Screenshots from the Walter Reed Middle School Library website reprinted with permission from Mark Bobrosky, Library Media Teacher, Walter Reed Middle School. Paideia School Library website screenshots reprinted with permission from Natalie Bernstein, Elementary Librarian, Paideia School.
Why Go Virtual?
CHAPTER
Libraries and digital information resources can play a critical role in the education of today's students” (Lippincott 13.1) as we “provide collections, organized information, systems that facilitate access, and in-person and virtual assistance to encourage students to further their education to follow. the classroom” (Lippincott 13.2). As David Warlick notes in his Knowledge Quest article, "Building Web Sites That Work for Your Media Center," as library media specialists.
Where are the students?
Like a school-published textbook or a traditional library, students view the Internet as the place to find primary and secondary source materials for their reports, presentations, and projects” (Digital Disconnect iii). According to Born to be Wired, “The internet has become THE medium of choice for young people.
Implications
When asked why they prefer the Internet, students say that the Internet is easier to use and more convenient than traditional libraries, that it does not require transportation to and from it, that it is open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, that it has up-to-date materials, it is “always available to everyone (unlike a book in the library that a classmate might check out)” (Digital Disconnect 8). Additional areas in which the Internet dominates traditional libraries: Libraries offer a limited selection of multimedia and require students to wait in line to check out materials and pay to use a photocopier.
From what location do the students go online?
Of the teenagers who go online at school and not at home, only 7% say they go online several times a day and 15% say they go online about once a day. In seven of the schools, less than 40% report using the site outside of school" (Interface).
What of our younger children?
Students use library websites from home, some on weekends, but more in the evenings. It is important for not only high schools and middle schools, but also elementary schools to provide virtual library services via the school library website.
How do students find what they need on the Internet?
Are they successful?
Guided access to appropriate information on the free internet and subscription databases, as well as early instruction in information literacy are valuable to our younger students. They also need to learn that a search tool may not be the best place to start their research process.
Where do school libraries fit?
Students reported using the school library sometimes or often for research papers (54 percent), school projects (53 percent), Internet access (41 percent), and assignments (41 percent)” (14). Interestingly, data analysis showed that “students with higher test scores were more likely than students with lower test scores to use the library sometimes or often for assignments, school projects, and research papers” (15).
Where do teachers fit?
Findings revealed that teachers encourage students' Internet use in the SLMC, but that most students do not instruct them to use databases. Teachers should be aware of and trained in the use of subscription databases and other library information sources.
What do students want, in general?
Williams, Grimble and Irwin conducted an exploratory study at an Indiana high school to examine teachers' awareness of electronic resources and to determine whether their cues influence students' use of these resources in the SLMC. We need to train teachers in the use of available information technologies and we need to work with teachers to ensure that student research is as effective and productive as possible.
What does this research mean for virtual school libraries?
The Born to be Wired study reports that “this generation has had a very structured upbringing and they are looking for more structure online. He also notes that “the online world is seen as vast and limitless for young people, but it can also be frustrating if they seem directionless and inefficient.
What features should we include, if we pay attention to students?
Another concept Rainie shares in his talk that has implications for web page development is that of former Microsoft executive Linda Stone - continuous partial attention: "Continuous partial attention is not the same as multitasking; it's about trying to achieve multiple things at once Our students will function in the mode of continuous partial attention, scanning for elements or information that best meet their needs.
What should we know as we develop virtual school libraries?
To engage students, virtual websites we develop should offer interactivity, email/chat/instant messaging-ask-a-librarian capabilities, and perhaps even blogging capabilities. Video and audio streaming is possible due to the number of students with broadband Internet access.
Conclusion
Lippincott urges library media specialists to "think of your library as an environment rather than a facility - a place of interaction, learning and experience rather than a place for storage and equipment" (13.11). Libraries have been adapting their collections, services and environments to the digital world for at least 20 years” (13.1).
Information Access and Delivery
From
Information Power: Building Partnerships for Learning,
- Information Access and Delivery
- The library media program provides physical access to information and resources for learning
- Principle 3: The library media program provides a climate that is conducive to learning
- Principle 4: The library media program requires flexible and equitable access to information, ideas, and resources for learning”
Through a quality school library media center website, the library media specialist can provide accurate and up-to-date information that meets students' learning needs. With a quality school library media center website, the library media specialist demonstrates leadership, creates a virtual presence for the library, presents information, and provides guidance in its use.
