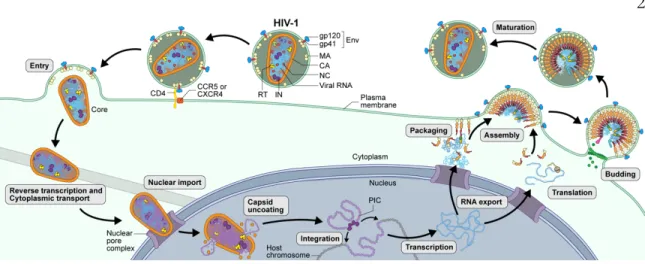
Native glycosylated HIV-1 env structure reveals novel mode for antibody recognition of the CD4 binding site. Tyrosine sulfation of human antibodies contributes to the recognition of the CCR5-binding region of HIV-1 gp120. Binding to the co-receptor facilitates further changes leading to insertion of the gp41 fusion peptide into the host cell membrane and subsequent fusion1.
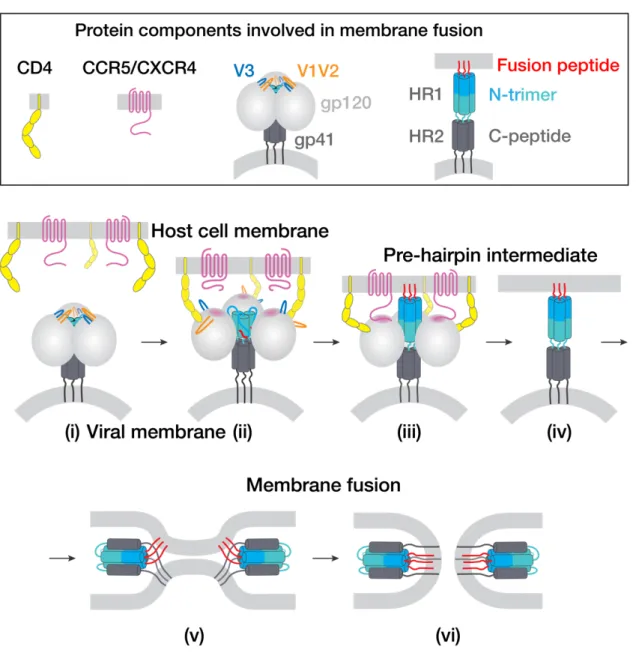
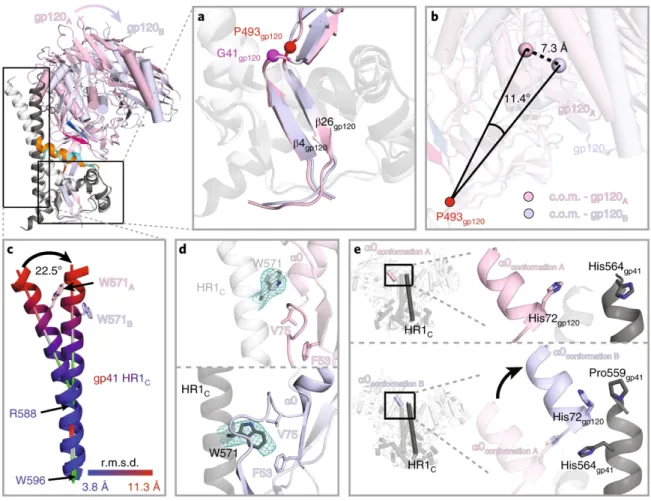
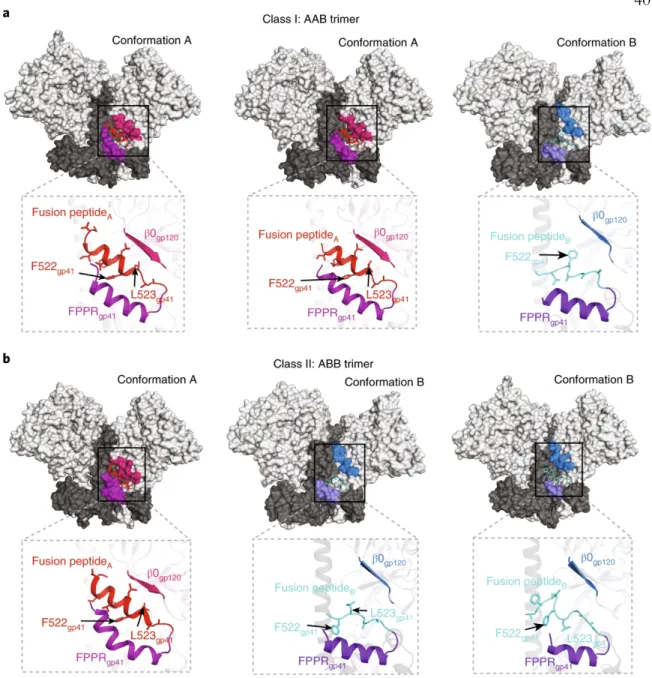
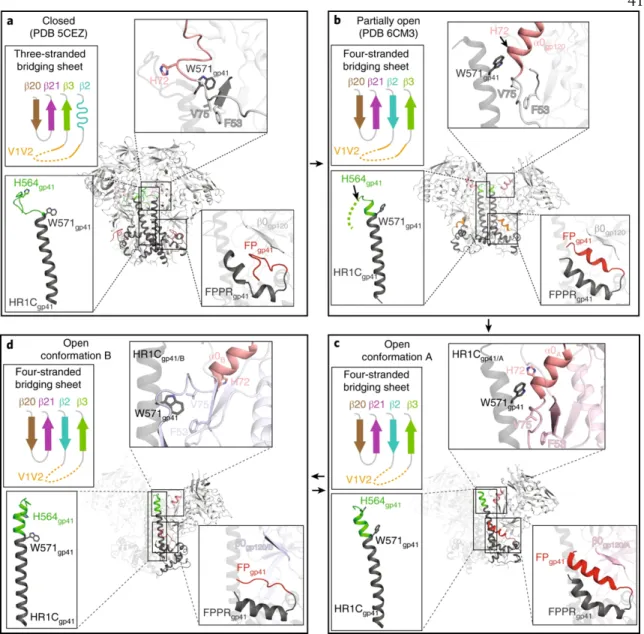
After superposition of the A and B protomer chains of gp120 β4 and β26, the C-terminal part of HR1C. The HR1C helix, but not the bent helix of protomer A HR1C (Fig. 4c), causes the displacement of the protomer B fusion peptide from the hydrophobic