With a quantitative study, we wanted to check the influence of factors that influence the innovation of schools that provide basic education. In addition, the results of the qualitative study showed that leadership competencies, transformation-based competencies, and organizational resources are important for an organization's innovation competence.
INTRODUCTION
- Statement and Significance of the Study
- Objectives of the Study
- Scope of the Study
- Benefits of the Study
- Academic Benefits
- Professional Benefits
- Policy Formulation Benefits
- Definitions of Terms
- Organization of the Study
Therefore, basic education becomes a challenging factor in the design of education policies to increase the country's competitiveness and ensure sustainable development. Innovation competence refers to the ability to continuously create innovation in an organization and apply such innovation to increase the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization.
EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM AND EDUCATIONAL INNOVATION
Background of Educational System in Thailand
Its missions and obligations are in accordance with the Law on the Administrative Organization of the Ministry of Education B.E. 2546. In addition, the Ministry of Education has been restructured and the new structure of the Ministry of Education therefore includes the following seven agencies under its supervision:
Educational System in Thailand
Differentiation of levels and types of basic education is done in accordance with those defined in the regulation of the ministry. Differentiation or equivalence of different levels of non-formal or informal education is in accordance with those defined in the regulations of the ministries.
Basic Education System
the Education Act B.E. 2542, which states that pre-school education and basic education must be given in the following institutions: 1) Early childhood development institutions, namely: childcare centers; child development centers; preschool child development centers in religious institutions; initial care centers for disabled children or persons with special needs, or early childhood development centers by other names, 2) schools, namely: public schools, private schools and those under the jurisdiction of Buddhist or other religious institutions, and 3) learning centers, namely: those, that are organized by non-formal education agencies, individuals, families, communities, community organizations, local management organizations, private organizations, religious institutions, businesses, hospitals, medical institutions, welfare institutions and other social institutions. In addition, the basic education system is classified into 2 major curricula, which are an English program and a Thai program.
Administrative Structure of Ministry of Education
In addition, for effective administration, the Ministry of Education divides the inspection area into 18 areas and one central inspection area in Bangkok, according to the requirements of the Ministry of Home Affairs. Inspection areas of the Ministry of Education are determined for the convenience of operation under their missions and duties, according to requirements.
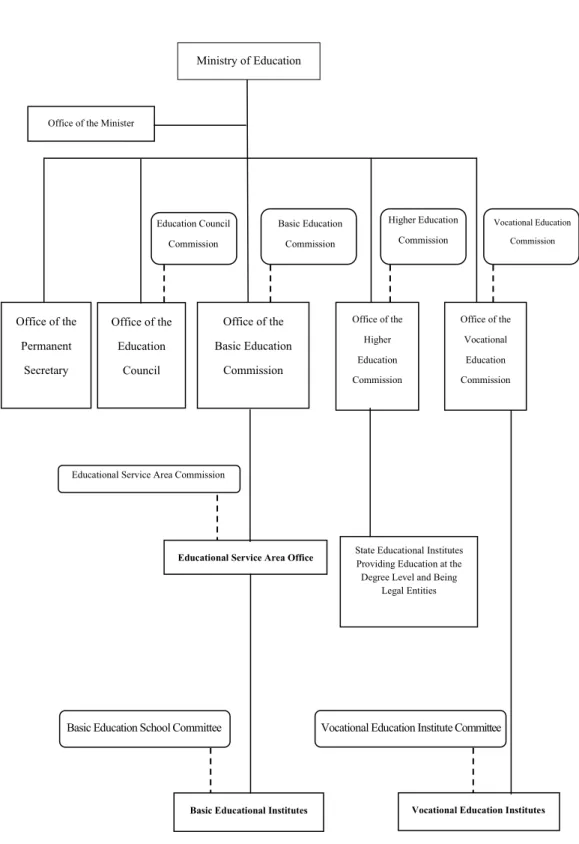
Implementation of Ministry of Education
In addition, the Office of the Basic Education Commission has established the policy, vision, and mission for K-12 education beginning in FY 2014 as follows: In addition, the Office of the Basic Education Commission establishes strategies and programs to respond to its vision, missions, and objectives, as reflected in Table 2.3.