Online Catalog
Citation of sources: Likewise, since MARC records contain required bibliographic information, a student completing
Access to eBooks: If you subscribe to eBooks, you can make them available via the OPAC. Websites: If you catalog websites, you can make them available via the OPAC.
Reading programs: If your school uses a reading program such as Accelerated Reader or Reading Counts and you
A catalog search for the book in question will then produce the link, giving the student direct access to the book's electronic text. For example, for our student, Sarah, who is researching the planet Saturn, if you have cataloged the website for The Nine Planets: A Multimedia Tour of the Solar System in your OPAC and paste the URL into the 856 MARC field when Sarah creates a subject or keyword search in the catalog for Planets, she will be directed to this site.
Subscription Databases
On the other hand, Albemarle County Public Schools (VA) subscribes to Britannica Online and Enciclopedia Universal en Español; Grolier Online; World Book Online (for elementary and middle school); Gale Resource Center Gold, Opposing Viewpoints, and Science Resource Center (for high schools);. Gale Resource Center Junior (for middle schools); EBSCO Primary Search (for elementary) and MiddleSearch (for middle).
General Periodical Databases
Albemarle High School chooses to add Congressional Quarterly and LitFinder, while Western Albemarle High School adds the Gale World History Resource Center and LitFinder.
General Encyclopedia Databases
Subject Area Specialized Databases
ProQuest biedt Culturegrams, eLibrary Science, ProQuest AP Science, ProQuest Career and Technical Education en ProQuest Historical Newspapers. Thomson Gale biedt Biography Resource Center, Business and Company Resource Center, Discovering Collection, Health and Wellness Resource Center, History Resource Center World, History Resource Center U.S., Literature Resource Center, LitFinder, Opposing Viewpoints Resource Center en Science Resource Center.
You may also want to provide links to good reference portals such as the Internet Public Library
Professional Collection
GEM: The Gateway to Educational Materials
Professional ebooks
Greenwood
Journal Access for Professional Development
Parents’ Space
Links to websites that focus on libraries, the Internet, and children (such as the American Library Association's Online Resources for Parents and Children
Ebooks (Fee and Free)
Project Gutenberg
Web Site Subscriptions
SKS WebSelect
Locally Selected Web Sites
If your library subscribes to one of the website subscription products, it should be available from the library's media center web page, either through the OPAC or as a clickable link.
Sample Dictionary Sites
Sample Ready Reference Sites
Sample Biographical Links
Sample Geographical Links
Sample Government Sites, Federal
Of course, you'll also want to provide links to state and local government websites.
Federated or Meta Searching
Products/ibistro.html> simultaneously searches local collections, other library catalogs, web search engines, journals, and databases.
Access from within Blackboard
User IDs and passwords can be easily made available; another advantage is the library's presence in Blackboard. Patrons and outsiders will judge the library by your website, so one should exist on the free internet.
Exemplary Web Pages for Information Access and Delivery
Includes online catalog, online resources, curricular links, about the library, using the library, book talks, research process, Reed home page, and LAUSD Digital Library. Includes about the library, databases, reading, search engines, searching the library catalog, recommended websites (grouped by subject in their Dewey Decimal categories), research guides, family resources, and teacher resources.

Learning and Teaching
Principle 8: The library media program fosters individual and collaborative inquiry
Principle 9: The library media program integrates the uses of technology for teaching and learning
THREE
Schools have evolved to focus on learning, and effective school library media programs have also shifted their focus from collections to learning, engaging students in the pursuit of knowledge within and outside of a formal curriculum” (American Association of School Librarians 59). In addition to making information readily available, it is the responsibility of the school library media specialist to teach and help students learn how to use these information resources.
Information literacy
The provision of virtual library services depends on the provision of access and distribution of quality information resources; ensuring access and distribution, however, is necessary but not sufficient.
