Tujuan penelitian ini untuk mengevaluasi penggunaan obat pada pasien epilepsi di poliklinik rawat jalan RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon tahun 2019. Subyek dalam penelitian ini adalah pasien yang didiagnosis epilepsi di poliklinik rawat jalan RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon tahun 2019. yang memenuhi kriteria inklusi penelitian. Berdasarkan hasil tersebut dapat disimpulkan bahwa penggunaan obat pada penderita epilepsi memiliki potensi interaksi obat yang tinggi.
Dari hasil penelitian ini akan diperoleh gambaran pola penggunaan obat dan evaluasi penggunaan obat terkait ketepatan dosis obat dan kemungkinan interaksi obat pada pasien epilepsi di Rawat Jalan RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon tahun 2019. Berapa jumlah kasus ketepatan dosis pada penderita epilepsi di RSUD Gunung Jati Jati Kota Cirebon. Berapa angka kejadian interaksi obat pada pasien epilepsi di RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon.
Mendapatkan gambaran prevalensi ketepatan dosis pada pasien epilepsi di rawat jalan RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon. Mendapatkan gambaran kejadian interaksi obat pada pasien epilepsi di poliklinik rawat jalan RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon.
KAJIAN PUSTAKA
- Tempat Penelitian
- Desain Penelitian
- Populasi dan Sampel 1. Populasi
- Sampel
- Kriteria Inklusi dan Eksklusi 1. Kriteria Inklusi
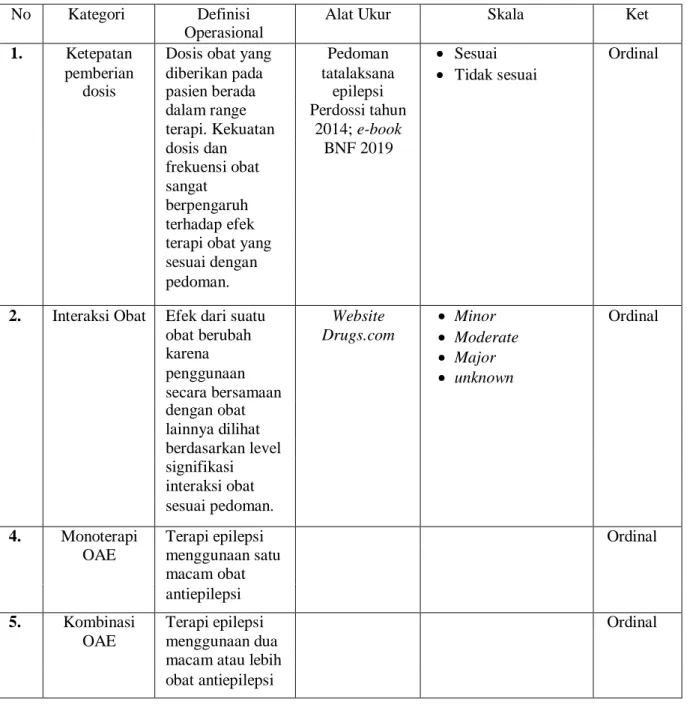
- Definisi Operasional
- Analisis Statistik
- Diagram Alir Penelitian
- Ketepatan Dosis OAE
Djamil Padang menemukan pada tahun 2017 bahwa ketepatan dosis rejimen adalah 97,2%, dan kejadian interaksi obat potensial adalah 47,7% (Sumarno 2018). DRP 2018 berupa potensi interaksi obat pada pasien gagal ginjal di RS Jakarta (Wulandari et al. 2018). Analisis data bertujuan untuk memperoleh gambaran penggunaan obat anti epilepsi pada pasien epilepsi di RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon periode tahun 2019.
