The current study fills the gap in knowledge and practice by assessing the potentials of security technology, factors influencing its adoption, and strategies to increase the level of adoption. The findings revealed that the main potentials of safety technologies are: improving hazard identification, strengthening safety planning and increasing safety inspection.
General Introduction
Background
In Malaysia, health and safety issues in the construction industry are regulated by the Occupational Safety and Health Act (1994). Health and safety are also core values in improving the well-being of every party involved in the construction industry.
Problem Statement
Numerous concerted efforts have been made to advocate and encourage these construction technologies and the importance of these technologies has been emphasized in many research studies (Skibniewski and Zavadskas, 2013; Li, et al., 2017). Moreover, despite various construction safety technologies that have been tested and proven effective for safety management, their uses are still not much predominant in actual construction projects (Nnaji, et al., 2019).
Research Aim
Therefore, research on these safety technologies, predictors and solutions to encourage the adoption of technology is extremely necessary to curb the unwanted work-related injuries and deaths in the construction industry. It also enables the construction stakeholders to make informed decisions in adopting their preferred safety technologies, resulting in a safer work environment.
Research Objectives
Research Questions
Research Scope
A questionnaire regarding safety technologies was prepared and distributed to construction practitioners, especially developers, consultants and contractors.
Research Significance and Justification
Report Outline
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature Review
- Chapter 3: Methodology and Work Plan
- Chapter 4: Results and Discussion
- Chapter 5: Conclusions and Recommendations
This chapter also evaluates the results generated with the aim and objective of the research to achieve the ultimate goal of the research. The main purpose of this chapter is to conclude the general findings of the research.
Summary
Moreover, the research limitations and suggestion for future research are also unfolded in this chapter to provide insights for other researchers to study on the similar research area in the future.
Introduction
Construction Safety
Construction Safety Technology and Technology Adoption Numerous previous studies advocated that construction safety can be enhanced
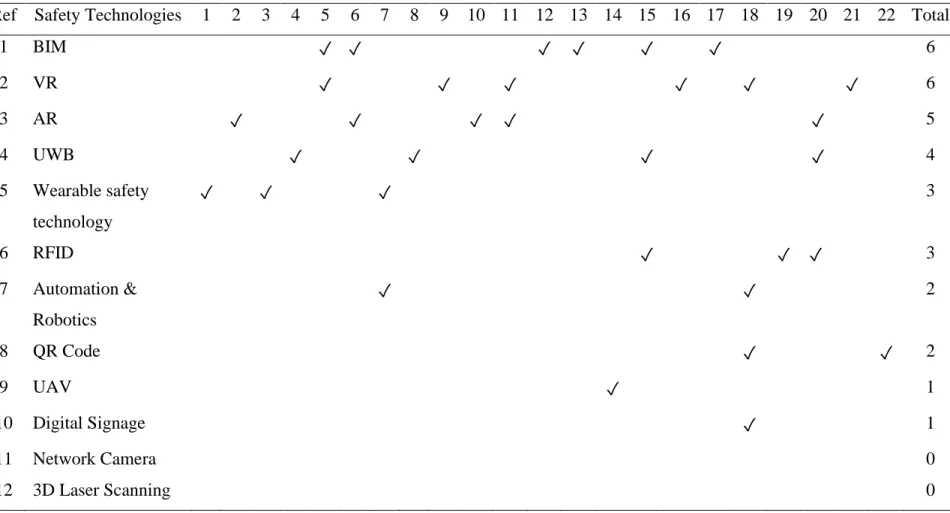
Types of Safety Technology in Construction Projects .1 Building Information Modelling (BIM)
- Wearable safety technologies
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)
- Automation and Robotics
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Ultra-wideband (UWB)
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
- Quick Response Codes (QR codes)
- Network Camera
- Digital Signage
Therefore, it is worth emphasizing that enriching workers' hazard recognition skills through a VR training scheme can be valuable (Karakhan, et al., 2019). In a previous study by Lorenzo, et al. 2014), the QR code is placed on worker badges or safety helmets.