Educational Innovation
- Selection of “One School One Innovation” performances of the Teachers' Council of Thailand is organized every academic year through the process
The Commission, which inspects and evaluates achievements of One School One Innovation, will select the qualified innovation that deserves the award of the "One School One Innovation" award according to the assessment criteria for quality specified by the Teachers' Council. Innovation that passes the assessment criteria and is approved by the Commission of Teachers' Council of Educational Service Area, according to the assessment criteria for quality as specified by the Teachers' Council.

Conclusion
In addition, it also contains the types of educational innovation and the "One School One Innovation" competition, including criteria, rules and conditions for submitting innovations to the competition.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Organization Innovation
Herkema (2003) Innovation is the adaptation of an idea or behavior that is new to the organization. Schilling (2008) Innovation is the practical implementation of an idea in a new product or process.
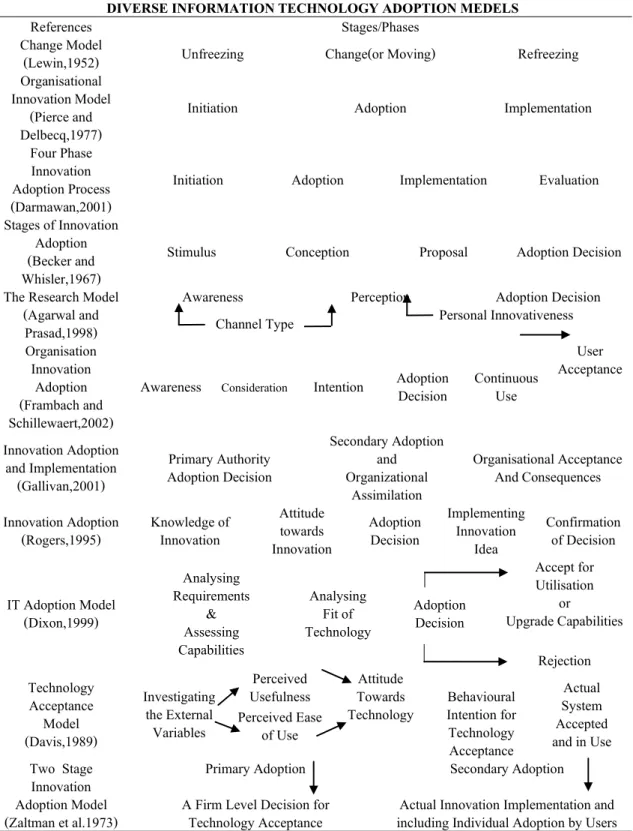
DIVERSE INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ADOPTION MEDELS
- Types of Innovation
- Educational Innovation
- Resource-based View Perspective
- Dynamic Capabilities Theory
- Competency-based View Perspective
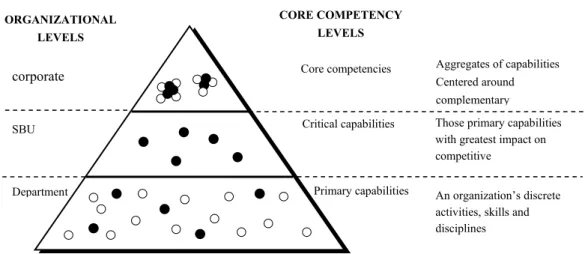
However, within the scope of an organization there are also competencies other than the core competency of the organization. According to the concept in Figure 3.4, it proposes that the organization's core competencies are the combination of the capabilities of their strategic business unit.
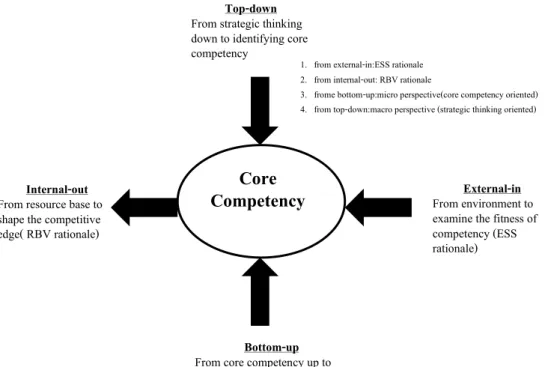
Core Competency
Innovation Competencies of Organization
Such competence ensures that the organization is excellent and unique in terms of performance compared to competitors. When “innovativeness” is combined with organizational component factors, the organization will be able to create the “capacity to innovate.”