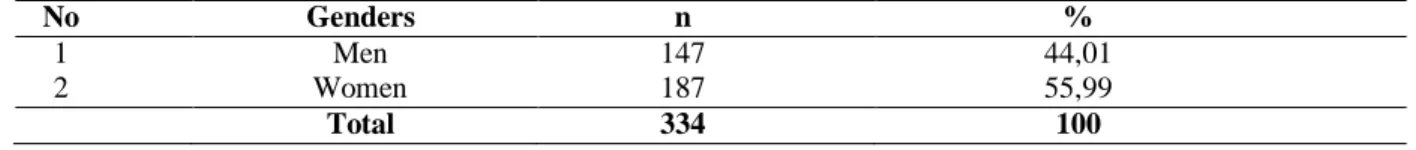
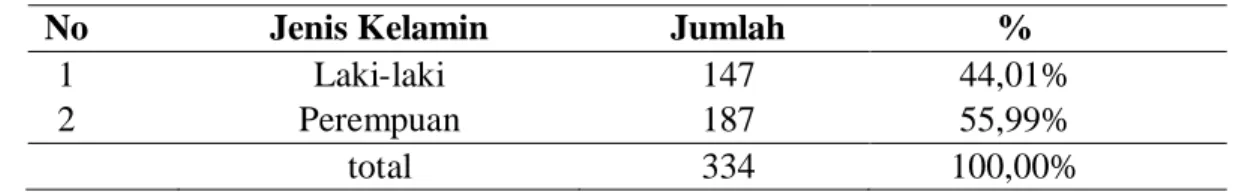
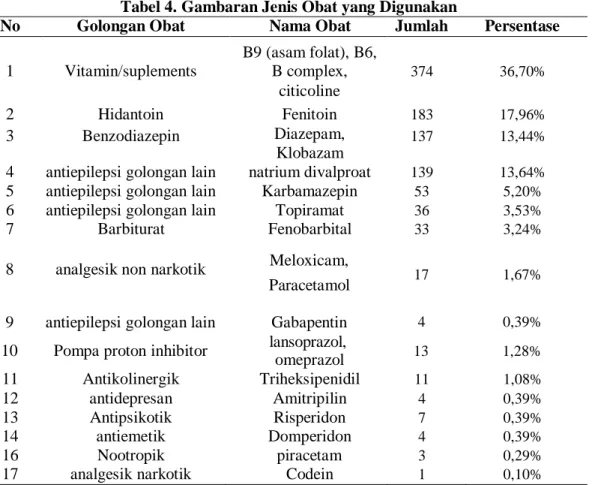
Penelitian ini dilakukan dengan mengumpulkan data medis pasien epilepsi rawat jalan di RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon periode tahun 2019 yang dilakukan pada bulan Desember 2019 – Januari 2020. Hasil observasi pasien epilepsi pada bulan Januari – Desember 2019 di rawat jalan Gunung RSUD Jati Kota Cirebon sebanyak 334 pasien, dengan rincian seperti pada Tabel 2. Saat meresepkan monoterapi untuk pengobatan epilepsi rawat jalan di RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon tahun 2019, digunakan 4 jenis OAE yaitu phenytoin, valproate, carbamazepine dan topiramate. .
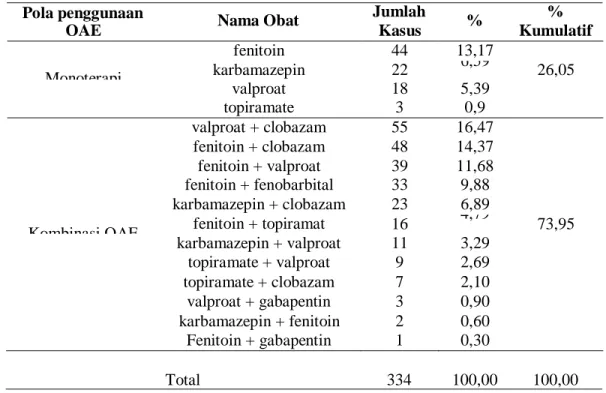
Fenitoin merupakan obat antiepilepsi yang paling banyak digunakan pada monoterapi OAE pada pasien epilepsi di RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon tahun 2019 yaitu sebesar 13,17% dengan frekuensi sebanyak 44 kasus. Politerapi dan potensi interaksi dengan obat lain meningkat seiring bertambahnya usia, dan lansia merupakan kelompok terbesar penderita epilepsi yang berisiko tinggi berinteraksi dengan obat yang biasa diresepkan (Johannessen & Landmark, 2010). Potensi interaksi obat yang terjadi pada penelitian ini adalah interaksi antara OAEs dan interaksi antara OAEs dan non-OAEs yang berpotensi menyebabkan DRPs.
