However, it has been suggested that pre-service teachers of English as a Foreign Language (EFL) around the world possess an insufficient level of Language Assessment Literacy (LAL). This study contributes to LAL conceptualization by involving the neglected stakeholders, pre-service EFL teachers and enriches the application of narrative research in LAL field.
Background of the Research
Unfortunately, however, pre-service English as a foreign language (EFL) teachers worldwide seem to have an insufficient level of LAL (Giraldo & Murcia, 2019; Hatipoğlu, 2015; Kavaklı & Arslan, 2019). Moreover, the voice of pre-service EFL teachers in China is still lacking (Gan & Jiang, 2020).
Research Context
Introduction of Pre-service Education in China
China's pre-service teacher education has been open, with normal universities acting as the main body and other comprehensive universities as participants (Ding et al., 2013; Zeng, 2016). Although they are the standards for in-service teachers, these standards still have a reference value for pre-service teacher education programs to respond to criteria formulated in the standards by regulating the programs accordingly.
English Assessment in Primary and Middle Schools in China
Problem Statement
Xu and Brown's (2016) model as a framework to explore the trajectory of LAL development among pre-service EFL teachers. Additionally, exploring pre-service EFL teachers' LAL development profiles enables comparison of LAL development profiles among different stakeholders.
Research Objectives
Thus, methodologically, narrative inquiry fits well with the research objectives of this study. Therefore, to bridge the research gap, the present study adopts narrative inquiry as the research method to explore the evolution of LAL among pre-service EFL teachers in China.
Research Questions
Background of the Researcher
The previous training experience enables me to become familiar with EFL teacher training in China. This educational background gives me personal experience of pre-service EFL teacher training in different types of normal universities in China.
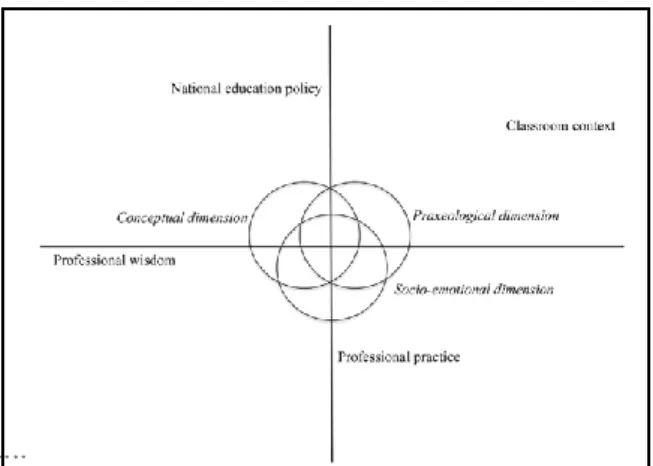
Theoretical Framework
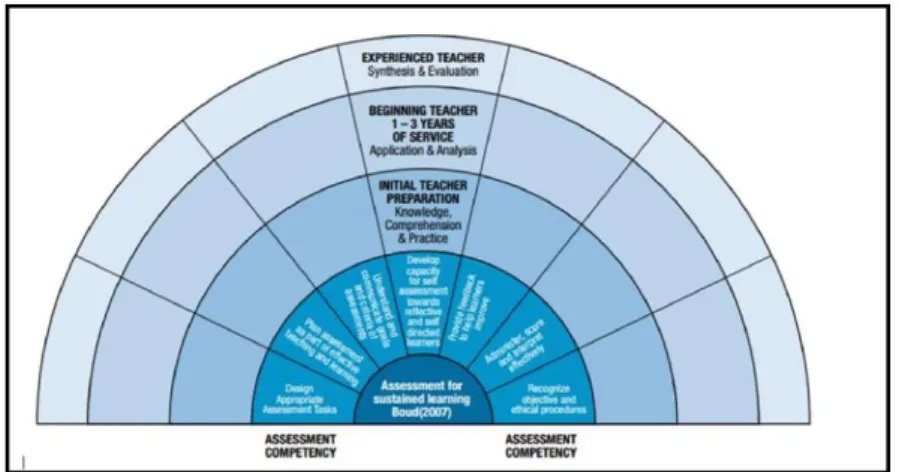
Second, this hierarchy is characterized by encompassing all phases of teacher education (Y. Xu & Brown, 2016). It could thus be applied to the analysis of the AL of student teachers during initial teacher education.
