Second, the book is written by a well-informed scholar who is well versed in the field. This book requires an understanding or introductory experience of core concepts in the study and practice of HRM and ER, as well as the application of common principles used in the use of case-based teaching and learning.
Theoretical Foundations of SHRM & ER
Malik (Ed.), Strategic Human Resource Management and Employment Relations, Springer Texts in Business and Economics,. Faculty of Business and Law, Central Coast Business School, University of Newcastle, Ourimbah, Central Coast, NSW, Australia.
Introduction
This presents challenges to some of the more prescriptive schools of strategic HRM thinking. There is evidence of application of the Competitive Forces model in the HR planning at Dorian LPG case study.
Strategic HRM & ER: Best-Practice Versus Best Fit
The universality of HR practices in all contexts is emphasized in the best-practice view of SHRM theories. The effect of high performance work practices on employee earnings in the steel, apparel, and medical electronics and imaging industries.
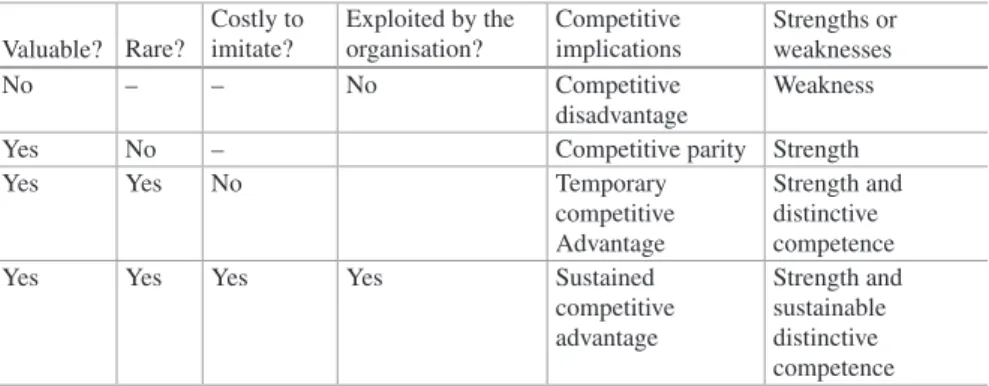
SHRM & ER: The Resource-Based View
The main focus of the RBV is to create SCA by investing in and organizing their resources and capabilities. Related to the above, Boxall and Purcell (2011) warn about the problem of appropriation of the value thus generated through the deployment of resources within the organization.
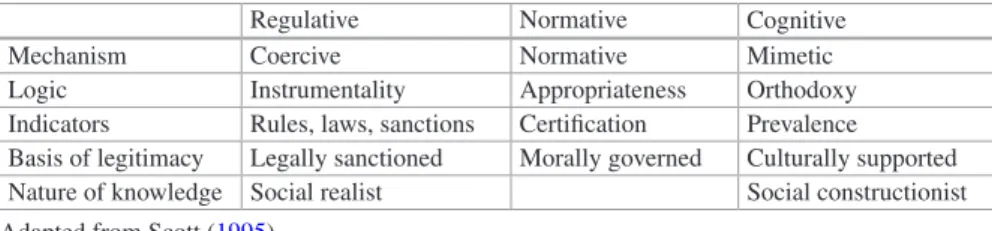
Institutional Theory and SHRM
This chapter focuses on the HR professional: the competencies he needs and the professional code of ethics he must apply in his daily work. Often, neglect occurs when the business community supports one group: shareholders over other stakeholder groups.
HR Profession and Design and Implementation
A Strategic Perspective
An overview is then given of the types of analyzes that can be performed. It is clear that HR planning is a much more integrated HRM practice and informs almost all practices of the HR work lifecycle. Although the idea of workforce flexibility is intuitively appealing, a number of researchers have criticized the approach, noting it as a form of neoliberal market management.
