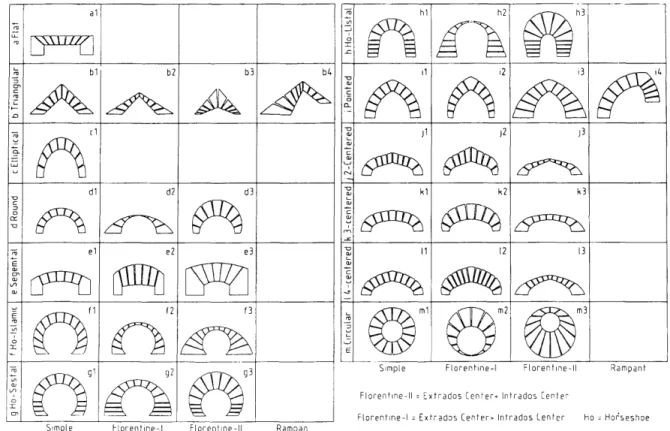
Improving the final quality of the arch design by providing many alternatives to a single design. Triangular arch: (Fig.2-b1) An arch whose intrados is composed of two oblique lines that meet at the upper point of the arch. It is the most basic type of bows from which the definition of the bow was derived.
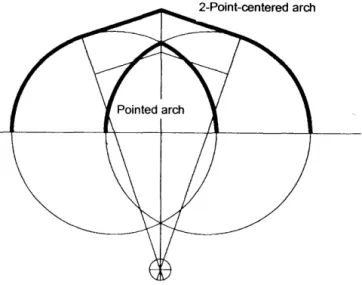
Each of the two radii of these circles is greater than half the distance between their centers. There are also some examples of the use of the pointed arch on elevations in pre-Islamic times (for example at Qasr Ibn Wardan - about 50 miles north-east of Homs - built between 561-564), but its development and extensive use was during the Umayyad period of architecture in cases, such as Qusayr 'Amra (712-15) and Hammam as-Sarakh (725-30) and many other examples [7, pI 02-1 03]. Two-centered arch: (Fig. 2-jl) an arch whose intrados consists of four parts: two arcs enclosing two lines, each of which is tangent to one of the two arcs.
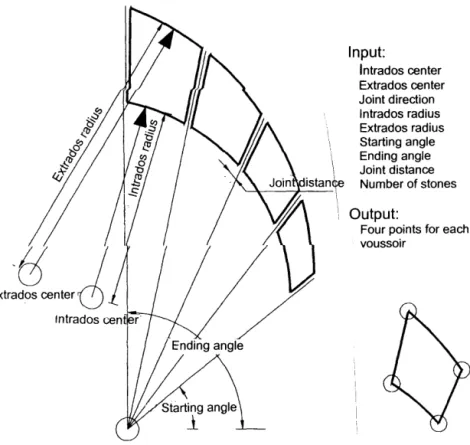
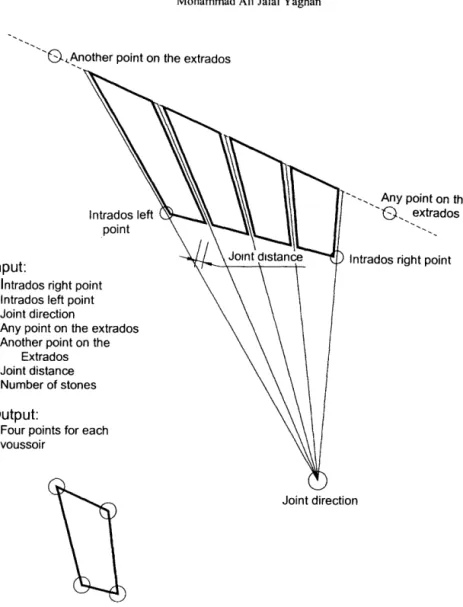
Shifting the two centers results in a completely different visual effect for the bow. To achieve a simple arc shape, the new variable (joint direction point) would coincide with the center point. Each section consists of two parallel lines representing half of the intrados and extrados of the arch, creating flat stones with joints directed to some point.
It must define the intersection points of these arcs and draw the stone according to these, as well as the joint direction and the locations of the centers.

