Furthermore, we appreciate the support, encouragement and understanding of our family members in our commitment to this Final Year Project. This attached research paper entitled "Current Experience, Stress and Conscientiousness as Predictors of Internet Addiction among University Students in Malaysia" prepared and submitted by Avinaash A/L Thiruselvam and Lim Shu Jing in partial fulfillment of the requirements for Bachelor of Social Science Psychology (Hons) Accepted. Internet addiction (IA) is identified as the technological dependence of frequent Internet use in relation to behavioral reactions associated with co-occurring disorders.
Internet addiction is also called problematic Internet use (PIU), computer addiction, Internet addiction, compulsive Internet use, and pathological Internet use. However, there are limited studies on the predictive effects of (a) flow experience; (b) stress; (c) attention to Internet addiction among students in Malaysia. Therefore, the purpose of the current study was to investigate the predictive effects of (a) flow experiences; (b) stress; (c) attention to Internet addiction among students in Malaysia.
In conclusion, the findings from this study provided an understanding of the predictors of Internet addiction among university students in the Malaysian context to develop a deeper understanding of the topic, which is essential to assist in the development of intervention programs. PIU Pathological Internet Use / Problematic Internet Use IOS-Qs Excessive Internet Use Screening Questionnaire (short form) FSS Flow Short Scale.
Introduction
Within studies of adolescent experiences of streaming and Internet addiction, there is little research investigating these factors (Yang et al., 2014). A study conducted by Liu et al. 2020) stated that mindfulness is an important factor in determining problematic Internet use. Evidence for a relationship between mindfulness and problematic internet use is sparse (Calvete et al., 2017).
Perceived stress is an important issue in basic and clinical neuroscience research (McEwen et al., 2015). University students are more susceptible to Internet addiction due to using the Internet for academic purposes on a daily basis (Lee et al., 2019), where continued use causes a decline in. Studies related to the variables of flow experience and Internet addiction have been implemented in South Africa (Thatcher et al., 2008), America (Kamssu & Siekpe, 2012), Taiwan (Yang & Wu, 2017).
Moreover, in the context of stress, the outcomes were specifically investigated in medical students (Radeef & Faisal, 2018), high school students (Gholamian et al., 2017). Flow Short Scale (FSS) by Rheinberg et al. 2003) can be known as a tool to examine the nine components of flow experience.
Literature Review
One of the influencing factors of stress that has been studied is the psychological field. While the Internet creates the development of positive feelings in engaging in Internet activities (eg, gaming and gambling). In terms of the cognitive-behavioral model of PIU proposed by the present study, it has shown the association of mood regulation drives in the addict's use of the Internet to relieve their stress.
There is research that has studied internet addiction and stress in the Malaysian context. They have suggested that stress may be one of the predictors of internet addiction (Radeef & Faisal, 2018). The features of the flow model have been implemented as conditions for the ultimate flow experience. The variables that will be examined in the current study are flow experience, stress, mindfulness and internet addiction.
Therefore, the correlation between stress and Internet addiction is expected to be positive in the current study. The key component specified in the cognitive-behavioral model of PIU is the lack of self-regulation.
Methodology
This sampling method was appropriate to use in this study as there were several criteria to be met, it gave the researchers the convenience of recruiting people by determining their qualifications. Moreover, previous studies used purposive sampling as the sampling method that was in the field of Internet addiction. The confidence interval and error probability rate are set at 0.95 and 0.5, respectively, due to Sharma et al. 2020) after stating that it is one of the sufficient significance levels.
The calculated sample size was 102 (refer to Appendix B, p. 97), with an effect size (mean) of 0.18, a power level of 0.95, a Type I error probability of 0.5, and three predictors in the present study. Students who were still in the foundation program, bachelor program, master program, and doctoral program while continuing their studies in private or state universities were included in the recruitment of the present study. Cronbach's alpha was 0.80 in the study conducted by Park et al. 2020), based on the first rule is considered good reliability.
While in this study the internal reliability of the pilot test was 0.83 and the actual study was 0.80, it was cited as high reliability. Nevertheless, this study reported .84 as the internal reliability of the pilot test and .85 as the reliability of the actual study. The Perceived Stress Scale (PSS-10) developed by Cohen and Williamson (1988) was used to measure the level of stress through feelings and thoughts during the past month.
The total score lies between 0 and 40 as higher scores indicate higher perceived stress in the past month. A pilot study was implemented before the actual study started, while it is to test the feasibility of the research that was done. The researchers of the current study invited 30 of the participants to become involved in this research and a.
There is a potential multivariate outlier found in the present study, while it did not violate any measures of indicators (Cook's Distance, Mahalanobis Distance and Centred-Leverage Value). It is the non-correlation of predicted variables in the research to observe variety of research fields (Berry, 1993). The residuals were not detected as if the points in the scatter plot were evenly distributed around the diagonal line with a fairly constant variance (Osborne & Waters, 2002).
Results
The histogram, Q-Q plot, skewness value and kurtosis value of each variable were tested and showed a good normality assumption, however, the value of Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for Internet addiction and awareness did not rank in the acceptable standard. All the examined variables were concluded to meet the assumptions of normality because four of the five indicators of two variables (Internet addiction and . consciousness), and five indicators of the experience of flow and stress showed no violations. The present study has implicated Cook's distance, Mahalanobis Distance and Centered Bark's range with standard deviations of both as analysis tools to investigate multivariate outliers.