Significance of the Study
This study therefore expands the scope by focusing on pre-service EFL teachers' LAL in China. Such understandings may better serve teacher educators to help pre-service EFL teachers develop LAL.
Definition of Terms
Rewinding assessments - knowledge of the potential impact of assessments, whether beneficial or detrimental, on teaching and learning. Pedagogical content knowledge – knowledge of how to teach curriculum-based content to learners and the competence to support learning.
Layout of the Thesis
Following this meaning, a number of definitions and frameworks for the concept are analyzed to clarify their meanings. The informative contributions to the existing body of LAL literature and the limitations of the study are also analyzed.
Summary
It also presents the implications for stakeholders such as EFL student teachers, teacher educators and teacher training colleges to further improve LAL.
Introduction
The Assessment Paradigm Shift
In addition, evidence collected by teachers is sometimes used within the classroom to determine a student's learning assessment or final unit test (Stiggnis et al., 2004). AfL intended to improve student learning is different from AoL designed to provide accountability or ranking (Black et al., 2004).
Rationales of Teachers’ AL
Mandated Demand of National Policy
Excellent teachers must also help students experience the facilitating function of assessment for learning and provide suggestions for improving the learning accessible to students. Through the listing of different requirements for teachers at different career stages, what can be clearly seen is the increasing complexity of LAL requirements that progress from mastery of awareness and assessment knowledge for beginning teachers, through achievement.
Professional Requirement of Teachers
Assessing EFL learners' performance is one of the most important roles of EFL instructors in the language classroom (Watmani et al., 2020). In summary, as AL is central to teacher professional development, AL appears to be a necessary commodity for teachers of all subjects in a variety of contexts (Bracey, 2000; Kelly et al., 2020; Newfields, 2006; Weigle, 2007).
The Academic Well-being of Learners
It is imperative that teachers acquire an adequate level of AL to participate in their professional activities (Fan et al., 2011; Stoynoff, 2012; Zhang & Yan, 2018) and language teachers are no exception. Therefore, AL is critical in the process of both teaching and learning (Volante & Melahn, 2005), serving first as a dual tool for the professionalism of the teachers, and then for the improvement of student learning in the classroom. second step (Amirian et al. al., 2016).
The Guarantee of Successful Curriculum Reform
The growing expectation of educators' AL will continue to be greater given the ubiquity of tests and daily assessments (Bracey, 2000) and ongoing education reforms (Kahl et al., 2013). The above discussion of AL and LAL has continued without formally defining AL and LAL.
Definitions of AL and LAL
For example, Paterno (2001) defined AL as “the possession of knowledge of the basics of sound assessment practice, including terminology, the development and use of assessment methodologies and techniques, familiarity with quality standards in assessment” (p. 2). . It was reconceptualized by Willis et al. 2013) as "a dynamic, context-dependent social practice that involves teachers in articulating and negotiating classroom and cultural knowledge with each other and with learners, in the initiation, development, and practice of assessment to achieve student learning goals" (p. 242).
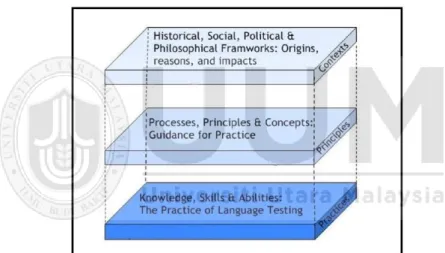
Frameworks of AL and LAL
- Competence Lists
- Three-component Models
- Scaled Models
- Negotiation Models
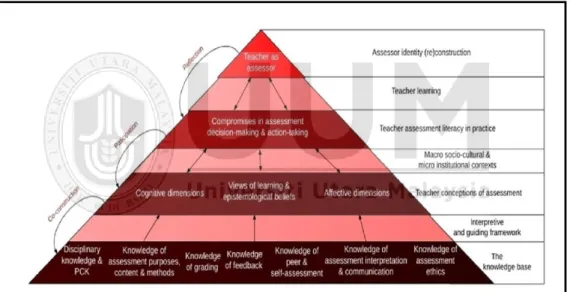
To be specific, the three components were the purpose or rationale for the assessment ("why"), the theoretical basis for the assessment ("what"), and the conduct of the assessment process ("how"). As a necessary but insufficient condition, the underlying knowledge base was interpreted and mediated by the teacher's conception of assessment.
