Effect of maintenance at different salinities against the infection level of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in postlarval Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp. Effect of maintenance at different salinities against the infection level of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in postlarval Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp. This study aimed to determine the effect of different salinity levels on WSSV infection level in postlarval vannamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei).
Deteksi white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) pada udang windu (Penaeus monodon) di Bali dan Jawa Timur menggunakan metode Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).

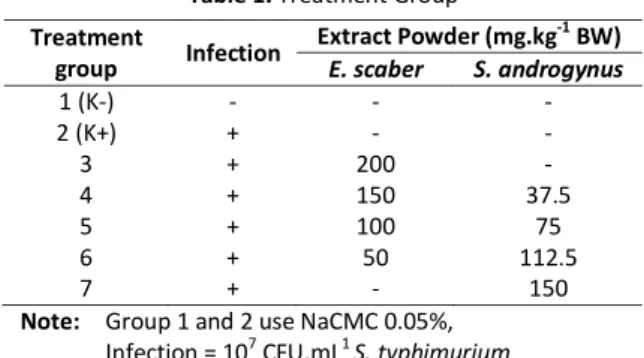
The relative number of CD4+IL2+ T cells used in this study to recognize the treatment effect of E. The highest amount of CD4+IL-2+ cells was found in pregnant mice that were infected and given extract E. The result of ANOVA shows that relative number of CD4+IL-2+ cells after infection with S.
It is shown by the significant increase in the mean amount of CD4+IL2+ and CD4+IL4+ T cells in pregnant mice that were infected by S.

Bioactivity of Combination Elephantopus scaber and Sauropus androgynus on the Level of B220 cells of Lymph Node in Pregnant Typhoid BALB/c Mice
The results showed that the extract treatment significantly increased the relative number of B220 cells in the lymph node-pregnant mouse model of typhoid fever. The relative number of B220 cells on day 12 indicates that infections in pregnant mice are lower than without infection. The activity can be seen by an increase in the number of B220 cells compared to infected pregnant mice.
Increasing numbers of B220 cells occurring are not significantly different from conditions in pregnant mice without infection.
Effect of Cilembu Sweet Potato Starch and Storage Times on Physicochemical and Microbiology of Synbiotic Yoghurt Ice Cream
Effect of Cilembu sweet potato starch and storage times on the physicochemical and microbiology of synbiotic frozen yogurt. The addition of cilembu starch limited to 6%, related to the texture of synbiotic ice cream. ANOVA showed that the addition of cilembu sweet potato starch with different concentrations to synbiotic frozen yogurt yielded a highly significant difference (P≤0.01) of the total LAB.
The quality of synbiotic yogurt ice cream with the addition of Cilembu sweet potato starch treatments. Analysis of variance showed that different frozen storage times of synbiotic yogurt ice cream yield a highly significant difference (P≤0.01) of the total LAB. The results of ANOVA showed that addition of Cilembu sweet potato starch with different concentration on synbiotic yogurt ice cream gives significant difference (P≤0.05) of the pH values.
Statistical analysis showed that the addition of Cilembu sweet potato starch with different concentrations to synbiotic frozen yogurt yields a highly significant difference (P≤0.01) of the EPS values. Analysis of variance showed that different frozen storage times on synbiotic yogHurt ice cream yield a highly significant difference (P≤0.01) of the EPS values. Analysis of variance showed that the addition of Cilembu sweet potato starch with different concentrations to synbiotic yogurt ice cream yielded a highly significant difference (P≤0.01) in the viscosity values.
Addition of different concentration of Cilembu sweet potato starch on synbiotic yogurt ice cream showed a highly significant difference (P≤0.01) of the melting rate values. Analysis of variance showed that addition of Cilembu sweet potato starch with different concentration on synbiotic yogurt ice cream gives highly significant difference (P≤0.01) of the exceedance values.

The Effectiveness of hrGFP Gene Reporter Role in Carp Fish (Cyprinus carpio) Transgenesis Process Based on Convocal Microscopy Analysis
Efficacy of hrGFP gene reporter role in carp (Cyprinus carpio) transgenesis process based on confocal microscope analysis. At the beginning, the primary material is selected to obtain the sperm and eggs of the carp Cyprinus carpio. Based on the observation of the level of fluorescence intensity, we found that the highest level of intensity on the sperm is achieved at a concentration of hrGFP of 30 ng.µL (A1B3 treatment) with an arbitrary fluorescence intensity of 1050.
The lowest fluorescence intensity is obtained from the concentration of 90 ng.µL-1 (Treatment A1B3) with fluorescence intensity of 2250 arbitrary. The lowest fluorescence intensity of hrGFP in electroporated sperm is still higher than control sperm. The low fluorescence may be caused by the growth and development of the carp embryo tissue and also correlates with the distribution pattern of hrGFP expression (fluorescence) in the carp embryo.
Following the result of observing the fluorescence of hrGFP in already hatching carp fish larva, it is shown that the fluorescence of hrGFP at 30 ng.µL-1 concentration (Treatment A1B1) can be explained as follows. The fluorescence intensity of the tail part of the carp fish is 4000 arbitrary, the belly part is 3800 arbitrary, and the head part is 3600 arbitrary. Display of hrGFP fluorescence in the tail of larval carp fish in SI screen (b).
The display of hrGFP in the tail of carpfish larvae on the screen based on 3D reconstruction (c). The highest hrGFP fluorescence in the head of carpfish larva (treatment A1B1) at 100 times magnification with a fluorescence intensity of 3900 arbitrarily (a).

