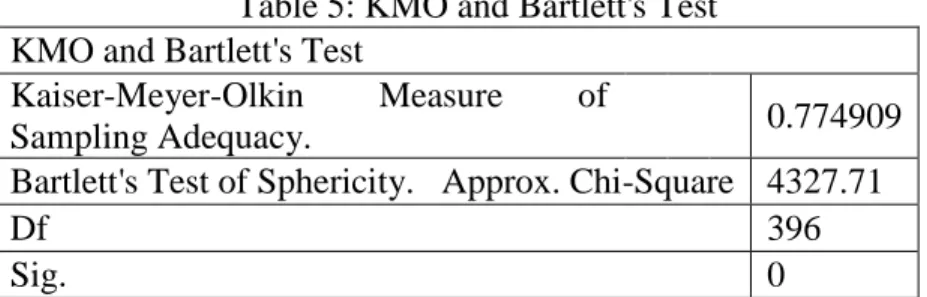
ASEAN International Conference on Islamic Finance (5th: 2017: Bandar Seri Begawan) Proceedings 5th ASEAN's International Conference on Islamic Finance (AICIF) (Vol. 1). The aim of the study is to discover factors influencing the adoption of financial inclusion in Indonesia for the realization of justice and well-being. For this purpose, the study involves 200 stakeholders involved in the development of financial inclusion, such as scientists, academics and government officials; public leaders, NGOs and companies sent the questionnaires.
The implications of this research offer benefits to stakeholders and every party involved in the development of financial inclusion. Financial inclusion (FI) is a condition where all people have access to the financial system, not only banks, but also other financial institutions. A financial inclusion strategy is indispensable for Indonesia as the financial inclusion level in Indonesia is 32%; this means that 68% of the poor are unaffected by banking financial services (Mulya E,S, 2012:1).
The goals of financial inclusion in general focus on serving the poor to have better lives, especially in terms of financial access. Some literature (McKinsey Chiba Radcliffe Dan and Voorhies Rodger introduced the detailed objectives are: First, everyone who is part of society has the same opportunity to access financial inclusion for both banks and/or other financial institutions, so that especially the poor have the opportunity get to improve their standard of living.The Special Target for Indonesian Financial Inclusion is primarily aimed at poverty alleviation as the poverty scale is 11.767% (Central Statistics Agency (BPS), 2014:1) The global financial inclusion movement under Alliance Financial Inclusion (AFI) plans to implement the model in cooperation with the Indonesian government to tackle the problem of poverty.
However, regardless of the high government vision and people's responses, the most important issue is how to develop financial inclusion in Indonesia, including the important factors that should be involved in the development process.
Research Methodology
353 To deal with this problem, some experts have suggested the use of ICT and mobile payment systems such as Morthi et.al. In addition, Fuller proposed a bottom-up approach by placing institutions heterogeneous model based on local community (Duncan Fuller et.al, 2014:265).
Theoretical Perspective
- Financial Inclusion Strategy in the World Wide
- Islamic Financial Inclusion (IFI) Versus Alliance Financial Inclusion (AFI) 1. Islamic Financial Inclusion (IFI) Concept
- Alliance Financial Inclusion (AFI) Concept
- The differences Between IFI and AFI Concept
- Barriers and Challengers for Financial Inclusion Development
- The Obstacles and Determinants Factors in the Financial Inclusion Implementation
This study found that the significant role of microfinance sectors for strategies for viable financial inclusion of the poor and of small producers. The role also involves the initiative that education does for people; there is no financial inclusion without education activity. 355 connectivity, convenience, reliability, flexibility and continuity in order to achieve greater financial inclusion in Africa.
Essentially, this research focuses on community credit unions in Britain, which has elaborated on the role of community agency in the success of financial inclusion. A study of the geography, society, politics and culture of the financial inclusion movement in Indonesia is neglected. Microfinance in developing countries and India also plays an important and strategic role for the successful financial inclusion of poor and small producers.
4 Chiba (2008) The role of public sector support / government has a central role to facilitate financial inclusion in terms of regulations and legislation, policies, procedures, programs. Financial inclusion has been initiated in 112 countries in the world and only 14 countries are at the maturity stage. India The public sector provides the overall framework, FINANCIAL INCLUSION policy/product guidance from the central bank.
CEMEX as a non-financial private sector firm that helps FINANCIAL INCLUSION through a savings and credit scheme for the poor and unbanked. With guidance from the public sector, the formal financial sector has developed a Financial Sector Charter (FSC) for FINANCIAL INCLUSION to serve the poor. He described the development approach of financial inclusion, which is not in line with Chiba, who proposed the theory of four pillars.