environment it occupies in the protomer A conformation. The HIV-1 Env trimer functions in the first step of viral infection: fusion of viral and host of the lipid bilayer to allow entry of the HIV-1 capsid and its RNA into the cytoplasm of the host cell1.
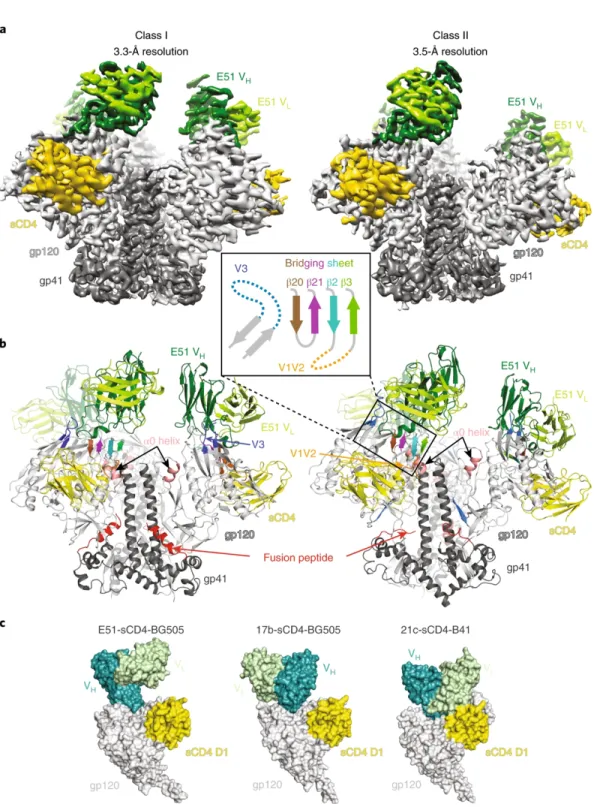
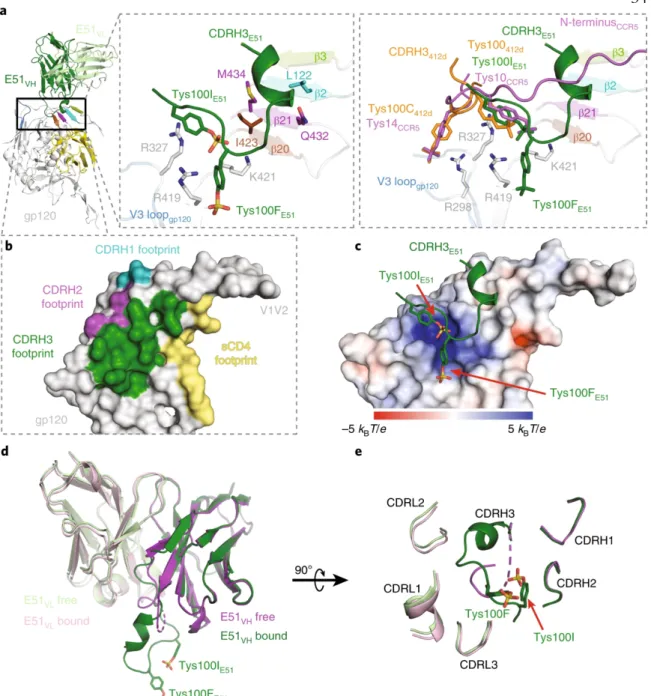
As in other CD4-CD4-Env trimer structures5-7, the E51 interaction with V3 involved the bottom of the loop (Fig. 1b). Structural comparisons of the E51, 412d and CCR5 complexes with trimeric (for E51) or monomeric (for 412d and CCR5) Envs showed that each of the tyrosine sulfated CD4i Fabs included a sulfated tyrosine (Tys100IE51 HC and m041 Tys10 direct) CCR5 sulfated tyrosine and an additional sulfated tyrosine (Tys100FE51 HC and Tys100C412d) that made distinct interactions with gp120 (Fig. 2a). Ordered sulfated tyrosines are highlighted as sticks on CDRH3 of the bound E51 Fab structure.
Complete epitopes for vaccine design derived from a crystal structure of the broadly neutralizing antibodies PGT128 and 8ANC195 in complex with an HIV-1 Env trimer. The native glycosylated structure of HIV-1 Env reveals a novel mode for antibody recognition of the CD4 binding site. Cryo-EM Structure of an HIV-1 Open Envelope Trimer Bound to CD4 Reveals Structural Rearrangements of the gp120 V1V2 Loop.
Structures of the CCR5 N-Terminus and a Tyrosine-sulfated Antibody to HIV-1 gp120 and CD4. Coreceptor binding to gp120 results in further conformational changes including insertion of the gp41 fusion peptide into the host cell membrane6. We first compared the structures of unbound Fabs with their structures when bound to the Env trimer.
