempts to define the process of behavior must explain how information is accessed. The process of cognition is a personalized, individual task, influenced by experience and inadvertent contextual cues. There are three aspects of knowing – the knower (the consciousness of the participant), the known (the field of study), and the process of knowing (which connects the knower to the known).
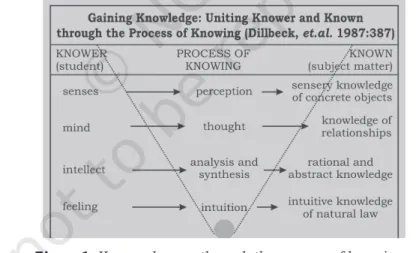
Perception is the process of achieving awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory stimuli. Therefore, knowledge is a composite structure consisting of the knower, the process of knowing, and the known. The role of the knower and the known in the process of constructing knowledge thus becomes crucial.
Organisation of Knowledge in Schools
Ideally, the organization of knowledge should be flexible so that it meets the requirements of the organization. Observe the school's efforts to organize these activities according to the needs of the individual student. As knowledge expands, many areas of knowledge offered in the schools become known to the common man.
It should include the study of the environment through illustrations from the physical, biological, social and cultural spheres. Arts Education: The NCF–2005 (p-55) believed that “the arts, visual and performing, should become an important part of learning in the curriculum.” The curriculum should introduce students to the country's rich and varied artistic traditions. The Commission for Revision of the Curriculum for the Ten-Year School (Patel 1978) proposed socially useful productive work (SUPW).
S ElECTIon of K nowlEdgE C aTEgoRIES In S Chool E dUCaTIon
Totality: The basis of selection of knowledge categories keeps in view the totality of the experiences that a child
Diversity and elasticity: categories of knowledge must develop different talents among individuals in different areas of life and work. It is therefore necessary to allow for individual differences among students and to use different teaching techniques, such as the use of multimedia, to make classroom situations interesting for both the student and the teacher. For example, in the context of India, there is a need for inclusive education (providing education to all regardless of caste, gender, physical disability, etc.).
Leisure: An effective school curriculum trains students for proper utilisation of leisure. Report of the Secondary
Flexibility: Effective knowledge categories take care of local conditions (e.g., weather, etc.) to cater to the
Disse er Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), Council for the Indian School Certificate Examination (CISCE) og National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS). Kashmir Jammu & Kashmir State Board of School Education, Jammu (november til april) Srinagar (maj til oktober). Tamil Nadu Tamilnadu State Board of School Examinations and Board of Higher Secondary Examinations, Chennai.
P RoCESS foR d EvEloPIng C URRICUla , S yllabI
These recommendations were included in the first curriculum – The Curriculum for the Ten-Year School – A Framework developed by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) in 1978. It also envisioned elimination of disparities and equalization of educational opportunities with the title of the needs of disadvantaged sections of society. Report of the National Review Commission for Secondary Education with Special Reference to Vocational Education.
Teacher Autonomy and Accountability
NCF-2005 advocated that teacher autonomy is essential to ensure learning and to meet the diverse needs of children. Studies show that teachers' decision-making in this area is related to the teachers' position in the school. In this chapter we have discussed autonomy in general and teachers' autonomy in particular.
Learner Autonomy
It was only the teacher who decided what information was appropriate for the particular age and stage of the student. Learner autonomy can be conceptualized as the individual's ability to engage in 'critical reflection, decision-making and willingness to act and experiment on their own.' It can be defined as the ability to take personal or self-regulated responsibility for learning. Formally, learner autonomy can mean that the learner takes responsibility for his/her learning in several aspects from different sources.