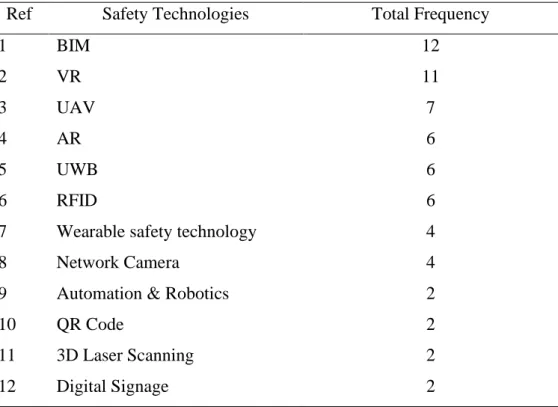
Summary of types of safety technologies in construction projects The following Table 2.1 and 2.2 present the summary of the application and
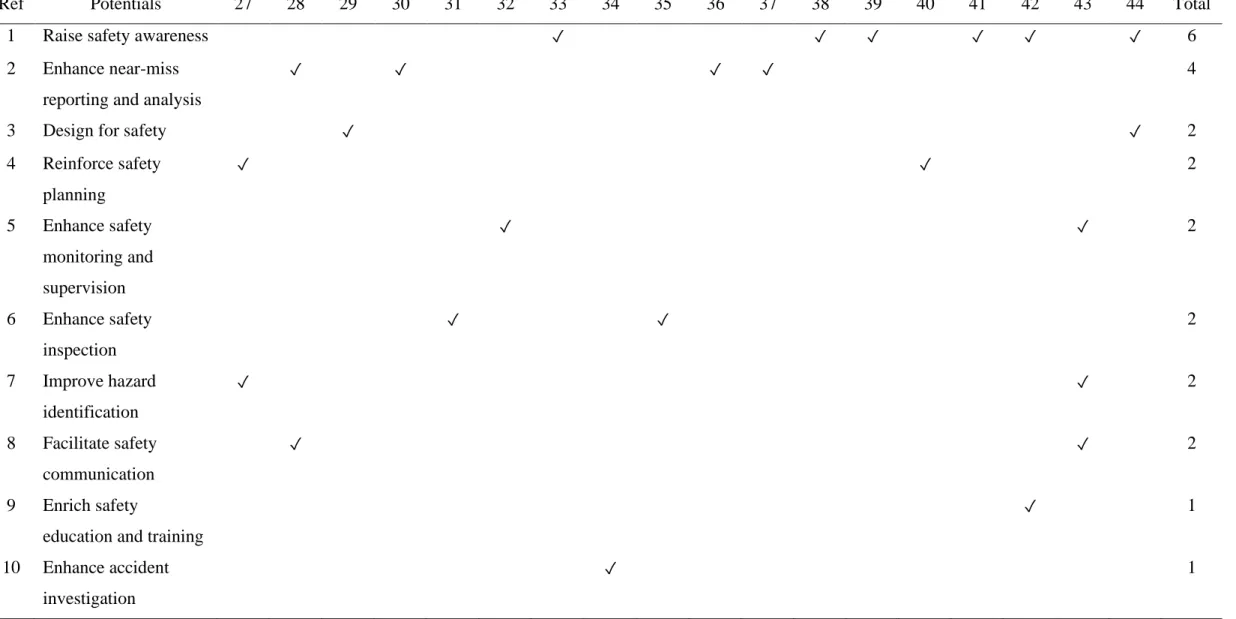
Potentials of safety technology adoption in construction projects .1 Design for safety
- Reinforce safety planning
- Enhance safety monitoring and supervision
- Enhance safety inspection
- Improve hazard identification
- Enrich safety education and training
- Raise safety awareness
- Enhance near-miss reporting and analysis
- Enhance accident investigation
- Facilitate safety communication
However, the traditional communication approach used in most construction projects makes the safety inspection process ineffective. Safety awareness of construction workers is directly related to safety (Yu, et al., 2014).
