First and foremost, I want to express my deepest appreciation to my MBA research project supervisor, Assistant Professor Dr. Corrinne Lee, for her guidance, wisdom and support. I cannot thank him enough for all the helpful suggestions he gave me throughout my study. Live streaming allows two-way communication between live broadcasters and viewers, which improves viewers' product knowledge and increases viewers' purchase intent.
This study examined the impact of live broadcasters' social capital on viewers' purchase intention to better understand this. The results showed that the social capital of the live broadcaster, in which professionalism, trust and reciprocity contributed to the viewer's purchase intention.
INTRODUCTION
- Research Background
- Problem Statement
- Research Questions
- Research Objective
- Significant of Study
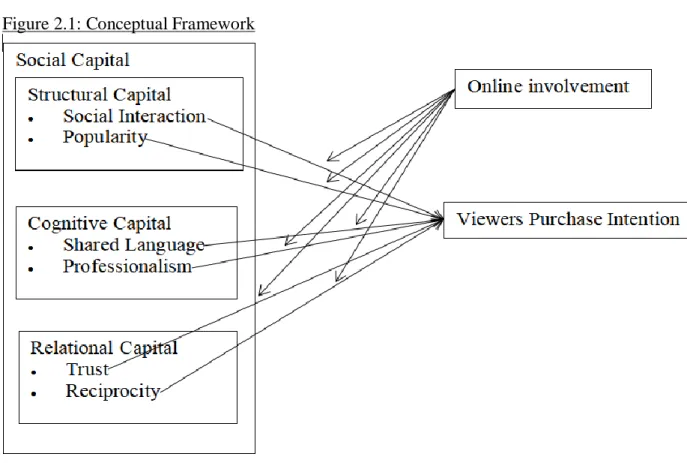
Customers' undivided attention and active participation in a live stream makes it an ideal medium for two-way communication. Using the concept of social capital theory, we aim to give concrete form to the one-to-many connection in live streaming platforms. Empirical testing of this model is then conducted by collecting survey data from viewers engaged in live streaming purchases and analyzing it in light of social capital theory to determine the effect of social capital on viewers' purchase intentions.
Marketers can use the study's findings to their advantage by better understanding the impact of live streamers' social capital on viewers' purchase intent. As a result, marketers can better anticipate viewer preferences for streamers if they have a deeper grasp of live streaming.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Social Capital
- Purchase Intention
- Structural Capital
- Cognitive Capital
- Relational Capital
- Online Involvement
- Conceptual Framework
Purchase intention is the phenomenon where a customer wants to buy a product but does not necessarily make the purchase (Jayesh, 2015). The term "purchase intention" according to Hajla et. 2017) refers to the stage of negotiation between the buyer and the seller before the latter finally accepts the sale from the former. A customer has purchase intent when they go to a store with the mindset that they will buy a product or service because they are looking for a specific feature or benefit, or if they have a generally favorable impression of the product or service.
Consequently, a streamer's structural position in online streaming is expressed in the amount of viewers they have. Although Nahapiet and Ghoshal's (1998) model emphasizes group-level elements of social capital, social capital can also explain viewers' purchase intention in live streaming e-commerce, according to study.
RESEARCH METHOD
- Research Design
- Data Collection Method
- Sampling Design
- Research Instruments
- Self-Administrative Survey
- Questionnaire Design
- Pilot Test
- Construct Measurement
- Data Processing
- Common Method Bias
- Data Analysis
- Descriptive Analysis
- Inferential Analysis
- Reliability Analysis
Researchers collect primary data, often known as “raw data,” from a statistically valid and reliable sample of the population (Sekaran & Bougie, 2019). The target population of a research project consists of all the things or parts of the population in which the researchers have an interest. The accuracy and validity of a questionnaire can be tested through a pilot test, which is a smaller version of the full one.
Researchers can learn more about the demographic makeup of the sample population by asking the appropriate questions. Section A of the questionnaire deals with the respondents' demographic information, and the researchers use an ordinal scale to create the questions. My attention is always drawn to the products when the live streamer suddenly changes the volume.
