This selection and arrangement of the content as a collection is copyrighted by the National Council of Professors of the Educational Administration.

The Changing Roles of Leadership and Management in Educational
Theories of Educational Management
Distinguishing Educational Leadership and Management
- The Significance of the Educational Context
The challenge of modern organizations requires the objective perspective of the manager, as well as the flashes of vision and commitment that wise leadership provides” (Bolman & Deal, 1997, pp. xiii-xiv). The contemporary emphasis on leadership rather than management is clearly illustrated by the launch of the English National College for School Leadership (NCSL) in November 2000.
Conceptualising Educational Management
The Relevance of Theory to Good Practice
- The Nature of Theory
- The Characteristics of Theory
Griffiths (1997) provides strong arguments to support his advocacy of "theoretical pluralism". “The basic idea is that all problems cannot be fruitfully studied with a single theory. In formal models there is an emphasis on the accountability of the organization towards its sponsoring body.
Managerial Leadership
- The Limitations of Formal Models
- Are Formal Models Still Valid?
- Central Features of Collegial Models
- Participative Leadership
- Limitations of Collegial Models
- Contrived Collegiality
- Is Collegiality an Unattainable Ideal?
- Central Features of Political Models
- Transactional Leadership
- Are Political Models Valid?
- Central Features of Subjective Models
- Subjective Models and Qualitative Research
- Postmodern Leadership
- The Limitations of Subjective Models
- Central Features of Ambiguity Models
- What Do We Mean By Culture?
They can be considered "anti-theories" in that they arose as a reaction to the perceived limitations of formal models. The uncertainty arising from the external context increases the ambiguity of the decision-making process in the institution.
Societal Culture
The edifice of the formal models is shaken by the recognition that conditions in schools may be too uncertain to allow an informed choice among alternatives. Societal cultures differ most at the level of fundamental values, while organizational cultures differ most at the level of more superficial practices, which is reflected in the recognition of special symbols, heroes and rituals.
Central Features of Organizational Culture
- Moral Leadership
- Limitations of Organizational Culture
- Comparing the Management Models
- Attempts at Synthesis
- Using Theory to Improve Practice
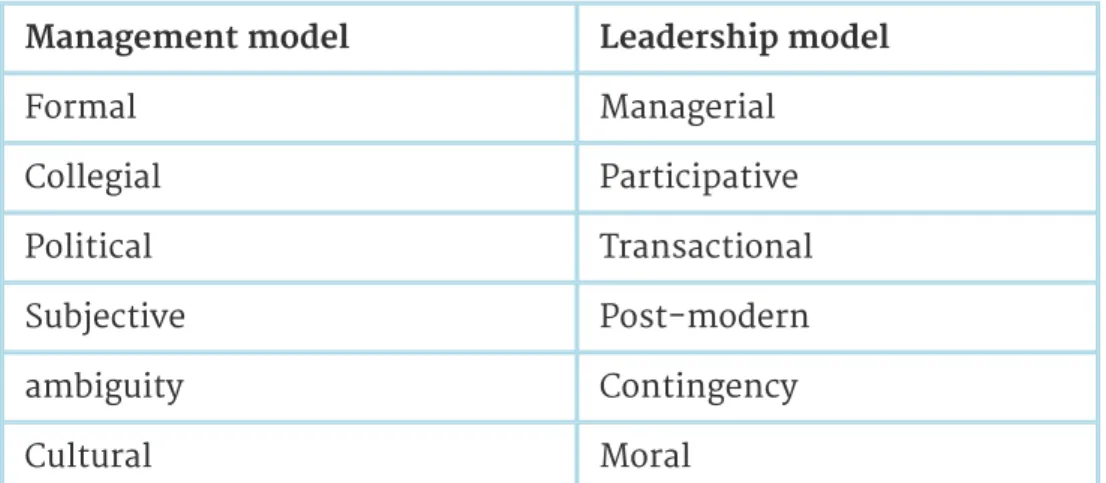
Rational within a framework of values Physical manifestation of culture Table 2.2: Key features of the six models. Each of the models discussed in this volume provides valuable insights into the nature of leadership and management in schools and colleges.
