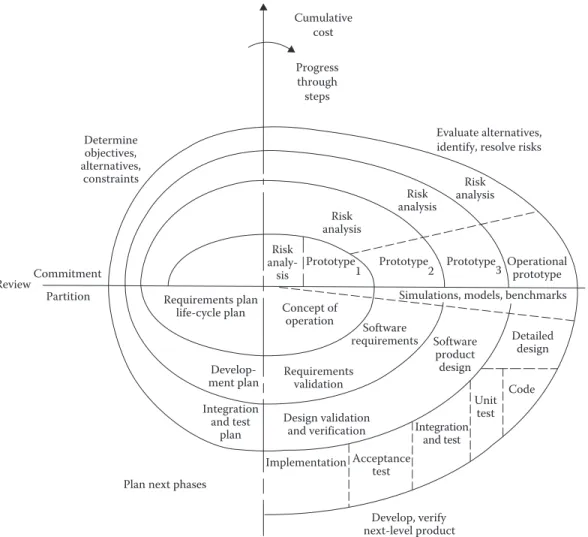
Human factors engineers generally work at the interface of the technology/system and human operators. For less complex products, such as computer software, training can be a built-in part of the design. But this hypothesis clearly shows that being in close proximity to the optimal is critical.
Zadeh from the University of California, Berkeley, conceived the idea of fuzzy set theory in the 1960s. One notable example is the design of the gasoline tasks on the Ford Pinto model. While this feature is part of the challenge, it is also part of the brilliance.

Discuss why ergonomics designers are advised NOT to try to fix things that the operating personnel do not feel are broken, even if the designer is sure of it
This field has emerged from the joint efforts of human factors and work design specialists whose interests have included time and motion studies, method design, and work simplification. This is especially true given the contemporary drivers of international competition and the need to compete in these markets. Ergonomic designers will need to be leaders in concurrent engineering design if they expect to manage product design to be user-centered while simultaneously being part of the manufacturing, product reliability, and maintenance service of those products as well as their manufacturing operations. .
Since buyers of a company's products determine perceived quality and sales, who is better equipped to help lead concurrent design efforts.
If an ergonomic intervention was estimated to increase sales by $80,000 within 2 years, what is the maximum investment if the cost of capital is 15%, the cost of
This initial chapter has been written as an introduction to the field of ergonomic design, particularly as it is practiced in industry. It is clear that the role of this activity has greatly increased, both in breadth and depth. Ergonomic design must satisfy both the needs within the company as well as the needs of the customers who use the manufactured products.
If you were to measure human performance in using this device, what criteria would be important.
Why would an ergonomic designer want to know the standard deviation of the means of different people performing a specified task? If human tasks need to be
Second, suggest how you might identify variables that are likely to change performance measures and why you feel performance would change.
Think of the LIMET acronym and describe a situation that represents each interac- tion between LxE, IxT, and LxT
What is meant by a “robust design” and what do critical incident studies have to do with it?
What are the implications of Helson’s U-hypothesis with regard to developing designs that optimize human performance?
Suppose that you were asked to rate objects that were good examples of being “big”
How can a study of design failures help one find a better design?
What is the biggest drawback of doing field studies in ergonomic design practice?
What is the principal difference between experimental simulations and laboratory experiments? What are some of implications of these differences?
The single humerus bone of the upper arm connects to the scapula in the shoulder. Bursitis - Inflammation of the bursa (small pockets of slippery fluid that lubricates the points where the tendons pass over the bones). Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, which often contributes to tendonitis in the shoulder.