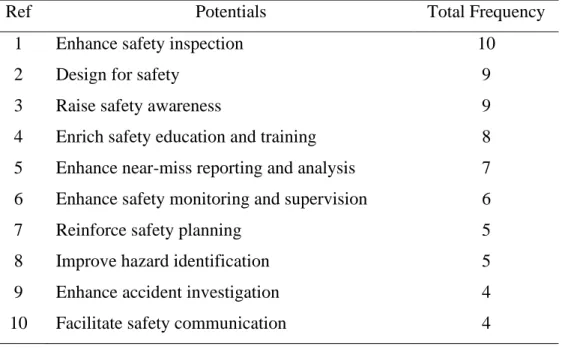
Summary of potentials of safety technologies in construction projects
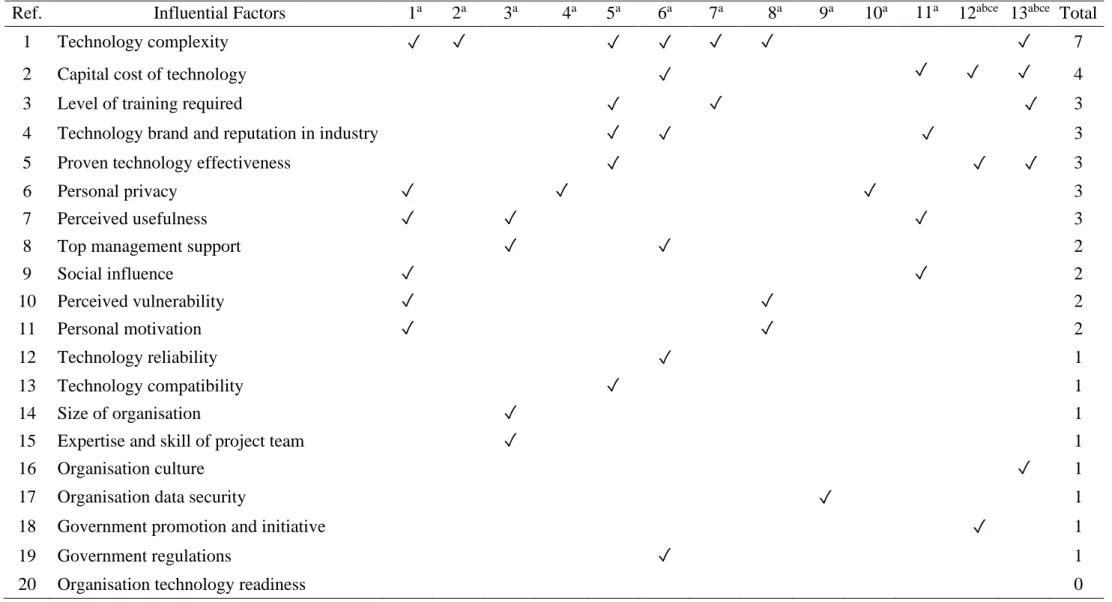
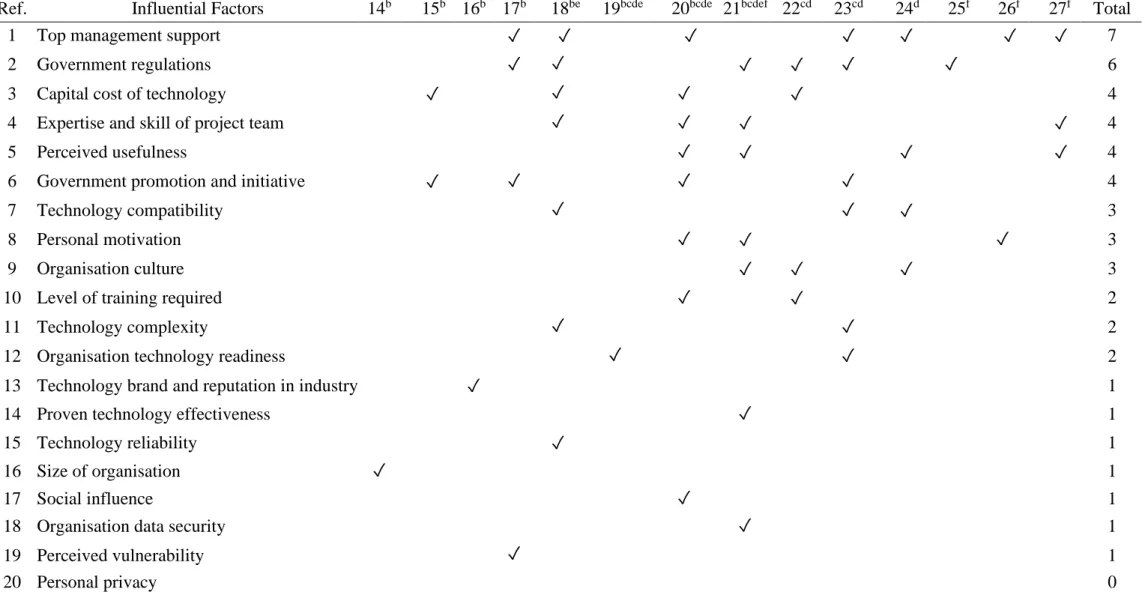
Influential factors of safety technology adoption in construction projects
- Capital cost of technology
- Level of training required
- Technology brand and reputation in the industry
- Proven technology effectiveness
- Technology reliability
- Technology compatibility
- Technology complexity
- Size of organisation
- Top management support
- Expertise and skill of project team
- Organisation culture
- Social influence
- Organisation technology readiness
- Organisation data security
- Personal privacy
- Perceived vulnerability
- Perceived usefulness
- Personal motivation
- Government promotion and initiative
- Government regulations
In addition, they can establish a solid practical foundation for the implementation of new technology (Hong et al., 2018). It includes a series of triggers that attract them to adopt a new technology (Hong et al., 2018).
Summary of influential factors of safety technology adoption in construction projects
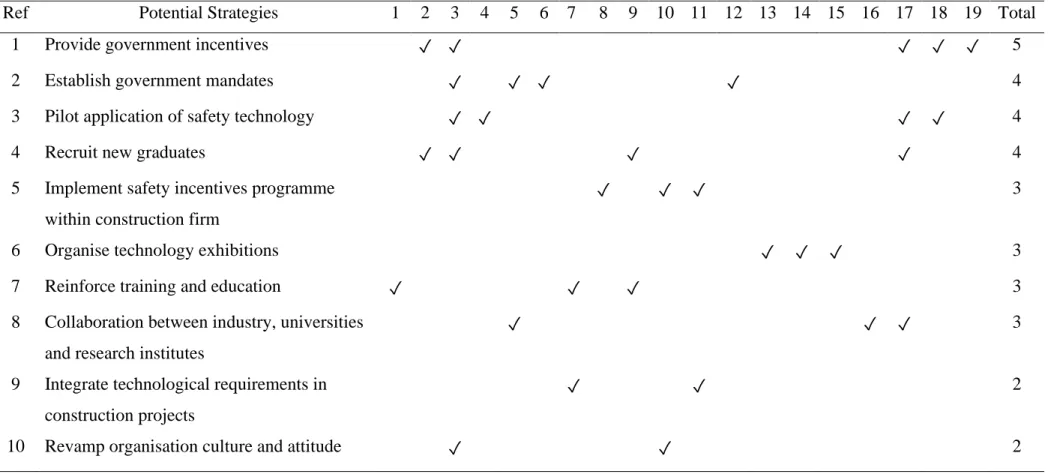
Potential strategies to enhance safety technology adoption in construction projects
- Integrate technological requirements in construction projects Nnaji and Karakhan (2020) advocated the view that certain technological
- Implement safety incentives programme within the construction firm
- Pilot application of safety technology
- Organise technology exhibitions
- Provide government incentives
- Establish government mandates
- Revamp organisation culture and attitude
- Reinforce training and education
- Recruit new graduates
- Collaboration between industry, universities and research institutes
It has also been studied that most customers in the Chinese construction industry acknowledged that government policies are extremely valuable for the adoption of technology such as BIM (Yuan, Yang and Xue, 2019). Due to the exposure of graduates to university courses based on the latest technologies in the construction industry, graduates are seen as valuable in the perspectives of innovative companies. More technology-related courses should be covered in universities to immerse graduates in technical knowledge and expertise that can contribute to the construction industry (Ahuja, et al., 2018).