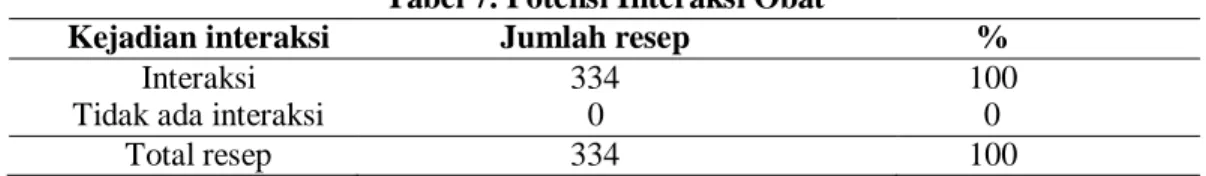
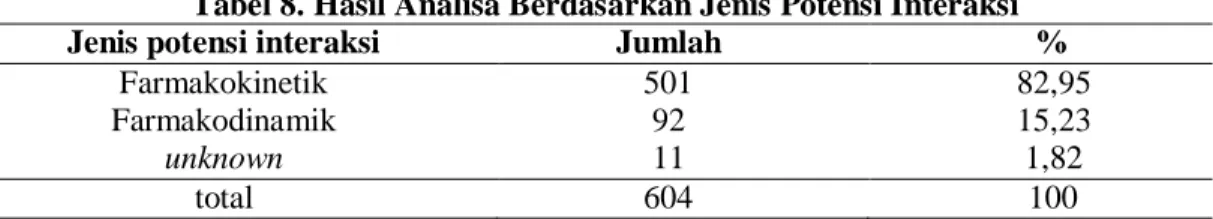
Berikut hasil penelitian pada pasien epilepsi di rawat jalan RSUD Gunung Jati Kota Cirebon periode Januari – Desember 2019. Berdasarkan Tabel 7, jumlah resep yang memenuhi kriteria adalah 334 resep, yang berarti bahwa setiap resep memiliki potensi interaksi obat, baik interaksi antara OAE maupun interaksi antara OAE dan non OAE. Potensi interaksi antara OAE dan asam folat merupakan jumlah interaksi farmakokinetik potensial terbanyak yaitu 319 kejadian.
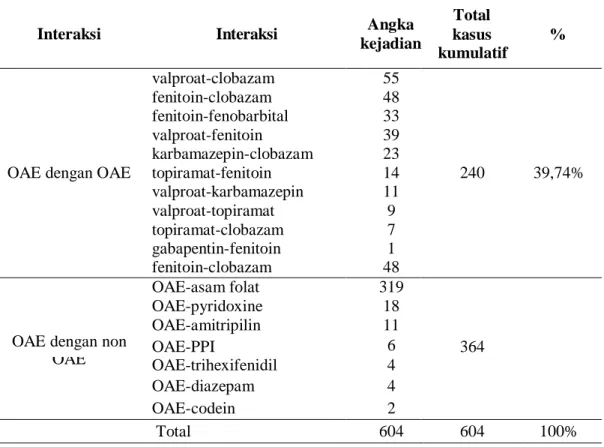
Hasil analisis total potensi interaksi obat antiepilepsi adalah 604 kejadian, OAEs potensial 240 kejadian dan interaksi OAEs serta kemungkinan interaksi. Sebanyak 603 peristiwa mengidentifikasi interaksi potensial antara OAE dan semua kasus melibatkan tingkat signifikansi sedang, dengan interaksi paling potensial adalah valproate dan clobazam dengan 55 peristiwa, interaksi antara valproate dan clobazam, yang merupakan kelompok benzodiazepin berdasarkan studi yang dilakukan antara dengan valproate. dan diazepam, valproat dapat menggantikan diazepam dari tempat pengikatan protein plasma dan menghambat metabolismenya, sehingga pemantauan ketat diperlukan untuk toksisitas benzodiazepin (sedasi berlebihan) (drugs.com 2020). Interaksi paling potensial kedua yang terjadi adalah antara fenitoin dan clobazam, terhitung 48 peristiwa, mengingat fenitoin dan clobazam adalah kombinasi OAE kedua yang paling banyak diresepkan.