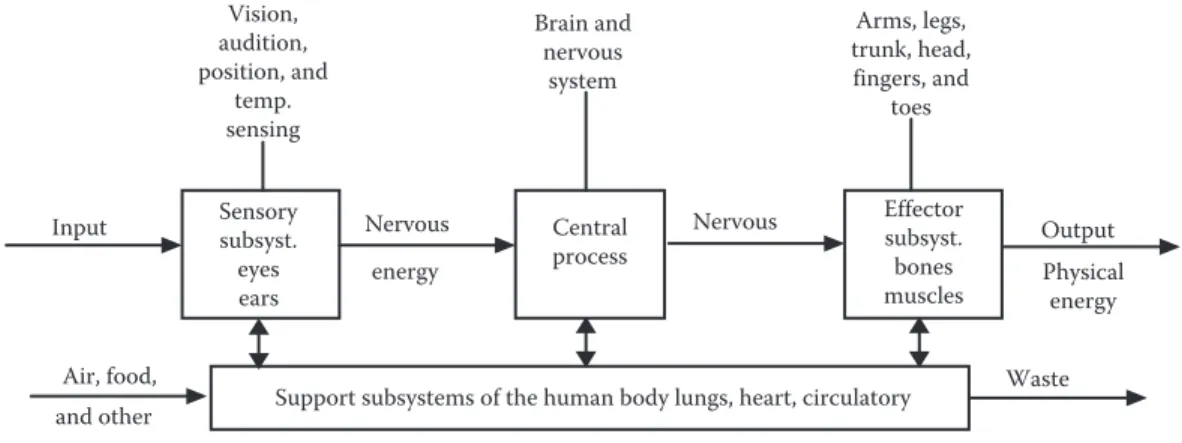
Some of the fibers within striated muscles are called red fibers (because of their myoglobin pigment). Other senses of the human sensory subsystem include the sensations of pain (free nerve endings), temperature and pressure (skin and underlying tissue), touch and vibration (mainly skin), smell (tip of the nasal cavity), taste (tongue and mouth). ), position and movement (muscle and tendon endings) and kinesthesia (joints of the skeletal subsystem).
When a person has his or her lower arm in a horizontal position and the palm is fac- ing upward, why can he or she exert a greater upward force than a downward force?
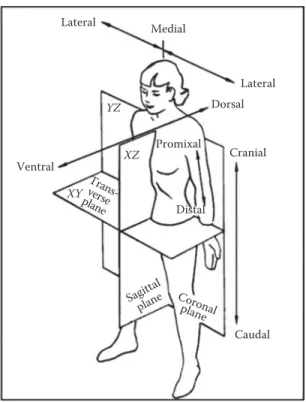
This chapter provides an overview of the general structure of the human body to help readers understand how the body works and how its size and capabilities affect task performance. This background will help you understand the topics in the following chapters that deal with specific problems. Another aim is to demonstrate the need for knowledge about body size and movement so that usable, safe and efficient tools and products can be designed.
Knowledge of the human dimension is especially important for designing products that people wear and setting up assembly stations. Some of these applications are shown later in this book, with special emphasis on principles of economy of motion, hand tool design, and industrial safety.
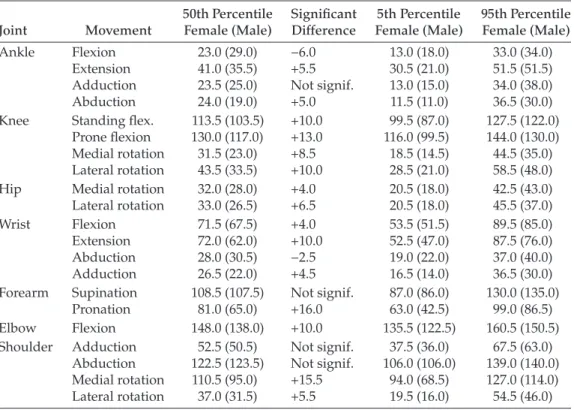
What is the two-thirds rule relative to arm and leg strength and what are its implica- tions in ergonomic design?
Name three principal factors that affect muscular strength and state how muscular strength changes with each of these factors. Discuss how each of these factors affects
When metabolism is measured by the rate of oxygen consumed, the metabolic rate increases rapidly at the onset of a physical task in an exponential fashion to meet the
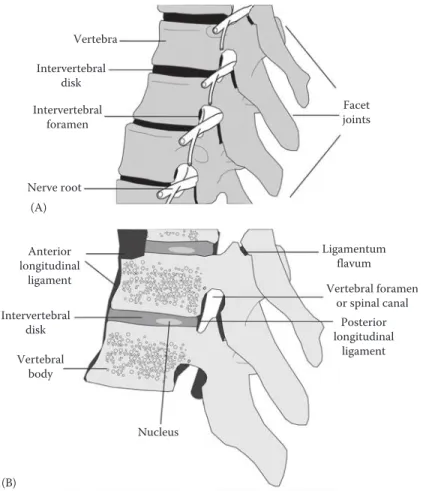
What are ligaments, their elastic properties, and the role they serve in body move- ments? How does this knowledge relate to how products or hand tools should be
Why lung reserves at the maximum limit of the volume of air taken in during the breathing cycle. If this measure was used as part of personnel selection, what are the implications of high or low readings by the applicant.
