The primary objective of this study is to determine the banking efficiency of local banks and foreign banks and to make a comparison between them. Also, this study sheds light on whether bank size, government intervention, and merger and acquisition activities will affect banking efficiency in domestic banks when competing with foreign banks. Hence the importance and concern over banking efficiency that exhibits a snowball effect over decades.
The banking efficiency of the banks determines the ability of the banks to generate maximum output with minimum input. The primary objective of this paper is to determine the banking efficiency of local banks and foreign banks and make a comparison between them. The findings for this study suggest that foreign banks are more efficient than domestic banks in terms of banking efficiency for this particular period.
RESEARCH OVERVIEW
- Research Background…
- Problem Statement
- General Objectives
- Specific Objective
- Research Question
- Hypothesis of Study
- Significance of Study
- Chapter Layout
- Conclusion
How local banks and foreign banks differ in terms of their banking efficiency. The purpose of this research is to compare the banking efficiency between local banks and foreign banks in Malaysia. To examine whether bank size contributed to the banking performance of local banks in competition with foreign banks in Malaysia.
To examine whether government intervention contributed to the effectiveness of local banks in competing with foreign banks in Malaysia. To study the impact of bank mergers and acquisitions towards the banking efficiency of local banks to compete with foreign banks in Malaysia. There are several hypotheses included in this paper to conduct the empirical study of banking efficiency between the local and foreign banks in Malaysia.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Review of literature
- Input Variables
- Output Variables
- Dependence Variable