There is an increasing trend in zero-hours contracts and their spread now extends to all levels of the workforce (managerial, professional, technical and manual). These two processes are activated once the organization has an idea of the nature and extent of its resource requirements from its HR planning exercise. Organizations must adopt a systematic and strategic approach to ensure that every resource decision adds value to the strategic needs of the business.
Person-job fit refers respectively to the extent to which the profile of the preferred candidate matches the requirements of the job offered.
Management
From a strategic perspective, the basic principles of goal-setting theory are very relevant here (Locke and Latham 1990). The concept of internal fit was also discussed in the chapter “Strategic HRM & ER: Best Practice versus Best Fit” of the book. Managers and leaders must therefore address each of the above elements for an effective performance management system.
Part of the problem also arises because of managers' and employees' interpretation and design of advocates. Overall, the performance-HRM link, although on a strong foundation, with a wealth of studies pointing to its positive relationship with performance, requires further research from studied geographic contexts, especially from emerging markets, which can further test the evidence base. Although there is extensive research on this topic, there is far from a consensus regarding the 'set' or 'bundle' of HRM practices central to high performance.
Executives at XYZ emphasize that the requirement for daily and excessive monitoring is part of the customers' contractual requirements.
Strategic Learning and Development
Building on research undertaken in the UK, Smith and Hayton (1999) analyzed the factors influencing the provision of enterprise training in Australia. Read the following case study about managing careers in a multinational firm operating in the UK. The organization operates in the ICT sector, offers cloud computing technologies, and employs more than 1500 staff.
The dominant culture of the organization is similar to that of host American multinationals, where a high-performance work culture prevails. A key issue for individual careers in the organization is the nature of the performance management process. This question was investigated in the vocational training sector in European and UK companies.
In general, learning and development are key functions in the HRM arsenal and have been found to have a direct and indirect impact on business and individual performance levels.
Managing Employee Voice
From a strategic perspective, regardless of the nature of employee voice mechanisms – direct or indirect voice – the central question is the extent to which employees should have an influence on the decisions affecting their employment. The conflict has escalated between small groups of employees on this floor who claim "the air conditioner is too cold" or conversely, others complain "the air conditioner is too hot". Based on the nature of the job, Jennifer had to pay attention to every detail in the application.
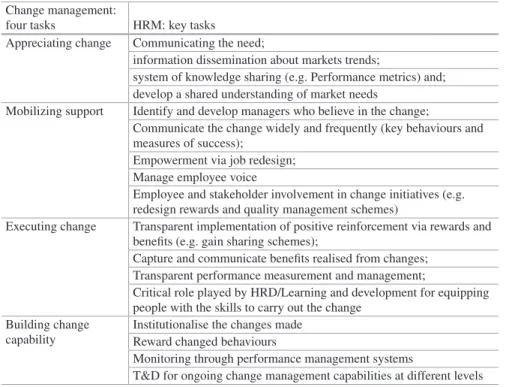
She was also able to exceed the normal lending ratio of the loan given in recognition of the nature of her employment.2 The disadvantage was that she felt "trapped" in that she was bound by her employer to a bond knowing that if she were to leave her current job, struggle financially to either replace the loan with another loan provider, or at least pay a much higher interest rate if she continues the loan through her current employer. Jennifer replied, "she did" but "...the General Manager was not very responsive to her concerns or needs". The key tasks of managing change are overlaid with the role that HRM can play at various stages of the change management process.
The head of research and development felt that the consultant should intervene with the group president, especially in the interests of the acquired unit.
Strategic Compensation and Benefits Management
HR practitioners must initially be aware of the broader strategic context, a company's business model and the company's ability to afford the payment of a given set of compensation and benefits. In addition, consideration should be given to accommodating 'employee flexibility' in the design of both compensation and benefits. Annual wage and salary surveys also provide a basis for strategic choices in the design and implementation of compensation and benefits.
