The 2008 crisis also caused an increase in the public's negative perception of banks (Arner et al., 2015). This increase in public interest in fintech is at odds with the performance of banks during the pandemic. Bank stocks have crashed during the pandemic, especially in the early stages of the pandemic.
Several previous studies have investigated the relationship between fintech and banks. 2017) has conducted research aimed at clarifying the role of fintech digital banking start-ups in the financial industry. Furthermore, to our knowledge, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the dynamics between fintech and banking has not been investigated in the literature. This study also considers the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the relationship between fintech and banks.
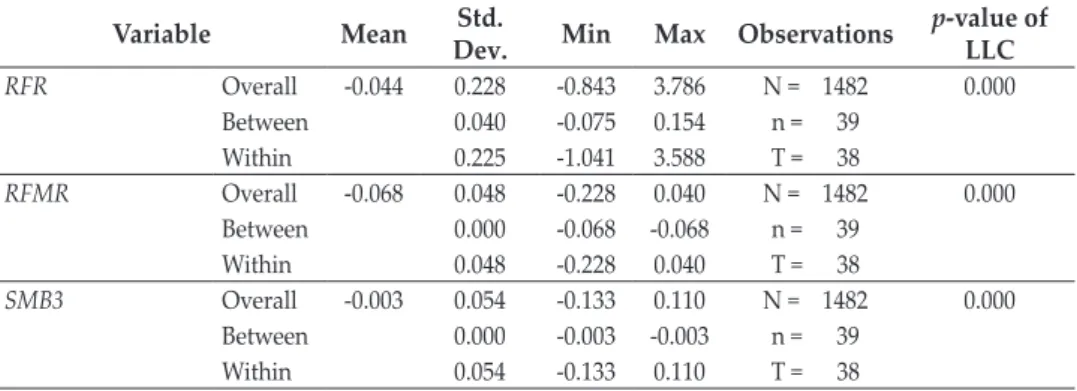
Indonesian banks experienced significant stock declines and increased volatility in the early stages of the pandemic (Mirzaei et al., 2020; Olivia et al., 2020). Fintech can replace banks in the industry by offering an alternative with lower costs and more efficient services, thus "stealing" banks' customers (Cole et al., 2019;. We then obtain the value of δ1 to δ3 to see the changes in the relationship between fintech and banks in these five different time horizons.
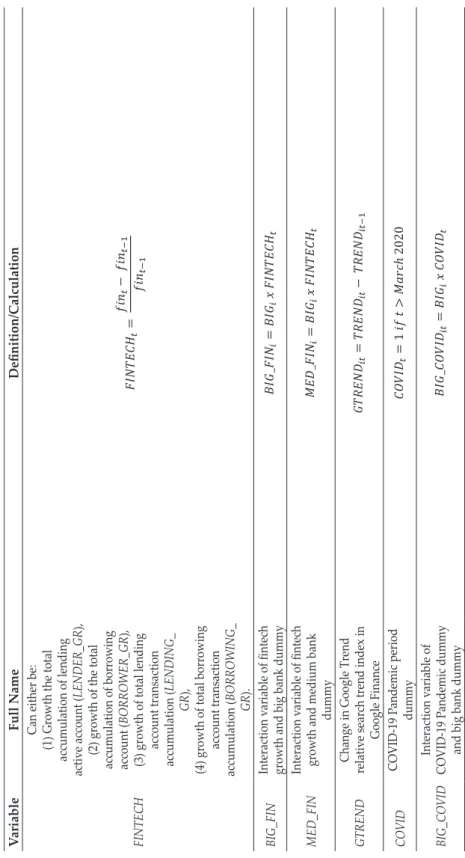
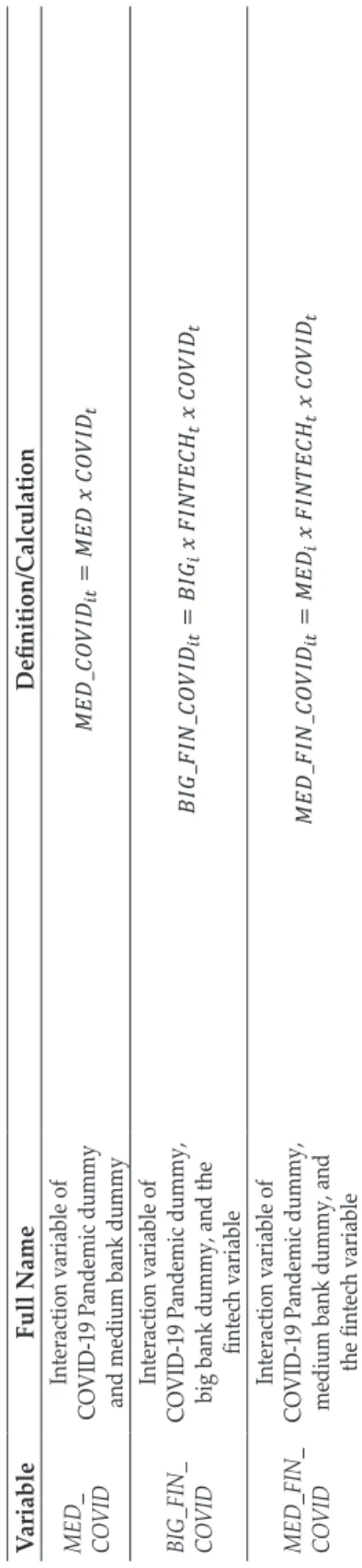
For the FINTECH variables: fintis one of the four fintech representatives in month t, and fint-1 is its value in the previous month, respectively.