- Literature on Comparison between Foreign Banks and Local
- Review of Relevant Theoretical Models
- Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA)
- Stochastic Frontier Approach (SFA)
- Hypothesis Development
- Conclusion
This chapter describes the research background, description of the problem statement, research objective such as general objective and specific objective to be achieved, research question to be solved and hypothesis to be tested in the research.
METHODOLOGY
Research Design
Data Collection Method
- Secondary Data
Sampling Design
- Target Population
- Sampling Frame and Sampling Location
- Sampling Element
- Sampling Technique…
- Sampling Size…
Research Instrument…
Construct Measurement
Data Processing
Data Analysis
Conclusion
DATA ANALYSIS
Descriptive Analysis
- Respondent Demographic Profile
- Trend analysis
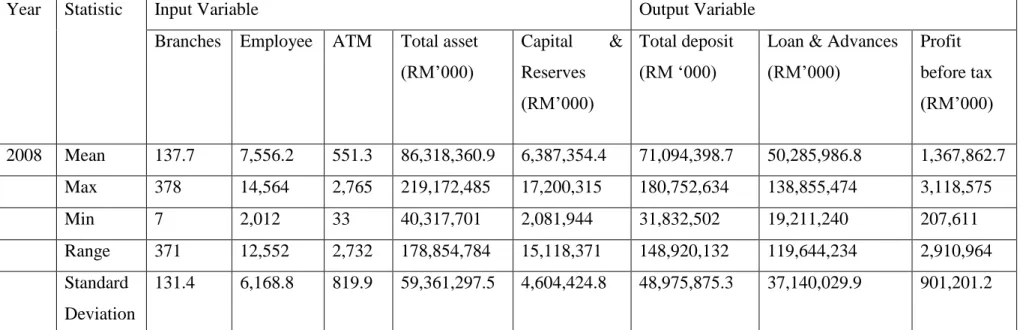
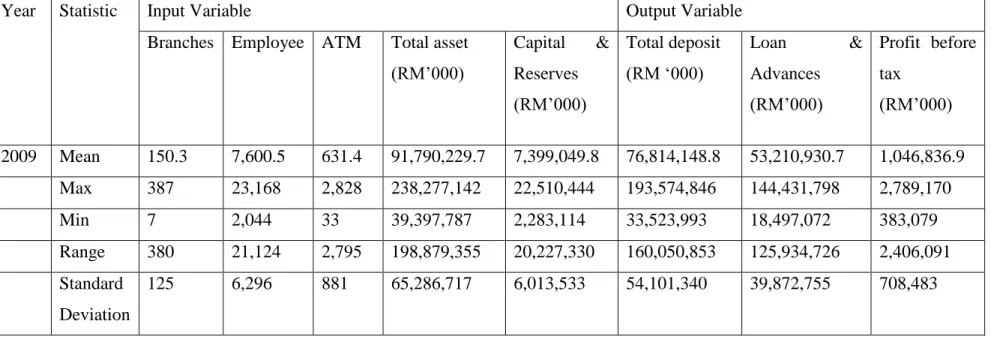
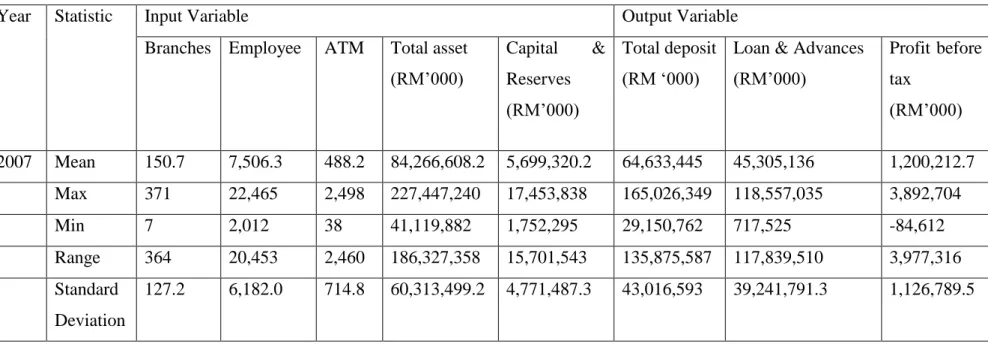
The data set is different for each bank because the value is different for the same input or output. The value of inputs and outputs for each bank increases from year to year. Therefore, some banks prefer to use high input to produce high output, while part of banks prefer to use high output to produce low output, or vice versa.
Based on table 4.1.1 to 4.1.8, the mean value, maximum value, minimum value and range from the year 2007 to the year 2014 showed that the input and output of each of the banks in the banking industry is increasing. The value of range increases in the first 4 years and decreases in 1 year, but it slowly increased back in 2 years. However, the value of the standard deviation is not stable and fluctuates over the entire period of 8 years.
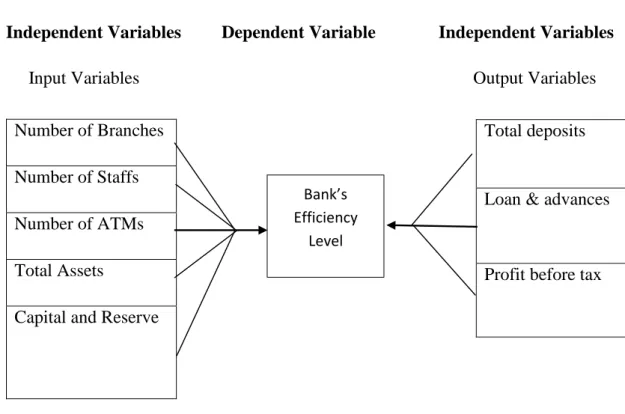
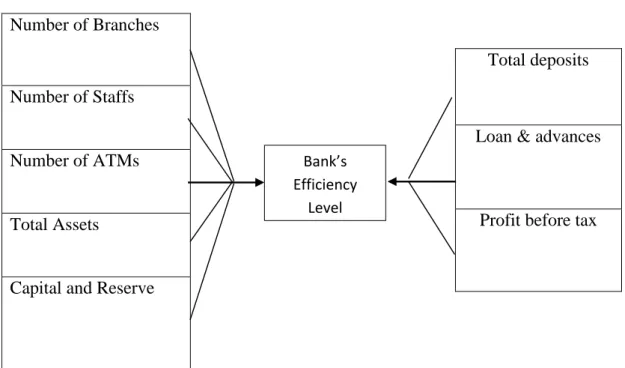
The input variable included total assets, capital reserve, branches, ATM and employees, while the output variable included loans, total deposits and profit before tax.