Innovation Performance of Organization
According to the concept of innovation organization, it is the adoption of knowledge to systematically create innovations for an organization to add values, develop and produce quality products and services to respond to customer needs and satisfaction, including creating competitive advantages for the organization. . Indicating the quality and performance level of an innovation organization can be considered based on the innovation performance of the organization.
Factors enabling Innovation Competency
Organizational culture, research and development, and organizational learning can enhance this type of organizational competency. Investing in research and development of new products is an attempt to differentiate the organization's results.

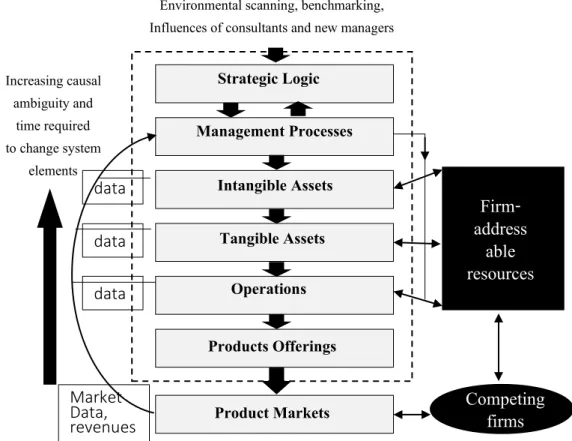
Strategic Logic Management Processes
An organization manages its resources and turns them into outputs that can respond to the organizational environment, such as marketing competition. The process begins with the management process, which sets the strategic framework for the development and management of the organization's operating system, so that organizational resources are transformed into organizational outputs that can respond to the organizational environment, such as market competition.
Intangible Assets Tangible Assets
In terms of the organization's competitive advantages, organizational results that generate competitive advantages are considered innovation, which creates value for the organization's customers and a sustainable business operation.
Operations Products Offerings
Product Markets
The organization's outputs will affect the organizational environment, such as competition, market conditions, and society's demands. Environmental feedback about the organization's products will flow into the organization's management process.
Transformation External Environment
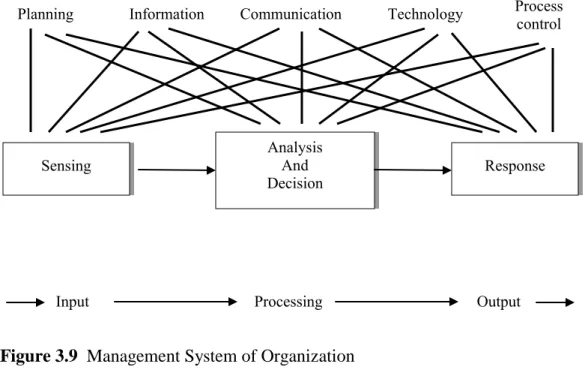
The open system starts with an organization determining and identifying an input such as organizational resources or external resources. Potocki and Brocato (1995) introduced the model applied from the open system theory in a form of a management system as shown in Figure 3.9.
Inputs
Such resources will be transformed from the internal process into a product that is distributed outside the organization and interacts with the organizational environment, resulting in the endless cycle of the organization.
Outputs
Process Feedback Loops
The model shown in Figure 3.9 verifies the relationship of management of the organization and the organizational resources in which inputs will be transformed to outputs and this requires the internal process such as planning, communication, technology and internal process of organization. The management process of the organization should empower its staff to have skills and abilities, quality and commitment to the organization through human resource management.