Empirical Studies on AL and LAL among In-service Teachers
AL and LAL Proficiency Level
- AL Proficiency Level
- LAL Proficiency Level
Focusing solely on classroom AL among primary teachers, Zhao (2020) used a classroom AL questionnaire developed by DeLuca et al. of 1,032 primary teachers in mainland China. In general, they did not feel confident in developing and designing assessment activities (Berry et al., 2019; Tsagari. & Vogt, 2017).
Factors Mediating AL and LAL Evolvement
- Contextual Factors
- Experiential Factors
National assessment policies and curriculum standards were powerful drivers of teachers' use of assessment data (Abrams et al., 2016). EFL teachers' language assessment practices were deeply rooted in what they had experienced in the classroom in the past (Berry et al., 2017; Newfields, 2007).
Empirical Studies on AL and LAL among Pre-service Teachers
AL and LAL Proficiency level
Most pre-service teachers usually associated assessment with traditional summative objectives (AoL), although only a few manifested AfL concepts (Smith et al., 2014; Volante & Fazio, 2007). Preservice teachers were indicated to be less confident in handling the assessment questions in the later teaching career (Volante & Fazio, 2007).
Factors Mediating AL and LAL Evolvement
Active and ongoing participation in peer assessment practices has helped preservice teachers become more literate evaluators (Grainger & Adie, 2014). A challenging situation was also what faced EFL teacher education in its initial phase.
The Development Trajectory of AL and LAL
To summarize, various contextual and experiential factors that mediate the development of AL or LAL among pre-service teachers have been found in the existing literature. In addition, pre-service teachers appeared to feel increasingly confident in understanding a wide range of assessment methods.
Summary
To summarize, much has been done on the topic of AL and LAL in the aforementioned literature, but what remains unclear is EFL teachers' conceptualization of LAL, their self-assessed LAL proficiency level, their LAL development trajectory, and the interplay between the mediating factors and LAL development.
Introduction
Research Design
In addition, narrative inquiry is therapeutic in nature and beneficial to storytellers who have the opportunity to express their stories (Murray, 2018). Given that the research objective of the current study is to explore the inner world of pre-service EFL teachers in terms of LAL conceptualization, LAL knowledge level, LAL development trajectory, and interaction between mediating factors and LAL, narrative inquiry is appropriate for understanding human complexity, especially in cases, when the influencing variables cannot be controlled (Josselson, 2010).
Research Settings
Background Information of X Normal University
The university covers an area of more than 680,000 square meters and is home to more than 16,000 students. Orientation to university management is the establishment of a university in an applied way, which includes teacher training, with multiple disciplines and levels to serve the economic development of society.
Background Information of Pre-service EFL Teacher Education Programme
Before starting teaching in field schools, all student teachers are required to complete the intensive two-week teaching training course offered by the university to strengthen their teaching skills under the guidance of the mentor. The last type of courses are innovation and entrepreneurship courses, which require student teachers.