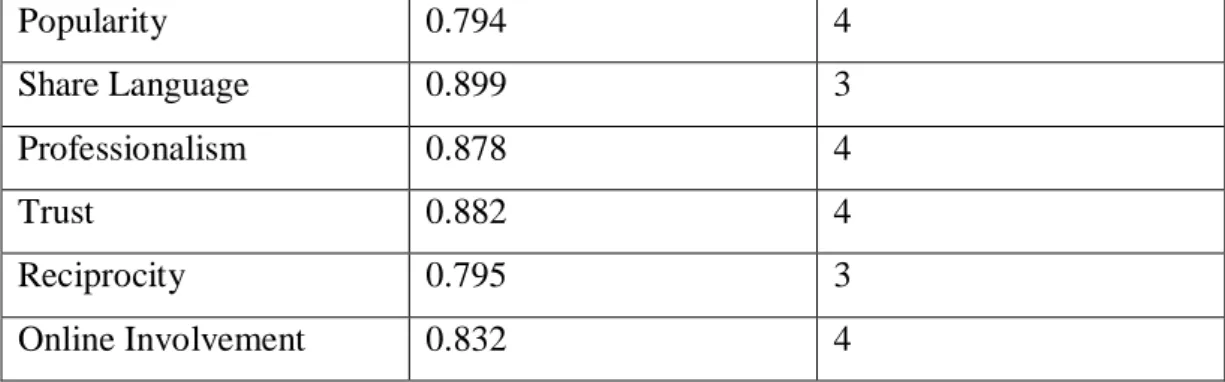
A live shooter has enough experience (eg work experience, trial experience) to evaluate the products he recommends. Trust The data provided by the live streamer corresponds to the actual state of the products. The live shooter has earned my trust based on the knowledge I have of it from various online platforms.
The platform where the live streamer does his work gives me the feeling that he is a trustworthy presenter. One of the most important criteria for valid measurement, reliability analysis, is often used to assess the stability of an existing measurement system by measuring its internal consistency. In this study, Cronbach's alpha was used to assess the internal consistency of the multi-item scale.

RESEARCH RESULTS
Descriptive Analysis
- General information
- Gender
- Age
- Race
- Location
- Education level
- Employment Status
- Individual Income Level
- Household Income Level
- Live Streaming Shopping Purchase Frequency (Times Per
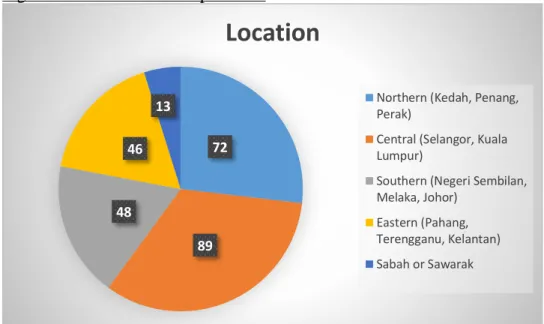
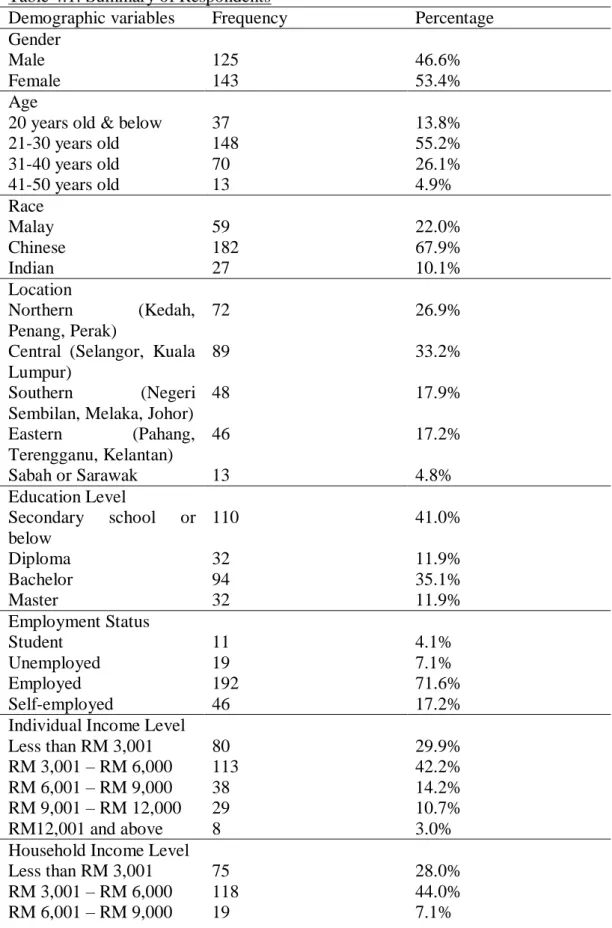
The demographic results by gender of the respondents who participated in this study are presented in table 4.1 and figure 4.1. Based on the data presented in table 4.1 and figure 4.4, it appears that the location of origin of the respondents seems quite scattered. The main reason it happened is because the way the respondents were collected is spread across groups of different types.