Antibacterial Activity of Some Herbs Water Extract against Escherichia coli
Treatments were P0 = Aquadest; P1 = tetrachlorine; P2 = aqueous extract of ginger; P3 = aqueous extract of red ginger; P4 = aqueous extract of galangal ginger; and P5 = Zerumbet aqueous ginger extract. While the minimum inhibition concentration was performed by testing only red ginger because it has the best inhibition zone diameter [8]. The result showed that red ginger had the largest diameter among herbs, which was mm, and significantly different (P<0.01) ability to inhibit the growth of E.
Although the ability of red ginger to inhibit the bacteria was still significantly lower compared to the positive control (tetrachlor/P1). The result may also indicate that bioactive compounds in red ginger may inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Red ginger contains phenylpropanoid, gingerol and shogaol as active substances that could have an antibacterial effect [10].
The high content of essential oil in the red ginger can also play an important role as an antibacterial. This finding on Diameter of Inhibition Zone for red ginger is categorized as strong. Test for Minimum Inhibition Concentration Since the best result of Diameter of Inhibition Zone was obtained for red ginger, further testing is needed if dilution of red ginger with water will show similar antibacterial effect.
The trend of results showed that the higher the concentration of red ginger, the lower the population of E. It can be concluded that red ginger has the largest diameter of the inhibition zone, so the use of 100% water extract of red ginger could be applied to poultry. farms to replace the use of tetrachlor antibiotics.

Potency of Green Cincau Leaves (Premna oblogifolia merr) Juice as Prebiotics and its Effect on Laying Hen Performances
Potency of Cincau (Premna oblogifolia merr) green leaf juice as a prebiotic and its effect on laying performance. Pectin in the juice of green zincau leaves has been suspected as a substrate to support the growth of lactic acid bacteria (LAB). The pectin in the juice of zincau green leaves could be fermented by microflora into short-chain fatty acids (VFAs), and some specific microflora produced Latin acid, so that the pH decreased and inhibited pathogenic bacteria [14].
The juice of green cincau leaves as an additive in the feed of laying hens had no significant effect on feed intake (Table 9). This indicated that the fiber component in the juice of green cincau leaves can be tolerated by laying hens. Treatments with different levels of green cincau leaf juice did not significantly affect egg weight (Table 9).
Green cincau leaves juice as an additive in laying hen diets did not significantly affect feed intake and egg weight, so feed conversion ratio (Table 9). The potential effect green cincau let juice as prebiotics could not be able to change the performances. This study found that the adverse effect of pectin could be eliminated by cellulose content in green cincau leaves juice, so that feed conversion did not change.
The use of cincau green leaf juice up to 12.5 mL.bird.-1day-1 in feed did not significantly affect (P>0.05) the performance of laying hens. Effect of water green leaves of Cincau (Cyclea barbatas merr) on acetylsalicylic acid-induced gastric acidity and characteristic gastrohistopathology in rats.

Tapak liman (Elephantopus scaber L) Extract Induced CD4 + and CD8 + Differentiation from Hematopoietic Stem Cell/Progenitor Cell Proliferation
Tapak liman (Elephantopus scaber L) CD4+ and CD8+ differentiation from hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell extract.
Sasmito Djati 1* , Hindun Habibu 2 , Nabilah A Jatiatmaja 3 , Muhaimin Rifai 1
It is expected due to the negative feedback from the administration of Tapak Liman leaf extract. It is caused by the abundant compound of lupeol and flavanoid in the extract of Tapak Liman as anti-inflammation. With the increased doses of Tapak Liman leaf extract use, but tend to decreased cell numbers found in the treatment group of mice P3.
It was believed that the increase in the number of B cells was due to the flavonoid and lupeol compound contained in Tapak Liman. It indicates that the leaves extract of Tapak Liman 1 g.g bw.-1day-1 is sufficient to stimulate the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells on the lymphoid and erythroid pathway. Based on absolute cell counts, the number of TER119+CD34 cell populations was not increased after treatment with Tapak Liman leaf extract.
Based on the study, the group of mice fed Tapak Liman (E. scaber L) leaf extract for two weeks compared with the control group showed no significant effects on erythropoiesis in female BALB/c mice. B lymphocytes in the bone marrow and the increasing number of B cells (CD62L+) in the spleen. Based on the number of cell populations from all treatment groups, it is shown that the cell population tends to increase with the addition of Tapak Liman extract dose of 1 g body weight.
In addition, the increased expression of TER119+VLA-4+ is hypothesized to be due to the iron content in Tapak Liman, which acts to stimulate the progenitor hematopoietic cell to proliferate and differentiate into an erythroid precursor (TER119+VLA-4+). It appears that Tapak Liman extract leaves at a dose of 1 g.t.t.-1day-1 stimulate the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells in the lymphoid and erythroid pathways.

Title Typed in Bold, Capitalize each First Letter of Each Word, Except Conjunctive, Scientific name should not be Abbreviated
Calibri 14 Bold Center, should not exceed 12 words, except conjuctive)
Title entered in bold, each first letter of each word capitalized, except subjunctive, scientific name should not be abbreviated. Combination Halftone, combine figure and text (image containing text) and color graphics or in grayscale format. Black and white figures must be in grayscale mode, while colored figures must be in RGB mode.
If the figures come from the third party, they must take over the copyrights of the sources. References typed into numbering list (format number 1,2,3,…), arranged sequentially as they appear in the text (Vancouver system or author number style). In the manuscript, only the reference number is typed (not the author and year), for example: Obesity is an accumulation of fat in large quantities that would cause excessive body weight (overweight) [1].
Conclusion of the study's findings is short, concise and solidly written, without additional new interpretation. This section can also be written about research novelty, advantages and disadvantages of the research, as well as recommendations for future research. (Calibri 10 Justify). This section describes gratitude to those who helped in kind as well as financially.
Importance of CD80/CD86-CD28 interaction in target cell recognition by CD8+CD122+ regulatory T cells.