Physical human movements are constrained by the body joints required by it
When a muscle is held in a contracted position continuously for long time periods, there is a reduction of blood flow to a bundle of muscles. What is the physiological
Give an example of the following types of joints in the human body and associated movement characteristics: spheroid, pivot, hinge, and saddle joints
If a partial load is placed on a muscle for a sustained time period, how does the body react in order to reduce fatigue? How does this body functioning affect the way
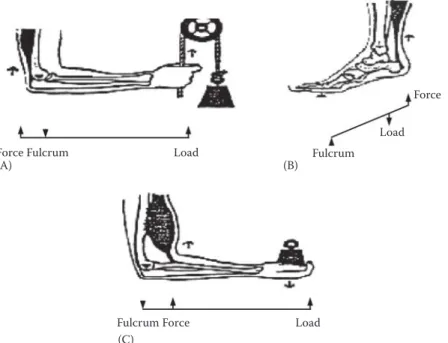
When a muscle contracts to pull up a bone structure from one end, using the other end as a fulcrum, and raising a load in the middle, then what class of lever is being
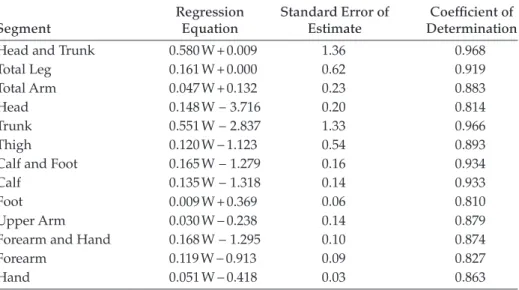
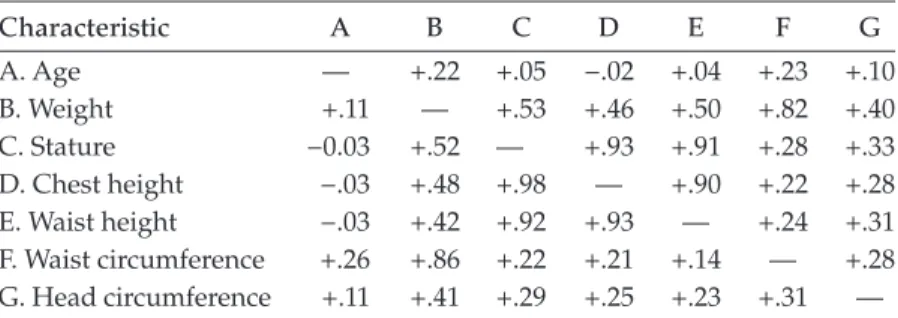
How do the approximate dimensions of the human body differ between males and females? Discuss how these differences might impact design
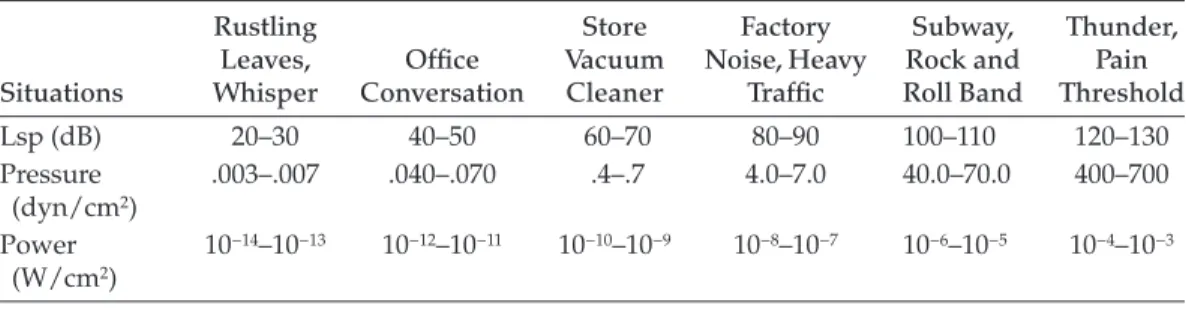
What is the difference between phons and sones in terms of what they measure?
If two sound sources are each 10 dB and they are of the same frequency, what is the difference in the resulting sound level between the situations where they are totally
How does one use Landolt rings to measure visual acuity?
What part of the eye regulates the amount of light entering and falling on the photoreceptors? How does it work?
What kinds of eye movements occur during reading and about what percentage of the total reading time is spent in each or those movements?
