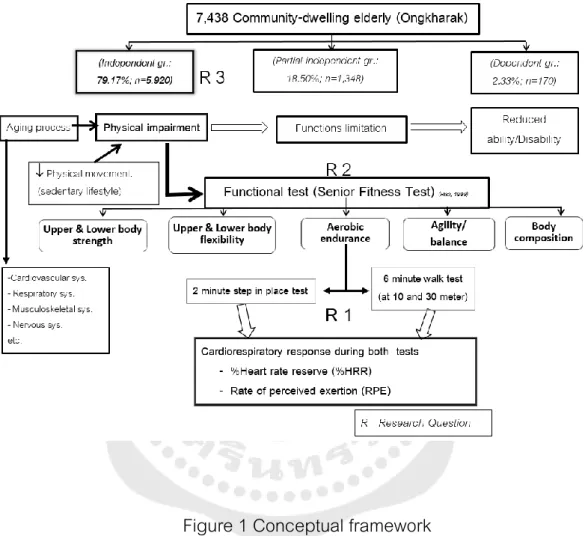
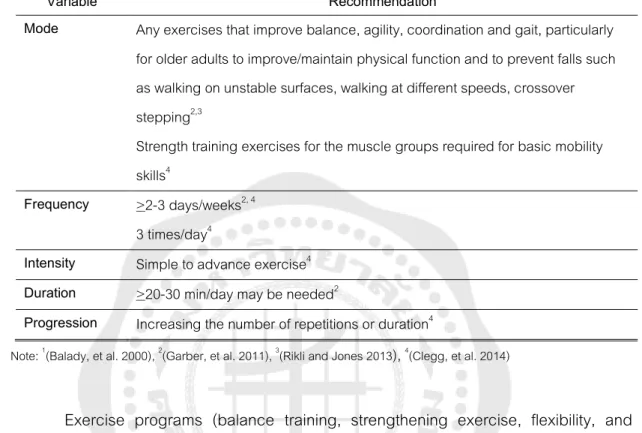
INTRODUCTION
REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
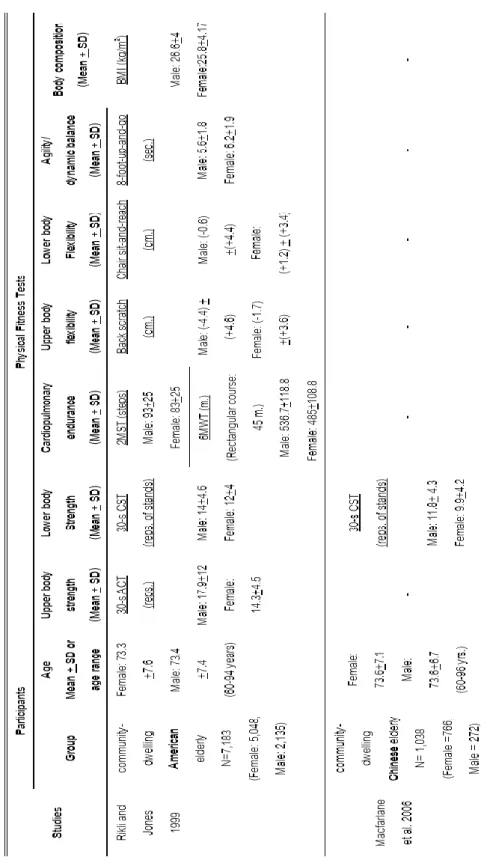
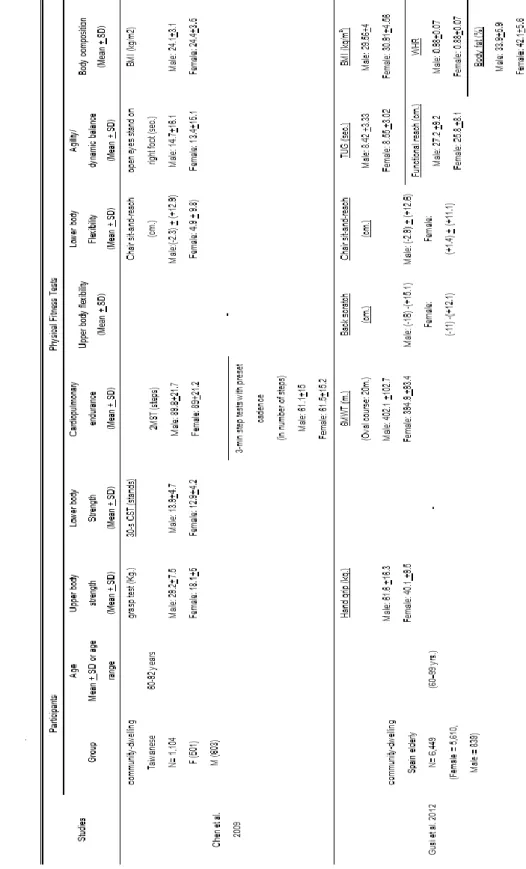
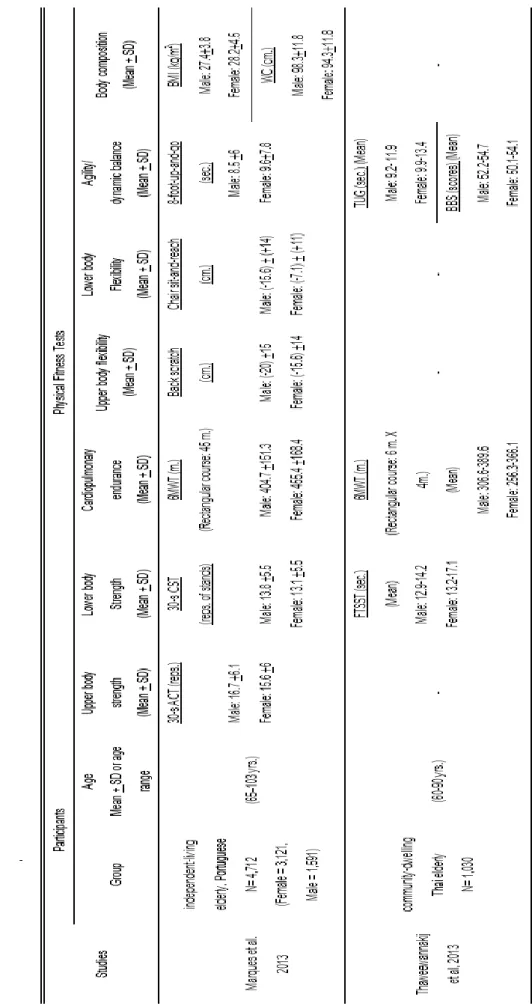
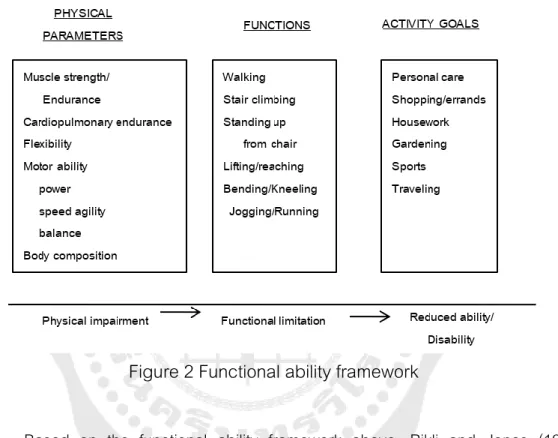
The reductions in age-related physical fitness are often attributed to the decline in body system functions, the increased comorbidity and the sedentary lifestyle. Cardiopulmonary endurance depends on the functional state of the skeletal muscles, the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. These six studies of normative physical fitness level showed that all components of fitness level decline with aging (Table 3).
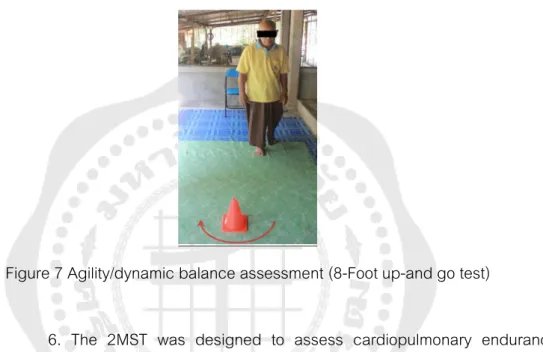
However, the Portuguese population performed better than Americans on the agility/dynamic balance (8-foot up and go test). A study was conducted for the Thai population, but it did not cover all normative parameters of physical fitness. The data of the tested parameters (6MWT and time up and go test) showed that the Thai population performed worse than the American one.
