This letter now confirms that your research project entitled: Required and Acquired Skills in STEM: Comparing Employers and Graduates' Perceptions in Kazakhstan has been approved by the Graduate School of Education Ethics Committee of Nazarbayev University. The changes recommended by the reviewer have been addressed and the proposed study now meets all the requirements of Nazarbayev University. Using mixed methods research design, it seeks to identify the most important skills for entry-level STEM professionals, to reveal how satisfied employers are with graduates' skills and how graduates themselves rate their university-acquired skills to contribute to a better understanding of the role of universities, employers and students in the development of students' skills.
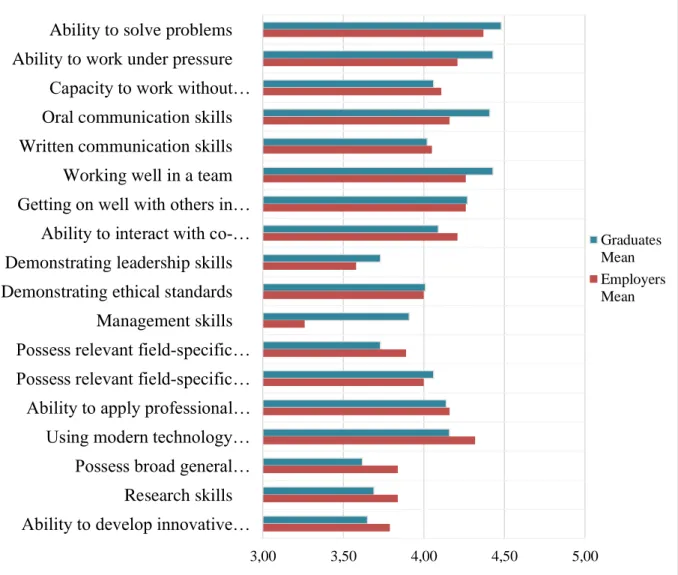
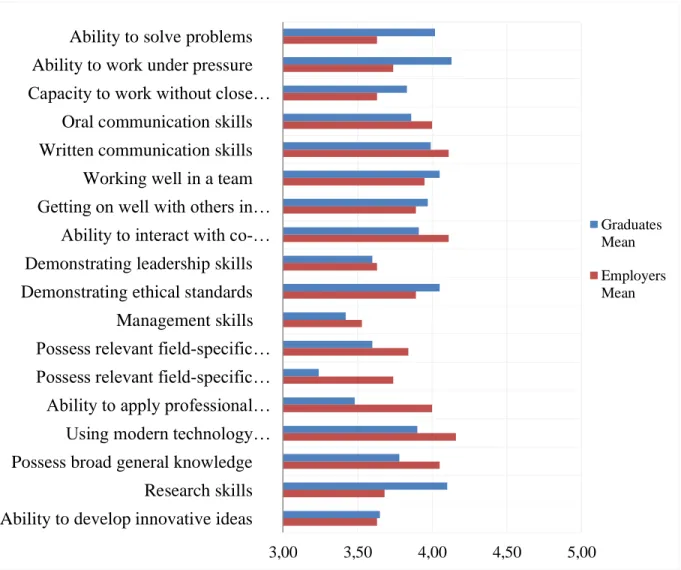
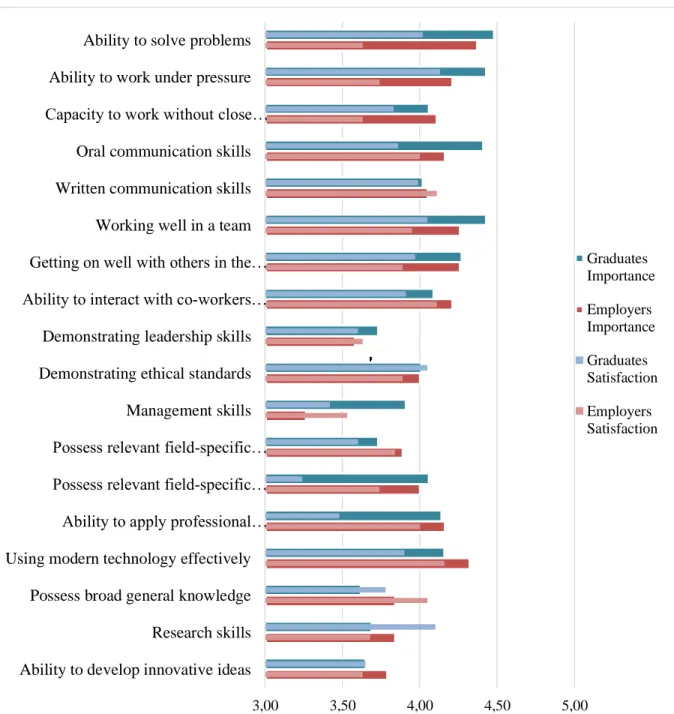
In particular, the ability to solve problems, work well in a team, the ability to work under pressure, get along well with others in the workplace and the ability to learn quickly appear to be the most important skills for STEM graduates . Graduates appear to be particularly dissatisfied with their field-specific knowledge and skills, while employers see the biggest shortcomings in graduates' ability to solve problems, the ability to work without close supervision, the ability to work under pressure and interacting with others in the workplace.