AFI membership is open to any financial involvement, including central banks and other financial regulatory institutions. Policy orientation for optimal impact and the role of the private sector in financial inclusion efforts. In addition, in terms of principles, Islamic and conventional financial inclusion is a difference, Islamic value is based on investments.
A number of common themes emerge in the development of financial inclusion around the world: the main barriers, supports and factors (Madhur, Jha, culture and traditional (Juan, 2014) are the major barriers facing community-based financial inclusion is confronted.
Result and Discussion 1. Results
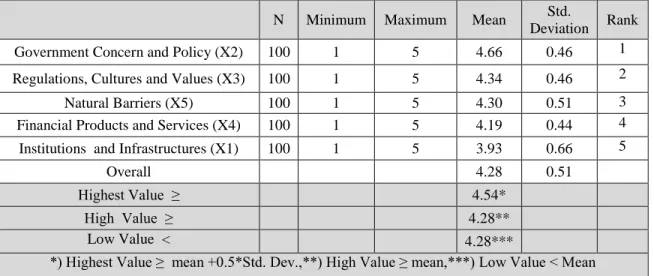
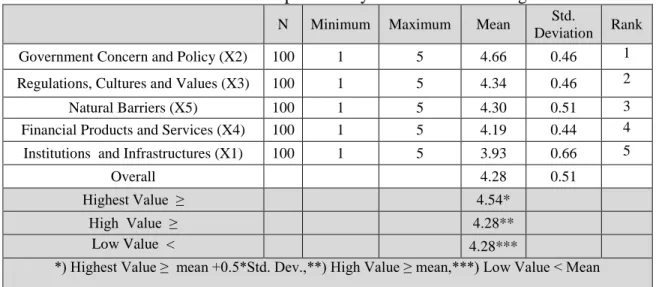
Descriptive Analysis
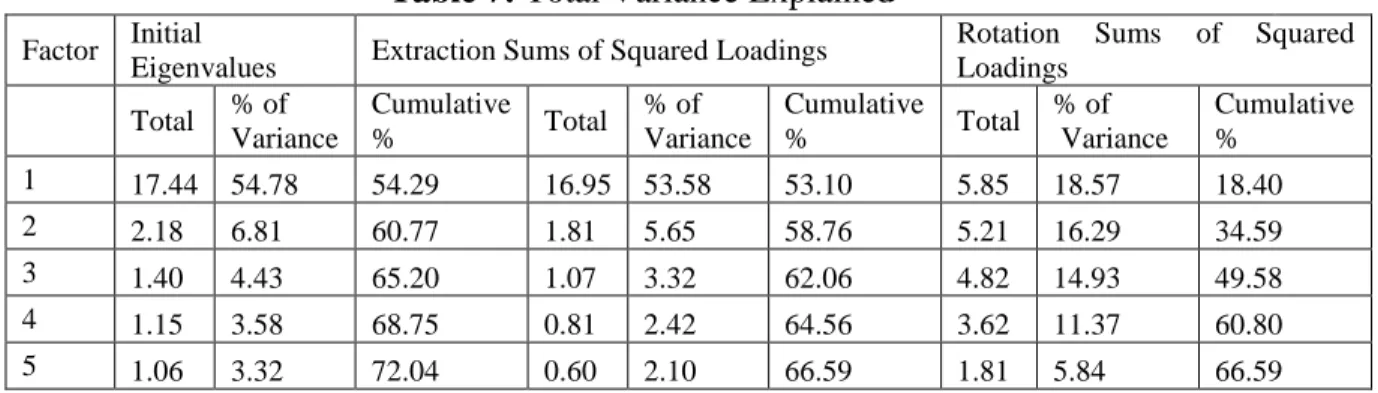
The figure above shows that there are links between the development of financial inclusion and institutions and infrastructure (X1), government concern and policy (X2), regulations, cultures and values (X3), financial products and services (X4) and natural barriers (X5) ), however further research is needed to elaborate the relationship.
Discussion
This factor has six indicators, namely; national and international regulatory policies, regulatory quality, government effectiveness, political stability, financial strategy and level of corruption. These findings declared that the public sector is the most important factor for implementing financial inclusion. This result is consistent with the statement of Suharo U (2015) that in terms of poverty alleviation program, a sustainable and integrated government program is needed, especially in financial assistance, attitude and financial literacy.
This factor has been measured by the banking system, the non-formal financial sector and microfinance, IFC (Global Financial Sector, Product Innovation and Creation). Regulation, culture and value are important because these factors will accelerate financial inclusion and work faster and in the right way. The result is consistent with Demirguc-Kunt (2012) who found that geographical conditions, distance and culture, and heterogeneity of culture and value influenced the development of financial inclusion.