METHODOLOGY
The sample size of the elderly from this phase II was calculated by the following equation (Stratified random sampling) (106); So from this formula, sample size of each of the elderly in 11 Tambon in the Amphoe Ongkharak is (9) (Table 8). The inclusion and exclusion criteria of the present study were the same in phase II.
From the above calculation, the sample size in the present study is 30 participants in each group. The data were presented using mean +SD. The details of statistical analysis results are presented in Appendix. The test-retest reliability of the adapted senior fitness test Thai version found a high test-retest reliability.
The results found in this study were accepted and show a moderate correlation. Heart rate reserve percentage is used to show exercise intensity because it has shown a high correlation with VO2 max. (120) An advantage of using %HRR in this study was its suitability for community field testing. This exercise program is designed to suit each individual based on the fitness level of the elderly. In addition, Matsuda et al studied the effect of participation in a 6-week home exercise program on physical fitness in frail elderly.
Dynamic balance as measured by the 8-foot stand up and walk test in this study was also improved in the exercise group. training program on physical fitness in frail elderly people. The individualized home-based progressive exercise program used in this study is safe and easy to perform.
32
Research design
Participants
The sample size of community-dwelling elderly in a correlational study was calculated using the following equation (101).
Outcome Measures
Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, height, weight, percent oxygen saturation, chronic disease (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia) and BMI were measured for each participant.
Material and research tools
Procedure
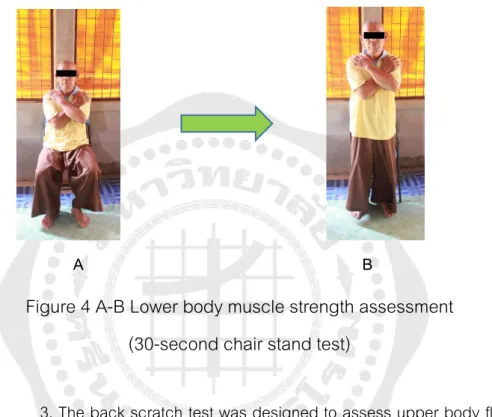
Participants were asked to do as many bicep curls as possible in 30 seconds, using a 5-pound dumbbell for women and an 8-pound dumbbell for men. Participants were asked to sit in a chair with their arms crossed over their chest and were encouraged to do as many standing postures as possible in 30 seconds. Participants were asked to sit on the edge of a chair with the left knee bent at 90o and the left foot flat on the floor, keeping the right knee straight and the right leg extended forward.
Participants were asked to stand in place and raise the knee to a height halfway between the hip bone and the knee cap. Scoring was based on the total number of times the right knee reached the appropriate height within 2 minutes. Participants were instructed to walk as fast as possible in 6 min to cover as much ground as possible.
Exercise heart rate (HR exs) is heart rate averaged at 5 minutes and at 6 minutes for 6MWT, and at 1 minute and 2 minutes for 2MWT steady state heart rate (steady state heart rate is two heart beats within 5 beats/min. ) (104) . After the test, the participants were measured for BP, RPE, HR and total walking distance (7). Participants were asked to step into position while raising their knees to a height halfway between the hip bone and the knee cap.
Scoring was based on the total number of times the right knee reached the correct height. After the test, participants were measured for BP, RPE, HR, and the total number of times the right knee reached the correct height.
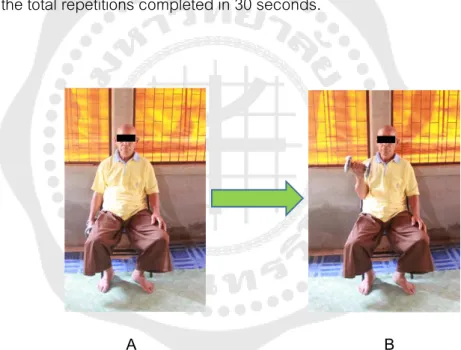
Data Analysis
One way of repeated measures ANOVA was to determine the difference between groups in the performance of physical fitness tests and pre-post tests. RPE was used in this study to determine exercise intensity, which can be subjective. Therefore, a modified Thai version of the Physical Fitness Test for the Elderly can be used in Thai elderly.
