BOND Bond University Canberra University of Canberra CQU Sentrale Queensland University CSU Charles Sturt University. QUT Queensland University of Technology RMIT Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology SCU Southern Cross University.
Benchmarking
- Some background context
- Terminology and description
- Terminology
- Description
- Necessary underpinnings
- Why benchmark?
- Benefits
- Models and methodologies
- Process benchmarking
- Performance benchmarking
- Other approaches
- Applying benchmarking in the Australian academic
- Partners
- Processes suitable for benchmarking
- Reasons for benchmarking
- Lessons for successful outcomes
- Benchmarking projects undertaken
- Useful sources
- Australasian sources
- International sources
In 1996, the University of Melbourne established a 'Benchmarking Project Team' as part of its quality improvement program to identify, inform and train staff involved in benchmarking activities. 1999, Benchmarking, (http://www.ntu.edu.au/admin/isd/qsdc/) In 1994, as part of the Australian Best Practice Demonstration Programme, NTU's Coordinator of Quality and Staff Development, Anne Wilson, initiated two benchmarking projects as part of the University Libraries Best Practices in Research Information project.
Performance measurement
Terminology and description
- Definitions
- Criteria for performance indicators (IFLA)
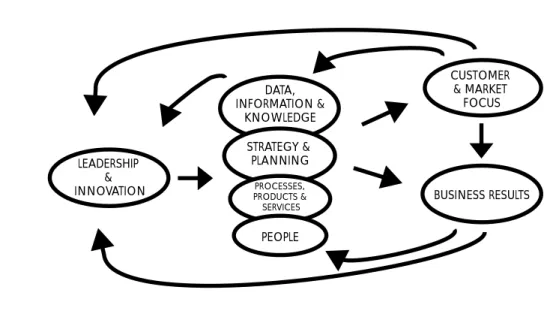
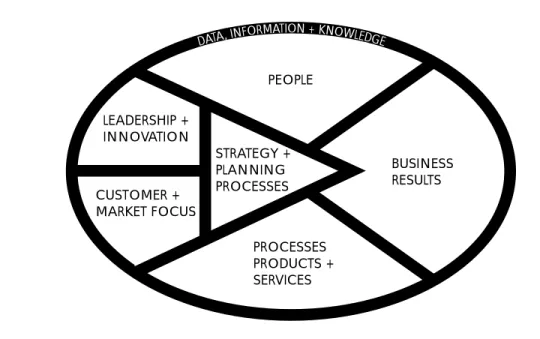
Performance indicators function as a supporting framework for almost all elements of best practice, including leadership, benchmarking, customer focus, technology and quality. The development and use of performance indicators should form the basis for analysis of an organization's current performance, its future requirements, and improvement strategies for continued success (Key Performance Indicators Handbook, 1995).
Methodology
- Measurement and evaluation process
- The performance indicator route map
- Development and use of key performance indicators
- Characteristics of appropriate KPIs
- Typical applications for KPIs
- Putting it all together
Setting goals which define what 'should be', the standards against which performance should be judged. Progress against each KPI for each of the five critical success factors is reported annually in the Library's Annual Report.
Points to remember
- General advice
- Difficulties
- Training and awareness
Improve students' search and information locating skills to enhance use of collection and other available resources. The library management must focus on the central issues, which have been determined by the institution's management and the library users. This can be done by integrating relevant library staff into the institution's planning efforts at all levels.
When developing performance indicators, the focus should be on those that are useful for the institution's purposes. Since the evaluation effort has costs, the measurement should be concentrated on areas where the performance can be changed. Richards states: 'Difficulties in implementing performance indicators relate to criticisms of their adequacy: their use for control; the lack of an integrated data system; insufficient knowledge; lack of interest; and other various implementation factors.
Library performance indicators
- IFLA: Measuring quality: international guidelines for performance
- ISO 11620: International Standards Organisation, 1998,
- EAL: Joint Funding Council. Ad-hoc group on performance
- CRANFIELD Project: Performance indicators for academic libraries,
- MIEL2: Management information systems and performance
- CAUL: Council of Australian University Librarians, performance indicator
- Performance indicators database: Selecting the best performance
- CEC: Library performance indicators and library management
- NPLS Project: National Public Library Statistics and
- ICOLC: International Coalition of Library Consortia
- WOREP: Wisconsin-Ohio reference evaluation program
- SCONUL: Performance indicators for university libraries
- Performance indicator matrix
A number of manuals, including the IFLA guidelines, were used in the development of the standard. Effectiveness•turnover rate; average number of issues/uses EAL: P4 Efficiency per item (per topic); procurement share •P4.8 volumes in inventory/FTE requests filled staff (by topic); items on loan •P4.9 total expenses/volumes in stock as a percentage of total stock (by topic) continues SCONUL. Number of questions received per day •User satisfaction Resource Management •Number of sessions on each ser.