Outcomes of Relative Efficiency Score (Scale Measurement)…
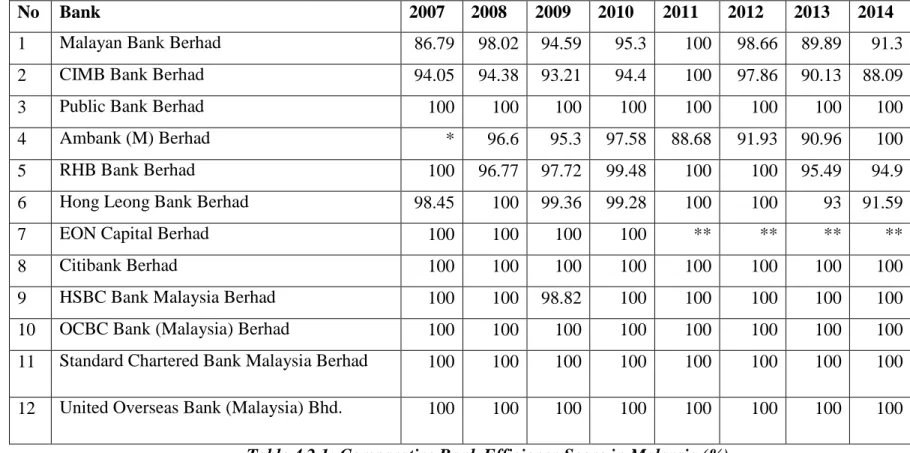
After acquiring Eon Capital Berhad, Hong Leong Bank Berhad managed to operate successfully for two years, namely 2011 and 2012. From Table 4.2.3, Public Bank Berhad, Malayan Bank Berhad and CIMB Bank Berhad are recognized as large banks, while while Ambank (M) Berhad, RHB Bank Berhad, Hong Leong Bank Berhad and EON Capital Berhad are known as small banks. Public Bank Berhad is the only major bank in Malaysia that is able to maintain its operations efficiently throughout the period.
The other two big banks, Malayan Bank Berhad and CIMB Bank Berhad's banking efficiency varies over the years and operate efficiently only during the year 2011. As for the small banks, the banking efficiency for RHB Bank Berhad and Hong Leong Bank Berhad is inconsistent and shaky. Eon Capital Berhad is the only small bank that can operate efficiently before it was acquired by Hong Leong Bank Berhad in 2010.
According to Table 4.2.4, government-linked banks include Malayan Bank Berhad, CIMB Bank Berhad, and Ambank (M) Berhad. Public Bank Berhad, RHB Bank Berhad, Hong Leong Bank Berhad and EON Capital Berhad are known as private banks. Table 4.4 shows that government-linked banks are inconsistent in terms of banking efficiency.
The banking efficiency of government-linked banks fluctuates over the period and most of the time the banks are considered to be inefficient. For example, the banking performance of Standard Chartered Bank Malaysia Berhad, United Overseas Bank (Malaysia) Berhad and OCBC Bank (Malaysia) Berhad are concrete evidences for this claim. For example, Hong Leong Bank Berhad, which became effective two years after the acquisition of Eon Capital Berhad.
For example, private banks such as Public Bank Berhad show a better result in terms of banking efficiency than government link banks such as Malayan Bank Berhad, Ambank (M) Berhad and CIMB Bank Berhad.
Inferential Analysis
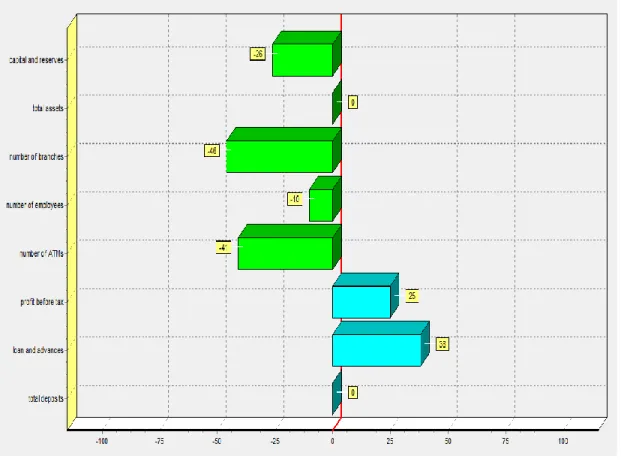
Based on the efficiency score in the table above, Malayan Bank Berhad needs to work on its input variables to become efficient. Malayan Bank Berhad also needs to cut 1.34% of the number of branches to reduce operational costs. In terms of production, Malayan Bank Berhad only has problems with the total deposit obtained.
CIMB Bank Berhad had to lay off 2.14% of its employees to regain efficiency. Hong Leong Bank Berhad will have to reduce the number of ATMs by about 538 units or 84.42% of current ATMs. Last but not least, it is proposed that the Malayan Bank Berhad will reduce the number of employees by 59.44%, amounting to about 28,248 persons.