Introduction
The concerns of policymakers and employers therefore indicate that there is a gap between the demands of the labor market and the skills of graduates. The purpose of this study is to investigate the perceptions of graduates and employers regarding the skills of STEM graduates at a Kazakhstani university. University. The findings also show that there is room for improvement in the skills of STEM graduates.
This study is expected to increase the understanding of the skill sets of STEM graduates in Kazakhstan by exploring the gaps between industry requirements and the skills of graduates. The discussion chapter analyzes the findings in relation to other studies of the skill sets of STEM graduates.
Literature Review
Several researchers found the mismatch between industry needs and graduates' field-specific knowledge and skills. Indian employers also appeared to be dissatisfied with the technical skills of engineering graduates (Blom & Saeki, 2011). Similarly, study based in USA revealed that employers were also quite satisfied with the technical skills of engineering graduates (Lattuca et al., 2006).
MENA) region showed that employers are more satisfied with engineering graduates' ability to use modern technology and ability to apply mathematical knowledge (Ramadi, et al., 2016). On the other hand, American employers were found to be quite satisfied with the ability of engineering graduates to learn and grow professionally (Lattuca et al., 2006).
Methodology
This fact was taken into account when drawing conclusions and is discussed further in the limitations of the study. The online format was purposefully chosen due to the geographical diversity of the sample (Sue & Ritter, 2007). After the study author received approval from the Ethics Committee, the data collection process began.
It informs participants about the objectives of the study, data collection procedures and participants' rights. Participants in the study were asked to read it and indicate whether or not they agreed with participating.
Findings
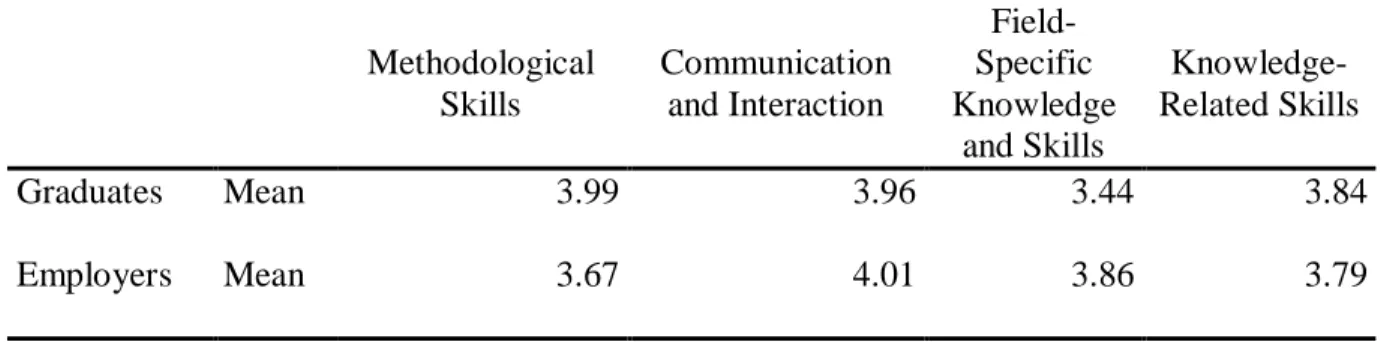
Getting along well with others in the workplace .778 Ability to communicate with colleagues from different or multi-. Possess relevant field-specific technical skills .839 Possess relevant field-specific theoretical knowledge .783 Ability to apply professional knowledge and skills on the job. F2: Field-specific knowledge and skills (e.g. having relevant field-specific technical skills, having relevant field-specific theoretical knowledge, ability to apply professional knowledge and skills to tasks);
F3: Methodical skills: (e.g. ability to work under pressure, ability to solve problems, ability to work without close supervision);. F4: Knowledge-related skills (e.g. research skills, ability to develop innovative ideas, possess broad general knowledge, effective use of modern technology). Although significantly important (with averages greater than average 3.0 but less than 4.0), broad knowledge, research skills, ability to develop innovative ideas, management skills, demonstration of leadership skills and possession of relevant field-specific theoretical knowledge appeared to be the least important skills perceived by candidates and employers participating in the survey.