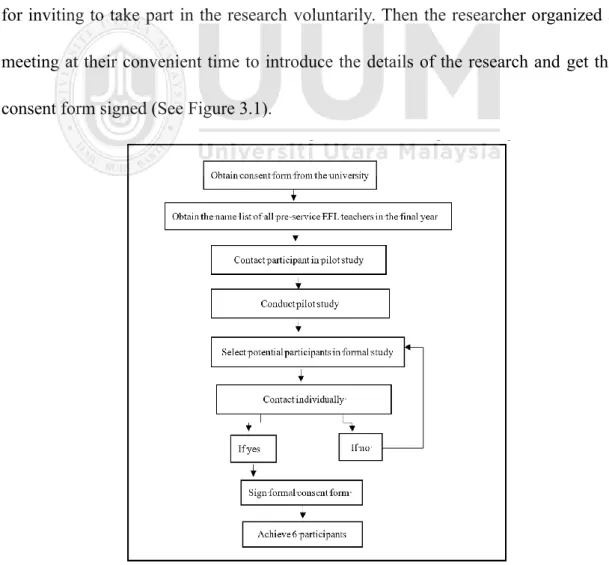
Participants’ Selection
To be specific, one participant in the pilot study and six participants in the formal study were selected. They were final-year pre-service EFL teachers from X Normal University in the western region of China.
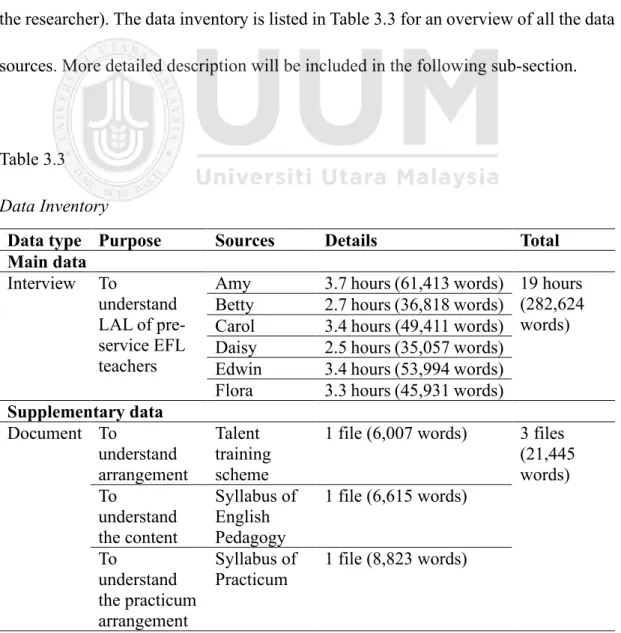
Data Collection
- Semi-structured Interview
- Development of the Interview Protocol
- Refinement of the Interview Protocol
- Implementation of the Interview Protocol
- Documents
- Artifacts
- Journals
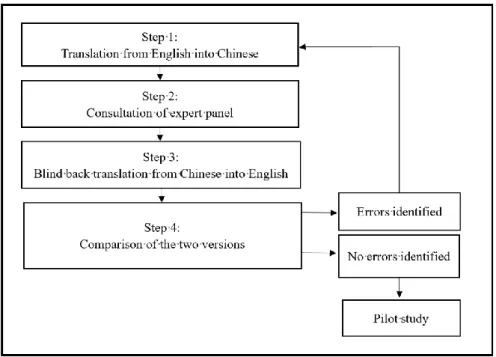
Fontana and Frey (2008) state that the interview is one of the powerful tools for understanding people. If no errors were found, the translation of the interview protocol from English to Chinese was complete.
