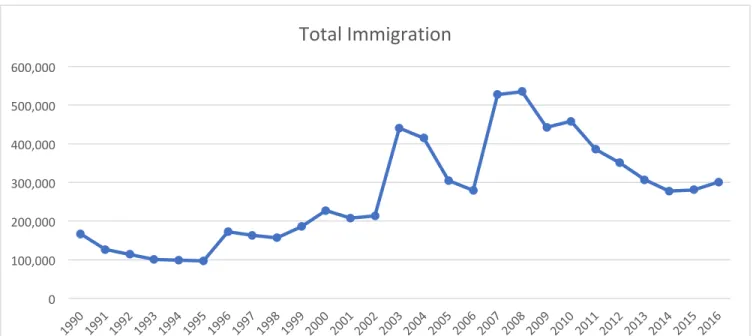
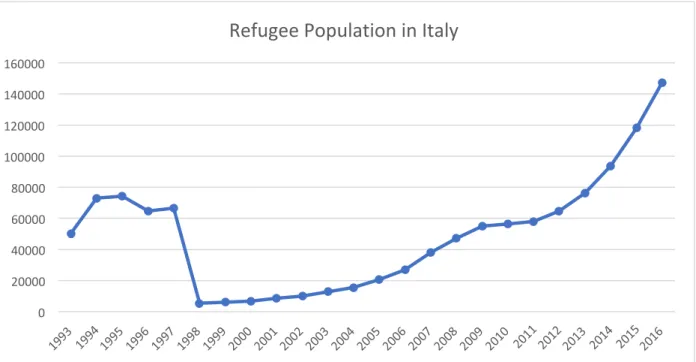
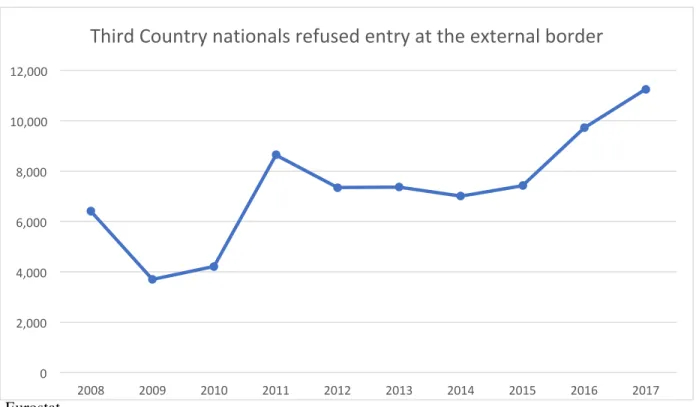
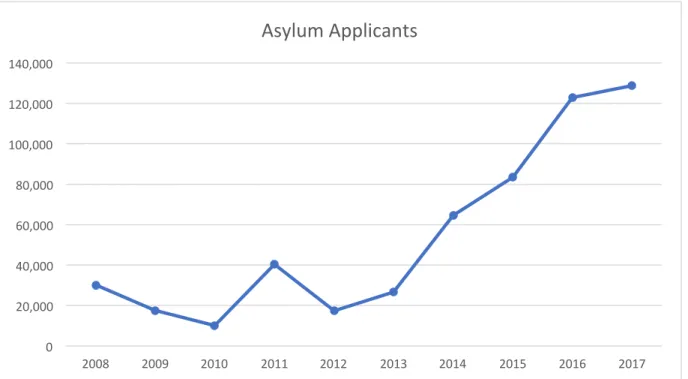
The research found that European Union and Italian policies were different, but not contradictory, regarding international migration. The research also found that EU and Italian policies had not successfully reduced the amount of migrants entering Italy via the Mediterranean before 2018.
Italy and the EU Contradictory attempts to regulate migration
Migration Theories
Contemporary migration theory has had to shift away from simple social and economic contributions, due to the more current migration situations in the world (Massey, 1998). Previously, distance was one of the few intervening factors discussed by scholars in migration theory.
Methodology
English is used by most countries of the European Union in international communication. This thesis focuses on how the policies of the European Union and Italy have affected migration flows through the Mediterranean. Referring to an article from the website, the Subway Wall, which they produce, it says that the "the flow has not yet assumed the dimensions of an exodus" (Vanelli and Balbo 2018).