Two ways of measuring eye movements include a method where electrodes on the sides of the eyes disclose horizontal movements and another method where
What additional sensory information does the brain receive about the orientation of the human body other than from vision and audition?
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method of indirect calorimetry
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of designing for a fixed percentage of a population. When is this approach likely to be problematic?
More frequently used items should be in the normal or primary area of the reach envelope. It is usually also recommended that the seatback be tilted backwards. This tilting back makes it possible to distribute some of the weight to the backrest.
Legroom must be provided under the seat and in front of the person. The Dvorak layout assigns the most frequently used key to the stronger fingers and the middle row of the keyboard. Notice that all the vowels are in the middle row of the left hand.
This protection can be achieved by enlarging the grip cross-section in front of the hand position. When the narrower oval section is in the direction of the hammer head, a correct orientation can be easily felt. Most hand tool testing was done at the Kansas City, Mosby plant in the 1960s.
Tool bending can also provide more power for certain orientations of the human body. As previously mentioned, the maximum grip strength varies greatly with the size of the palm opening. While the use of the torque arm proved effective, there was considerable resistance from the worker.
Warning labels must be placed adjacent to the catch points and in direct view of the operator.
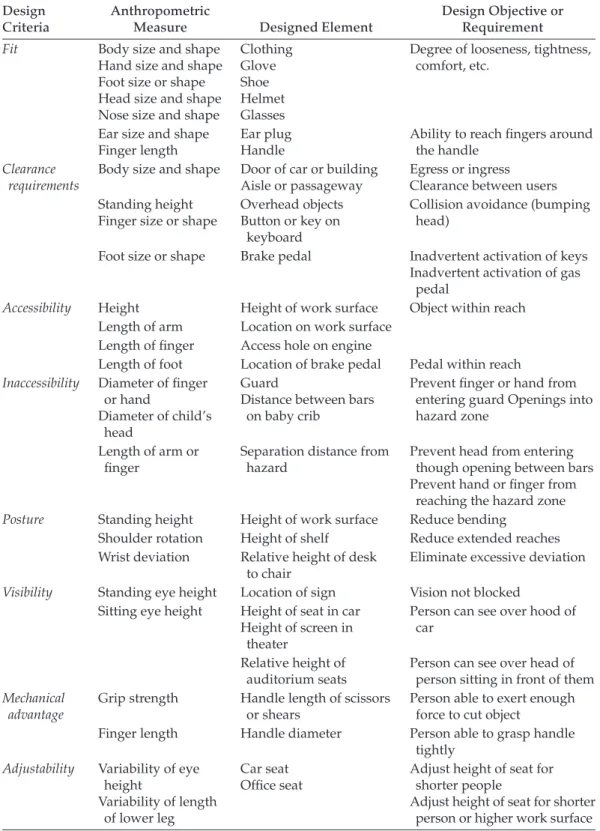
What are some basic anthropometric criteria and measures? Give some associated design objectives
This would quickly lead you to the point where stairs and curbs are barriers that impede the mobility of wheelchair users. Unfortunately, compliance with building regulations does not guarantee that all forms of mobility aids can be used. Older buildings are a particular problem, as they were designed before housing wheelchair users was an issue.
Entrances in older buildings usually include stairs, and elevation changes often occur even on the same floor of a building. Sometimes it is possible to install an elevator between adjacent buildings that has doors on both sides to accommodate the different floors between the two buildings. At the same time, the number of potential applications is rapidly increasing due to changing technology and the current regulatory environment.
Why should bench height differ between work tasks? How does the normal area differ from the maximal area for males and females, respectively?
Why is it important in designing seating to allow operators to change their posture?
How do automotive seats differ from chairs at work and why should they differ?
What part of a person’s back particularly needs support from the chair?
What is the Frankfurt plane and what is its significance?
What is the recommended height of the top of a computer VDT and how would you determine it?
At what height should the armrests of a chair be?
Why should chairs have open space beneath them and how much is needed?
If you wanted to place a foot-actuated pedal for a seated operator at a workstation, what range of positions in front of the operator would be the best to choose for toe actuation?
Differentiate between radial and ulna deviation of the hand and between extension and flexion of it
What is the principal difference and advantage of the Klockenberg–Kroemer or Apple keyboards over the regular typewriter or computer keyboard? What is your
What do you believe is the most important principle in the design of seating?
Why would you expect computer graphic models of people to be more useful to ergonomic designers than using templates?
Explain why there should be a definite and fixed place for all tools and materials
What does QWERTY mean and what is its significance?
