The Severity of the Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Small-Scale Fisheries in Thailand: A Preliminary Assessment Calendar of Events. The COVID-19 pandemic has had major consequences for the fishing sector, especially on the socio-economic conditions of the stakeholders, e.g.
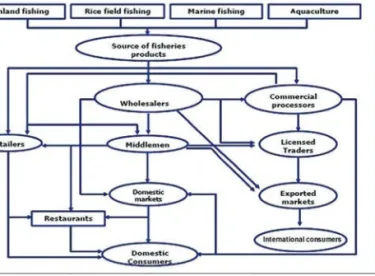
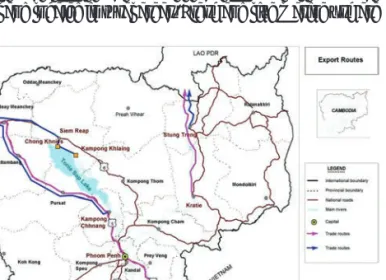
Fish Trade Practices: Southeast Asian Perspective
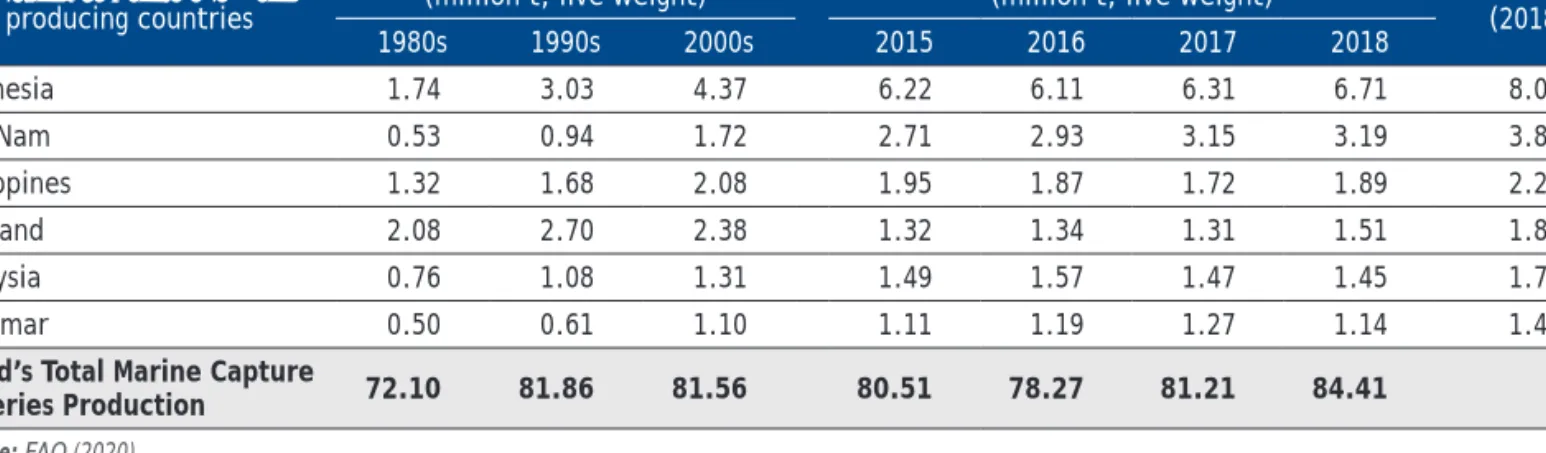
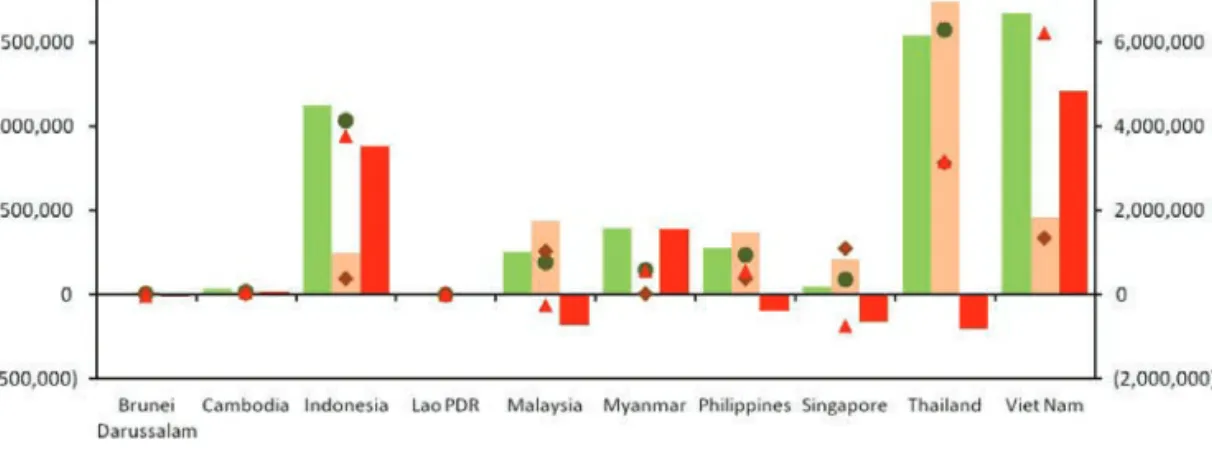
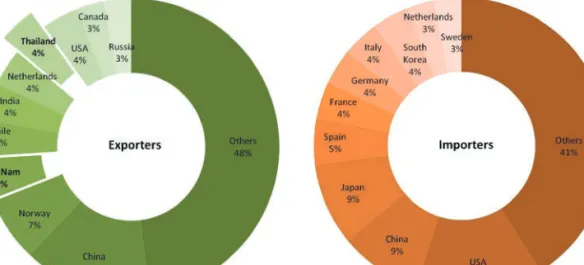
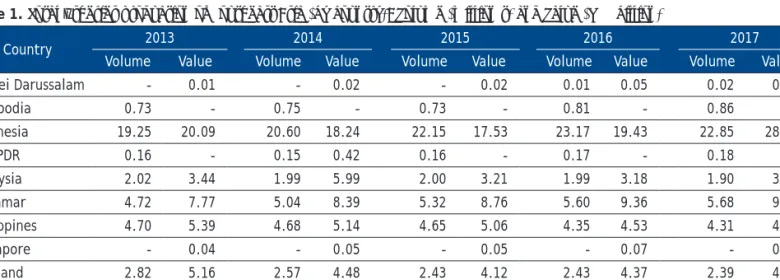
