JOINTS
PROSES MANUFAKTUR I
MACAM-MACAM SAMBUNGAN
Las
Paku keling
Baut
Lem
Sambungan Las
Definisi Las
LAS ADALAH IKATAN METALURGI PADA
SAMBUNGAN LOGAM ATAU LOGAM PADUAN YANG DILAKSANAKAN DALAM KEADAAN LUMER
ATAU CAIR
- DIN -
Macam – Macam Pengelasan
Pengelasan cair
Pengelasan tekan
Pematrian
Welded Joints Design
Butt joint
Corner joint
Edge joint
Lap joint
Tee joint
Bevel Groove J Groove Vee Groove
U Groove Square Groove
Butt Joints
Open Corner Closed Corner
Corner Joints
1 2 1 2 3
4
Some considerations in selecting a type of joint to use on a fabrication
Accessibility for welding
Strength requirements
Cyclic or static loading
Material thickness
Welding process to be used
Material type
Code Requirements
Cost
Weld Quality (Size)
Effective Throat
Actual Throat Leg Size2
Leg Size1
Theoretical Throat
Convexity
Weld Quality
After selecting specified size gauge from set, measure Leg1
Measure Leg2
Verify throat with other side of gauge (face of gauge should touch weld)
L
1L
23/8
Weld Quality (Fault)
Undercut – most predominant weld fault
◦ Fix: Short arc length, proper amperage and speed
Weld Quality (Fault)
Porosity:
Lack of shielding gas Wet electrode
Greasy material
Weld Quality (Fault)
Slag Inclusion:
Improper cleaning / removal of slagWelding Joint Design & Welding Symbols – Chapter #5
Weld Quality (Fault)
Porosity
Undercut
Poor Fitup
Lack of Penetration
Weld Quality - Review
Weld Position (Plate)
F = Fillet G = Groove 1 = Flat
2 = Horizontal 3 = Vertical 4 = Overhead
Weld Position (Pipe)
G = Groove
1 = Horizontal Rolled 2 = Vertical
5 = Horizontal Fixed 6 = 45 Incline
Welding Symbols
Arrow
Reference Line
Tail
3 parts of the welding symbol body:
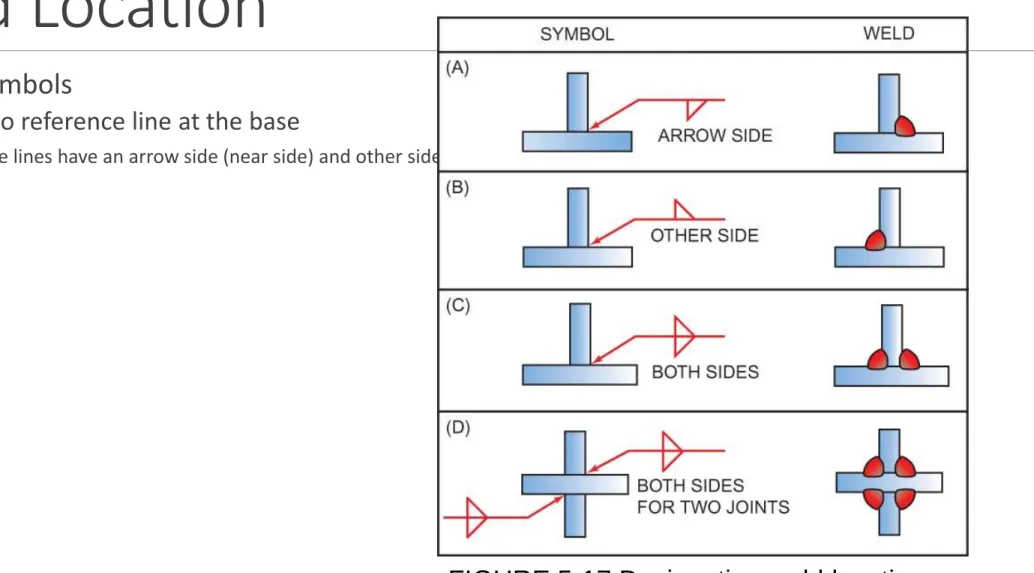
Weld Location
Welding symbols
◦ Applied to reference line at the base
◦ Reference lines have an arrow side (near side) and other side (far side)
FIGURE 5-17 Designating weld location.
