The moral rights of the author(s) have been confirmed. Database Right Oxford University Press (maker) First published 2010. Inquiries regarding reproduction outside the scope of the above should be sent to the Rights Department, Oxford University Press, at the address above.
Selective toxicity
Penicillin is therefore a true antibiotic, while synthetic compounds such as sulfonamides and trimethoprim are not. However, there is general use of the term to cover all systemic antibacterial agents and so the term antibiotic will be used in the modern sense.
Parenteral versus oral
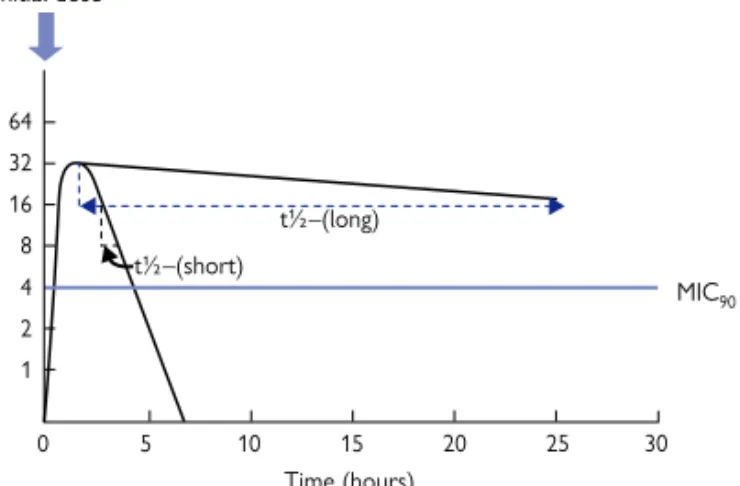
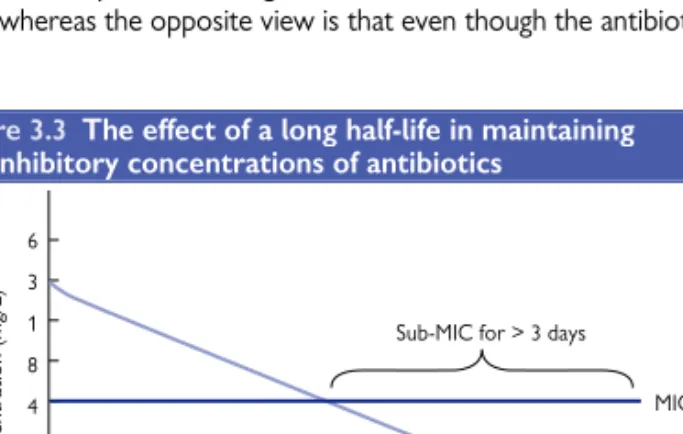
Short and long half-lives
Broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum antimicrobial drugs
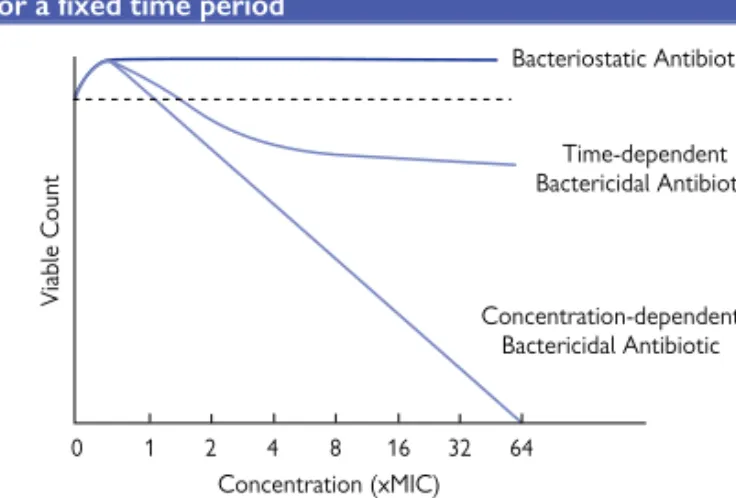
Bactericidal and bacteriostatic antimicrobial action
Of the four main groups, all but β-lactams produce a bactericidal response that is dependent on the concentration of the antibiotic. The β-lactams produce their maximum bactericidal response at approx. 4-10 times the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), so their bactericidal activity is dependent on the time the bacteria are treated with the antibiotic (Fig. 1.1).