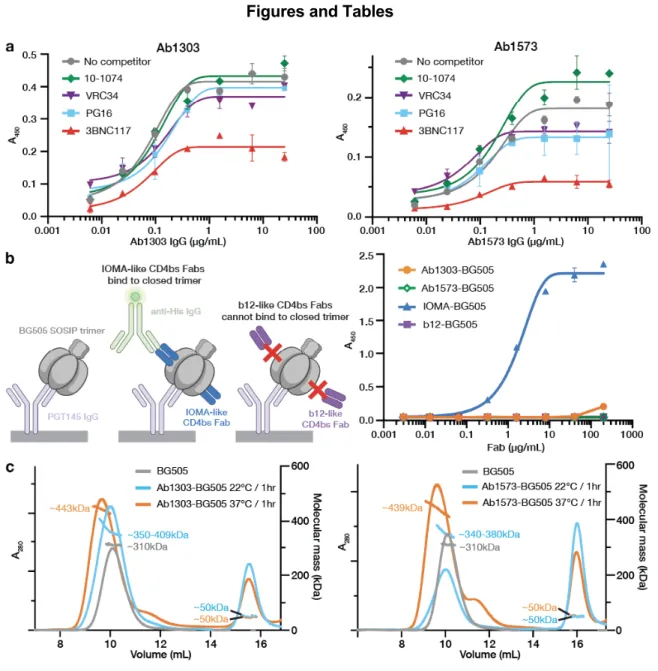
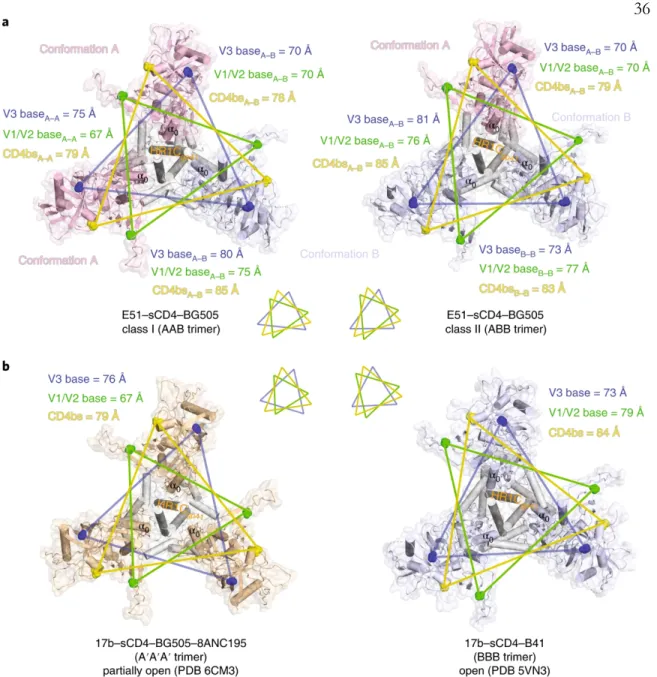
The trimers in the Ab1303-Env and Ab1573-Env complexes differed in conformation from the closed, prefusion conformation of Env, each exhibiting a more open state that exposed parts of gp120 that were otherwise buried (Fig. 5a,b). For both complexes, part of the epitope was solvent-inaccessible in the closed trimeric state, but was exposed in the open, antibody-bound state (Fig. 5a,b; red highlighted regions). The conformation of the C-terminal part of the gp41 heptad repeat segment 1 (HR1C) also showed changes between the closed, Ab1303 and Ab1573-bound open, and CD4-bound open states of the Env trimer.
Outward rotations of the gp120 subunits in the Ab1303-/Ab1573-bound open Env created space for the gp41 HR1C to expand its three-helix coiled-coil structure, extending the -helices by 1.5 turns (Fig. 6c, middle).