For trade balance, Brunei Darussalam, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand had a deficit in terms of the amount of fish and fishery products exported;. This indicates that the exports of these respective countries are not sufficient to compensate their imports of fish and fishery products.
Fish Trade Practices of Southeast Asian Countries
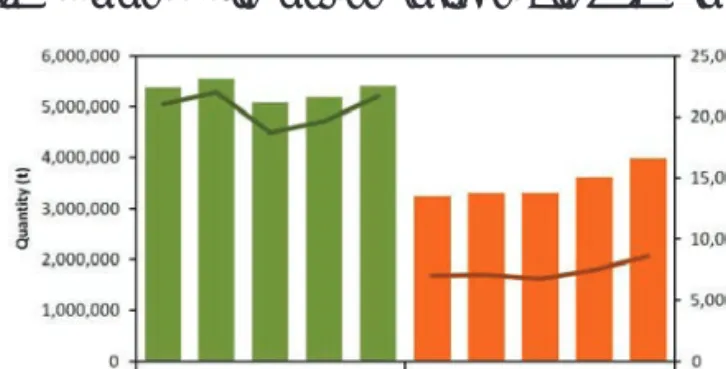
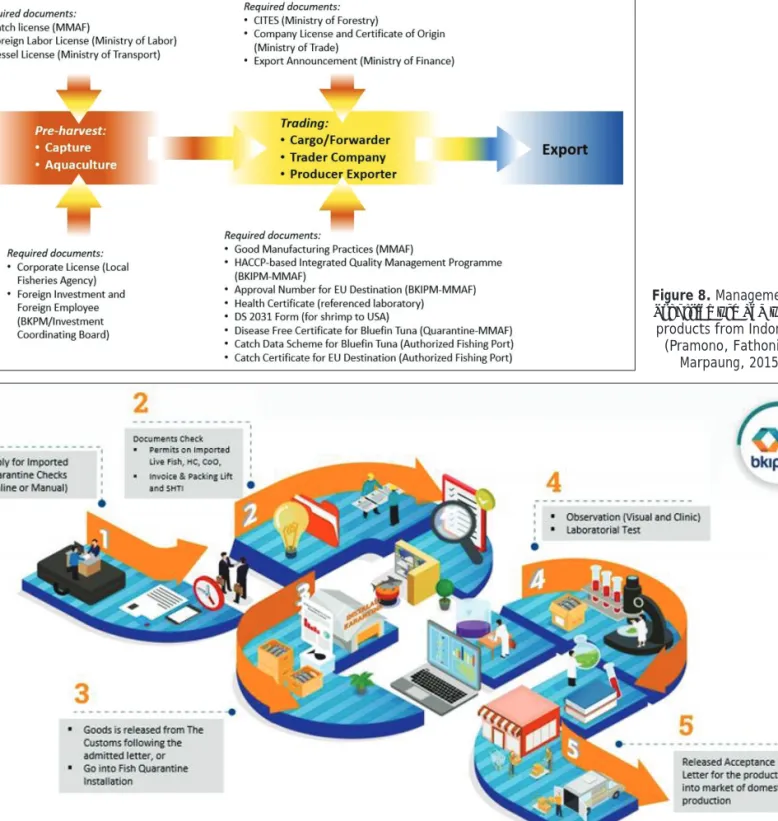
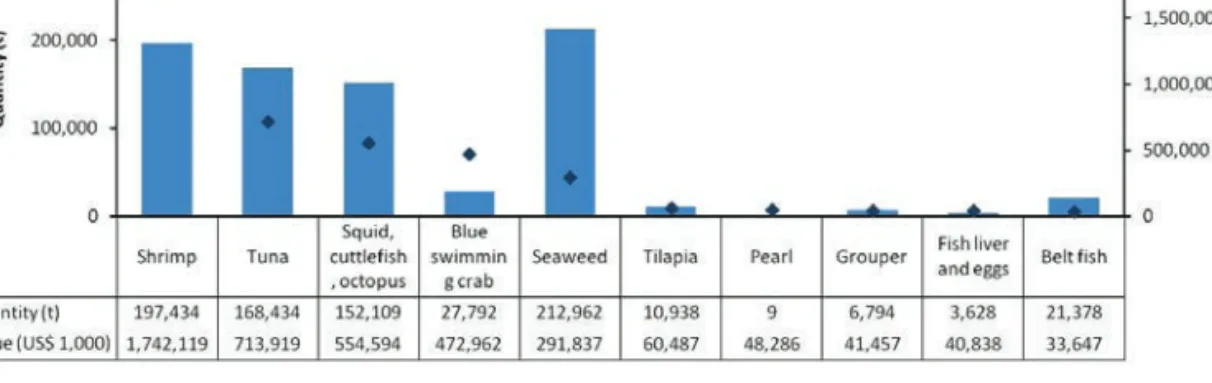
Quantity (t) and value (USD 1,000) of Cambodia's exported and imported fish and fishery products in 2017. Exports of fish and fishery products from Indonesia are facilitated by national government authorities (Figure 8).