Summary of the potential strategies to enhance safety technology adoption in construction projects
Introduction
Quantitative research
Research design
Research instrument
Sampling design
Sampling method
Target respondents
Sampling size
Data collection
Questionnaire survey design
Respondents were then asked to rate possible strategies to increase adoption of security technology (10 items) in Section D. The length of the questionnaire was limited to 15 minutes to prevent respondents from feeling overwhelmed and to encourage higher quality responses. The fundamental reasons for the adoption of the five-point Likert scale were its ability to facilitate the respondents' expression of opinions and generate unequivocal findings (Darko, et al., 2018).
Pilot survey
Data analysis
- Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Test
- One-sample T-tests
- Mean ranking
- Kruskal-Wallis Test
- Spearman’s Correlation Test
- Factor Analysis
As mentioned above, the questions in Section B, Section C and Section D of the questionnaire were rated using a five-point Likert scale. In this case, Cronbach's alpha reliability test was used to assess the reliability level of the five-point Likert scale measurement. This test does not require normal distribution and homogeneity of data (Gunduz and Ahsan, 2018), which is the main basis for adopting this technique in this study.
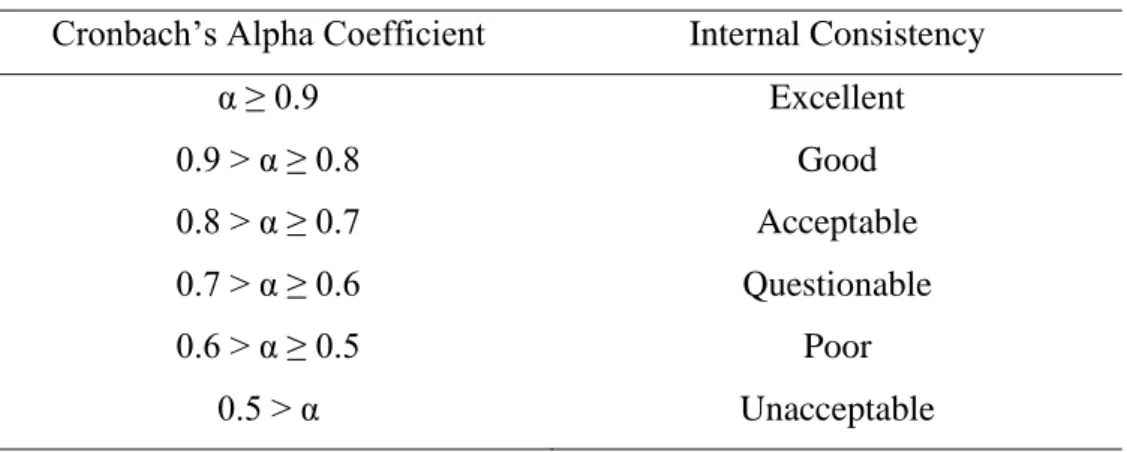
Summary
As specified by Yap and Lee (2019), this test is used to ensure that the population correlation matrix is not an identity matrix. This is because the existence of the identity matrix will make factor analysis meaningless (Zhang, et al., 2018).