The Prime Minister, Giuseppe Conte, stated that "the Schengen zone of visa-free travel through large parts of Europe was at risk if the EU did not reach an agreement on the issue of migration", because the Italian administration feels that the burden of large numbers of refugees, that arrive is not shared with all the countries across the EU (BBC 2018).
Textual Analysis
Introduction
This issue must be discussed before approaching any textual analysis because of the potential consequences. Therefore, the target language for this research will be English, because it is the native language of the researcher and the language in which it will be published. They pointed out how translation lost the personality and creativity used in the various letters.
European Union documents address all the European Union member states, which include a diverse range of languages.
Corpus Selection
English has become important in the political interactions between the EU and Italy, so I chose English as the target language of this study. The term coined for it is “Euro-English” and “EU English” (Modiano, 2003). A summary lexical table is a chart showing the segmented terms that appeared most often in the texts and includes the corresponding frequencies.
The span of twenty-five years is long but significant because it includes the first year that Italy signed the Schengen Agreement from the EU, marking a major shift in how migrants will move not only within Italy but across the rest of the country. European Union.
Corpus Description
These documents show how current migration policy in Italy has been shaped by the interaction of EU policies and then their national policies over time. He also outlined the creation of permanent residence permits that migrants can apply for after having legally stayed in Italy for at least five years. In addition, non-EU members now have to be fingerprinted to stay in Italy, and long-term residence cards changed from staying in Italy for five years to six years.
In 2016, the European Agenda on Migration came into force, a more restrictive policy that ensured more search and rescue efforts in the Mediterranean, reduced incentives for irregular migration, better management of external borders and strengthened common asylum policy.
Test Statistics: Aggregated Lexical Table
Some graphic shapes that are different have the same meaning, while some behave differently in the context of the text that will be noted. An aggregate lexical table is formed by dividing the text into text units of similar size, which are then "statistical individuals whose variables are the entire vocabulary used in the corpus" (Benzécri). The aggregated lexical table shows text segments that are statistically significant due to how often they appear in the texts, which will help.
The results of the program are multi-word expressions which appear more often in the focus corpus than in the reference corpus and, therefore, conform to the typical format of the terminology in the language.
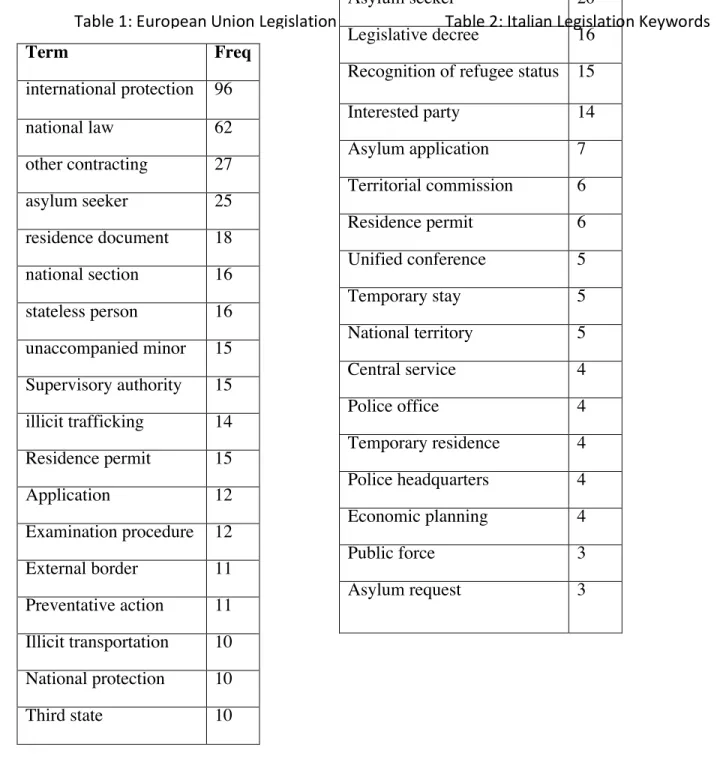
Textual Analysis Results
Rejecting the null hypothesis of Italian government documents, Italian policies have an effect on the number of refugees entering Italy. The policies of the European Union and Italy "attract" them to Italy and make it a more attractive choice. I fail to refute my hypothesis that the policies of the European Union and Italy had not successfully reduced the amount of migrants entering Italy via the Mediterranean before 2018.