Preparing and Training Superintendents for the Mission of Executive
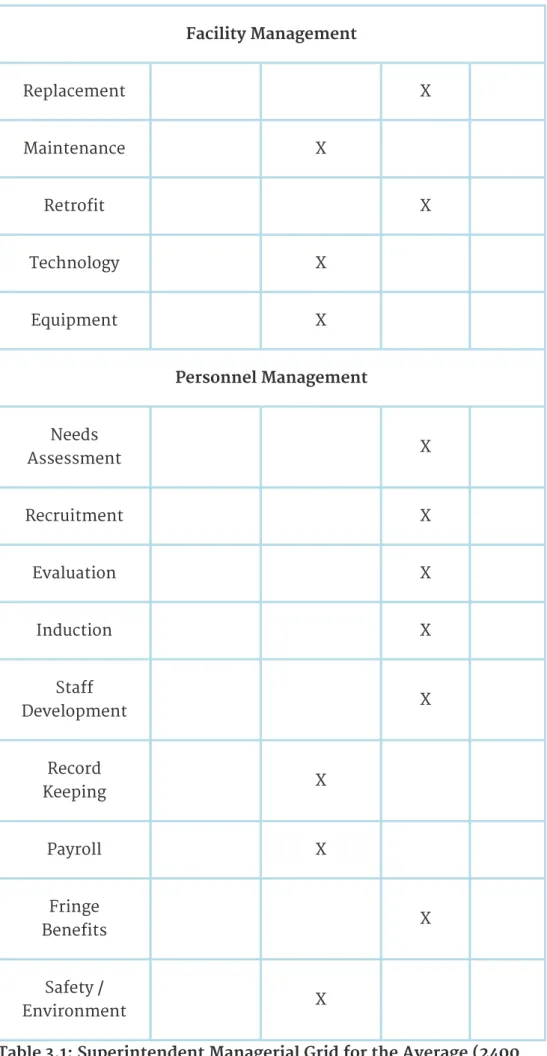
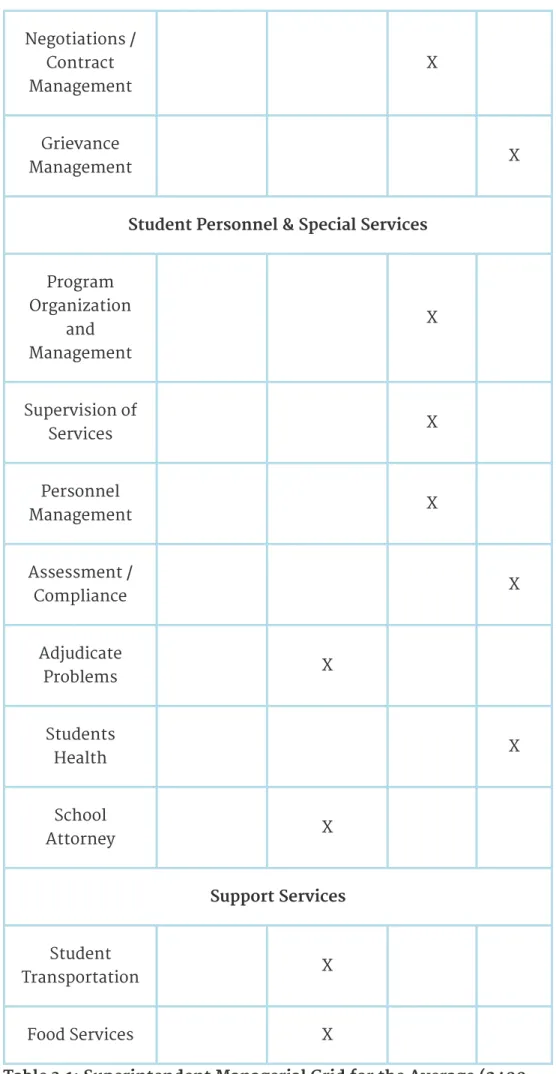
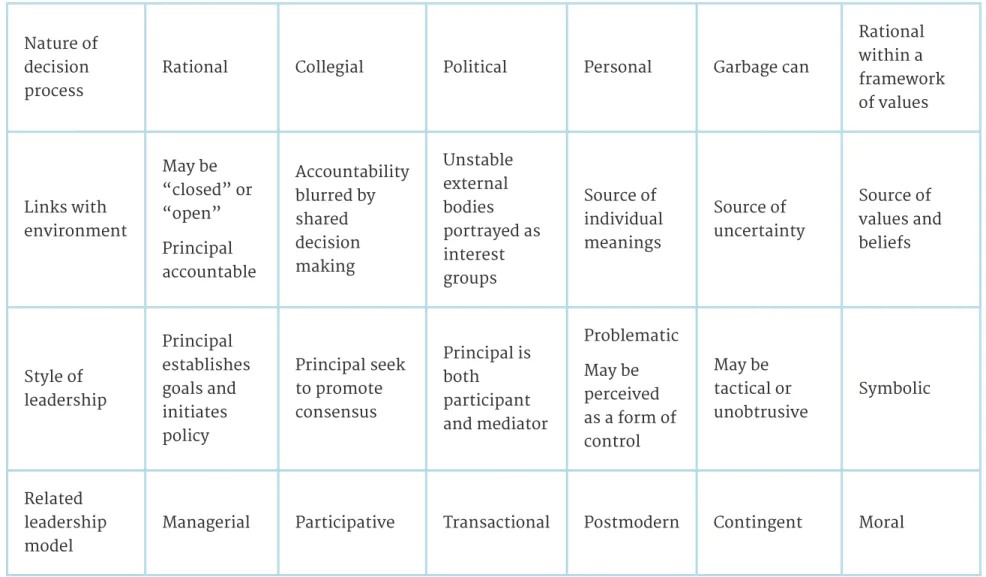
The reform era has so 'politicized' the role in some districts that the chief inspector is the 'chief political officer'. Performing this role removes a superintendent from the district and, in extreme cases, eliminates the role. If this management support is not in place, directors are likely to be in a constant battle 'against' the head office. The average size of the nearly 14,000 functioning school districts in the United States is approximately 2,400 students (Glass, Bjork, & Brunner, 2000).
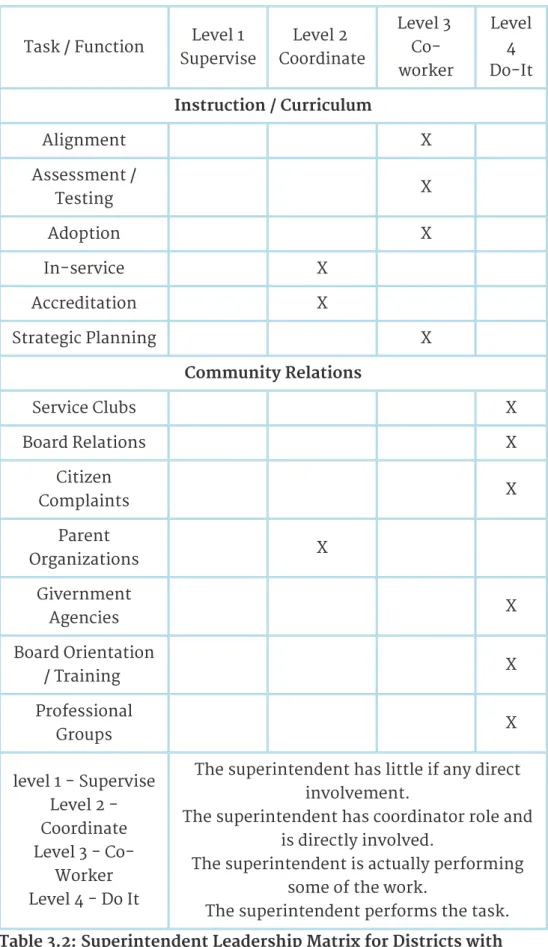
Districts with between 3,000 and 5,000 students offer unique opportunities for superintendents who want their "hands on" the pulse of the school district. The role of the superintendent is a "management worker." There is simply no one else to do the job. In the table (Table 3.2), the superintendent in the 2,400 student district coordinates others, works with others and does a lot of "hands on" leadership.
Each of the activities must have leadership and management support from the central administration to be effective at the building level. For schools to work at the neighborhood level, they must have the timely and appropriate support of their "corporate headquarters" the central administration. This is despite the need to replace aging infrastructure in a majority of the nation's school districts.
The most intensive part of the internship and apprenticeship would be in the area of fiscal, budget and operational management.
The Art of Successful School-Based Management
Shape: Two-dimensional area
The IL will function as part of the teaching committee, but leadership within the committee will reside with another person. This data will be collected as part of the teacher's overall evaluation in terms of retention, tenure and promotion. Regardless of the career stage, the nature of the teaching support will be in the form of developmental supervision or mentoring.
Each mentor will provide reports to the IL on dates of mentor contact, the nature of the observation and any issues the IL may need to address. Based on the three reports, the MP will compose a letter to the Director of Personnel summarizing the findings and making a recommendation regarding the continued employment status of the teacher. It is in the form of mentoring as a supervisory practice that some of the more powerful benefits for teacher growth and development appear to be (Reiman 1999; Glickman, 2002; Pajak, 2002).