Introduction
Pilot Study
Response Rate
Profile of Respondents
Reliability of Results
Expected effectiveness of safety technologies in construction projects
One sample T-test
Mean Ranking
Based on its visualization, coordination and modularization, BIM plays a favorable role in construction safety (Wen, et al., 2021). According to Tang, et al. 2021), BIM offers opportunities for the practice of design for safety concept due to its powerful data integration and visual modeling capabilities. For example, Zhang et al. 2015) incorporated safety rules into BIM to identify and prevent fall hazards.
Kruskal-Wallis Test
For example, robots can be used to perform high-risk tasks such as welding, bricklaying, excavator control, building interior finishing, infrastructure inspection, and so on (Kim, et al., 2020). The generally positive and consistent views of the developers and consultants on the expected effectiveness of BIM could suggest that BIM will be increasingly adopted in the Malaysian construction industry in the coming years. In addition, metals and concrete in construction projects can influence the RFID information exchange process (Valero, Adán and Cerrada, 2015).
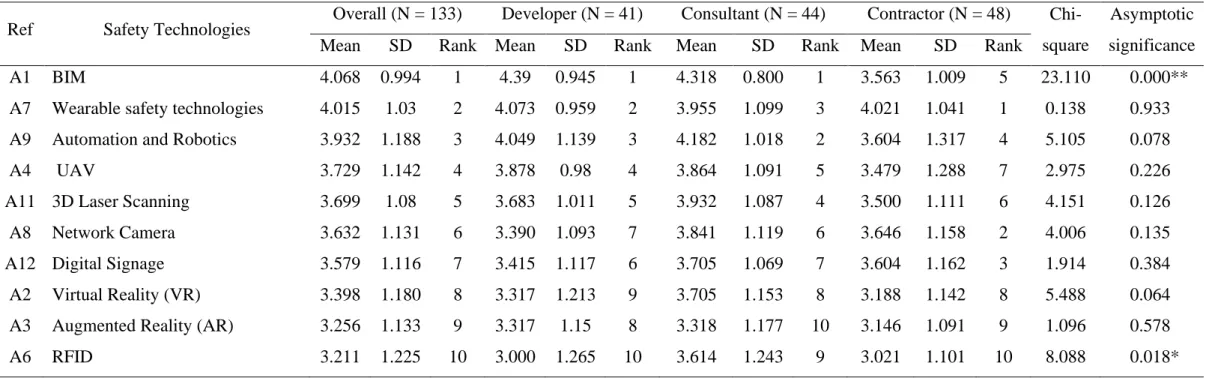
Mean Ranking
Security planning includes activities such as risk identification, risk assessment and risk control (Zolfagharian, et al., 2014). These activities determine the high-risk tasks that require close monitoring and determine the checklist items for safety inspections (Zhang, et al., 2017). In addition, traditional security planning is highly error-prone and labor-intensive (Kim, Cho and Zhang, 2016) as it mostly relies on tacit knowledge, rules, organizational security policies and 2D drawings (Choe and Leite, 2017; Zhang , et al., 2015 ).
Kruskal-Wallis Test
To address these error-prone inspection problems, some enabling safety technologies such as BIM, UAS and AR have leading potentials in the development of a proactive and automatic inspection system to improve construction safety (Martinez, et al., 2021; Park, et al., 2013). For example, a case study conducted by Melo, et al. 2017) in Brazil found that UAV allows for good visualization of working conditions and offers useful data on compliance with safety regulations on site. In this regard, it is essential for developers to promote the concept of design for safety by adopting safety technologies for consultants and contractors, as previous studies have argued that developers are the most influential group to drive design for safety practices in construction. projects (Lingard, et al., 2009; Votano and Sunindijo, 2014).
