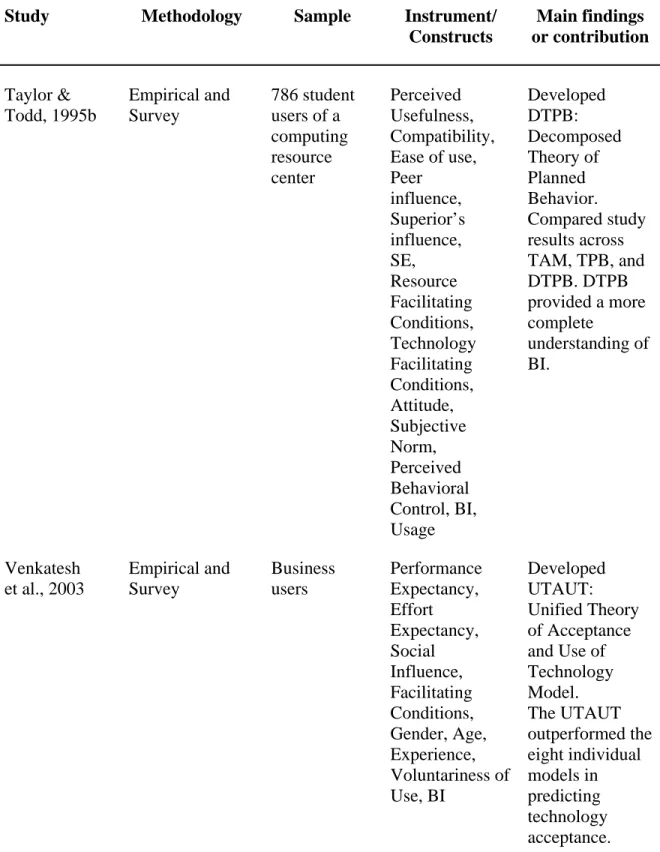
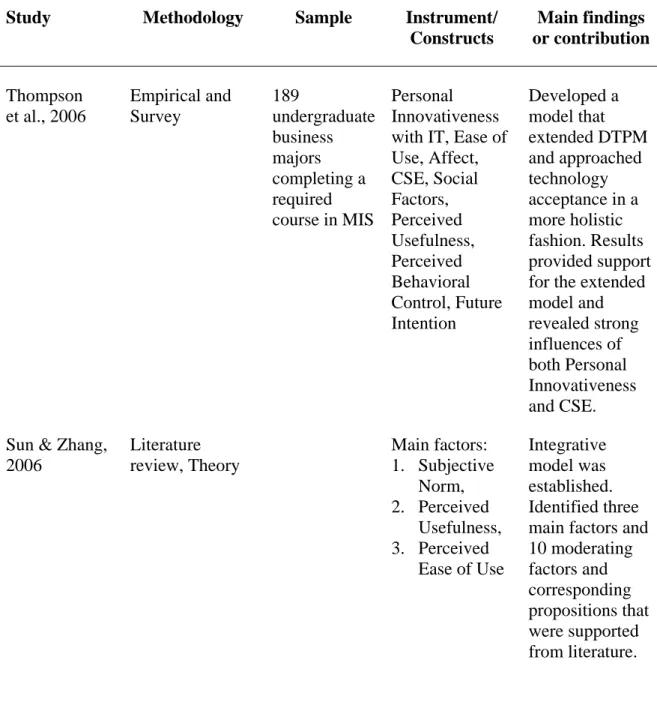
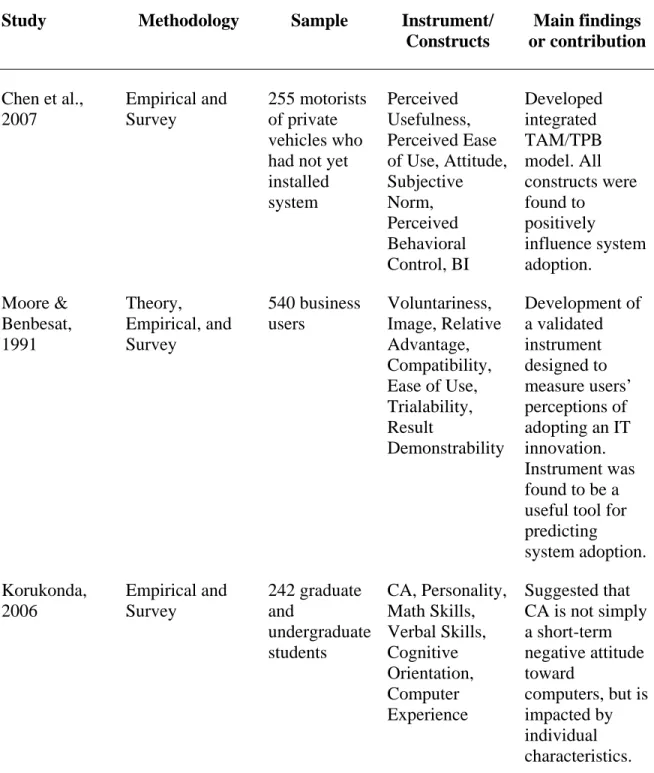
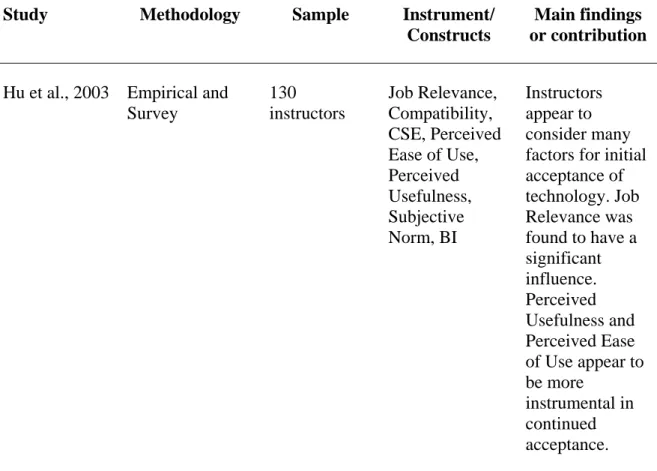
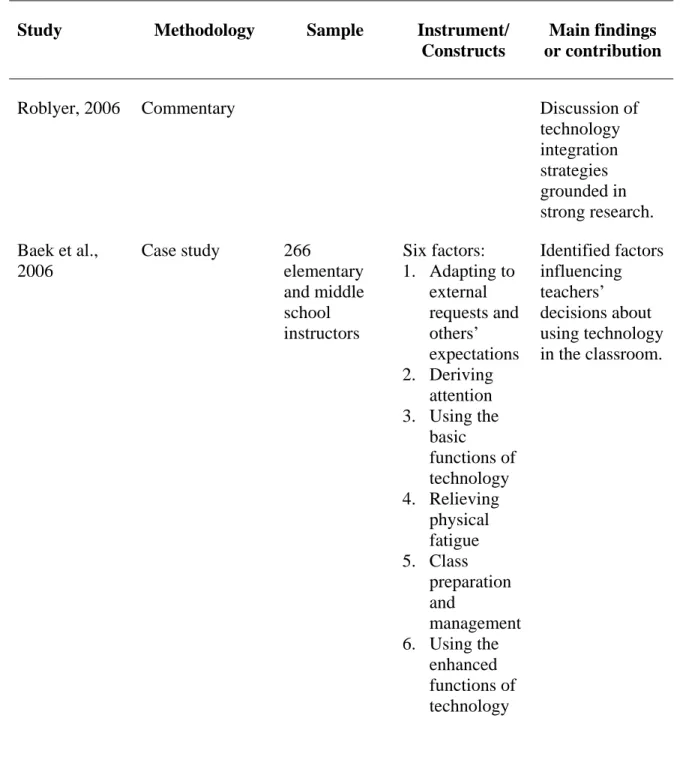
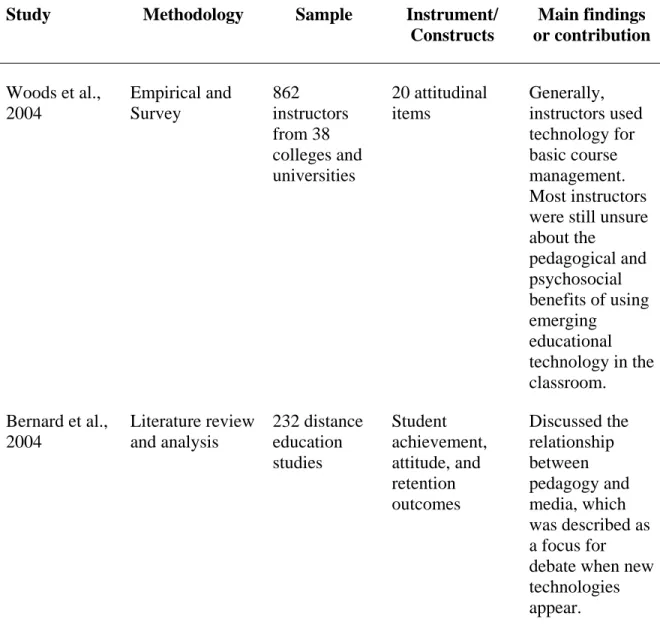
CSE, CA, and EUT were predicted to have a significant impact on instructors' . intention to use emerging educational technology in the classroom. Results showed overall significant models of the three aforementioned factors in predicting instructors' . use of emerging educational technology in traditional classrooms. In addition, results showed that CSE was a significant predictor of the use of emerging educational technology in the classroom, while CA and EUT were not found to be significant predictors.
Walker (2005) suggested that, despite the many benefits noted by researchers such as Hiltz and Turoff (2005), Wozney et al. 2006), as well as Debevec, Shih, and Kashyap (2006), a significant number of higher education instructors still do not integrate emerging educational technology into the classroom. To what extent does EUT contribute