Terdapat 364 interaksi potensial antara OAE dan non-OAE, dan potensi interaksi yang paling sering terjadi adalah OAE dan asam folat dengan total kejadian 319. Hasil interaksi potensial antara OAE dan non-OAE memiliki dua tingkat signifikansi yaitu sedang dan besar.
KESIMPULAN DAN SARAN A. Kesimpulan
Saran
IDENTITAS JURNAL
IDENTITAS SEMINAR
RENCANA TINDAK LANJUT DAN PROYEKSI HILIRISASI Hasil Penelitian Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa Dari 334
Temuan dalam penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa prevalensi masalah yang terkait dengan pengobatan epilepsi, terutama interaksi obat, masih sangat tinggi (100%). Rencana tindak lanjut Perlu dilakukan penelitian lebih lanjut terkait kejadian aktual potensi interaksi obat pada pasien epilepsi. Selain itu perlu dilakukan penelitian lebih lanjut tidak hanya pada pasien epilepsi tetapi penyakit kronis lainnya untuk menambah informasi tentang data kejadian DRP di rumah sakit, sehingga semakin banyak informasi data tentang kejadian DRP akan memberikan gambaran nyata yang diberikan untuk lebih mengembangkan panduan dalam kaitannya dengan pencegahan atau pengobatan pasien dengan epilepsi atau penyakit kronis lainnya yang dirawat di rumah sakit.
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
Evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions among outpatients with epilepsy in a regional public hospital in Indonesia. The subjects of this study were the records of patients diagnosed with epilepsy at Gunung Jati Cirebon Hospital in 2019. In conclusion, all the patients prescribed drugs that had pDDIs with most of the potential interaction of AEDs with non-AEDs.
Epilepsy is a significant public health problem, representing 0.6% of the global burden of disease, which significantly affects people living in the lowest income countries, where the prevalence of epilepsy can be ten times higher than in the developed world (3). Epilepsy is a chronic non-communicable disease of bran that affects about 50 million people worldwide, accounting for a significant part of the world's disease burden. The pDDIs were classified based on pharmacological mechanism and the level of significance of the interactions - the mechanism of pharmacological classification consisting of pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and unknown.
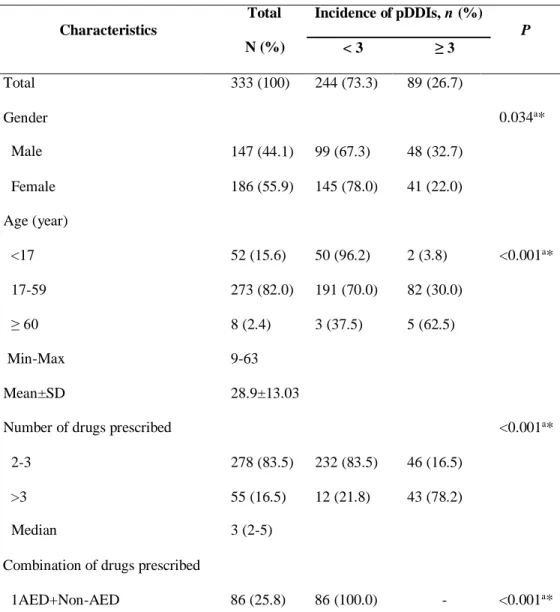
Meanwhile, the significance level of the interaction classification consisted of major, moderate, and minor interaction. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Gunung Jati Regional Public Hospital Cirebon with No. We found that 73.3% of patients had less than three pDDIs, while the rest had three and more pDDIs.
The study also showed that sex, age, number of prescribed drugs and prescribed combination drug significantly related to the occurrence of the pDDIs. Based on the analysis, we found 604 of the pDDIs in the prescriptions that the patients received. We found an overall 39.74% incidence of pDDIs between AEDs and 60.26% AED and other medications prescribed with the summary of the pDDIs shown in Table 3.