Combinations of antibiotics
There are many disadvantages to giving combinations of antimicrobial drugs when one drug would suffice. Combinations of drugs in fixed-dose preparations may apparently be convenient for administration, but do not allow the dose of each drug to be adjusted independently.
Short or long antibiotic courses
CHAPTER 1 Antibiotic action—general principles 5 spectrum, especially for empiric therapy, to ensure that all likely. In this case, the drugs may not reach the site of infection in the correct sequence or concentrations, which may counteract the benefits of prescribing the combination.
Which member of antibiotic class to use first?
The action of penicillins and cephalosporins together with vancomycin - inhibitors of bacterial cell wall synthesis. The action of antimicrobial agents can be regarded as inhibitors in five areas of bacterial metabolism and also as moderators of all permeability.
Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis
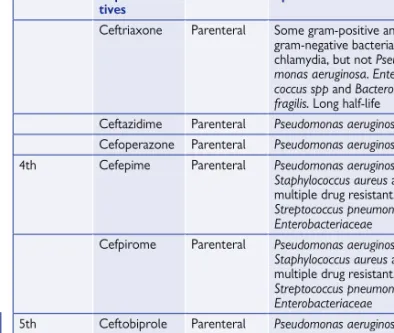
Ceftriaxone Parenteral Some Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and Chlamydia, but not Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is active only against gram-negative species and does not work against gram-positive bacteria.
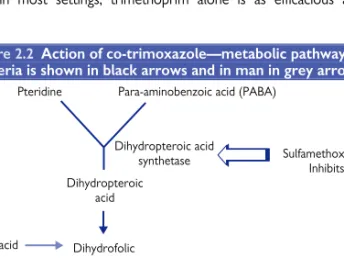
Inhibitors of folate synthesis
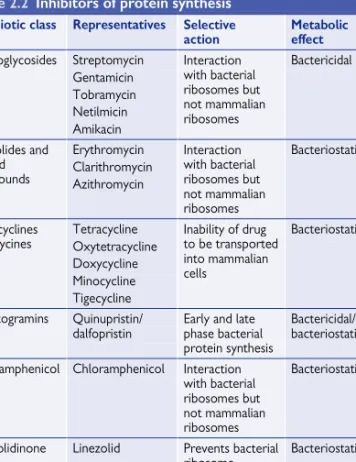
Inhibitors of protein synthesis
Like chloramphenicol, it binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit but instead of preventing peptide bond formation, it prevents the binding of the 50S to the 30S subunit to form the 70S ribosome. The components are metabolized when they enter the body and their metabolites also contribute to the antimicrobial activity of the streptogramin combination.
Inhibitors of DNA synthesis
Inhibitors of RNA synthesis
Permeability moderators
Clearance - the removal of drug from plasma and relates the rate at which a drug is delivered and eliminated to the resulting plasma levels. Cmax—the maximum concentration reached at the site of infection, usually taken as the peak serum level. Half-life (t½) - the time required for the concentration of the drug in the plasma to decrease by half.

Area under the inhibitory curve (AUIC)
CHAPTER 3 Pharmacokinetics in Antimicrobial Agents the antibiotic residues above the MIC are usually the most important. Some consider this to be decisive, for example, 90% protein binding will remove 90% of the available antibiotic, while the opposite view is that even if the antibiotic can. However, this is considered to affect the half-life of the antibiotic.
Phenotypic tests
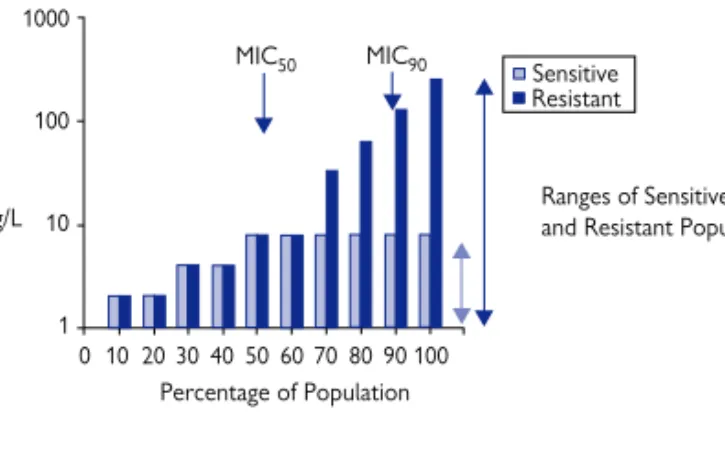
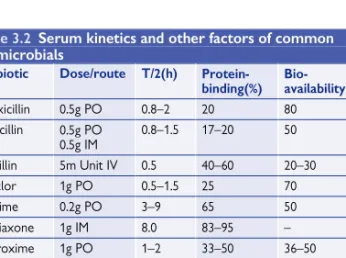
The advantage of the solid media test is that many bacterial cultures can be tested on the same agar plate. MIC90 is obtained in a similar manner to MIC50, except that it is the MIC value of the strain appearing 90% in the series. In the disk susceptibility test, at the zone boundary, the concentration of the antibiotic is equal to the MIC.
