The Secretary of State designated OAR Chapter 437 as the "Oregon Occupational Safety and Health Code." The rules initiated by Oregon in this division of the Oregon Occupational Safety and Health Code are numbered in a uniform system developed by the Secretary of State. The terms "subdivision" and "subpart" are synonymous within OAR 437, Oregon Occupational Safety and Health Code.
Oregon Occupational Safety & Health Division (Oregon OSHA) 350 Winter St. The rules referred to in this section are available for inspection in the Office of the Secretary of State. Administrative Rules and Office Documents Division, Oregon State Archives Building, Salem, Oregon 97310, or the Central Office, Oregon Occupational Safety and Health Division of the Department of Consumer and Business Services, Room 430, 350 Winter St. These standards are available from the Oregon Division of Occupational Safety and Health, Oregon Department of Consumer and Business Services, and the US Government Printing Office.
Cross supports means the horizontal members of a support system installed perpendicular to the sides of the excavation, the ends of which abut against either uprights or walls. Wales means horizontal members of a shear system that are placed parallel to the excavation face, the sides of which abut the vertical members of the shear system or the ground.
P SPECIFIC EXCAVATION REQUIREMENTS
These precautions include providing adequate respiratory protection or ventilation in accordance with subparts D and E of this part, respectively. iii) Adequate precautions such as the provision of ventilation shall be taken to prevent exposure of workers to an atmosphere containing a concentration of a flammable gas above 20 percent of the lower flammable limit of the gas. iv) When controls are used that are intended to reduce the level of atmospheric pollutants to acceptable levels, testing should be performed as often as necessary to ensure that the atmosphere remains safe. i) Emergency rescue equipment, such as breathing apparatus, harness and safety rope, or basket stretcher, should be readily available where it is dangerous. atmospheric conditions exist or may reasonably be expected to develop during work on an excavation. This device must be handled with care. ii) Workers entering bell pier holes, or other similar deep and confined excavations, shall wear a harness with a lifeline securely attached to it. The rescue line shall be separate from any line used to handle the materials and shall be so. attended individually at all times while the lifeline worker is in the excavation. h) Protection from risks related to water accumulation.
A registered professional engineer has approved the determination that the structure is sufficiently removed from the excavation to be unaffected by the excavation activity; or. iv). Such protection shall consist of skimming to remove loose material; installing protective barricades at intervals as needed on the face to stop and contain falling material; or other means that provide equivalent protection. Protection shall be provided by placing and holding such materials or equipment at least 2 feet (0.61 m) from the edge of excavations or by the use of restraints sufficient to prevent materials or equipment from falling or rolling into excavations , or by a combination of both if necessary.
The inspection is carried out by a competent person before the start of work and, if necessary, during the entire shift. Guardrails complying with §1926.502(b) shall be provided where walkways are 6 feet (1.8 m) or more above lower grades.
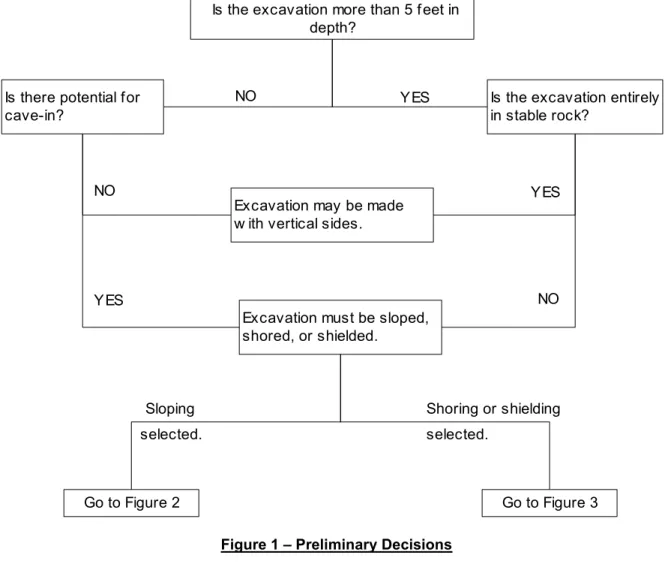
1926.652 Requirements for Protective Systems
P REQUIREMENTS FOR PROTECTIVE SYSTEMS
At least one copy of the tabulated data, which identifies the registered professional engineer who approved the data, must be kept at the work site during the construction of the protection system. After this time, data may be stored outside the workplace, but a copy of the data must be made available to the secretary upon request. A plan indicating the sizes, types and configurations of the materials to be used in the protection system; and.