to instructors' intention to use emerging educational technology in traditional classrooms, as measured by the weight of EUT's contribution to the prediction of BI. Which construct from the three independent variables (CSE, CA or EUT) makes the most significant contribution to instructors' intention to use (i.e. BI) emerging educational technology in traditional classrooms.
The second specific aim of this study was to empirically assess instructors' GR and its contribution to their intention to use emerging educational technology in. The third specific aim of this study was to empirically assess instructors' EUT and its contribution to their intention to use emerging educational technology in traditional. Thus, the significance of this study is that it examined key constructs that contribute to instructors' intention to use emerging educational technology in the classroom.
While the use of emerging educational technology in the classroom has increased in recent years, the adoption and use of technology remains problematic. Personal use of computers outside the classroom was found to be the most important predictor of teacher use of emerging educational technology in the classroom. The contribution of this study is that it has expanded technology adoption research related to CSE, CA, and EUT as it applies to instructors' intent to use emerging instructional technology in traditional classrooms.
Methodology
Cassidy and Eachus found the correlations to be significant, demonstrating the validity of the constructs. Cronbach's Alpha reliability coefficients were calculated for each of the four scales using the actual data collected. The only change made was in the names of the specific technologies investigated.
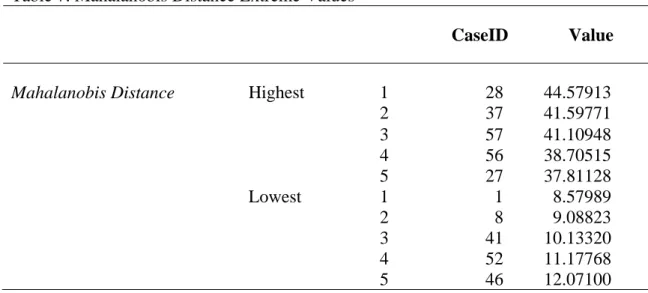
Demographic data was collected from the participants in order to determine whether the sample is representative of the population. The first reason for pre-analysis data screening is to ensure the accuracy of the data collected. The coefficients of the independent variables were compared to determine which independent variable (CSE, CA or EUT) had the most significant contribution to the dependent variable (BI).