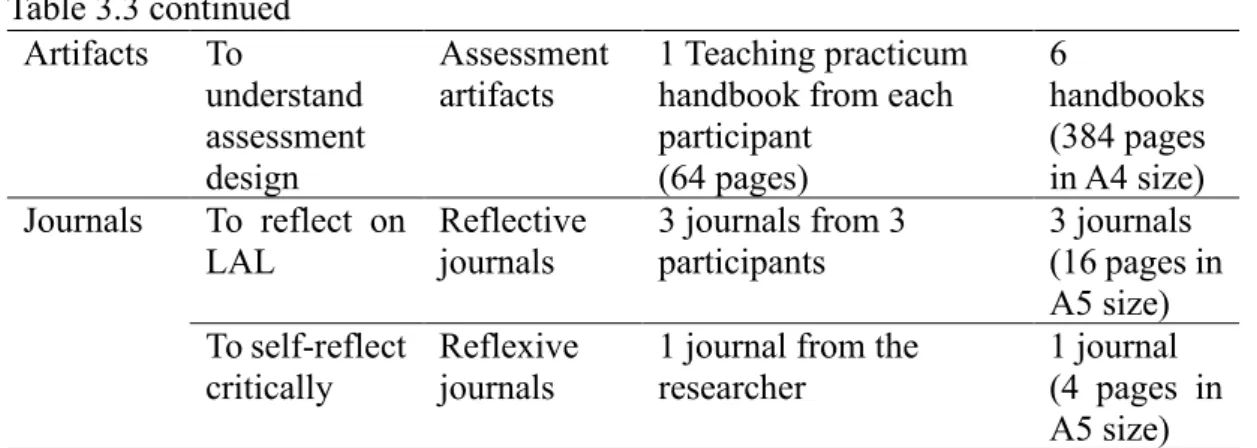
Research Procedures
Following the suggestions mentioned above, the researcher kept a reflexive journal from the beginning of the research, through data collection and data analysis to the completion of the data presentation. After completing each round of the interview, the researcher transcribed the audio recordings verbatim into Chinese.
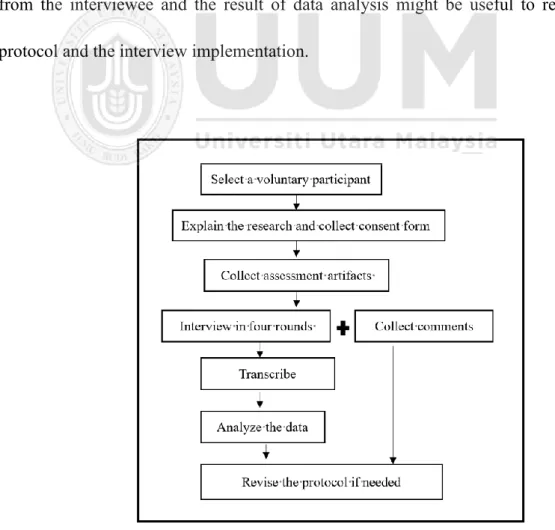
Data Analysis Methods
In addition, participant reflective diaries and researcher-led reflective diaries were also collected for inclusion in the data analysis. Coding helps the researcher develop an insightful understanding of the data and provides a thorough basis for analysis.
Researcher’s Role
For this reason, the researcher is supposed to reflect on contributions to the shaping of the narrative (Murray, 2018). With regard to reflexivity, it is in the form of a constant account of the researcher's self-criticism and self-assessment to reveal what is happening (Koch & Harrington, 1998).
Ethical Considerations
Research participants were also informed of their right to withdraw at any time during or after the study (Braun & Clarke, 2013). In this study, the researcher prepared some small gifts for the participants involved in the study for their time and cooperation.
Trustworthiness of the Study
In this study, research findings were triangulated from different data sources to maintain the rigor of the study. Spending a long time in the field enables the researcher to develop a deep understanding of the issue under study.
Summary
Details of data collection and data analysis procedures are outlined in this chapter for readers to determine the transferability of the research. The role of the researcher is also given attention throughout the research process.