Techniques that are used to determine a better hand tool design are chronocy- clegraphs, infrared photography, EMG, subjective appraisals, television, timing
What are important considerations in the grip design of a ratchet-activated hand drill that converts vertical hand motion into a drill twisting motion?
Describe some of the principal differences between precision and power grips in hand tool design
Describe the features that should be included in the design of soldering irons that are used for fine industrial assembly operations
Explain why bending a tool’s handle is not always a good ergonomic idea
Why is it necessary to explain to users how a new tool should be operated during the introduction of a new tool design?
What are some methods for improving the safety of tools and machines at the point of operation? Discuss the role of ergonomics with respect to each method
Discuss ergonomic issues that might arise for each form of protective equipment covered in this chapter
A new manufacturing tool is expected to cost $150,000.00, but it would change the production rate from 15 assemblies per day (in two daily shifts) to 40 during a sin-
It is easy to see that the first step of the 5S procedure can free up space and eliminate clutter. Some of the benefits of 5S reported to the group by Wabash International included (1) reduced space requirements, allowing them to roughly double production without investing in larger facilities; (2) an 80% reduction in accidents; (3) major improvements in productivity and product quality; and (4) greatly improved employee morale. To begin with, the energy of the emitted radiation in the visible range is called light energy (see Box 4.3).
After light from the source strikes an opaque surface, some of the light is absorbed and the rest is reflected. Instead of directing the light at the viewed object, 90% or more of the light is directed upwards, towards the ceiling. After correction of photometric measurements for the sensitivity of the human eye, the luminous intensity (I) of a light source is determined.
The first quantity is normally measured in terms of the visual angle (α) subtended by a visual element to the viewer's eye. Visual acuity is the eye's ability to perceive fine details, as explained earlier in Chapter 2. The light reflected from the surface of the screen is called fogging, because it can be seen as a veil of light passing over the viewed surface. object is drawn. .
On the other hand, if it is focused on a small part of the visual field, even a small amount of light can cause glare. Match the colors and color rendering properties of light sources to the needs of the people using the task-related environment.
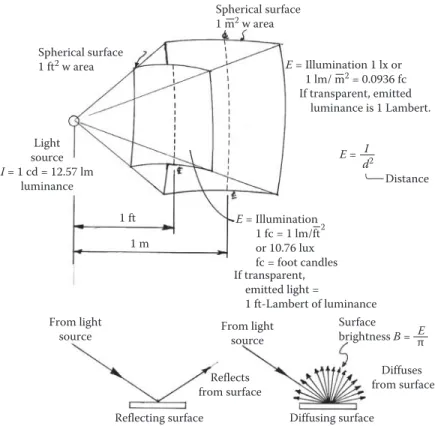
Enclose the source
These responses include shivering, which increases the heat generated by metabolism, and decreased blood flow to the limbs and skin, which reduces the rate at which heat is transferred from the body. To calculate the metabolic rate of a specific person doing a specific task, the values in the table must be multiplied by a conversion factor and the skin area of the evaluated person. Encounter units reflect both the size of the person being evaluated and the level of activity.
The rate of heat loss or gain through conduction-convection depends on the exposed area of the person's skin, the difference in skin and air temperature, the insulating values of the clothing covering the unexposed skin, and the air velocity around the body. Note that the constant k depends on the units used to measure air speed and temperature, body skin area, and the presence of clothing. Evaporative heat losses depend mainly on the wetted skin area, air velocity and air saturation deficit.
The temperature values are plotted along the horizontal axis at the bottom of the graph, and the curved lines running from the top left to the right are the relative humidity lines.* The upward slope of each relative humidity line describes how the water vapor pressure increases with temperatures when the relative humidity is kept constant. Enthalpy is the inherent amount of heat energy held by moist air, for various combinations of temperature and humidity, and is measured in units such as kilojoules per kilogram of dry air (as shown in Figure 4.5), the number of British thermal units (BTUs) per pound, or watt-h per gram of dry air. For pure heating and cooling, or, in other words, the addition or subtraction of heat without changing the humidity, the change of state corresponds to a horizontal shift on the psychrometric chart from one temperature to another.
Equipment can be provided to help people perform some of the more strenuous tasks, such as lifting. Such gloves have been shown to provide both good insulation and high levels of dexterity.* The concept of layering has a long and far-reaching history.† It should also be noted that mittens are warmer than gloves, but gloves allow for better dexterity .