Curriculum Support
Pathfinders
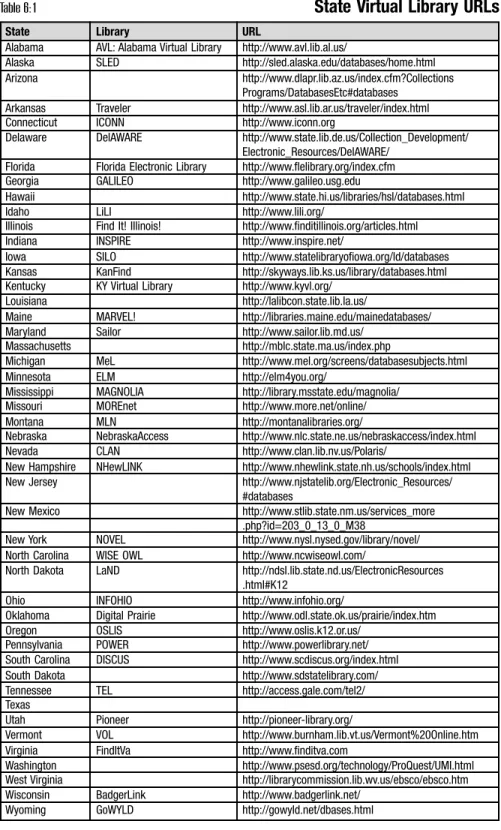
Middle School Pathfinders by Lakewood Public Library for Lakewood Public Schools, Lakewood, OH Arab Cultural Arts Day" to "The El Niño Project" to "Types of Government/Branches of Government," these guides offer links to selected Internet resources appropriate to the topic. Information Literacy Skills Instruction Also for older students, this guide deals with effective searching, evaluating information found and citing sources. Information Literacy and You, Penn State University Libraries Finding Information on the Internet: A Tutorial, University of California, Berkeley Ulaagaalee Shan Fuula Weeb Madaaluuf, Mana Kitaabaa Yuunivarsiitii Korneel, Ithaca, NY Griekenland Athena Media Research Guide (Big 6™): Getting It Done—Six Steps to Success, Rochester, NY OSLIS/Oregon School Library Information System Citation Maker for Elementary (based on MLA style) Reading Promotion Advice from Aaron Schmidt, in his article "The Young and The Wireless" School Library Journal: "IM is and The Wireless" School Library Journal article: "IM is a must...If e-mail is the only electronic format you use to communicate with teenagers, your library risks being seen as outdated" (45). As we develop our school library media websites to provide that virtual library presence to our patrons, we we must keep in mind our role as educators and teachers of informational education. The attractive and user-friendly site features a reference desk, online lessons, catalogs and databases, teacher links, student, school and career links, librarians, our district and wayfinders. Principle 6: Ongoing assessment for improvement is essential to the vitality of an effective library media program Clear communication of the mission, goals, functions, and impact of the library media program is necessary to the Effective management of human, financial, and phy- sical resources undergirds a strong library media program” (100) As noted in Principle 10 on page 65, effective management of resources is key, and in Principle 6 continuous assessment for improvement is essential. Here in Chapter 4, we discuss conducting a needs analysis for your library website, considerations for developing virtual collections, paying attention to policies that affect your page, marketing for your virtual library, and evaluating the virtual library. Book Stuff (A surprising number of responses asked for more resources related to books.): "Include the suggested reading lists in the library on the page." "Organized book lists by genre or author." "Link to the OPAC." "Book of the Month, trivia about books?" (Teens and Virtual). By conducting a needs assessment, you can develop a virtual library that meets the information needs of your users. Teacher/Project Links (You get our connections and partnerships.): 'Direct links to teacher websites.' 'More of what teachers go over in class to make sure we understand.'. In addition to the traditionally used criteria of purpose, audience, authority, accuracy, arrangement, scope, currency and cost for electronic formats, you will also consider accessibility, ease of use, appropriate delivery of the content and any special features. Attention to Policies Since you are granting access to subscription databases, you must be absolutely sure that you are not violating any license agreements. You want to work with the technology staff at the school or district level to provide appropriate access to resources, both within the school walls and from home, without violating your licensing agreements. The objective is to provide legitimate users with as easy access as possible to subscription databases, while respecting licensing agreements. If you plan to blog or offer virtual referral help via email or chat, timing issues are involved. Again, if you intend to offer real-time virtual reference help, there are questions to answer:. Use one of the commercially available instant messaging services such as AOL Instant Messenger, Yahoo Messenger or MSN Messenger. Ability to conduct an effective referral transaction in online environments, including creating and using online environments, including creating and using prescriptive messages. Ability to assist online users in applying critical thinking skills in finding, using and evaluating information skills in finding, using and evaluating information. Ability to create and enforce reference transaction policies in an online environment (e.g. service range, time limits, obscene callers, harassment). Commitment to continuous learning and motivation to improve skills in all areas of reference services. Multi-task and manage multiple windows; effective use of windows keyboard commands and shortcuts use windows keyboard commands and shortcuts 12. On-Paper Possibilities In-Person Possibilities Promotional Item Possibilities It was a battle to get them to use the website,” she says, “and I got every single one of them.” Now that a cart of Apple iBooks is moving around the school, students are doing more research away from the library. Since she has compiled her subscription databases and recommended websites on the website, students, both at home and at school, have been logging into these resources more frequently” (37). Evaluation of the Virtual Library Value of the page/site as a model for other school libraries and/or school librarians" (IASL/Concord School Library) Or, you may want to use the criteria and explanations outlined by Annette