IFLA: Remote use •[15] remote uses per capita: number of remote uses by primary members. Usage •total number of items used in the library but use of materials in the library: total number of items used in not billed by the library but not charged •Total number of uses of library materials of Total use of materials: number of total library uses all types of materials of all types Internet-mediated research Van House: Information Services •Economics•proportion of budget carried out Evaluation of Internet research •Market penetration•current users as a percentage of users potential•satisfaction with search performance •Efficiency•time taken for search broker. Van House: Reference Transactions •Total number of reference transactions during a period of time (includes knowledge, use, recommendations, interpretation, or guidance in the use of one or more information resources by a member of the library staff).
Activity in Australia
- Use of performance indicators in Australian academic libraries
- How have libraries used performance indicators?
- Priorities for development
There are a number of other performance indicators in use in Australian academic libraries that are not included in the list above. In 1999 the emphasis will be on improving and making the current indicators more relevant as part of an effort to improve the quality management framework. Internal benchmarks have been established with most teams and some external benchmarking has begun, for example process improvement and communication success KPIs have been benchmarked with other organizations as part of the leading and managing improvement and change network.
The performance indicator survey carried out in November-December 1998 as part of the CAUL EIP 'Best Practice for Academic Libraries' project identified a number of additional and important indicators for future development. Some of these indicators have in fact already been developed either through overseas publishers such as ISO, IFLA, or internally by individual CAUL libraries. A number of useful articles and websites covering all aspects of performance measurement are included in the Useful Resources list.
Useful sources
- Australasian sources
- International sources
1998, 'The cost of library services: Activity-based costing in an Australian academic library,' in Journal of Academic Librarianship, vol. 1998, 'Recommendations of the Cranfield Project on Performance Indicators for Academic Libraries' SCONUL Newsletter, Summer/Autumn, pp. It summarizes an Association of Research Libraries project on 'The character and nature of research library investments in electronic resources.' at American Research Library answers to supplementary questions about electronic resources as part of collections or accessible through library system terminals and their impact as part of library materials issues.
Proceedings of the 1st Northumbria International Conference on Performance Measurement in Libraries and Information Services held at Longhirst. Proceedings of the 2nd Northumbria International Conference on Performance Measurement in Libraries and Information Services held at Longhirst Management and Training Centre, Longhirst Hall, Northumberland, England, 7 to 11 September 1997. Newcastle, Information North, 1998. Proceedings of the 3rd Northumbria International Conference on Performance Measurement in Libraries and Information Services held at Longhirst.
Quality frameworks
Quality and Australian university libraries: an overview
The current interest and activity in quality and best practice across the Australian university library sector may also be influenced by the structural settings of libraries within universities. Mergers between higher education and TAFE, and the convergence of library and computing services, have both played a role in libraries becoming interested in, and in some cases adopting, frameworks such as the ISO 9000 series of standards or quality frameworks designed for vocational education and training . Some Australian universities, including RMIT University, Swinburne and Curtin University, have dedicated quality offices or units that encourage and support the implementation of quality practices across the university.
Why implement a ‘quality’ program or framework?
- Criteria for successful quality programs
- Theory into practice: successful quality program outcomes
- Who drives quality?
- Relationship between quality frameworks and tools
Ownership' of the program by staff at all levels achieved through employee involvement in the development and. Development and maintenance of effective teams, armed with knowledge of the principles of quality management and the tools. Strategic benefits for staff and the library through alignment of institutional and organizational planning and strategic direction.
A designated quality • A member of senior management is the coordinator's quality coordinator, this has facilitated success. We favor a model that has 'quality issues' mainstreamed rather than setting up 'quality management' separately, risking staff seeing quality and continuous improvement as something extra. Wollongong (via internal 'Quality and Service Excellence' programme, 1996 Award for Business excellence, 1998 Finalist in the Outstanding Achievement category).