A score of 37.74% of occurrences were identified with potential interactions between AEDs and all cases were of moderate level of significance, with the most common of pDDIs being valproate and clobazam as many as 55 occurrences (9.11%). Combination clobazam with carbamazepine and topiramate should be carefully monitored, as it has been reported that co-administration of the drugs may increase the potential for CNS effects such as increased sedation or respiratory depression (14). The potential interaction between AED and non-AED was found in 60.26% of cases, and the most common pDDIs were between AEDs and folic acid (52.81%).
It was concluded that all patients were prescribed drugs that had pDDIs with most potential interaction between AEDs and non-AEDs. Your presentation time will be added to the conference program after the payment process is complete.
Profile of Antiepileptic Drugs Utility in Outpatient with Epilepsy in a Regional Public Hospital Indonesia
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates the incidence (new and old cases) of epilepsy requiring treatment at 8.2 per 1000 world population; 80% of them are in developing countries. The prevalence of epilepsy in children in developing countries is approximately 40 cases/100,000 children per year [3]. Treatment of epilepsy in the elderly is complicated as these patients are very often prescribed other long-term medications for disorders other than epilepsy that can lead to adverse drug interactions [5].
The purpose of this study is to evaluate drug use and possible drug interactions in the treatment of epilepsy in patients with epilepsy at Gunung Jati Hospital Cirebon for the period 2019. Samples The inclusion criteria listed were patients with a diagnosis of epilepsy and drugs prescribed for each of these 2 medicines. Evaluation of medication use using the literature Guidelines for the management of epilepsy Perdossi 2014; and the BNF 2019 e-book.
In several studies, the incidence and prevalence of epilepsy was slightly higher in men than in women, but was not statistically significant. This small difference can be explained by differences in the prevalence of the most common risk factors and the concealment of the condition in women due to sociocultural reasons in certain areas. There was no significant difference between the number of epilepsy patients in men and women.
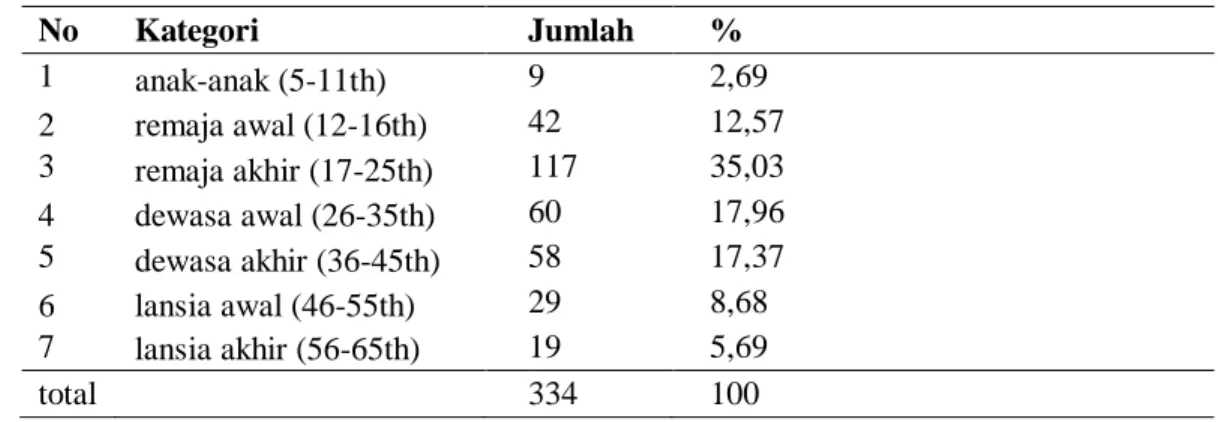
The prevalence of epilepsy patients, which also showed that women were higher, was 60% (52 patients) in the Lakshmi study in a hospital in India, while for men it was 40% (34 patients) [11]. The most outpatient age of epilepsy patients at Gunung Jati Cirebon Hospital was between 17-25 years, i.e. 117 patients (35.03%). According to IDAI [3], the peak prevalence of epilepsy is found in early adolescence to young adulthood.
The prevalence of epilepsy in the elderly (>65 years) in developed countries is estimated to be >. In contrast, the prevalence of epilepsy in developing countries is higher at the age of 10-20 years than in the elderly. If the maximum dose of the first AED still cannot control the rise, it will be replaced by the second OAE.