Standards and guidelines
Similarly, the class B metallo-B-lactamases capable of conferring carbapenem resistance can be predicted with a strip prepared with imipenem on one side and imipenem plus ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) on the other. These principles can be incorporated into the automated susceptibility testing procedures, so that predictions can be made along with susceptibility results. These class C β-lactamases can be identified by Єtest® with cefotetan on one strip and cefotetan plus cloxacillin on the other.
Identification of bacteria and molecular tests
Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and the European National Breakpoint Committees. Breakpoint standards are set, but these are not as comprehensive as those provided by the longer established CLSI. The recommendation of the Scottish Management of Antimicrobial Resistance Action Plan (ScotMARAP) 2008 was that all laboratories in the country should test to the same set of guidelines.
Phenotyping and genotyping
Early methods were based on random PCR amplification of different parts of the genome of repetitive extragenic palindromic and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (REP- and RAPD-PCR). PFGE relies on extracting bacterial DNA and digesting it with restriction enzymes that cut infrequently. However, it is now quantified and the image of the band pattern produced can be captured and interpreted by a computer algorithm such as Bionumerics.
Patient management, surveillance, and epidemiology
PCR amplification of each of the genes and subsequent sequencing of the products means that the sequence of the seven genes can be compared. To compare the sensitivities within a species or species subcategory, accurate species determination of the bacterium is essential to provide valid results. This cannot be done for all samples, but epidemiology usually extrapolates from relatively small numbers and it would give a more accurate picture of the denominator.
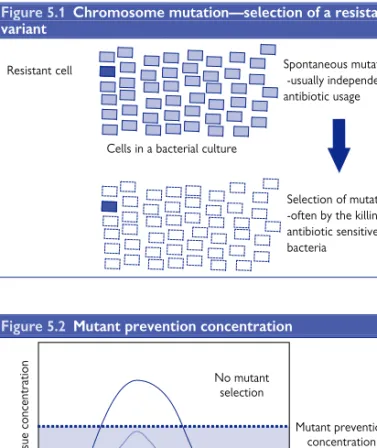
Mutation to drug resistance
However, this inherent resistance has not traditionally been a major concern because antibiotic selection has taken this into account. The maximum concentration (Cmax) of antibiotic A exceeds the MPC, so mutants would not be expected while the Cmax of antibiotic B does not and therefore mutations can be expected. Selection of mutation - often by killing antibiotic-sensitive bacteria Cells in a bacterial culture.
Transfer of plasmid-borne antibiotic resistance
The selective plates are incubated and transconjugants are identified by growth on the selective plates inoculated with the conjugation mixtures provided there is no growth on the control plates.
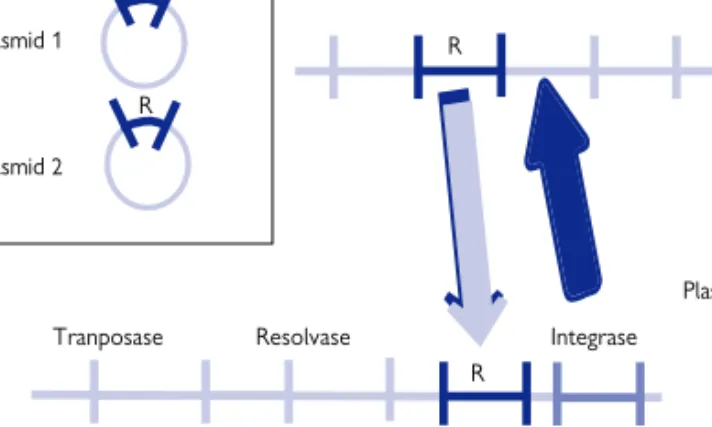
Transposition
The transposon gene product acts on the repetitive sequences to form a cointegrate that physically links the original replicon to the target replicon. Another enzyme, resolvase, cleaves this cointegrate so that the original replicon and the target replicon each have a copy of the transposon and the resistance genes (Figure 5.5). IS can also carry promoter sequences so that it can turn on a gene when inserted in front of a resistance gene that was not previously expressed.