Applying a quality framework
- Australian Quality Awards—Business Excellence Framework
- Seven criteria in the Australian Quality Awards for
- Organisational self assessment
- Benefits of self-assessment
- Australian Quality Awards for Business Excellence
- Implementing the Australian Business Excellence Framework
- Case Study 1: University of Wollongong
- Case study 2: University of Melbourne Library
- The Swinburne Quality Management System (SQMS)
- Framework description
- Implementing SQMS: Swinburne University library
- The balanced scorecard
- Framework description
- Deakin University Library balanced scorecard
- Implementing the balanced scorecard
- Case study: Deakin University library
- International Standards Organisation ISO 9000 series
- Possible requirements of the standards
Benchmarking visits to partner businesses helped establish the library's role in a financially/for-profit oriented framework. In 1998, the Library completed an internal self-assessment against two QA categories—Information and Analysis, Customer Focus. A commitment to see the recommendations made as a result of the self-assessment process implemented supports staff.
A key aspect of BSC's adoption was its ability to provide a quality management and continuous improvement tool. Focus groups have been successfully used to identify a hierarchy of customer values as part of BSC development and implementation. Simple and thorough follow-up with customers after they receive service is part of the service requirement.
Useful sources
- Australasian sources
- General overview/texts
- Experiences/case studies
- Frameworks and other tools/manuals
- International sources
- General overviews/texts
- Experiences/case studies
- Frameworks and other tools/manuals
The University was one of ten libraries visited as part of the 'Best practice in Australian University Libraries' project. The results of this study indicated that a significant number of university libraries were involved in the development of quality assurance processes and management and have formed a basis on which subsequent progress can be measured. The NTU Library was one of only a few service organizations to adopt and work with guidelines largely aimed at commercial operations, and their experience remains a leading case study in the adoption of best practice and quality improvement processes and programs within for the Australian academic library sector. 1995, 'TQM and quality assurance at Monash University Library', Australian Academic & Research Libraries, vol 1997, 'Quality assessment: combating complacency', Australian Library Journal, vol 1995, 'TQS at Victoria University of Technology', Australian Academic & Research Libraries, vol.
One of the few that provides some guidance to service-focused organizations on the need for and interpretation of the standard. 1995, Towards library excellence: Assessing best practice in the library and information sector, BLRD Report, London, British Library Research and Development Division. This model is also included in the Loughborough University report on the application of quality frameworks mentioned above.
Training and related topics
Training and Australian university libraries: an overview
- Training for benchmarking
- Additional sources of information on training for benchmarking . .115
- Additional sources of information on training for
- Training for quality
- Use of the self assessment process as a training mechanism
- Additional sources of information on training for quality
- Training for quality: Some overseas case studies
- Client skills training
- Useful sources of information for client services training
What is clear is that for libraries that wish to offer training opportunities for staff in one of the following areas, there is little in the way of an overview of where, how and with what results others have approached the training. The aim of what follows is only to provide a starting point for those wishing to explore staff training for benchmarking. In addition, the major commercial training providers regularly advertise in other issues of the journal.
It should include an understanding of relationships and interfaces with other processes and departments. For a number of library staff M-Quality was the first and only source of supervisor training and they are grateful for the extensive nature of the training. This practical book describes an alternative agile approach to staff development based on work-based learning methods, self-development and internal resources, which provides a means of focusing learning on the needs of the individual.
Competency standards
- Standards
The Australian Quality Council has also produced Quality Management Competencies that are nationally endorsed standards, such as the Library Standards. Arts Training Australia 1995, Library Industry Competency Standards, Arts Training Australia, Woolloomooloo, N.S.W. Australian Library and Information Association 1999, Job Level Guidelines for Librarians and Library Technicians 1998,. http://www.alia.org.au/publications/wlg/). Australian Library and Information Association 1996–7, Competence Standards and the Library Industry: A Workshop Series, ALIA, Canberra.
The ALIA Board of Education has produced four workshops on competency standards and the library industry. Workshop topics designed as self-paced packages are: An overview of competencies and competency standards; An introduction to competency levels and Library Industry Competency Standards; Linking industry competency standards to your organization;. Further information and an overview of relevant publications available from (http://www.alia.org.au/competencies.html).