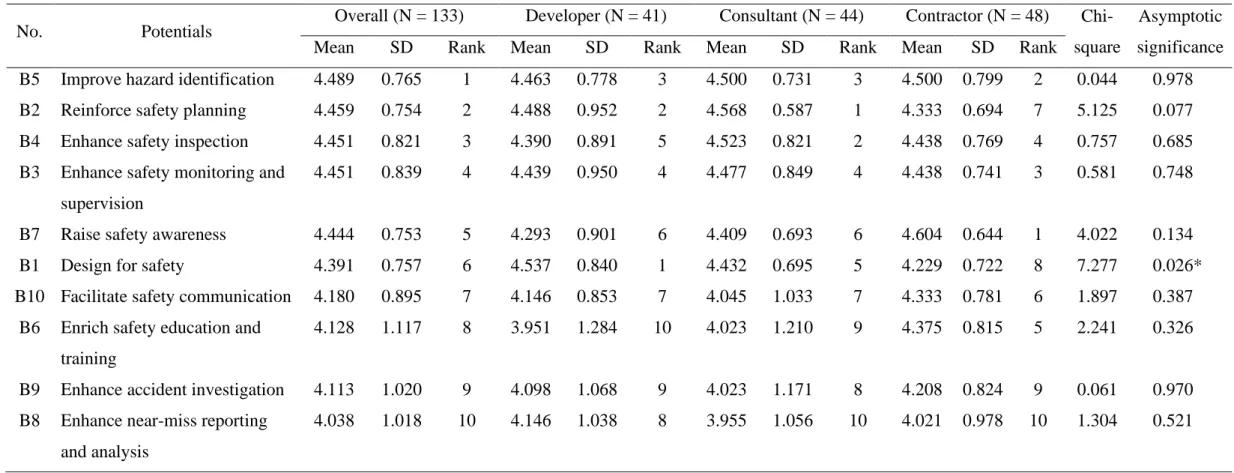
Mean Ranking
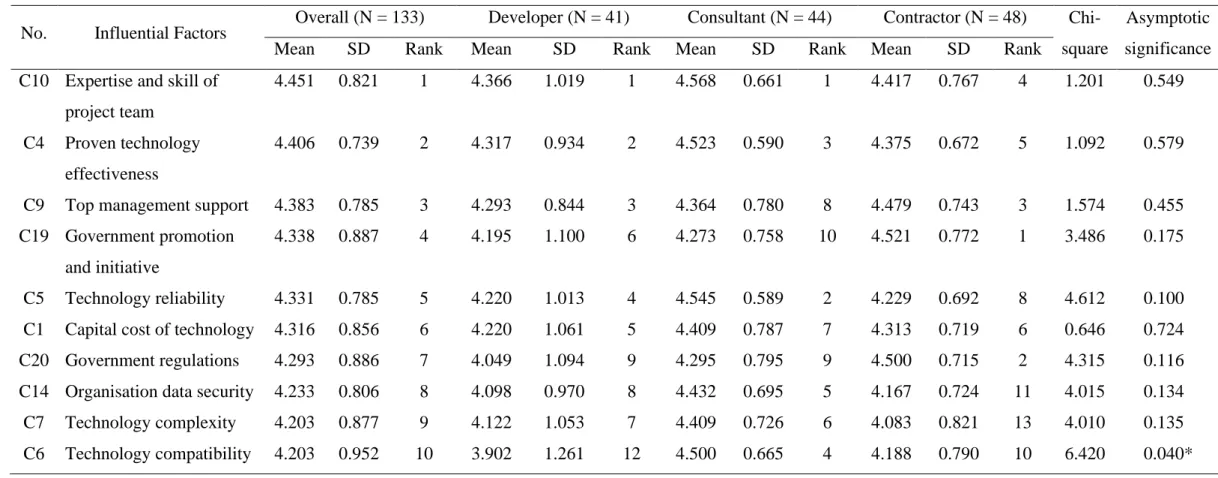
This finding parallels a recent study in the US, which found that proven technology effectiveness was seen as the second most influential predictor of security technology adoption (Nnaji, et al., 2019). It should be pointed out that a technology with unproven effectiveness simply means that the technology is immature (Delgado, et al., 2019). Essentially, this means that top management plays a key role in this aspect (Zheng, et al., 2017).