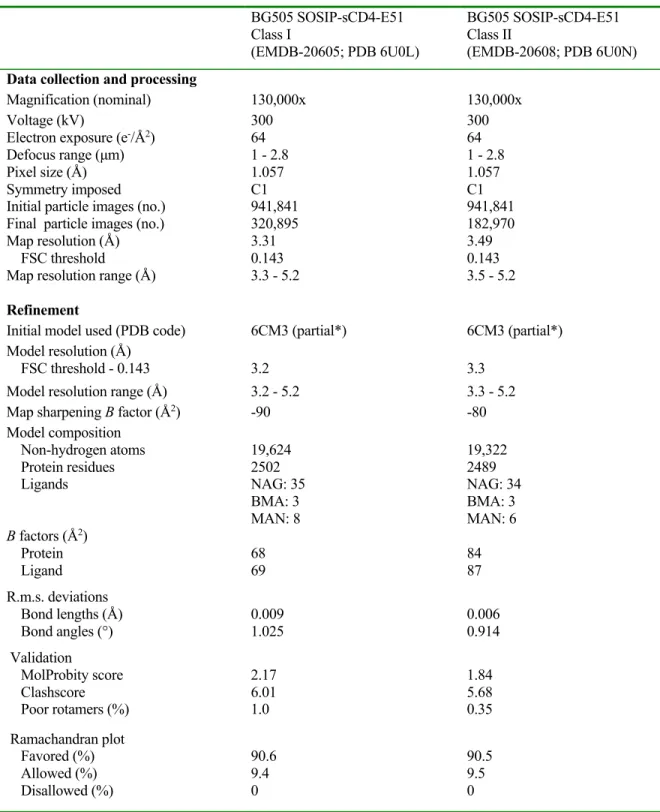
Thus, the 37˚C temperature of the Fab:Env incubation would probably have been maintained during the few seconds in the 12°C Vitrobot. Coordinates for gp120, gp41, Ab1303 Fab and Ab1573 Fab were fitted into the corresponding regions of the density maps. Pulse lengths were optimized via nutation experiment but ranged from 21 to 22 ns (π/2) and 42 to 44 ns (π); Observer frequency was set to a spectral position 2 G downfield from the low and central resonance crossing minima in the absorption spectrum, and the pump envelope frequency was a 50 MHz half-width square-chirp pulse (generated by a Bruker arbitrary waveform generator) set 70 MHz downfield from the observer frequency.
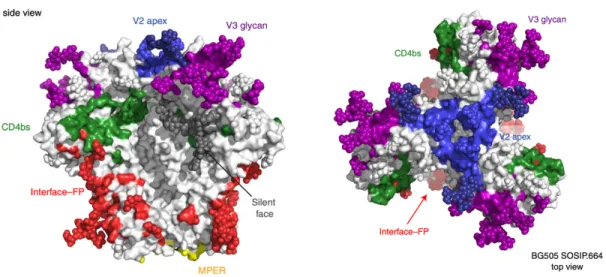
Left: Scheme of the experiment: PGT145 IgG, which restricts BG505 to a closed pre-fusion conformation, was immobilized and captured by BG505. Top and bottom left: surface representation of the HIV-1 Env trimer (top) and gp120 monomer (bottom), showing the locations of the 3-fold axis associated with the Env protomers (red arrow), the gp120 internal domain, V1V2, V3, and gp41. Remaining panels: cartoon diagrams of the VH-VL domains of the indicated bNAbs bound to HIV-1 gp120 (grey area, pink beads for N-linked glycans, V1V2 in orange, V3 in blue).
Regions of the antibody epitope that are buried in the closed state but accessible in the Ab1303- or Ab1573-bound state are outlined in red on the closed-open Env trimer structures. Secondary structures and relative locations of the 3-stranded sheet (left and center) and the rearranged 4-stranded bridging sheet (right) are highlighted, and the respective topology models are shown in insets. A cleaved, soluble, next-generation HIV-1 Env trimer, BG505 SOSIP.664 gp140, expresses multiple epitopes for light-neutralizing but not non-neutralizing antibodies.
Sequential immunization of macaques elicits heterologous neutralizing antibodies that target the V3 glycan patch of HIV-1 Env. Gaps in the glycan shield of the native HIV envelope are a target of trimer-induced neutralizing antibodies. Epitopes for neutralizing antibodies induced by HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein BG505 SOSIP trimers in rabbits and macaques.
A global panel of HIV-1 Env reference strains for standardized assessments of vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibodies. A broadly neutralizing antibody targets the top of the dynamic HIV envelope trimer via a long, rigid, and anionic beta-hairpin structure. Cryo-EM structures of the HIV-1 trimer bound to the CD4 mimetics BNM-III-170 and M48U1 adopt an open conformation bound to CD4.
Structural basis for germline gene use of a potent class of antibodies targeting the CD4 binding site of HIV-1 gp120. DEER spectroscopy measurements reveal multiple conformations of HIV-1 SOSIP envelopes that show similarities to envelopes on native virions.