Integrons
Increasing importance of efflux pumps especially in the early stages of resistance development. The ability of a bacterium to change the target of an antibiotic so that it no longer binds. When the target of the antibiotic changes so that the drug can no longer bind to it.
Impermeability
CHAPTER 6Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance If resistance is determined by plasmid, transposon or.
Efflux pumps
Like the mutational chromosomal mechanism, the plasmid efflux pump mechanism only increases cell resistance by 10–100-fold and is often ineffective. Their contribution is difficult to measure because they are often present but may not be functioning. Their contribution is probably as a first line of defense that keeps some bacterial cells alive until a stronger resistance mechanism is established.
Destruction
However, the β-lactamase has been able to mutate to prevent the binding of the inhibitor. An increasing number of the class B β-lactamases have been shown to be plasmid-mediated, particularly the IMP and VIM groups, and these are not inducible but are constitutively produced. However, they have been shown to be part of the chromosomal β-lactamase complement of Acinetobacter spp.
Modification
Alteration of target
In the vanA operon, the product of the first (vanX) changes the linkage of two D-alanine residues to form D-alanine-D-alanine.
Additional target
The plasmid produces an additional dihydrofolate reductase that cannot easily bind the drug, but can still reduce dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate. Often the plasmid-encoded enzyme binds the drug about 10,000 times less effectively than the chromosomal enzyme and there is a corresponding increase in resistance to the host bacteria (MIC > 1,000 mg/L). Similar mechanisms are observed in sulfonamide resistance and the plasmid production of altered dihydropteroate synthetase.
Hyper-production of target
These bacteria could easily spread, colonize healthcare workers and survive in the environment when other bacteria would have been eradicated. First, in the mid-1990s, intermediate resistant strains (VISA or GISA for vancomycin-intermediate or glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus, respectively) emerged, initially in Japan. Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium are commensal bacteria in the human gut and have not been considered particularly pathogenic.
Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa
In the Netherlands, they succeeded in preventing MRSA from becoming established by screening all patients who entered the hospital. Soon, these bacteria became resistant to most of the antibiotics used to treat them, including the glycopeptides, which were thought to be the final defense against these bacteria. Ten years ago, these bacteria were almost impossible to treat as they had become resistant to most antibiotics; however E.
Carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii
It is an anaerobic bacterium, which allows it to grow in the oxygen-depleted environment of the intestine. Normally, it can only reproduce after the normal gut bacteria have been removed with antibiotics. However, the rapid emergence of type 027 has created particular problems, as it produces far more toxins than most other types because the mutation has knocked out a gene that normally limits toxin production.
Penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae (PRSP)
Many of the MDR bacteria currently causing problems spread clonally throughout the clinical population. In the case of the CTX-M-15 β-lactamase, there is a close association of the plasmid with a particular strain of E. Within the last 40 years, considerable progress has been made in the knowledge of the pathogenesis, epidemiology, prevention and treatment made of tuberculosis.
Anti-mycobacterial agents
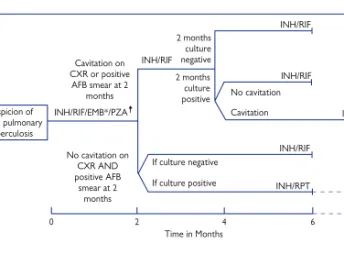
These drugs allowed shorter regimens to be instituted and intermittent therapy to be used. The latter approach has proven to be of particular value in developing countries where supervised daily drug administration is not standard. It has been shown to be of great value in primary therapy as well as for the treatment of relapses.
Treatment regimens
For the treatment of 'atypical' mycobacteria it is preferable to tailor the regimen to the susceptibility pattern of the isolated strain. In the UK, tuberculosis therapy is still active against the vast majority of the approximately 6,000 cases seen annually. In some cases identification of the pathogen is not so important, but in other infections it is crucial.