This factor needs to be given more attention because it is consistent with the fact that Indonesia is a unique archipelago, which means a very large and long distance from the starting point to the ending point, about 14,000 km, which includes 13,000 inhabited islands, so it is very difficult to develop the best financial inclusion model in Indonesia. In addition, government concern and policy (X2) is the most influential factor for the implementation of financial inclusion in Indonesia. This is followed by regulations, cultures and values (X3), natural barriers (X5), financial products and services (X4) and institutions and infrastructures (X1).
This finding means that any party may need to pay attention to the government's concerns and regulations, cultures and values for the development of financial inclusion in Indonesia. The support of respondents can serious participation and willingness to be involved in the development of financial inclusion, as the respondents believe that there are strong correlations between poverty alleviation and financial aid and financial inclusion system. The implication of the findings of this study is significant for stakeholders and parties such as the government, public sector, financial sector, private sector and NGOs involved in the development and design of financial inclusion in Indonesia.
Indonesia is a unique country, which is very large and wide area, in addition to including a thousand populated islands very far from each other, the government should be aware of their role as a central agent. 369 For further research, it is suggested that difference perspective such as scope, location and time should also be considered. Future research could also be examined focusing on the effectiveness, process and strategy in all phases of the implementation process.
Summary and Concluding Remark
1] Adele A, and FloreA., (2013), Promoting Financial Inclusion through Financial Education, Working Papers on Finance, Insurance and Private Pensions, Paris Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD p. 1. 14] Dave Grace , (2006 ), Central Banks Commit to Financial Inclusion, by Dave Grace, Advisor, CFI 2011), Branchless and Mobile Banking Solutions for the Poor: A Survey, Journal of the Social Science Research Network-USA, SRRN-id1986316, January 23, 2011, Innovations, Vol. 18] Duncan Fuller, Mary Mellor, Lynn Dodds and Arthur Affleck (2014), "Community consultation advancing financial inclusion in Newcastle upon Tyne, UK", Emerald Insight International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy Northumbria University, Newcastle.
20] Elizabeth Rhyne, Three Ways Financial Inclusion Makes Life Hard for Lawmakers, by Elisabeth Rhyne, CFI CEO. 21] Harjono K, (2015), Baitul Mal Wa Tanwil (BMT) Concept of Financial Inclusion, Unpublished Paper, Model Venture, Jakarta. 25] Jhon Gitau, (2013), Center for Financial Inclusion, Policy, Technology: Alliance for Financial Inclusion, M-PESA, M-Shwari, Mobile Money, Safaricom, South Africa.
2014), Banking on Change: Breaking the Barriers to Financial Inclusion, NPM Platform for inclusive Finance, Head of Corporate Affairs, Barclays Bank Uganda, New Expanding Credit Access: Using Randomized Supply Decisions to. 29] Khalif RA, (2015), ICT-Based Financial Inclusion and Microfinance, Unpublished Paper, Rowasiya PT, Jakarta. 2010), Global Financial Inclusion Achieving Full Financial Inclusion at the Intersection of Social Benefit and Economic Sustainability, Mc Kinsey Company 2010. 372 [34] McKinsey (2008), “Research conducted in partnership with the Initiative on Financial Access, New York University, Harvard , Yale, for action against poverty; Journal of Banking.
35] Michelle Baddeley, 2004, Using e-cash in the new economy: an economic analysis of micropayment systems, Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, VOL. 37] McKinsey, (2010), 'Global Financial Inclusion: Achieving full financial inclusion at the intersection of social benefit and economic sustainability', pp.1-44, Retrieved from:. 2009), Strategies for Optimizing FI in South Africa, Thesis, University of Pretoria SA Branchless banking services by Corporation Bank – A brand perspective. Retrieved from http://tejas.iimb.ac.in/articles/10 accessed on 26 July Banking on Change: Breaking the Barriers to Financial Inclusion, NPM Platform for inclusive Finance, Head of Corporate Affairs, Barclays Bank Uganda, Nov 2014, pp. 74.
44] Santoso, Bedjo, (2015), Frame Work Design of Community Mobile Financial Inclusion in Indonesia, Proceeding on International Conference on Public Policy, Banda Aceh March 2015. 47] Savita Shankar, 2013, Financial Inclusion in India: Do Microfinance Institutions Address Access Barriers?, ACRN Journal of Entrepreneurship Perspectives, Vol. 48] Susy Cheston, Seven trends to watch in March to achieve full financial inclusion for all, posted by Susy Cheston, Senior Advisor, CFI.