At least one copy of the design must be kept at the workplace throughout. the construction of the defense system. After that time, the design may be stored off-site, but a copy of the design will be made available to the Secretary upon request. Before temporary removal of individual parts begins, additional precautions must be taken to ensure worker safety, such as installation of other structural parts to support the loads placed on the support system. v) Removal shall commence and proceed from the bottom of the excavation.
The elements should be released slowly, observing any signs of possible failure of the remaining structural elements or possible intrusion of the sides of the excavation. you). This appendix describes a method of classifying soil and rock deposits based on location and environmental conditions and the structure and composition of soil deposits. The classification of deposits is made based on the results of at least one visual and at least one manual analysis.
Visual and manual analyses, such as those listed as acceptable in paragraph (d) of this appendix, shall be designed and conducted to provide sufficient quantitative and qualitative information as may be necessary to properly identify the characteristics, factors, and conditions that affect the classification of applications. Observe the side of the open excavation and the surface adjacent to the excavation. Subsection P P-21 Appendix A for sources of vibration that may affect the stability of the excavation face.
If the excavation is later exposed to wetting influences (rain, flooding), the classification of the soil must be changed accordingly. The basic purpose of the drying test is to differentiate between cohesive material with fissures, unclumped cohesive material and granular material. To distinguish between the two, pulverize the dried clumps of the specimen by hand or by stepping on them.
The support or shielding system shall extend a minimum of 18 inches above the top of the vertical side. All excavations with a depth of 20 feet or less and having lower portions with vertical sides shall be screened or supported to a height of at least 18 inches above the top of the vertical side.
P TIMBER SHORING FOR TRENCHES
If water is to be retained, use special tongue and groove supports to form tight linings. The size and spacing of the elements for the section of trench that is more than 15 feet in depth is determined using Table C-1.3. Tight cladding refers to the use of specially edged wooden planks (eg, tongue and groove) at least three inches thick steel sheet piles or similar construction that, when driven or placed in place, provide a tight wall to resist the lateral pressure of the water and to prevent loss of backfill material.
Close Sheeting refers to placing boards next to each other allowing as little space as possible between them. If the vertical distance from the center of the lower cross brace to the bottom of the trench exceeds two and a half feet, uprights must be firmly embedded or a mud bank must be used. Where uprights are embedded, the vertical distance from the center of the bottom cross brace to the bottom of the trench shall not exceed 36 inches.
When the vertical spacing of cross braces is four feet, place the top cross brace no more than two feet below the top of the trench. When the vertical spacing of cross braces is five feet, place the top cross brace no more than 2.5 feet below the top of the trench.
P ALUMINUM HYDRAULIC SHORING FOR TRENCHES
From Table D-1.1: Find vertical shores and 2-inch-diameter cylinders spaced 8 feet on center (o.c.) horizontally and 4 feet on center (o.c.) vertically. A trench is dug in Type B soil that does not require lining, 13 feet deep and 5 feet wide. From Table D-1.2: Find vertical shores and 2-inch-diameter cylinders spaced 6.5 feet o.c. 3) A trench is dug in type B soil that does not require cover, but which nevertheless experiences a minor crack on the trench surface.
From Table D-1.2: Locate the vertical banks and the 2-inch-diameter cylinder (with special sleeve as defined by footnote #2) spaced 5.5 feet o.c. A trench has been dug in previously disturbed type B soil, with characteristics of a type C soil, and will require casing. From Table D-1.3: Find horizontal waves with a section modulus of 14.0 divided into 4 feet o.c. vertically and 3-inch-diameter cylinder placed at a maximum of 9 feet o.c. 3x12 lumber is required in a narrow space vertically.
For applications other than those listed in the tables, refer to §1926.652(c)(2) for use of manufacturer's tabulated data. 2) Cylinders of 2 inch diameter, at this width, must have structural steel tube (3.5x3.5x 0.1875) bore sleeves, or structural ear sleeves of manufacturer's specification, extending the full, collapsed length. Oregon Administrative Rules Oregon Occupational Safety and Health Division. i) 2-inch cylinders shall be a minimum 2-inch inside diameter with a safe working capacity of not less than 18,000 pounds of axial compressive load at maximum extension.
