The effect of self-regulated learning to improve dietary management and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Dr. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by hyperglycemia caused by dysfunction of insulin secretion, insulin function. or both.1 The prevalence of DM has been increasing in both developed and developing countries over the past decades. Differences in the characteristics of the respondents after the dietary educational intervention based on the self-regulated learning approach in Dr.
The significant improvement observed in the quality of life aspects in this study indicated that the self-regulatory learning-based educational intervention had an impact on the quality of life of people with diabetes. Effects of predisposing, reinforcing and facilitating factors on self-care behavior of patients with diabetes mellitus in Minoodasht city, Iran.
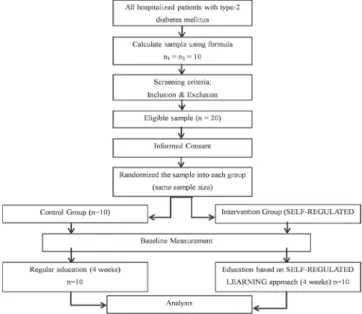
Maternal Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices about Traditional Food Feeding with Stunting and Wasting of
The aim of the study was to determine the relationship between maternal knowledge, attitude and practices in traditional feeding and infant stunting and wasting in farming families in Central Bengkulu District. According to height-for-age index, nutritional status was associated with maternal knowledge of traditional foods, while maternal dietary practice with traditional foods had a significant association with weight-for-age index. Relationship of Maternal Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices Regarding Traditional Foods with Weight-for-Age Z-Score Index WAZ Index.
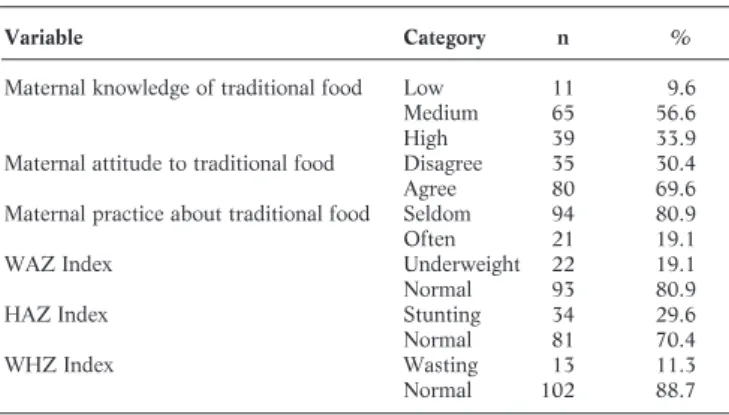
Overweight and Obesity Status with Dental Caries among Children Aged 7–12 Years Old in Badung District, Bali
Dental caries and obesity in children are multifactorial diseases associated with eating habits and certain lifestyle factors. This study aimed to assess the association between overweight, obesity and dental caries among children aged 7-12 years in Badung District, Bali Province in 2018. Overweight and obesity status with dental caries among children aged 7-12 years in Badung. District, Bali.
Furthermore, a statistically significant relationship was observed between overweight and obesity and the incidence of dental caries (odds ratio (OR): 1.72; relationship between maternal and child characteristics, diet, oral hygiene behavior and obesity status. Dental caries status. This study found that covariate variables, such as family income, eating habits and sweetened drinks, and oral hygiene behavior, influence the strength of the relationship between childhood overweight and obesity and dental caries.
Whereas, the diet of snacks and sweet drinks, family income and oral hygiene influenced the association of overweight and obesity with the incidence of dental caries in children aged 7-12 years in Badung District in 2018. This study suggests that obesity plays a significant role in the incidence of dental caries in children aged 7-12 years after controlling for variables such as family income, oral hygiene behaviour, snack food diet and sugary drinks. Association between body mass index, diet and dental caries in 6th grade boys in Medina, Saudi Arabia.
A longitudinal study of the relationship between dental caries and obesity in late childhood and adolescence.