RESULT AND ANALYSIS
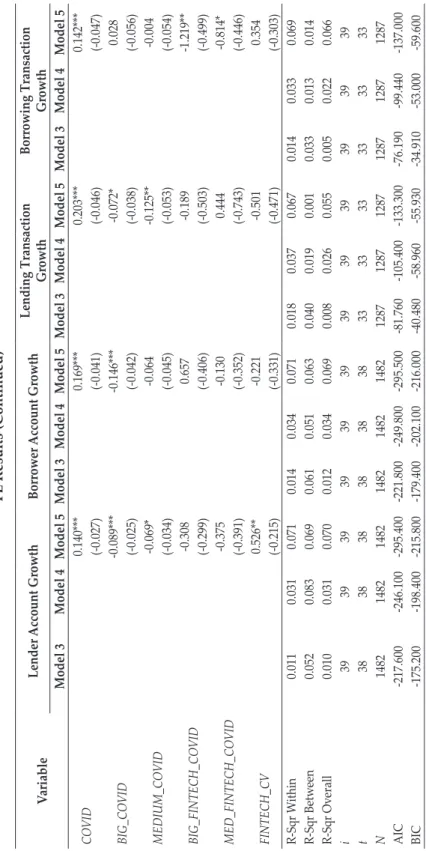
We use four financial technology proxies: (1) growth in total active loan account collection, (2) growth in total loan account collection, (3) growth in total collection of loan account transactions, and (4) growth in total borrowing account transaction accumulation. In models three and four, the fixed effect estimates show that the fintech variable is consistently negative and significant in both models with four different fintech proxies. When other proxies of financial technology are used, the interaction variable between financial technology and the COVID-19 dummy shows no statistical significance and mixed signs of the coefficients.
These findings suggest that we conduct further analysis on the changes in the relationship between fintech and banks during the COVID-19 pandemic. This table presents the results of the fixed effect model with robust standard errors using models three to five corresponding to equations (3) to (5) for each fintech proxy. The first row of the table describes the fintech proxies used in estimating the models (detailed in the second row).