In 2018, Myanmar was the top source of imported fish and fishery products in terms of quantity (more than 300 thousand tons), but China posted the highest value (about USD 400 thousand) of the country's imported fish and fishery products (Figure 27). Meanwhile, fish and fishery products are transported from the processing facilities and exported through the cargo ports. In recent years, the country's seafood export turnover has ranked fourth among major export products, including textiles, footwear and crude oil.
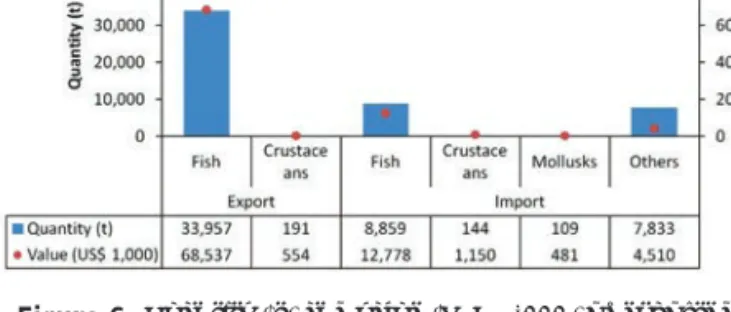
In 2018, about $8.3 million worth of fish and fish products were exported from Vietnam to more than 160 countries (Figure 31).