They noted that by moving the registration form, they accidentally lost contact with half the staff. However, empathetic writing can have many of the same benefits as effective interpersonal communication.
Space: Area around, between, above, below, or within an object
Reflection as a method of making sense of the teaching experience remains an important part of instructional supervision (Glickman, 2002; Pajak, 2003; Rucinski, 2005; Sullivan & Glanz, 2005). This step is the first one that requires evaluation by the observer. In other words, first the conversation focuses on the technical dimensions and then deals with the aesthetic elements of the lesson.
As in the description of Feldman's method above, teachers and instructional leaders can easily get involved in "describing" and "analyzing" a lesson, but it is an entirely different story to "interpret" and "evaluate" a lesson. The last two steps require the instructor and observer to attend more closely to the feelings, implications, and subtleties of the lesson (Heid, 2005). Applying Feldman's method to works of art was new to the instructional leaders, and this newness reminded them of the power, the frightening power of innovation.
The author asked the same eight students to apply their new knowledge of the Feldman method to teacher observations. By the end of the semester, several instructional leaders noted that after their teachers began to trust the leader's intentions, they became more comfortable discussing the aesthetic steps (i.e., steps three and four) in the Feldman -method.
Color: Property of objects coming from reflected light
More specifically, how can the principal support a shared value through workforce development initiatives that include diverse approaches to effective teaching. Even if a workforce development program adopts a core values approach, it will continue to face challenges in implementing successful professional development. In contrast, when school leaders link core values to a purposeful, ongoing reflection process, they can significantly increase the chances of successful staff development.
Have we provided information about the initiative and how it supports the core values of the district. In order to achieve the desired results of a particular staff development initiative, principals will answer all of the above questions in order. At the beginning of the school year, before students arrive, the principal and teachers agree on the following core value: "We value students with knowledge, reflection, and thoughtful students." At the school, a committee led by the head of staff development then looked at different deployment models that would support the articulated value.
The discussion about team teaching shifted to the consequence for student scheduling or student performance. And only after individuals began to understand how they would cope with the change could staff development move to its most important point.
Texture: Feel or appearance of an object or surface
It doesn't take us long to recognize the source of much of the stress many principals and teachers face. As an instructional leader, another principal built trust and understanding when she gave all her teachers a "wild card." The wild card was a small, colored index card that said, "This card entitles me to one day, no observation, no reason or reason." The principal knew that there had been a few days when, for reasons beyond the teacher's understanding and control, things had not been going well. However, leadership can create and sustain a school culture where student and teacher learning is at the heart of the matter.
In that part of the agenda, teachers discussed their needs, celebrated successes and outlined goals for the coming month. The teachers also suggested a strategy that they would ask the principal so that he could support them in pursuing the goal. While strategies for student achievement and teacher effectiveness were always part of the discussion, the principal also encouraged private or personal goals.
Most of the conversations and support during the month came in the form of emails and “random” contacts during the normal schedule of the school day. By understanding the interconnected nature of the elements, she is able to organize a successful learning and teaching experience for her students and teachers.
Why Is School Leadership Preparation So Complex
These giants of the human relations movement provided insight into the relationship between formal and. These movements have raised awareness of the injustices suffered by women, people of color, and those caught in the web of poverty. Note: Decision rules on the six criteria will be made based on the data collected on schools and districts for graduates recommended by their program.
In the final step of the process, interview data collected from approximately 30 successful graduates will involve the use of mixed methods. First, the researcher will analyze the responses of five graduates from each program and look for parallels in the responses to courses, professors, activities that may be directly related to it. However, it is not unusual for a superintendent to create political power struggles among members of the school community.
Shared decision-making was the norm as the team created a framework for analyzing instructional aspects of the school programs. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the University Council on Educational Administration, Louisville, KY.
Challenges Facing Black American Principals: A Conversation about
The first few years of the directorship are critical in influencing the practice of administrative leadership (Hart). In the analysis portion of this study, many of the participants used pronouns when referring to principals, established culture, and school districts. Most participants (80%) obtained their administrative certification in the southern states of Mississippi or Louisiana.
He was the direct contact between White boards and superintendents and members of the black schools. A budding paradigm shift occurs when ethnic minority principles know the paradigm of the dominant culture. Many of the participants noted humor or laughter as a temporary solution to challenges associated with the principalship.
Again, most of the study participants cited music as a stress-reducing factor for school-related challenges. An invited address at the annual meeting of the University Council for Educational Administration, Houston, TX.