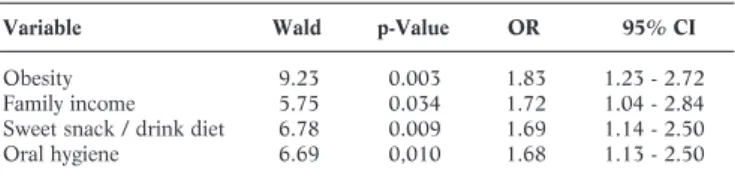
Personal Exposure of Traffic Policeman to Particulate Matter in Jakarta: Distribution of Size, Chemical
The aim of this study was to analyze the personal concentration of PM2.5 and its composition among police working at the roadside in Jakarta. The weekday concentration of PM2.5 and PM0.25 among Jakarta police officers was higher than the weekend concentration. The purpose of this study was to analyze the personal concentration of PM2.5 and its composition among police working at the roadside in Jakarta.
A sample apparatus placed in the breathing zone of a police officer for 8 hours during his shift. While on weekends, the afternoon shift is higher than the morning shift, except for Harmoni. Another study indicated that the average concentration of fine particles, especially with a size within µm, decreased with increasing distance between the highway and the sampling site.
The appearance of potassium (K) in the air is due to the number of vehicles using diesel engines with a lack of maintenance on the highway. A previous study conducted in the year showed a significant difference compared to the results obtained in the current study. Furthermore, BC measurements carried out at 12 sites in the UK in 2006 alone showed that the average annual concentration of black carbon in the UK reached µg/m3.
Variation in characteristics of ambient particles at eight locations in the Netherlands – The RAPTES project.
Users’ Perception of the Hospital Information System in a Maternity Hospital in Lampung, Indonesia
A maternity hospital in Lampung Province is currently implementing the Computerized Provider Order Entry system as a clinical information system to support health care services in the outpatient clinic. Therefore, the aim of this study was to describe the use of information systems from the perspective of users, by applying the TAM framework in the early phase of the implementation of a clinical information system in a maternity hospital in Lampung. The use of the application model of the information system in the outpatient clinic by the end user includes the outpatient clinic registration, the polyclinic/practice room, the cash register and the pharmacy/drug storage.
The workflow begins at the registration unit, when the patient arrives and shows his or her medical treatment card. Some problems related to the application features in each unit in the outpatient polyclinic in a maternity hospital in Lampung can be described as follows (Table 1). The screen displayed on the control panel (the screen for patients on the waiting list) had a small font feature due to the small size of the monitor.
The primary problem was that there were no interface functions that cross-referenced the prescribed medication with the medication inventory available in the outpatient clinic of this maternity hospital in Lampung. The firmness of the higher management commitment, so the user will implement the current information system in the outpatient clinic and began to develop the potential initiative for the information system development in the outpatient clinic. Not to mention when prescription drugs prescribed for room control were not available in the hospital drug inventory.
A unit cashier is an indispensable unit in the ambulatory service, 14,15 included in a maternity hospital in Lampung.
Knowledge, Attitude, Practices, and Health Beliefs of Pregnant Women about Urinary Tract Infection and Its
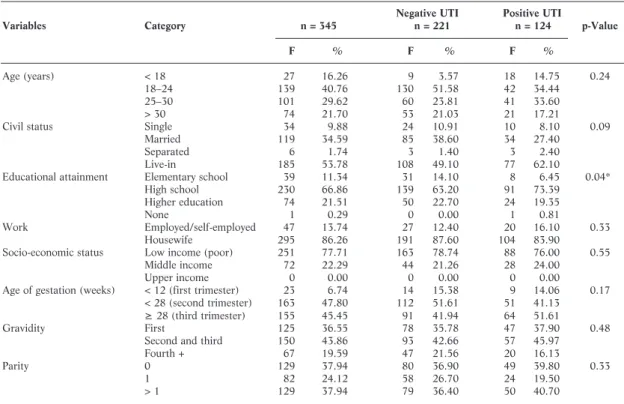
It also shows the test results of the association of sociodemographic variables with the occurrence of UTI in pregnant women significant at p value <0.05. Participants in the study were pregnant women, regardless of their gestational age, parity, gravity and age. Almost all respondents had a positive attitude about UTI prevention during pregnancy.