About the Authors
Boosting the Management of Economically Important Fishery Resources in the Southeast Asian Region
Biology, ecology, and fisheries of two seer fishes
Pacific king mackerel, Scomberomorus guttatus (Figure 4) migrates along coastal waters through the Indo-Western Pacific Ocean.
Stock and risk assessments of seer fishes
- Narrow-barred Spanish mackerel (Indian Ocean side) For the narrow-barred Spanish mackerel in the Indian Ocean
- Narrow-barred Spanish mackerel (Pacific Ocean side) Results of the stock assessment of the narrow-barred Spanish
- Indo-Pacific king mackerel (Indian Ocean side) Results of the stock assessment of the Indo-Pacific mackerel in
- Indo-Pacific king mackerel (Pacific Ocean side) Results of the stock assessment of the Indo-Pacific mackerel
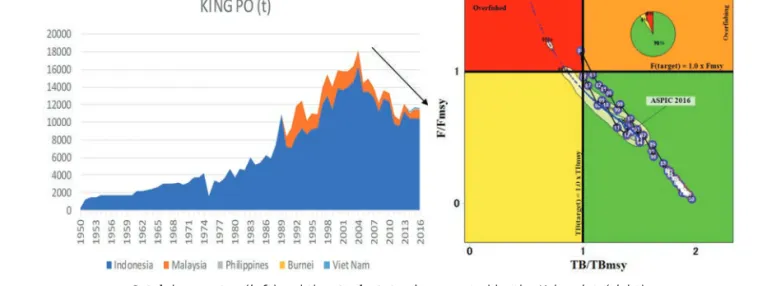
The results of the risk assessment (Kobe II strategic risk matrix) suggest that the TAC should be Spanish narrow bar mackerel (Pacific Ocean side) Spanish narrow bar mackerel stock assessment results The results of the Spanish narrow bar mackerel stock assessment on the Pacific Ocean side (Box 2) suggest that MSY= 129,200 t and the stock status (2016) is in the red zone of the Kobe plot well away from the MSY levels, i.e. Indo-Pacific king mackerel (Indian Ocean side) Indo-Pacific mackerel stock assessment results in Indo-Pacific mackerel stock assessment results on the Indian Ocean side (Box 3) suggest that MSY=15,130 t and the status of stock (2016) is in the green zone of the Kobe plot well away from the MSY levels, i.e.
The results of the risk assessment, strategic risk matrix (Kobe II) suggest that the TAC may be < MSY (21,500 t) the level to ensure MSY (TB and F) with risk probability exceeding MSY (TB and F).
Conclusion and Recommendations
Stock status summary of Spanish narrow-barrier mackerel and Indo-Pacific king mackerel (2016), and TAC management advice. Note) current catch level, MSY and TAC values are rounded to 100 t. Stock status of six management species in the IOTC Competence Area (IOTC, 2019 and 2020) Species considered Stock status TB/TBmsy, F/Fmsy Year of stock status. Comparison of Spanish narrowband mackerel stock statuses between IOTC (whole Indian Ocean) (2015 and 2018) based on Stock Reduction Analysis and SEAFDEC (Southeast Asian waters in the Indian Ocean) (2018) based on ASPIC.
For reference, the stock status results of neritic tuna, including Spanish narrow-band mackerel and Indian Ocean king mackerel, throughout the Indian Ocean, assessed by SEAFDEC and the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC), are summarized in Box 5.
Acknowledgement
Tom Nishida is a resource person for the SEAFDEC Neritic Tuna Project and a scientist at the National Research Institute of Far Seas Fisheries, Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency. One of the effective strategies is to establish a temporally closed area and season where catches (density) of these two species are high, while others are low. Finally, for seriously unhealthy stocks such as the narrow-barred Spanish mackerel in the Pacific side, stock assessment should be carried out every 1-2 years until the stock status changes to the safe state, otherwise it may be too late to manage the recovery of the stock. stock.
For healthy stocks, the stock assessment cycle can occur every three to four years, but routine monitoring of catch and CPUE trends is essential.