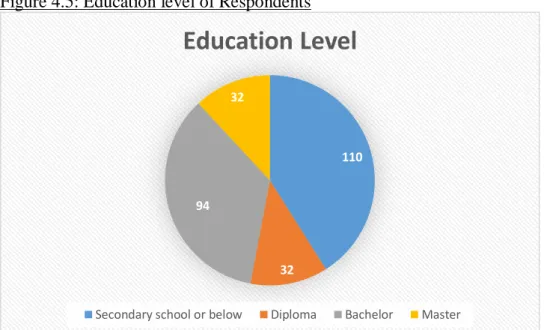
There were 110 people out of 268 respondents (41.0%) with no schooling beyond secondary school which is the highest percentage among all these respondents. 192 out of 268 respondents (71.6%) are employed, making employment status the most common among the respondents. The data shows that the proportion of respondents whose individual income was between RM 3,001 and RM 6,000 was the highest, which is 113 respondents (42.2%), after the percentage of respondents whose monthly income was less than RM 3,001, which 80 respondents (29.9%) are. .
The data shows that the proportion of people whose household income was between RM 3,001 and RM 6,000 was the highest, which is 118 respondents (44.0%), after the percentage of respondents whose monthly income was less than RM 3,001, which is 75 respondents is (28.0) %). Based on the analysis as illustrated in Table 4.1 and Figure 4.9, a total of 185 respondents (69.0%) spent 1-3 times per month on live streaming purchases. Although 30% of the respondents do not spend on live streaming purchases, but these respondents still watch live streaming.
Although viewers haven't had a live streaming experience with a purchase, they might have the intention.
Inferential Analysis
- Reliability Test
- Pearson’s Correlation Analysis
- Relationship between Variables
- Moderating Effect of ONL Towards SI & PI
- Moderating Effect of OI Towards POP & PI
- Moderating Effect of ONL Towards SL & PI
- Moderating Effect of OI Towards PRO & PI
- Moderating Effect of OI Towards TRU & PI
- Moderating Effect of ONL Towards REC & PI
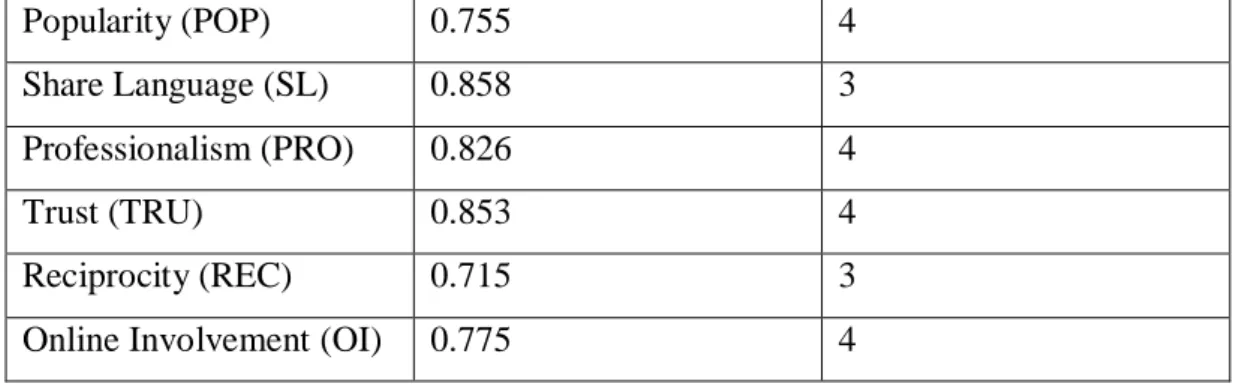
But the interaction term between social interaction and online engagement has a positive significant effect on viewer purchase intent (β = 0.0394, p < 0.001). The interaction term between popularity and online engagement also found an insignificant effect on viewer purchase intent (β= 0.6664, p>0.05). Clearly, online engagement does not moderate the relationship between popularity and viewer purchase intent.