MANAGERIAL LEADERSHIP
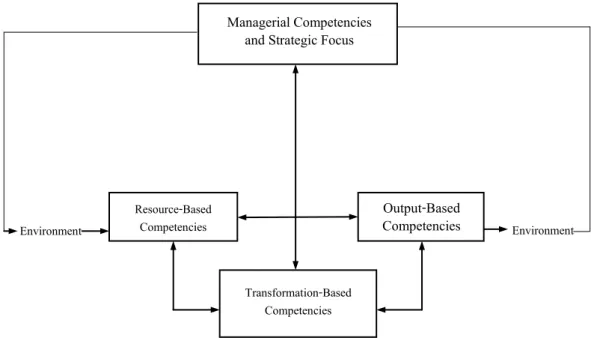
Meanwhile, the management of the organization must be able to perceive and understand the pressure of the organizational environment and use the organizational environment in the decision-making process to further determine the operational direction of the organization. As for input-based competencies, it includes organizational resources that the organization has or has acquired from any sources, both internal and external.
ENACTING ORGANIZATIONAL ENVIRONMENT INPUT-BASED
The components of organizational competencies are aligned in a form of the open system theory as shown in Figure 3.10. In terms of quality management, management competence includes the process related to establishing the organization's vision through the leadership process down to the individual level of the organization to drive the organization to achieve its goals and mission.
EMPLOYEE KNOW-HOW EXTERNAL COOPERATION SKILLS
TRANSFORMATION BASED CREATION OF A COLLECTIVE MIND
Meanwhile, the management of the organization must be able to perceive and understand the pressure of the organizational environment and use the organizational environment in the decision-making process to further determine the operational direction.
ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT
ENHANCEMENT OF ORGANIZATIONAL LEARNING SPEED AND FLEXIBILITY IN THE DESIGN OF NEW PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
OUTPUT-BASED REPUTATION
Managerial Competencies
Meanwhile, the organization must manage its personnel so that they have sufficient authority and ability to perform their work in accordance with the vision of the organization (Escrig-Tena and Bou-Llusar, 2005). Organizational strategy is very important for the functioning of the organization, as the strategy is similar to the organizational resource allocation model (Smith, 2007).
Management Functions
According to a study on internal management that lists the functions of management, the four basic functions of management are planning, organizing, leading and controlling (Daft and Marcic, 2004: 8). Consequently, according to the study questions related to organizational management and leadership competencies, it can be concluded that leadership competencies consist of leadership, strategy, top management support, and human resource practices.
Controlling
From Figure 3.11, it was found that the management model includes the executive function regarding management, planning function regarding action plans and strategies in the organization, internal management regarding personnel management, etc. Oliver (2001) has compiled the definition of organizational strategy. which was defined by many academics as follows; organizational strategy is like the plan of action and approaches for implementation of all sections of the organization, including policy and methods of organizational resource allocation.
Performance
Resources
Organizational Resources
The skills and abilities, including creativity and competencies of an organization's employees are attributes of the organization's quality human resources. Bollinger and Smith (2001) stated that an organization's knowledge will continuously increase when the organization has good knowledge management.
Transformation based Competency
An organization's knowledge is the organization's resources that are needed to increase marketing effectiveness and innovations in the organization (Egbu, 2004). The salient characteristic of organizational learning is commitment to learning by organizational members (Hill, Hazlett, & Meegan, 2001).
Organizational Environment
According to the author, uncertainty can be characterized when the environment becomes uncertain, for example when customer preferences change or shift. According to the above literature review, it can be concluded that the environments that influence organizational innovation consist of government support, competition, and uncertainty about the organizational environment.
Previous Studies and Researches
From the literature review, the authors divided innovation competencies into two categories; generic innovation competencies and specific industry-related innovation competency. For specific industry-related innovation competencies that come with the specific type of industries, have been described in terms of industry-specific innovation competency.
Human factors 2. Facilitating unit
2006) studied organizational innovation in vocational education and proposed a model containing factors influencing the success of innovation. The authors developed the constructs of organizational innovation capability as the level of the organization and facilitating factors of innovation as the level of innovative activity.
Consensus achievement
- Conceptual Framework of Research
Organizations must have the skills and abilities to use resources for the highest benefits according to the needs of the organization. Competence state 4 relates to the resource flexibility to be used in the organization's processes.