Lamb under Information Architecture for the Web: Web: Web Development for Schools and Libraries—Website Evaluation Or a third option for evaluation would be to use the standard basic five criteria for evaluating web pages: accuracy, authority, currency, objectivity, and coverage (Five Criteria) to see how well your page measure. Observe users as naturally as possible: Lipow suggests that you recruit a user for a period of time and observe her as she uses the library's web page, asking her to think aloud as she searches. You must choose a method of evaluating your library web page that works for you in your school library. Technological Aspects Information Power: Building Partnerships for Learning Use these notes and keep these thoughts in mind as you begin to create your virtual library. The purpose of this chapter is to help you get started with creating or revitalizing your school library's website. Before you start building or rebuilding your website, spend some time online browsing and looking at school library websites. Once you have the answers to these basic questions, you're ready to start designing your library website. Your ability to upload files affects the currency of the material you can put on your site. If you have the ability to update your library's website as needed, you can certainly plan to update the website more often than you could if you had to send files to the webmaster for upload. When designing your website, keep your users at the forefront of your mind; the library website is for them, not you. OPAC' instead of 'Library Catalog' or 'Book Search'. We need to make our website user-friendly and use terminology that patrons understand. A good rule of thumb is to have no digital photos larger than 35K.) Consider download times when using multimedia files as well. Remember that your library's website is your library's presence outside the library and school walls. If you are designing a site for elementary school students, consider Nielsen's full report on usability guidelines for designing websites for children, available at Readability View your site in black and white to ensure that color is not a critical element in navigation or understanding of the page. If you really want to check your page against Section 508 guidelines and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), you can consider using the following services. In this chapter, we explored the technological context in which you will develop a school library website. When you develop your school library website, you want it to be accessible to all of your users, and you want to plan for continued maintenance and upkeep. By creating the school library web page and providing that virtual library presence for patrons, we are able to guide and connect them to resources in the greater learning community. Baumbach, professor of educational media/instructional technology at the College of Education, University of Central Florida, Orlando, studied 100 school library websites in the United States randomly selected from the School-Libraries.net list. She reported that 70 percent of the sites surveyed included a link from the school's main website. From these studies, it is clear that library media specialists have played an active role in technology in the past 10 years and that school library websites have evolved greatly to provide access to information resources. Kansas KanFind http://skyways.lib.ks.us/library/databases.html Kentucky KY Virtual Library http://www.kyvl.org/. What better way to meet both of these charges than by highlighting and promoting the use of state-level electronic resources on the school library website. The school library website can be an element that connects them to their home school. We currently serve as guides for patrons through the chaos of information; we do it in person, and we need to do it with our library web presence. Set a goal that your library website will be the first place your patrons look for information. List of Sites Mentioned Fifty years of supporting children's learning: A history of public school libraries and federal legislation from 1953 to 2000 (NCES 2005-311). Teachers' connection to electronic resources in the library's media center: A local study of awareness, knowledge, and influence. IndexWebQuests
Basic Instruction in Information Literacy
Effective Use of Search Tools
Evaluating Web Sites
The Research Process: Research Guides
Citations and Ethical Use of Information
Virtual Librarian Services
Exemplary Web Pages for Learning and Teaching

Program Administration
FOUR
Chapters 2 and 3 presented suggestions for information that you might consider including on your library Web page. This chapter
Needs Analysis for Virtual Content and Services
Collection Development Considerations
District Policies Related to Web Page Content
District Policies Related to Web Page Services
Library Policies Regarding Virtual Reference Service
Training
Workload
Marketing for the Virtual Library
Virtual Possibilities
Evaluation Criteria
Feedback from Users
FIVE
Larger School Technology Context
Web Design
Planning
Layout and Appearance
Usability
Accessibility Issues
Testing, Upkeep, and Maintenance
The Larger Learning Community
Connections to the Learning Community
School Library Media Center Web Pages: 1996-2006
State-Level Virtual Libraries Providing Services for K-12 Schools
Virtual Libraries Serving Virtual K-12 Schools
Virtual Libraries: Present and Future
Works Cited
ALA, 2004