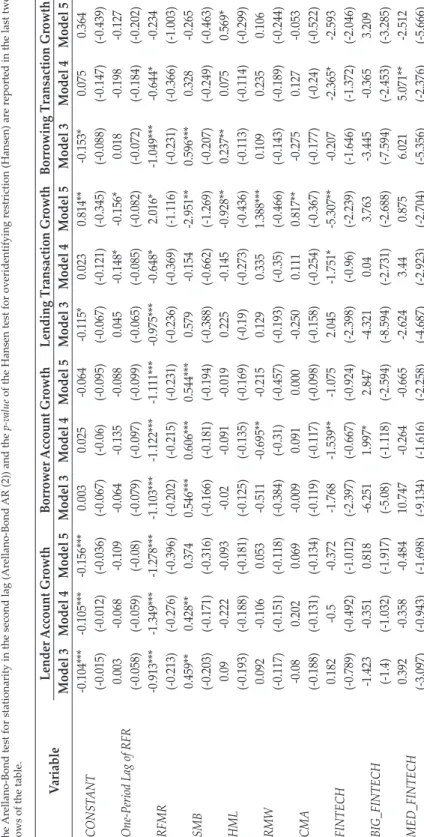
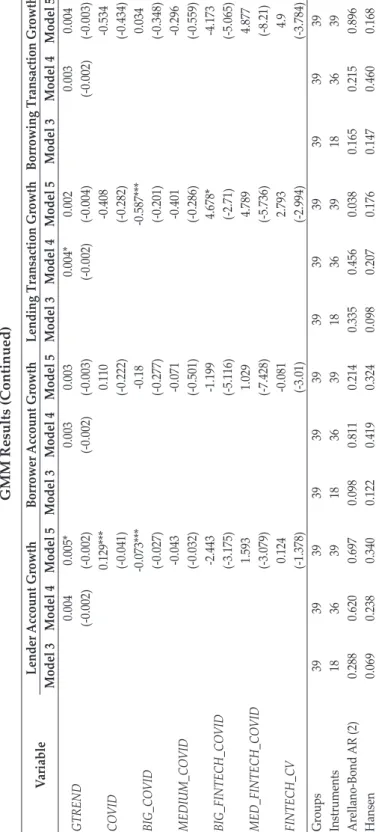
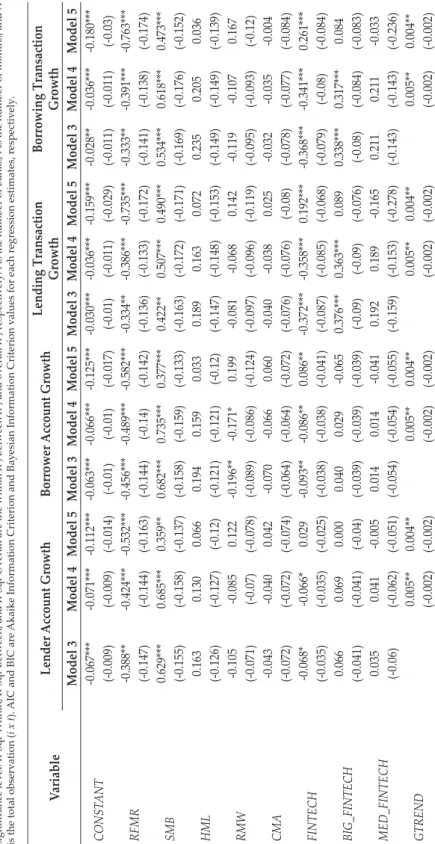
GMM Results This table presents the two-stage system generalized methods of moment models with robust standard errors using models three through five corresponding to Equations (3) through (5) for each fintech proxy. This figure shows the changes in the relationship between fintech and banks as shown by the value of the parameters δ1 to δ3 from equation (4). The changes in the relationship between fintech and banks during the pandemic also suggest an exemplification of fintech's relatively more positive (or less negative) impact on larger banks and the opposite for smaller banks.
These findings support the argument that larger banks tend to benefit from the rise of fintech. This rise of fintech poses both threats and opportunities to the Indonesian financial system (Sjamsudin, 2019). Sjamsudin (2019) also says that the development of fintech has been highly supported by financial authorities in Indonesia.
Looking at all these advantages and possible cooperation with existing financial institutions, it is obvious that financial authorities in Indonesia will promote the growth of financial technology and digitally transform existing banks by adopting an open banking business model strategy. The other four are "the integration of the digital economy and finance, the digital transformation of the banking industry, the management of risks and competition, and the management of national interests in the cross-border use of finance and digital technology" (Bank Indonesia, 2019). Financial authorities in Indonesia have been quick to confront the emergence of financial technology in the financial ecosystem (Davis et al., 2017).
This study found that the rise of fintech has a different impact on larger banks and smaller banks. Therefore, it is important that financial authorities pay more attention to smaller banks in the implementation of financial authorities' strategies to achieve a sound financial and economic ecosystem through the inclusion of fintech and the digital economy.
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Promoting the open banking business model to digitally transform legacy banks and develop financial technology as part of the financial ecosystem is what financial authorities in Indonesia are planning. This means that smaller banks will find it more difficult to implement an open banking business model than larger banks (which have already benefited from the growth of fintech). The severity of the negative impact is less for larger banks than the fixed effect estimates suggest.
Moreover, the analysis of the changes in the relationship between fintech and bank before and during the pandemic tells us that fintech, when estimated using only data for the COVID-19 pandemic period, tends to have a more positive impact on large banks, while the consequences for medium and small banks are significantly more negative. An additional delay of one period of the dependent variable (RFR) has been added to the models.