Maximum likelihood estimation provided estimates for each of the independent variables (CSE, CA, and EUT) to predict the likelihood of BI. These estimates were used to calculate the probability that the dependent variable would occur or not. The Wald statistic was used to determine whether any of the three independent variables were significant.
The logistic coefficients of the independent variables were compared to determine which independent variable (CSE, CA, or EUT) had the most significant contribution to the dependent variable (BI). The likelihood ratio test was used to test the statistical significance of each coefficient in the model and the overall fit of the logistic model. Chapter three provided a discussion of the methodology and research design used to conduct this study.
This discussion provided specific steps that were taken to ensure that the results of the present study were reliable and valid. The first issue discussed was data screening prior to analysis, which was used to ensure the accuracy of the data collected. The chapter concluded with a discussion of the resources needed to conduct the present study.
Results
To provide useful and accurate answers to the research questions, the sample used must be representative of the population (Sekaran, 2003). To determine the representativeness of the sample, demographic information was obtained from the survey participants. The distribution of the collected data appears to be representative of the university's teaching population.
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was performed to analyze the data to ensure that the distribution of the data conformed to a normal distribution. Multiple linear regression (MLR) was used to develop a predictive model to measure the contribution of CSE, CA, and EUT to instructors' intention to use emerging educational technology in traditional classrooms, as measured by the weight of the combined contribution of the three independent variables to the prediction of BI. The purpose of this chapter was to provide the results of all analyzes performed and the results of the four research questions.
Before each statistical analysis, pre-analysis data screening was performed to ensure accuracy. The distribution of data collected appeared to be representative of the population of instructors at the university. The response rate was approximately 53%, with the sample appearing to be normally distributed and representative of the population.
In the current study, 50% of instructors with higher EUT levels had also taught for over 10 years. The fourth research question was: Which construct of the three independent variables (CSE, CA, or EUT) makes the most significant contribution to instructors. Evidence from the MLR and OLR analyzes indicated that CSE made the only significant contribution of the three independent variables investigated in this study.
CA has also been identified as a barrier for instructors in integrating emerging educational technology into educational programs and, according to Yang et al. 1999), is one of the main reasons for instructors' limited acceptance of technology. Results showed overall significant patterns of the three aforementioned factors in predicting instructors' use of emerging educational technology in traditional classrooms. Additionally, results indicated that CSE was a significant predictor of emerging educational technology use in the classroom, while CA and EUT were not.
APPENDIX A Survey Instrument
Please indicate your level of experience with the following technologies, from one to five, with one indicating "None" and five indicating "Extensive."
APPENDIX B IRB Approval Letter
APPENDIX C
Time flies when you're having fun: Cognitive absorption and beliefs about information technology use. Research report: The evolving relationship between general and computer-specific self-efficacy - an empirical assessment. Development of the Computer User Self-Efficacy Scale (CUSE): Investigating the relationship between computer self-efficacy, gender, and experience with computers.
Predicting electronic toll collection service adoption: An integration of the technology acceptance model and the theory of planned behavior. Effects of web design instruction on preservice teachers' computer self-efficacy and correlates. Computer gaming and anxiety: Positive and negative mediators of system experience effects on perceived ease of use.
Differences that matter: A dialectical analysis of individual characteristics and personality dimensions contributing to computer anxiety. Determinants of perceived ease of use: Integrating control, intrinsic motivation, and emotion into the technology acceptance model. Predicting the use of web-based information systems - self-efficacy, enjoyment, learning goal orientation, and the technology acceptance model.