Introduction
Findings for Conceptualization of LAL
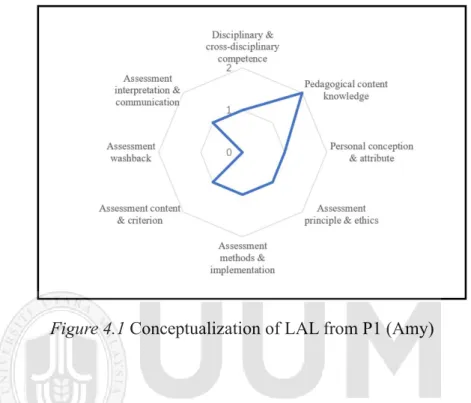
- Conceptualization of LAL from Participant 1
- Conceptualization of LAL from Participant 2
- Conceptualization of LAL from Participant 3
- Conceptualization of LAL from Participant 4
- Conceptualization of LAL from Participant 5
- Conceptualization of LAL from Participant 6
- Overall conceptualization of LAL
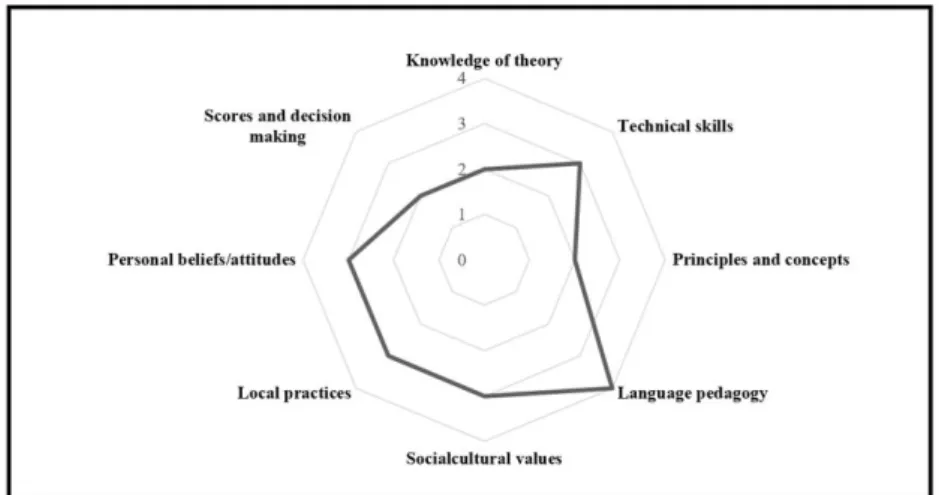
As demonstrated in Figure 4.6, the background of LAL is shaded to indicate the shaping effect of the social cultural context. For a more vivid presentation, the overall conceptualization of LAL of the six participants is summarized in Figure 4.7.
Findings for Self-evaluated LAL Proficiency
Self-evaluated LAL Proficiency
Four participants (Carol, Daisy, Edwin and Flora) identified themselves as insufficiently qualified for EFL teacher assessment jobs for various reasons: little readiness to enter the teaching profession (Carol), less satisfactory preparation for assessment in a teacher education programme. (Daisy, Edwin and Flora) and a personal late start to learning (Edwin). I didn't reach ... how can I say, I didn't reach such a professional level to stand on the podium.
Self-diagnosed LAL Improvement
Participant LAL improvement focus LAL improvement desire P1 (Amy) Feedback method To become a (good) teacher. But they seemed to be driven by the same power to become an effective and helpful teacher to facilitate teaching and learning in the future teaching profession.
Findings for Interaction between Mediating Factors and LAL Evolvement
The Identified Mediating Factors in LAL Evolvement
- Experiential Factors
- Contextual Factors
- Personal Factors
Methods that participants recognized when they were involved in the assessment activities are likely to carry over into their future decision-making. Assessor at university] I remember that in the first or second year of university, Ms.
Interaction between the Mediating Factors and LAL Evolvement
Findings for LAL Evolvement Trajectory
Summary
Introduction
Discussion of Findings for Conceptualization of LAL
Eight Dimensions
Scaled Importance
Context-dependence
Idiosyncrasy
Discussion of Findings for Self-evaluated LAL Proficiency
Self-evaluated LAL Proficiency
Self-diagnosed LAL Improvement
Discussion of Findings for Interaction between Mediating Factors and LAL
The Mediating Factors Identified in the Study
- The Experiential Factors
- The Contextual Factors
- The Personal Factors
The Interaction between the Mediating Factors and LAL Evolvement
Discussion of Findings for LAL Evolvement Trajectory
Implications of the Findings
Implications for Participants
Implications for Pre-service EFL Teachers
Implications for Pre-service EFL Teacher Educators
Implications for Pre-service EFL Teacher Preparation Programme
Contribution to the Body of LAL Research
Limitations of the Research
Recommendations for the Future Research
Summary