I have found that the migration policies of the Italian government and especially of the European Union have served as an attractive factor for refugees and immigrants.
Data and Analysis
Introduction
This part of the study aims to answer the research question: “How has policy influenced migrants' decision to move?” This article will follow the UNHCR definition. I will first describe the datasets used and then the results of the two-part analysis. The first part of the analysis is a comprehensive look at migration trends to Italy in recent years, comparing different aspects of the broader migration situation.
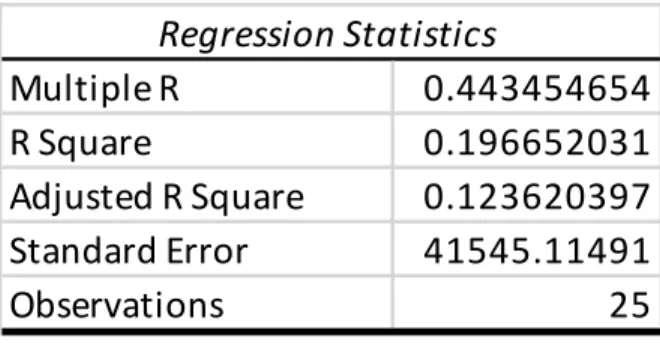
The second part of the analysis is the multiple linear regression which attempts to examine the hypothesis.
Data Set
What makes this research even more difficult is that the word migrant and refugee are used interchangeably when referring to the "crisis" in Italy and the Mediterranean. According to UNHCR, the mass amount of people who have arrived in Italy by boat has been both. According to the description of the data provided by UNHCR, refugees are defined as “people who are recognized as refugees under the 1951 Convention relating to the Status of.
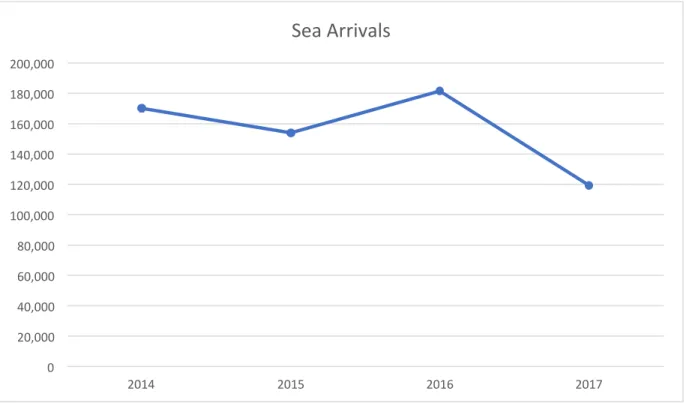
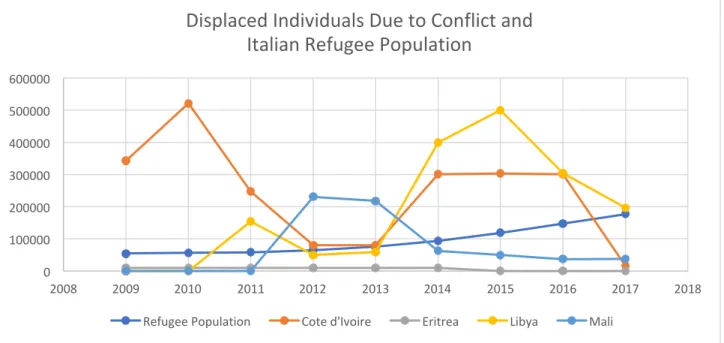
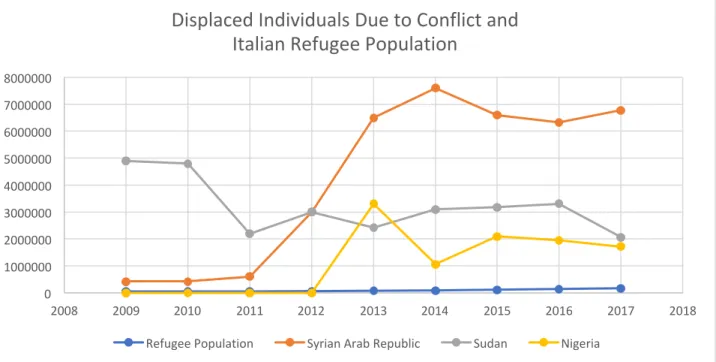
This data is relevant to the study because, as mentioned earlier, refugees make up a large proportion of people entering Italy via the Mediterranean.