Hong Leong Bank Berhad, CIMB Bank Berhad and Malayan Bank Berhad shared one common issue, which is their loan and advances are lower than expected. According to table 4.3.28, the two main variables that affected the efficiency score of RHB Bank Berhad are the number of bank branches and the number of ATMs. For Malayan Bank Berhad (Maybank), the main variable that seriously affected its efficiency score is the number of ATMs.
CIMB Bank Berhad needs to reduce the unit of branches and ATMs by 59.91% and 88.87% in order to get 100% efficiency score for these variables. CIMB Bank Berhad is efficient in using its outputs which are deposits and profit before tax. CIMB Bank Berhad also needs to grow its loan and advances by 3.92% to be efficient.
Based on Table 4.3.29, we can clearly see that for Hong Leong Bank Berhad, the efficiency score is only 91.59%. Their number of ATMs exceeded customer demand, eventually lowering Hong Leong Bank Berhad's performance rating. Hong Leong Bank Berhad also needs to increase its loan and advances by 7.33% to be effective.
Conclusion
DISCUSSION, CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS
Summary of Statistical Analysis
Also, according to the output variables result, most banks managed their products efficiently. The determinant of the size of a bank whether it is a large bank or a small bank is completely according to the size of the bank's assets (Fayman, 2009). According to Chortarea et al. 2013), excessive government interventions in the activities of the financial institution will negatively affect the efficiency of the bank's operation in the European Union.
From the findings, it revealed that most of the banks' inefficiencies were caused by misallocation of the bank assets and failed to utilize them properly. The efficiency of the bank employees in the bank branches should be highly monitored as they are the first line of the bank who represent the banks. In general, most of the banks' assets are used for loans and leases to generate interest-bearing profits.
In addition, this study also examined whether the size of banks influences the efficiency of the banks. In addition, this study is also supposed to examine whether the efficiency of banks is affected by government intervention. Most of the foreign banks such as OCBC Bank (Malaysia) Berhad, Standard Chartered Bank Malaysia Berhad, Citibank Berhad and United Overseas Bank (Malaysia) Berhad are able to maintain their efficiency and efficiency throughout the period.
In short, most local banks are worse at managing their deposits compared to foreign banks. Cost efficiency of the Chinese banking sector: A comparison of stochastic frontier analysis and data envelopment analysis. Determinants of the capital adequacy ratio of subsidiaries of foreign banks: the role of the interbank market and regulation.
Cost and Profit Efficiency of the Malaysian Commercial Banks: A Comparison between Domestic and Foreign Banks.
Discussions of Major Findings
- Local Banks versus Foreign Banks
- Larger Banks versus Smaller Banks
- Local banks without government intervention and
- Pre-merger Banks versus Post-merger Banks
Implication of The Study
- Managerial Implication
Limitations of Study
Recommendation for Future Study
Thus, it is recommended that future study include other acceptable input and output variables to obtain a more accurate result. For example, according to NIŢOI (2009), the author proposed that the main operating profits as well as other earning assets can be labeled as outputs, while deposits and loaned funds can be considered as inputs. For example, the Stochastic Frontier Approach (SFA) can be considered as an alternative to the DEA approach.
The main attraction for the SFA approach is that it contributes to a better specification, especially for the case of panel data (Hjalmarsson, Kumbhakar, & Heshmati, 1996).
Conclusion
Controlling the use of extreme weights in bank efficiency assessments during the financial crisis. The effect of Basel Accord capital requirements on the loan loss provisioning practices of Australian banks. Journal of Banking & Finance, 67, 23-36. Retrieved from http://www.magnifymoney.com/blog/eliminating- fees/should-banks-start-shutting-down-branches.
V Proceedings of the VIII Meeting of the Research Network of Central Banks of the Americas (str. Privatization, Foreign Bank Entertainment and bank efficiency in Croatia: a Fourier-flexible function stochastic cost frontier analysis. Impact of Bank Mergers on the Efficiency of Banks: Študija združitve banke Bharat Overseas Bank z indijsko čezmorsko banko.
Commonwealth/State Service Delivery Review Steering Committee (1997), Data Envelopment Analysis: A Technique for Measuring the Effectiveness of Government Service Delivery, AGPS, Canberra. Retrieved from http://keydifferences.com/difference-between-loans- and-advances.html Sufian, F., & Shah Habibullah, M.