Environment
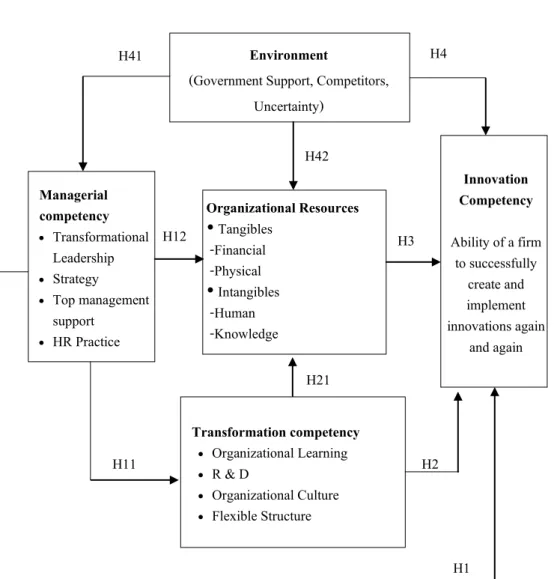
According to the resource-based view, dynamic capacity theory, competence-based view and literature review in previous subjects, the conceptual framework of the research is developed as follows. According to the study on organizational competences in section 3.9, management competence is important for the organization's innovative competence.
Organizational Resources
Based on the view of Lado et al. 1992), the management of the organization is comparable to the center of the organization, it formulates strategies, plans action plans or performs any operation that affects other components of the organization, including the management of the results of the organization as a form of products and services.
Transformation competency
Innovation Competency
Conclusion
Some scholars argued that both types of innovation processes have different methods and supporting factors. According to the development of the research framework developed based on the application of the theory of dynamic capabilities, the resource-based view (RBV) and the competency-based view (CBV), including studies related to organizational competencies, it can be concluded that management competency (leadership competency) Organizational strategies, management support, human resource management practice), transformation-based competency (organizational culture, organizational learning, research and development), organizational resources (tangible resources and intangible resources) and the organizational environment have a relationship with innovative competency .
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research Form and Method
Since the qualitative research method uses personal in-depth interviews with open-ended questions, respondents have the opportunity to present detailed information. With the qualitative research method, we obtain supporting data that cannot be discerned with the quantitative research method, for example, the reasons for the connections between the studied variables.
Population and Sample for Quantitative Research
- Population
- Samples
- Data Collection for Quantitative Research
A questionnaire developed based on a literature review is used to collect data for this research. Questionnaire validity refers to whether the questionnaire actually measured what it was intended to measure.