American Welding Society
Sambungan Mur - Baut
Nuts and Bolts
Threaded Fastener Issues:
Types
Materials/Grades
Tightening Torque
Threaded Fasteners
Did you know that?
the Boeing 747 uses about 2.5 million fasteners
◦ 70,000 titanium costing $150,000
◦ 400,000 other fasteners costing about $250,000
◦ 30,000 squeeze rivets, 50cents each installed
In certain applications (such as an engine head), you should tighten the bolt as much as possible, if it does not fail by twisting during tightening, there is a very good possibility that the bolt will never fail
Why are fasteners used?
Advantages
Removable
Easy to install
Wide variety of standard parts Disadvantages
loosening
failure
cost
Types
Machine screws
Wood screws
Tapping screws
Standard Thread Systems
Unified or American ACME
SI (ISO)
Pipe Whitworth (UK)
Typical Designation
1/2” - 13 UNC - 2 A
external thread (B means internal)
Class of fit
(1 is loosest tolerance, 3 is tightest) Thread Series
UNC (Unified Coarse) UNF (Unified Fine) Pitch (threads/inch)
Nominal Diameter
(also shown as decimal or screw #)
Terminology of screw threads Sharp vee threads shown for clarity; the crests and roots are actually flattened or rounded during the forming operation.
Bolt Grades
Grade indicates the tensile strength of the bolt Determined by bolt material and heat treating
Tightening Torque
It is typical on engines for bolts to have a specified tightening torque. Why?
It results in a quantified preload on the bolts Insures that parts never separate
Maintains friction (no sliding to shear forces) Insures even distribution of loading
◦ prevent warpage of mating parts
◦ uniform pressure distribution over seal or gasket
Prevents bolt from loosening Reduces fatique effects
Bolt Manufacturing Processes
Forging (upsetting)
Rolling
Thread-rolling processes: a) reciprocating flat dies; and b) two-roller dies.
Threaded fasteners, such as bolts, are made economically by these processes at high rates of production
a) b)
Manufacturing Processes - continued
Turning on screw machines
(a) Differences in the diameters of machined and rolled threads. (b) Grain flow in machined and rolled threads.
Unlike machining, which cuts through the grains of the metal, rolled threads have improved strength because of cold working and favorable grain flow.
Sambungan Paku Keling
Sambungan paku keling
Bagian-bagian paku keling
Pemasangan paku keling
Sambungan paku keling
Standard:
AISC (American Institute Steel Construction)
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) Parameter Desain:
Diameter
Material Desain:
Menurut Indian Standard, IS : 2998-1982 (ditetapkan 1992), Tensile strenght > 40 N/mm2
Elongation = 26 %
Keling dibuat dengan cold heading atau hot forging.
Sambungan paku keling
Aplikasi:
Sambungan kuat dan rapat, pada konstruksi boiler ( boiler, tangki dan pipa-pipa tekanan tinggi )
Sambungan kuat, pada konstruksi baja (bangunan, jembatan dan crane )
Sambungan rapat, pada tabung dan tangki (tabung pendek, cerobong, pipa-pipa tekanan)
Sambungan pengikat, untuk penutup chasis (mis ; pesawat terbang)
Sambungan paku keling
Kelebihan:
Tidak akan longgar karena adanya getaran atau beban kejut Relatif murah dan pemasangan yang cepat
Ringan
Lebih tahan korosi dibandingkan sambungan baut Kekuatan fatigue lebih baik dari sambungan las
Sambungan keling lebih sederhana dan murah untuk dibuat.
Pemeriksaannya lebih mudah
Sambungan keling dapat dibuka dengan memotong kepala dari paku keling tersebut.
Sambungan paku keling
Kelemahan:
Tidak dapat dilepas
Pencekaman tidak sekencang sambungan baut
Tipe kepala keling
Kepala keling secara umum (di bawah diameter 12 mm)
Tipe kepala keling
Kepala keling secara umum (diameter 12mm sampai 48mm)
Tipe kepala keling
Kepala keling untuk ketel
Tipe sambungan keling
Lap Joint (sambungan 2 lapis)
Tipe sambungan keling
Lap Joint (sambungan 2 lapis)
Tipe sambungan keling
Butt Joint (sambungan 3 lapis)
Kegagalan sambungan keling
Keretakan pada sudut plat
Retak pada seluruh plat
Pergeseran keling
Perubahan bentuk (crushing) pada plat atau keling