Maximum extension is to include the full range of cylinder extensions as recommended by the product manufacturer. ii) 3-inch cylinders shall have an inside diameter of at least 3 inches with a safe working capacity of not less than 30,000 pounds of axial compressive load at maximum extension. Maximum extension is to include the full range of cylinder extensions as recommended by the product manufacturer. Footnotes to tables and general notes on hydraulic support are found in Appendix D, paragraph (g) Notes (1): See Appendix D, paragraph (g)(1).
P ALTERNATIVES TO TIMBER SHORING
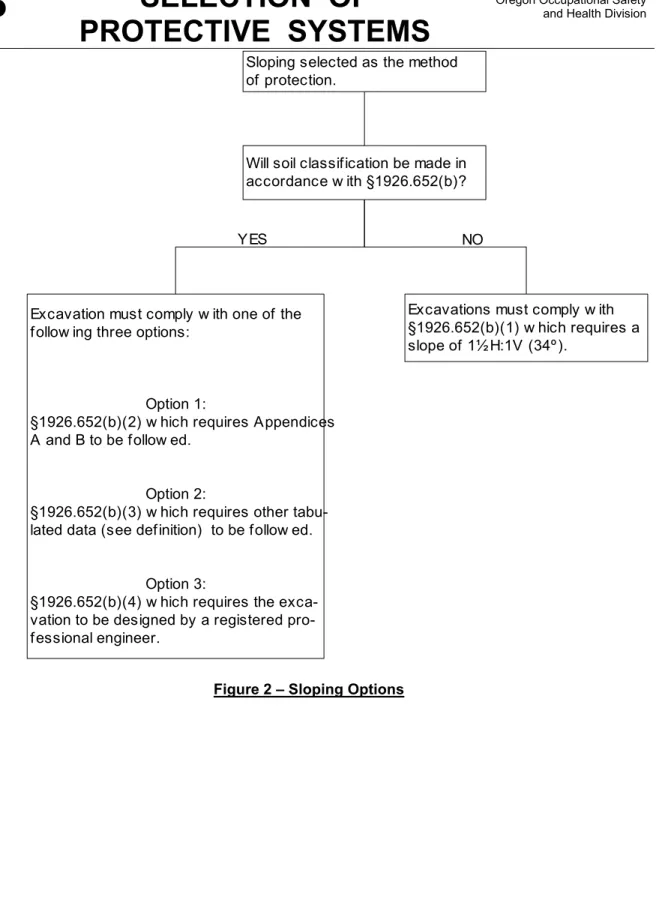
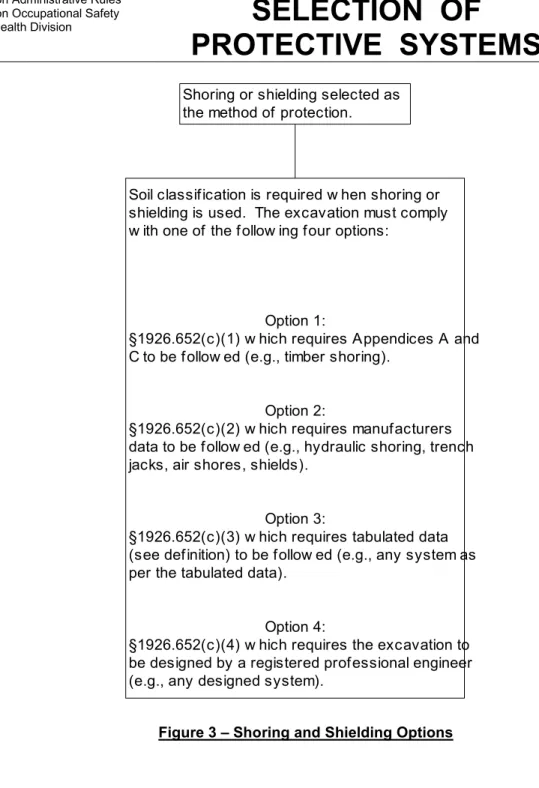
P SELECTION OF
PROTECTIVE SYSTEMS