The progressive exercise program prescribed in the current study included resistance exercises, cardiopulmonary endurance exercises, flexibility exercises and balance exercises. These results of strength are consistent with the results found by Matsuda et al., who studied the effect of participation in a 6-week home exercise program on the physical fitness of frail elderly people. In addition, Thiamwong et al studied the effect of a 12-week home-based balance training on balance capacity in the elderly.
The results of improved lower limb flexibility in the current study were consistent with other studies investigating the effect of engaging in a 12-week home tele-training exercise on physical performance in older adults. The dropout rate in the current study was lower in the exercise groups (16.2%) than the control group (25%). Also, studies in the elderly should be conducted in other age groups (>69 years).
The 2MST could be used to assess cardiopulmonary endurance in the elderly, similar to the 6MWT. Association of body mass index and weight change with all-cause mortality in the elderly.
44
Outcome measures
49
Materials and research tools
Progressive upper-body resistance training includes wall push-ups and lower-body sit-ups. Wall push exercise (exercise to improve lower body strength) (Fig. 12): The participant faced the wall; the distance from the wall was equal to the length of the straight arm. The participant bent the arm and slowly moved towards the wall and pushed the body away from the wall (6).
The participant slowly sat down on the chair and brought both arms forward to balance the movement (6). The participant stood next to a chair with feet shoulder-width apart while holding the chair for safety. The timing of marching exercise started at 20 minutes per day for the first 2 weeks(104), and the duration was increased by 5 minutes at 2-week intervals(111).
This marching exercise can be performed continuously or as two sets for the allotted time per day based on the perceived exertion rating < 5-6/10, indicating that the participants can still talk during the exercise (110). exercise to improve cardiopulmonary endurance). The flexibility exercise for the upper body was the shoulder and upper arm extension and for the lower body the standing calf extension (6). Shoulder and Upper Arm Stretch (Exercise to Improve Upper Body Flexibility) (Fig. 15): The participant stood with feet shoulder width apart and held the towel behind the back with both hands (6).
Standing calf stretch exercise (exercise to improve lower body flexibility) (Fig. 16): The participant faced the wall and stood with a straight arm away from the wall. The participant then stepped forward and bent the knee down against the wall while keeping the other leg straight and the foot on the floor.

FINDINGS
The percent heart rate reserve and dyspnea level responses to 2MST
Test retest-reliability of modified senior fitness test Thai-version
Reliability and validity of 2MST and 6MWT
The RPE mean of 2MST had low correlation with 6MWT-30m, both during test and post-test. In addition, RPR of 2MST and 6MWT-10m had low positive correlation with 6MWT-30m, both during test and post-test (Figure 20).
Effect of 8 weeks individualized home-based exercise program in
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
Sitting and chair reaching scores, which measure lower body flexibility, were higher than in the previous study. However, in this study, the participants lived in the community, and more than 60% of the participants reported no physical activity other than daily living tasks. Locks et al demonstrated improved performance in the 6MWT and the five-time chair stand test in the elderly following a 6-week twice-weekly resistance exercise program (138).
Progressive marching exercise used in the present study was a simple. cardiopulmonary exercise was therefore easy for the elderly to perform 3 times a week and could improve cardiopulmonary endurance after only 4 weeks. However, the incorporation of functional training exercises such as marching exercises in the present study may add beneficial effects on activities of daily living performance. Improvement of balance found in the present study can consist of both static and dynamic balance training components.
In this study, lower limb mobility increased as measured by the sit and reach test in the elderly at 4 and 8 weeks, whereas there was no significant improvement in upper limb mobility. A low dropout rate of 20% in the exercise group indicated that the exercise program was acceptable for 8 weeks (148). Follow-up every 2 weeks by home visit or by telephone, as was done in this study, was useful because this study was useful.
Simple individualized progressive exercise prescription as implemented in the present study would increase functional capacity in the elderly and could be implemented as part of home health promotion and prevention program. Future research should explore the effect of home-based individualized progressive exercise programs on quality of life, maximal oxygen consumption, and long-term follow-up after exercise in older adults. Reference values of physical performance in well-functioning, community-dwelling Thai elderly.
A community-based study to assess the test-retest reliability of the Elderly Physical Fitness Test in a geriatric population in a northeastern Indian city.