Independent Variable
The timing doesn't necessarily mean that there wasn't an earlier question or data to collect, but that it was when migration began to gain national attention, and therefore led to an increase in research. Unfortunately, the data and research in this case is reactive, so I will extrapolate this data to show a trend line. Policies are coded for the year immediately following their implementation to assess migrants' initial response to the policy.
In the years after the initial year after enactment, migration flows would either level off because the policy was effective or other migrants found that the policy was not as much of a barrier as originally expected.
Dependent Variable
The Analysis
Multiple Linear Regression
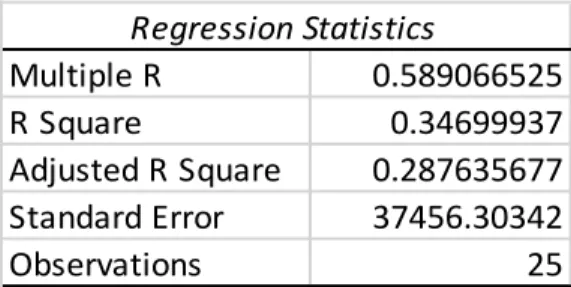
The popularity of the right-wing Five Star Movement is linked to the large number of migrants and refugees entering and residing in Italy. The R-squared is 0.34 which means that the political parties in control can explain about 34% of the variation in the refugee population. The European Union is concerned with the security of its member states as a whole and not with individual member states.
The EU and its neighbors: a textual analysis of key documents of the European Neighborhood Policy.
Conclusion and Current Climate
Introduction
This thesis sought to examine the effectiveness of policy responses to migration flows through the Mediterranean by both the European Union and the Italian government. New data and policies emerged in late 2018 that reflect a return to normal migration levels after this thesis began. My research is limited to 2017 and the response to the perceived immigration crisis in Italy in 2018.
Recent newspaper articles include quotes from Italian National Government officials outlining the government's view of the immigration crisis and the next steps to be taken with the policy.
Data Interpretation
The Eurobarometer collects public opinion on various topics from different EU member states. In doing so, I found that EU policies focused more on security and enforcement measures than the Italian government's policies, which addressed migrant and migrant application processes. The Italian national government legislation used the term refugee status with a frequency of 25, while the EU documents did not.
The data breakpoints between the set of EU policies and the laws of the Italian national government show that the EU has a higher frequency of words correlated with protection and policing.
Moving Forward: Opinions of Policy Makers, the Public, and the Individual
In 2011, 40% of the Italian public had a fairly positive image of the European Union and 13% a fairly negative image, compared to 2018, when 32% had a fairly positive image and 17% a fairly negative image. In 2018, 63% of Italian citizens had negative feelings towards immigrants from outside the European Union, down from 70% in 2015 at the height of the immigration crisis. I interviewed an Italian citizen about their individual professional experience with immigration and interestingly it differs from the public opinions collected by the immigration service.
The opinions of Italian citizens at local level reflect the most recent national elections.
Conclusion
They also supported the implementation of "regional disembarkation platforms", where migrants found to be in need of international protection will be resettled in one of the 20 member states, while others will be sent back to their countries of origin. European Union policies were more concerned with protection, while the status of migrants and their path to refugee status or citizenship was more of a priority for Italian legislation. Even if the politicians' intentions were not to reduce the number of migrants and refugees; the number of refugees and asylum applications continues to rise steadily.
Migrants and refugees choose to make the journey across the Mediterranean, although the risks associated with it are high due to the policies in Italy and the movement across Europe.