Kruskal-Wallis Test
It is suspected that a lower ranking given by the developers and consultants is probably due to their less use of these devices, so they may not be as sensitive as the contractors to this factor. From this perspective, if the contractors see that the safety technology is beneficial to mitigate these safety risks and improve the safety performance of the construction projects, they may be motivated to adopt the technology. In short, the contractors' roles, their work environment and their perceptions about the safety technologies may explain their higher ranking.
Potential strategies to raise safety technology adoption in construction projects
One sample T-test
Mean Ranking
In light of this, the Malaysian government should therefore actively support the construction practitioners in the innovation and implementation of technology in their projects by providing financial assistance. A survey conducted by CIDB (2017) in Malaysia reported that a high percentage of respondents agreed with the government's initiative to mandate the use of BIM in the construction industry. Such an initiative shows that the Malaysian government is committed to implementing BIM in the industry within a few years.
Kruskal-Wallis Test
In the construction industry, there is a large pool of specialist talent in the field of consultants, including architects, engineers, quantifiers, construction manager, project manager, building inspector, health and safety consultant, contract manager and many more professionals. In the UK, Cheng, Proverbs and Oduoza (2006) conducted a study to assess the level of satisfaction of construction clients based on the performance of the consultants and found that the clients believed that technical rigor and innovation in working methods are important performance characteristics for the advisors. These institutes are suppliers of knowledge and offer the consultants the latest solutions in the industry and the market.
Spearman’s Correlation Test
Factor Analysis
Discussion of factor analysis results
- Factor 2: Supporting technological attributes
- Factor 3: Personal perception and performance expectancy
- Factor 4: Government support
Essentially, successful implementation of technology requires significant attention and commitment from senior management (Zakaria, et al., 2018). Nevertheless, this study contradicts a Chinese study that denied the effect of management support on technology adoption (Ding, et al., 2015). For example, Ding, et al.'s (2015) China study suggested that the government could launch some demonstration projects to show the economic benefits and efficiency gained from the use of security technology.
Summary
In addition to financial support, knowledge support by the government is also essential to spread adoption. There is no doubt that government support can have a major impact on the success of technology adoption and can hinder or encourage technological change. On the other hand, the Kruskal-Wallis test revealed that there were significant differences in perceptions between the respondent groups about the expected effectiveness and capabilities of security technologies, influential factors of technology adoption, and possible strategies to increase the technology adoption rate.
Introduction
Conclusion
In the overall context, the three most effective strategies are strengthening training and education, providing government incentives and establishing government mandates, which indicate the essential roles that management and government play. Nevertheless, the analysis revealed that there were significant differences in the perceptions of the respondent groups about. Overall, the current study represents the first empirical effort focused on adding to the understanding of the influential factors influencing the adoption of safety technologies in the Malaysian construction industry.
Research implications
By conducting a survey on the adoption of safety technologies, it is expected that the implementation of emerging technologies at different stages of the construction life cycle will escalate. Accordingly, construction safety can be improved, thereby bridging the gap between the construction sector and other industries in terms of safety. Accordingly, enhanced technology adoption would benefit the construction industry by improving workplace safety, mitigating accidents and raising safety awareness among construction actors.
Research limitations
This study revealed that organizational factors are significant factors in making a decision on whether to adopt a security technology, followed by technological and governmental factors. Furthermore, the findings are also valuable to current and future technology developers and manufacturers as this study allows them to better understand the areas that require improvement and improve the approach to be taken to meet the demands of the construction industry. In addition, it must be cautioned that the scope of this study was limited to construction practitioners in the Malaysian construction industry, limiting the generalizability of the findings.
Recommendations for future work
This allows practitioners to make a more informed decision about the implementation of safety technologies in construction projects. I am currently conducting a study for my graduation project entitled "Research into factors influencing the adoption of technology in construction safety management". In your opinion, to what extent do you agree with the possibilities of safety technologies in construction projects.
In your opinion, what is your level of agreement on the following factors that influence the adoption of safety technology in construction projects. In your opinion, how effective are the following strategies in improving the adoption of safety technologies in construction projects.