The ability to solve problems therefore seems to be seen by graduates as an integral part of their professional skills. However, they appeared to be least satisfied with the subject-specific knowledge and skills. On the other hand, graduates ranked the ability to apply professional knowledge and skills to tasks, have relevant field-specific technical skills, and have relevant field-specific theoretical knowledge as among the least developed skills.
Employers are the least satisfied with graduates' ability to solve problems, ability to work without close supervision and research skills. The results show that employers ranked the following skills significantly higher: possess relevant field-specific technical skills (U = 2.135, p = .036) and ability to apply professional knowledge and skills to job tasks (U = 2.205, p = .015) . Use modern technology effectively Possess broad general knowledge Research skills Ability to develop innovative ideas.
Regarding the ability to work under pressure, graduates feel that they have well-developed skills. As for employers, they seem to be generally less critical of graduates' specific knowledge and skills, but believe that graduates' methodological skills could be better developed, especially in terms of working without close supervision, problem-solving skills and the ability to work under pressure.

Discussion
The findings also show that there is room for improvement in the skill sets of STEM graduates in Kazakhstan. Thus, similarly to Peng et al. 2016), graduates in this study are less satisfied with field-specific knowledge and skills, highlighting the importance of bridging the gap between higher education and employment prospects. In particular, the engineering graduates of this study pointed out that their Bachelor programs mostly did not take into account the realities of local industries, such as equipment and production standards inherited from the Soviet period, and instead focused on Western markets.
Therefore, this study argues that for higher education in Kazakhstan it is important to maintain a well-balanced mix of global and local and to bring about changes in higher education gradually and in accordance with the local economy. While the participants of this study did not claim that the only role of attending higher education is to find employment, they believe that universities should support graduates in the transition from university to the workplace as entering the labor market is the next logical step. . Regarding generic skills, graduates appeared to be mostly satisfied with these skills, emphasizing the role of extracurricular and social activities in the development of such skills.
On the other hand, the employers in this study appeared to be mainly satisfied with the graduates' field-specific knowledge and, contrary to Ramadi et al. However, while the study conducted by Tran (2015) revealed that employers, graduates and students share the same perception regarding the university's responsibility for how well students' skills are developed, in this study, graduates' and employers' perception of the importance of the role of these actors is different . Candidates thus ranked the students' role as the most important, followed by the university's role, whereas employers placed more importance on the university than students.
Moreover, the role of employers is perceived as less important than the role of the university and students and mainly limited to internships and careers. The findings are similar to the study conducted by Archer and Davison (2008) and Sin and Amaral (2017) who show that the role of the employer is usually very limited and mainly deals with the provision of internships and argues that employers should play a more great in the development of students' skills. Therefore, this study argues that all actors play an important role in student development and collaboration should be increased through a better employer.
Conclusion
Second, while participant contacts were obtained through the university database, some were obtained through snowball sampling which is a. Based on the findings of this study, several implications can be drawn for university authorities, employers, recent graduates and current students. Thus, universities should be aware of the existing requirements and pay attention not only to the transfer of theoretical knowledge, but also to the support of students in the development of skills.
One of the main reasons for the perceived shortcomings is the considerable distance between the academic environment and the realities of the workplace. Participants in the study, both graduates and employers, stated that the duration of internships should be extended to allow students to gain more work-related experience and interact closely with employers. Speech of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the leader of the nation, N.Nazarbayev "Strategy Kazakhstan-2030".
Address of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the leader of the nation, N. Nazarbayev "Strategy of Kazakhstan-2050": New political direction of the established country. An in-depth analysis of the labor market importance and outcomes of higher education systems: Analytical framework and report on countries increasing the effectiveness of the higher education system. One of the potential risks of this study is the discomfort that university graduates may feel when assessing their abilities after graduation.
Questions: If you have questions, concerns or complaints about this research, its procedures, risks and benefits, please contact the thesis supervisor of this student's work, Dilrabo Jonbekova at [email protected] or the author of the study Yevgeniya Serkova at [email protected]. According to the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan, a person under the age of 18 is considered a child. You will be asked about important skills for STEM university graduates' careers, evaluate how well the graduates' skills are.
In your opinion, how important is the role of the following actors in the development of students. P3 In your opinion, how important is the role of the following actors in the development of students.
Partnership between university and industry Students' role in developing students' skills Inner motivation to learn.