The interaction term between shared language and online engagement also found an insignificant effect on viewer purchase intent (β= -0.0935, p > 0.05). It can be seen that online engagement does not moderate the relationship between language use and viewer purchase intent. The interaction term between professionalism and online engagement also found a significant effect on viewers' purchase intention (β= 0.3380, p<0.001).
It can be seen that online involvement moderated the relationship between professionalism and viewers' purchase intention. But the interaction term between trust and online involvement found an insignificant effect on viewers' purchase intention (β= -0.0738, p > 0.05). It can be seen that online involvement does not moderate the relationship between trust and viewers' purchase intention.
The interaction term between reciprocity and online involvement also found a significant effect on viewers' purchase intention p <0.001). It can be seen that online involvement moderated the relationship between reciprocity and viewers' purchase intention. Based on Johnson-Neyman results that the slope between reciprocity and viewer purchase intention becomes increasingly positive over levels of online involvement.
Hypotheses Testing
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
Discussion
The results of H2 and H8 indicated that the streamer's popularity level had no impact on viewers' purchase intent during e-commerce live streaming. The findings did not match our general expectation, we thought that the popularity of live streamers has a direct impact on how well their live streams do commercially. Research results show that shared language and professionalism partly contribute to this research model, where professionalism is the variable that positively influences viewers' purchase intention.
In addition, the interaction term between professionalism and online involvement also found a significant effect on viewers' purchase intention. It can be seen that online involvement moderated the relationship between professionalism and viewers' purchase intention, which proved that H4 and H10 are significant. Thus, the results showed that viewers' purchase intention increased greatly due to the performance of the live broadcasters' professionalism cognitive capital.
In addition, shared language was found to have no significant significance between viewer purchase intention, the interaction term between shared language and online involvement also found an insignificant effect on viewer purchase. It can be seen that H3 and H9 that Internet involvement does not moderate the relationship between common language and viewers' purchase intention. But based on H5 and H11, our main goal is to investigate whether online involvement affects the relationship between trust and viewers' purchase intention, even though this trust can be proven to significantly affect viewer's purchase intention without any moderator.
However, regardless of moderate Internet involvement, this finding is consistent with findings from other research that trust significantly influences viewer purchase intention. When viewers feel their needs and concerns are being addressed, they build trust and are more willing to commit to a long-term partnership, but all of this moderates online involvement. The interaction term between reciprocity and online involvement also found a significant effect on viewers' purchase intention.
Implication
Limitation and Future Research
Live streamer's professionalism, which creates a credible image for viewers thanks to the live streamer's social capital, which successfully reduces the information asymmetry produced by viewers' online transactions, increasing viewers' purchase intentions. Surprisingly, the live streamer's structural capital (social interaction, popularity) and part of cognitive capital (sharing language) do not seem to increase viewers' purchase intention. Since live streaming commerce is a trending e-commerce platform considering the pandemic, it has a lot of room to grow and develop.
Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories. Retrieved from https://streamlabs.com/content-. hub/post/streamlabs-and-stream-hatchet-q1-2022-live-stream-industry- report. Assessing the role of social capital, tacit knowledge sharing, knowledge quality, and reciprocity in determining an organization's innovative capability.
The role of culturally moderated social capital in technology transfer – Insights from Asia and the Americas. Social commerce research on the role of trust in a social networking site on purchase intentions. How social networking site behavior and online social capital influence social trading intentions. 2016) Consumer Responses to Cause Marketing: Moderating the Impact of Cause Involvement and.
New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc. Social Networks and Collective Action: A Theory of Critical Mass III. The effect of celebrity conformity on celebrity sponsorship brand purchase intention: The moderating effects of. Factors influencing the popularity of customer-generated content in a company-hosted online co-creation community: A social capital perspective.