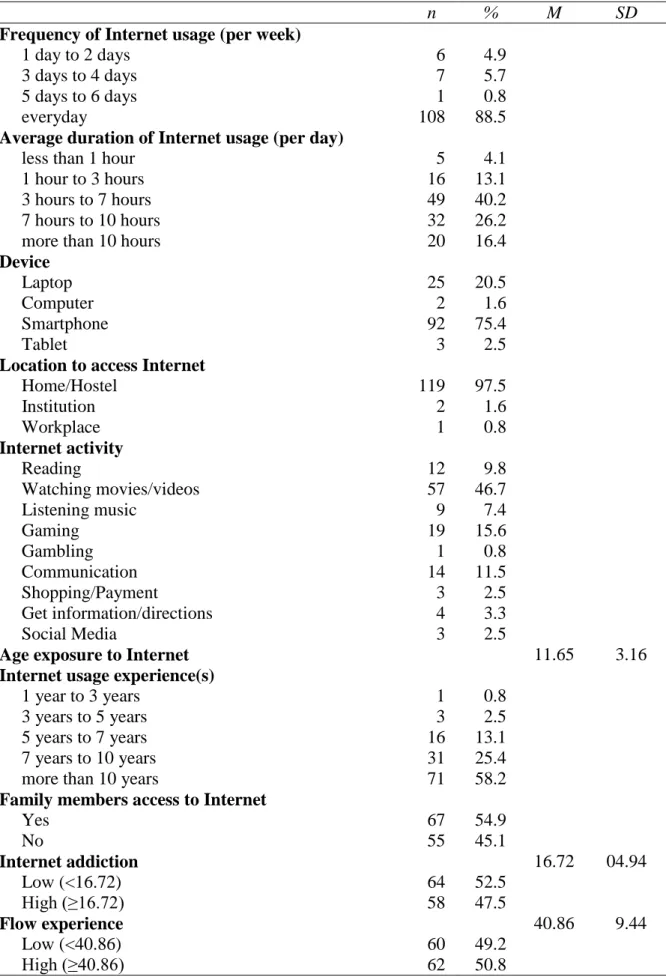
While the calculated range for centered leverage value is 0.0656 using the formula from Hoaglin and Welsch (1978), the case has been within specification. Therefore, Case 134 was not deleted as it has not violated the benchmark of Cook's Distance, Mahalanobis Distance and Centred-Leverage Value. The majority of the students were from Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (n=70) and the remaining were from other universities in Malaysia.
The frequency of the majority's internet use for recreational purposes in a week was everyday (n=108) with 88.5%. Based on the data shown, the average duration of Internet use for majorities was three hours to seven hours (n=49) with 40.2%. Heriot-watt University Malaysia 001 00.8 International Medical University 001 00.8 International University of Malaysia-Wales 001 00.8 INTI International University 002 01.6.
According to the research done by Berry (1993), the set of independences as the results of investigated variables were totally independent of each other. The data collected in the present study met the assumptions as the independent institutions existed. Durbin-Watson test was applied to examine the residual assumption in current study, while the criterion was between 1 to 3 (Champion et al., 1998).
Based on Figure 4.1, the scatter plot showed that the residuals were largely centralized on the baseline and the residuals were randomly scattered around it. Multiple regression analysis applied in the present study to investigate the significance of predictors of flow experience, stress and mindfulness towards the internet addiction. In conclusion, Table 4.9 led to the H3 hypothesis being supported, but the H1 and H2 hypotheses were not supported by the current study.
Discussion
Mindfulness also develops a self-control effect on Internet addiction and is therefore able to lower the risk of the addiction (Song & Park, 2019). In the current study, flow experience, stress, and mindfulness were used as predictors of Internet addiction. The current study implemented the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use (PIU) by Davis (2001) to examine the predictive effects of stress and attention on Internet addiction.
However, the non-significant findings of stress and Internet addiction imply that the Cognitive-Behavioral Model of PIU is not applicable to stress and Internet addiction among university students in Malaysia. In conclusion, the current study supports the third hypothesis which was that conscientiousness negatively predicts Internet addiction among university students in Malaysia. Loneliness, self-esteem and life satisfaction as predictors of Internet addiction: A cross-sectional study among Turkish university students.
Prevalence and factors associated with Internet addiction among medical students - A cross-sectional study in Malaysia. Development of the Internet Addiction Scale based on the criteria for Internet Gaming Disorder proposed in DSM-5. 2021) Perceived stress and Internet addiction among Chinese university students: Mediating effect of procrastination and moderating effect of flow.
Excessive Internet use: the role of personality, loneliness, and social support networks in Internet addiction. Ecological predictors and trajectories of Internet addiction from childhood through adolescence: A nationally representative longitudinal study. A study on internet addiction and its relation to psychopathology and self-esteem among college students.
Prevalence of internet addiction and its association with depression, anxiety and stress among medical students in Malaysia. Internet addiction and mental well-being among secondary school students in a Malaysian district: A cross-sectional survey. Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder,” in 104th Annual Meeting of the American Psychological Association.
Prevalence and associated factors of Internet addiction among university students in Ethiopia: A community university-based cross-sectional study.