HR managers are mainly perceived as representatives of the principal and not as experts who also have the task of playing the role of employee advocates. With the speed at which things are moving in the company and the limited number of experienced people in the company, they are struggling to cope. Motive to serve: Public service motivation in human resource management and the role of PSM in the non-profit sector.
Building ambidexterity: The role of human resource practices in the performance of Spanish firms.
Cases
To Cyber-Vet or Not to Cyber-Vet
An Ethics Question for HRM
Work-Life Balance in an MNE Context
Global work-life initiatives present unique challenges for HR departments in multinational enterprises (MNEs) due to the complexity of implementing policies that require sensitivity to local issues such as cultural traditions and legislation (e.g., Bardoel and De Cieri 2007; Scullion et al. 2007; Sumelius et al. 2008). However, specific discussion of work-life management in a global context is limited (eg, Allen et al. 2010; Lewis et al. 2007). Work-life management practices refer to those practices in organizations introduced to facilitate the integration of work and non-work demands of employees (McCarthy et al. 2010).
Corporate promotion of work-life balance (WLB) has attracted interest worldwide because of the potential role of these efforts in promoting effective recruitment, retention, and productivity among employees (Christensen and Schneider 2010). One well-known example of synthesis emerged in the mid-1990s, when HRM practitioners and researchers moved from the relatively exclusive term "work-family" to the more inclusive term "work-life" (Harrington 2007). Analyze three generic sources of tension identified in managing global work-life issues.
The relationship of perceived flexibility, supportive work-life policies, and the use of formal flexible arrangements and occasional flexibility to employee engagement and expected retention.
Crisis and IHRM
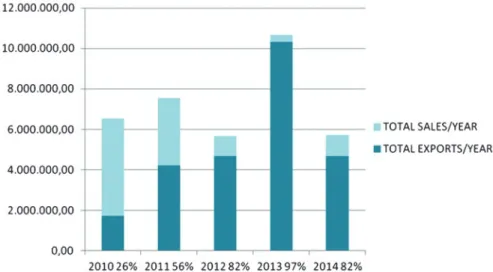
The financial crisis that has plagued the country since 2010 has played a key role in the evolution of SOFMAN's business activities. A €4 million milestone project in the firm's history involved the production of a bioethanol and power generation plant in Greece and its installation in Ebola-stricken Sierra Leone, using SOFMAN's own lifting equipment. The CEO led the team in the initial phase of the project in Free Town, the capital of Sierra Leone, where machinery and the steel structures were shipped, and then at the construction site in Makeni.
The team's manager was an experienced SOFMAN engineer who performed on-site management and communicated with the leadership team in Athens on an almost daily basis, especially in the early phases of the project. The CEO and the Greek project team of expats lived together in the best possible accommodation in Makeni, which became home to the project team for several months. This would have been a risk with significant cost implications, given the high volatility and uncertainty in the home country's construction market.
Critically evaluate SOFMAN's HRM practices in the internationalization process and provide suggestions for improvement.
Japanese Cross Border M&A
Dorian LPG’s Rapid Fleet Growth
A Story of Maritime HR Planning and People Management
Further, the client's requirements emphasized the qualifications and experience of the top four officers in the ship's hierarchy, 9 i.e., for this, “the only solution was to accept qualified LPG officers from different types and sizes of LPG and their training for existence. LPG fleet during the same period (four months in total, twice of two months each)”. The company's previous experience with the employment of Croatian seafarers was used.
Dorian's instructions to his officers' supplier Pasat were clear: "The naval expansion does not allow us to depend on a single country for the supply of senior officers." While Dimitris, the chief operating officer and a former seafarer himself, emphasizes the importance of a rigorous vessel maintenance program, he also emphasizes the role of the people, both on board and ashore: “The truth is that anyone can order a ship tomorrow. . The existing process focused more on the deadlines rather than the quality of the jobs.
Such unexpected reactions on the part of the employees prompted Nitin to decide to change the Performance Management System in the organization.