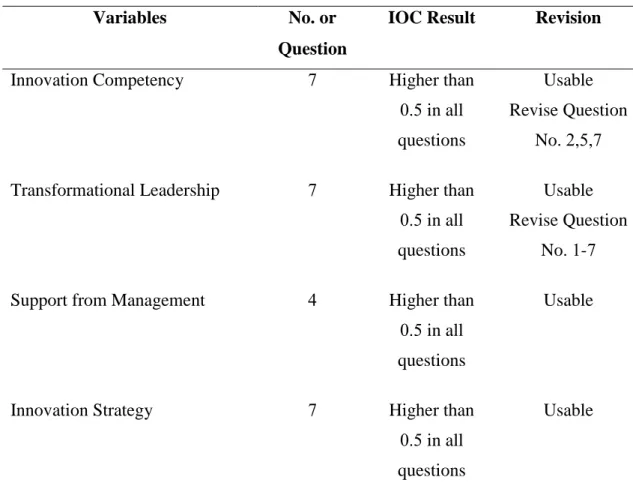
Population and Sample for Qualitative Research
- Sample for Qualitative Research
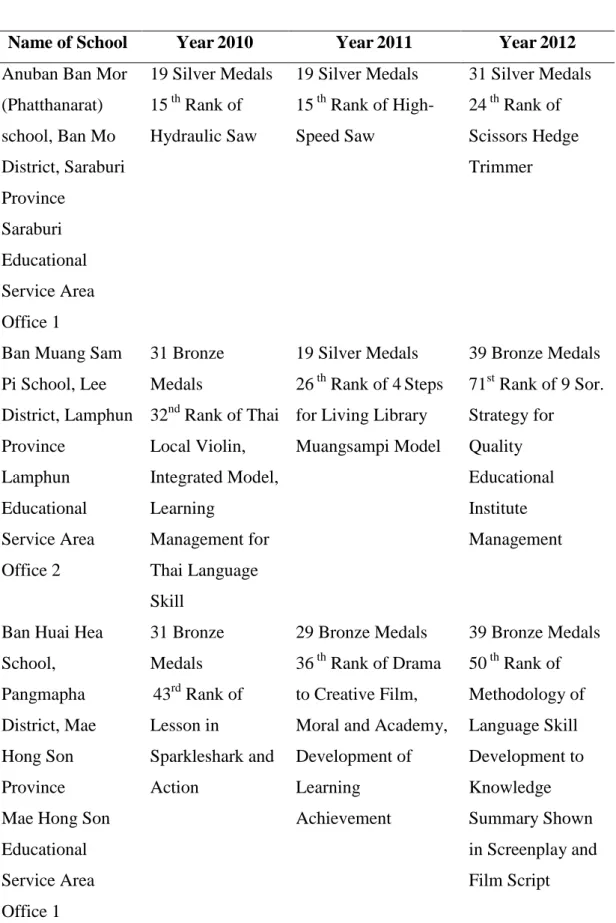
31 Silver Medals 29th Ranking of Flood Crisis Management through Natural Approach, Sathya Sai School, Lopburi Province. 29 bronze medals 36th ranking of drama for creative film, morality and academy, development of learning.
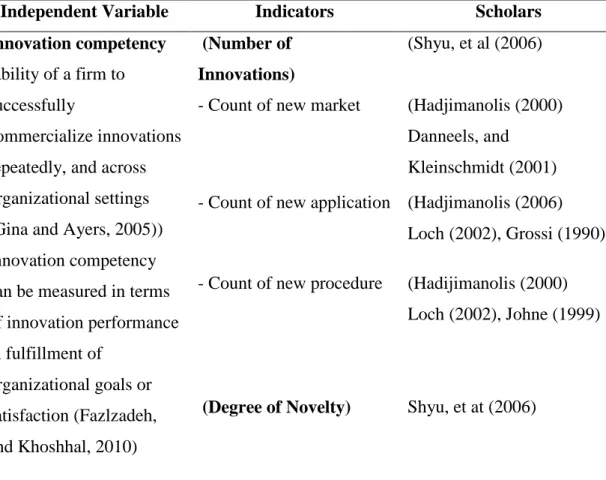
Measurement and Operational Definition
- Innovation Competency (Dependent Variable)
- Factors affecting Innovation Competency (Independent Variables) According to the research framework, there are 4 independent variables
- Table of Operational Definition and Measurement of Variables According to the previous section, the scholars’ perspectives of variables
Such satisfaction can be supported by the level of satisfaction of the organization's stakeholders with the quality of innovation. As discussed by Bollinger and Smith (2001), innovation depends on efficient management of organizational knowledge.
Data Analysis
- Quantitative Data Analysis
- Qualitative Data Analysis
In data analysis for the quantitative research method, data is obtained through the analysis of causal relationships of independent variables that influence the innovation competence of primary schools. Furthermore, data obtained from open-ended questions and suggestions from interviews can be used to support innovation competency approaches developed from the quantitative data analysis.
Conclusion
The results are used in the development of approaches for innovative competences in other primary schools, which can fulfill the third research objective. Such data can be used to create proposals and approaches for the development of innovative competence in primary education, which corresponds to the third research objective.
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH RESULTS
Analysis for the Data Collected from Participating Schools
- Basic Information and Innovation Competency of Each Selected Schools
The school buildings were located on the south and on the side of Tri Thong Road. The school offers education from kindergarten to primary school with eight classrooms and other activity rooms including a computer room, Dharma intellectual room (music and dance).