Towards Ensuring the Safety and Viability of Seafood
Thus, even if facilities and technologies are available to apply cold chain management in the handling of seafood, problems arise in maintaining the system throughout the supply chain. Most importantly, the adoption of cold chain management practices is still voluntary in most of the AMS and not yet enforced as a general policy.
Regional Guidelines on Cold Chain Management of Fish and Fishery
Way Forward
About the Author
Impeding the Outbreaks of Transboundary Aquatic Animal Diseases in Southeast Asian Aquaculture: the Aquatic
In order to strengthen regional cooperation to impede the spread of transboundary aquatic animal diseases, SEAFDEC, in collaboration with the Philippine government, has invested in the Regional Technical Consultation (RTC) on Improving Aquatic Animal Health Management. Furthermore, as also agreed during the RTC, the emergency preparedness and response systems (EPRS) should include contingency planning arrangements to reduce the impact of severe aquatic animal disease outbreaks through containment, i.e. in addressing the recommendations of the RTC, the Philippines-based SEAFDEC Aquaculture Department (SEAFDEC/AQD) and the Government of Thailand through the Aquatic Animal Health Research and Development Division (AAHRDD) of the Department of Fisheries (DOF) of Thailand in collaboration with the ASEAN Network of Aquatic Animal.
Policy recommendations on emergency preparedness and response systems (EPRS) for managing aquatic animal disease outbreaks in the Southeast Asian region.
Regional Technical Guidelines on Early Warning System for Aquatic Animal
Content of the ASEAN Guidelines on Aquatic Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems for Effective Management. Baliao is the chief of the SEAFDEC Aquaculture Department (SEAFDEC/AQD) based in Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines. Proceedings of the ASEAN Regional Technical Consultation on EMS/AHPND and Other Transboundary Diseases for.
Aquatic Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems for Effective Management of Transboundary Disease Outbreaks in Southeast Asia: Proceedings of the ASEAN Regional Technical Consultation on Aquatic Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems for Effective Management of Transboundary Disease Outbreaks in Southeast Asia, 20-20 August 2018, Bangkok Thailand.
Western Region of Indonesia: the Nucleus of Anguillid Eel Fisheries and Trade
Anguillid eel resources in the Western Region of Indonesia
Sungai Jenggalu, Kungkai dan Manna), di Provinsi Lampung (yaitu Sungai Muara Kelapai dan Sungai Way Ngaras) dan di Jawa Tengah (yaitu Sungai Serayu dan anak-anak sungainya).
Anguillid eel capture fisheries in Western Region of Indonesia
In addition, the eel fishery in Bengkulu Province, Sumatra Island (Figure 1) also uses a PVC trap to catch yellow eels from middle river basins and marshes. The fishing gear used to catch wrasse and yellow eel is a fishing line without a hook (Figure 6), a trap and a net (Figure 7). Eels caught from the West Coast Regency region of Lampung Province (Figure 8) are transported to Bengkulu and Jakarta, although data on eel traffic in Lampung Province could not be obtained.
Based on interviews with local fishermen and collectors, fishing is done around the marshes surrounding the rice fields.
Utilization of anguillid eels
Nevertheless, eel products could be promoted in many processed forms and prices reduced so that many people would patronize the products. In addition, the development of a simple farming method should be considered a priority step forward so that the market price of eel can be reduced. In addition, the distance between the fishing area and glass eel collection and the center of aquaculture is quite large, so mortality during transport is still high, although this can be addressed by developing improved eel transport technology.
While hatchery research for eel seed production is still ongoing, another concern is the cost of feed for the cultured eels, which can be expensive at around US$2.5-4.0/kg.
Marketing of anguillid eels
Thus, most eels produced in the region are destined for the export market. In this way, Indonesians would withdraw from processed food and increase their preference to consume anguillid eels. Currently, glass eel prices can be around IDR 1.0-3.0 million/kg glass eel or USD 70-250/kg, while the availability of glass eel depends on the wild catch, which is related to the season and the location.
To lower the price, the use of high protein ingredients could be minimized while carbohydrates are maximized through improvement of feed technology, culture medium and eel health.
Sustainable management of anguillid eel resources
Domestically, eels are still not widely recognized as a nutritious food fish, despite the market price that appears to be unaffordable by local residents. Nowadays, efforts to introduce eel products to local communities in Indonesia are beginning to take shape by producing processed food that suits the Indonesian taste, e.g. Product development attempts to change the appearance of anguillid eels on packaging to ensure that the edible fish does not look like a snake.