None of the sociodemographic variables showed a significant association with the occurrence of UTI in pregnant women; however, educational attainment showed a near-significant association with a p-value of 0.057. Description of health beliefs with the highest weighted mean based on the constructs of the pregnant women's health belief model. I strongly agree I agree I disagree I do not agree at all. None of the other sociodemographic variables showed an association with pregnant women's attitudes and practices.
Most of the pregnant women included in the study were housewives between the ages of 18 and 24 and were those with the highest incidence of UTI among the age groups. Level of education and socio-economic status were found to have a significant correlation with the respondents' unsatisfactory level of knowledge. The majority of respondents' low level of education contributed greatly to their unsatisfactory knowledge.
None of the sociodemographic variables showed an association with pregnant women's positive attitudes and satisfactory hygiene practices.
Midwife’s Role in the Mother-to-Child Transmission Prevention Program in Primary Health Care in Yogyakarta
Midwife's role in the mother-to-child transmission prevention program in primary health care in Yogyakarta. This study aimed to describe how midwives in Maternal and Child Health Clinics in Primary Health Care implement the PMTCT program for pregnant women and factors influencing their role. All midwives working in primary health care in the Mother and Child Clinics were assessed.
This study used the Precede–Proceed Model.8 Independent variables consisted of the midwives' socio-demographic characteristics, such as age, marital status, education level, work experience, HIV information available through lectures and outreach in the workplace, midwives' knowledge of HIV and PMTCT, plus their attitudes towards its implementation. The attitude variable included both those with positive and negative attitudes about the implementation of PMTCT, which scored in the good category, but this variable was not statistically significant (p-value = 1.000). Perception variable on institutional support showed that respondents who perceived institutions as good or poor implemented PMTCT in the good category.
Bivariate analysis concluded that the independent variables statistically related to midwives' role in the implementation of PMTCT were knowledge level and availability of information through socialization in the workplace. However, midwives who implemented the HIV/AIDS prevention program that scored in the good category in this study amounted to only 52.5%. The study also found that midwives' behavior in the implementation of PMTCT was influenced by the availability of information sources through socialization in the workplace.
Socialization in the workplace will usually include work steps and availability of facilities for implementation of PMTCT.

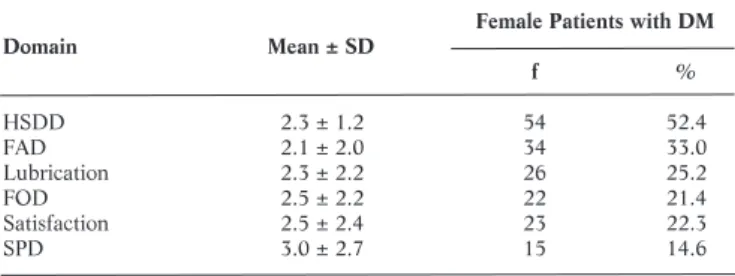
Sexual Dysfunction among Women with Diabetes in a Primary Health Care at Semarang, Central Java Province,
Sexual dysfunction among women with diabetes in a primary health center in Semarang, Central Java Province, Indonesia. This cross-sectional study was conducted to describe the status of sexual dysfunction among women with DM in Tlogosari Kulon Primary Health Care, Semarang, Indonesia, in March 2017. Sexual dysfunction among women with diabetes in a primary health care facility in Semarang, Central Province -Java,.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women with diabetes mellitus (DM) and in the control population has been reported to be 88% and 80%, respectively. Indeed, it is still necessary to investigate the factors associated with sexual dysfunction in women with DM. Based on the information described above, this descriptive study was conducted to explore the issue of sexual dysfunction in women with DM at a primary health care facility in Semarang, Central Java Province, Indonesia.
This descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted to measure the prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women with DM at Tlogosari Kulon Primary Health. Regarding psychosocial factors, the proportion of sexual disorders was higher among those with primary school education (80.5%). The results of this study showed that women with diabetes and hypertension stage II are at risk of developing sexual dysfunction.
Sexual dysfunction in women with type 1 diabetes: long-term findings from the DCCT/EDIC study cohort.
UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA BHPP BANK BNI UI DEPOK
SWIFT CODE: BNINIDJA
Reviewer Acknowledgment
Kesmas: National Public Health Journal Volume 14, August 2019 - November 2019
Author Index
Subject Index