This is because eels require foods with a high protein content (40-50 %) and some feed ingredients are still imported.
Issues and constraints
She was the project leader of the research Enhancement of sustainability of catadromous eel resources in Southeast Asia for 2015 and 2016. She was the project leader of the research Enhancement of sustainability of catadromous eel resources in Southeast Asia from 2017 to 2019. He was involved in the project Improving sustainability of catadromous eel resources in Southeast Asia for.
She was involved in the project Improving sustainability of catadromous eel resources in Southeast Asia for.
Severity of the Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic on Small- scale Fisheries of Thailand: A Preliminary Assessment
Fishing
Severity of the Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Small-Scale Fisheries of Thailand: A Preliminary Assessment. As one of the centers of the country's commercial fisheries, the insufficient number of laborers who are mostly migrants and issued a one-day boarding card that expires daily has affected their commercial fishing operations. This concern was exacerbated when the reissuance of the workers' boarding passes was suspended due to border closure.
The location of the respondents from small fishing communities in the 10 selected coastal provinces of Thailand.
Survey on the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on livelihoods of small-scale
The restrictions and limitations in direct marketing have prompted many fishermen to turn to e-commerce as a strategy to ease the impact of the pandemic on their livelihoods. The respondents had different opinions about the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the fisheries resources and habitats. They also indicated that the habitats can recover due to the closure of the tourism industry, so the environment will no longer be disturbed by human activities.
If such a situation is uncontrolled, it can lead to the depletion of the fishery resources due to increased fishing pressure.
Recommendations and Way Forward
Isara Chanrachkij ([email protected]) is Head of Research and Development, SEAFDEC Training Division, based in Samut Prakan, Thailand. Thanyalak Suasi ([email protected]) is Head of Fisheries Management, Research and Development Division, SEAFDEC Training Division, Samut Prakan, Thailand. Rattana Tiaye ([email protected]) is a Fisheries Management Scientist in the Fisheries Management Division, Research and Development Division of the SEAFDEC Training Division, based in Samut Prakan, Thailand.
Omar Riego Penarubia of the FAO Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture for collaborating with the SEAFDEC Training Department in monitoring the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on small-scale fisheries.
CALENDAR OF EVENTS
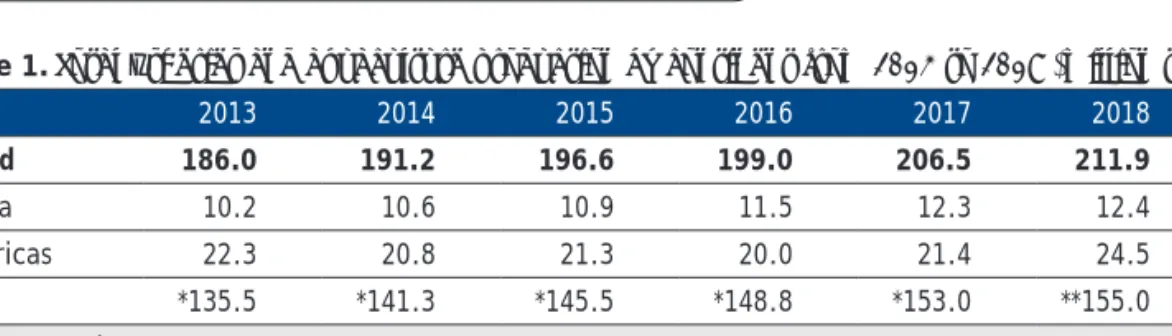
SEAFDEC currently consists of 11 member countries: Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Japan, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam. Sustainable management and development of fisheries and aquaculture to contribute to food security, poverty alleviation and livelihoods of people in the South East Asian region. Technology transfer and capacity building to improve the capacity of Member States in the application of technologies, and implementation of fisheries policy and management tools for the sustainable utilization of fisheries resources and aquaculture.
Monitoring and evaluation of the implementation of the regional fisheries policies and management frameworks adopted under the ASEAN-SEAFDEC cooperation mechanism, and the emerging international fisheries-related issues, including their impact on fisheries, food security and socio-economics of the region.