Special (singular) parts
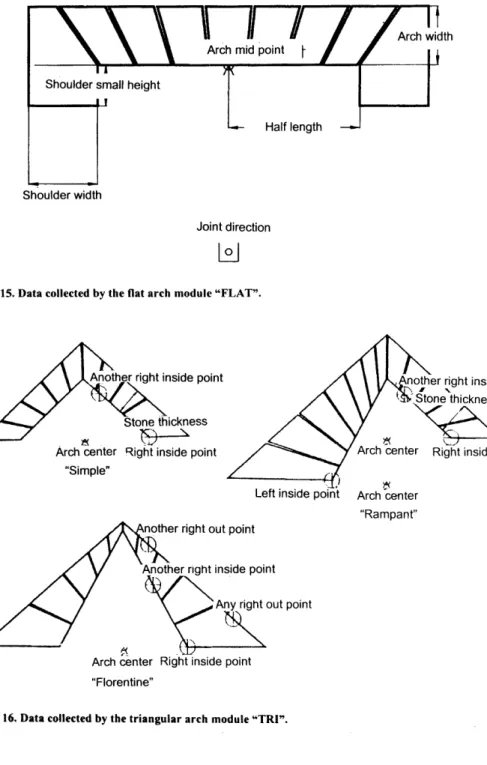
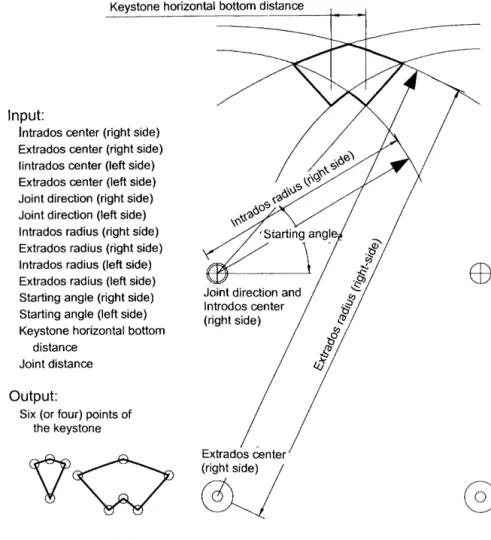
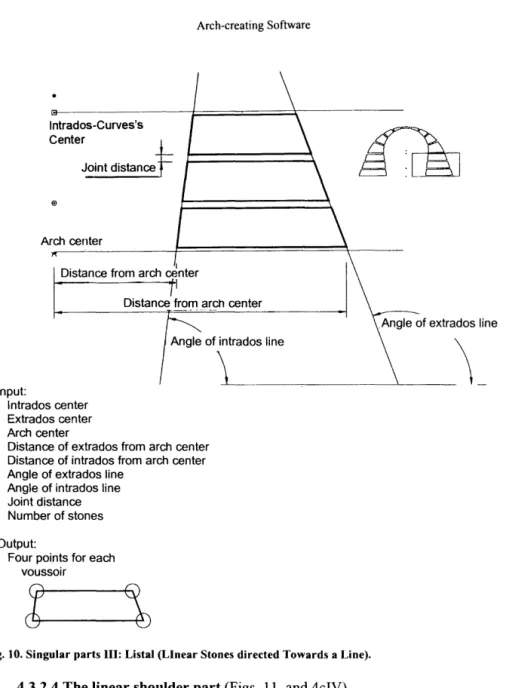
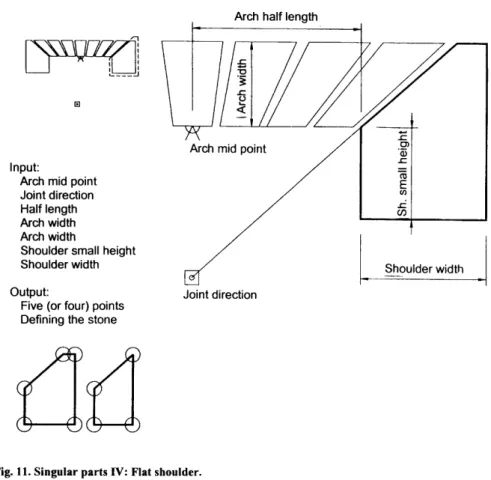
To apply the Florentine concept to this part so that it coincides with the previous modules, the middle of the extrados must be added to its list of entries (Figures 7 and 4dIII). The distance of the extrados from the center of the arch. The distance of the intrados from the center of the arch. The angle of the lines of the extrados. The input to the function will be the midpoint of the intrados, the direction of the joint, half the length of the arch, its width, the height of the shoulder from the inside and the width of the shoulders.
The result will be five (in some cases four, see Figure 11) points that describe the shoulder stone. It can be one of three shapes, depending on the shape of its upper line: a curve (continues the extrada), a straight line (similar to a linear shoulder), or without it (see Figure 12). The input to the function will be the midpoint of the arch, the intrados and extrados centers and radii, the direction of the joint, the internal height of the shoulder, and the type of shoulder (linear or straight).
To apply this concept to the arch design, no modifications to the functions described above are necessary; but in every arc where this concept applies (ie the pointed and the triangular arcs with their variations), the arc would not have a single set of variables applied to its two sides. Instead, there will be two sets of variables, one for each side (see Figs. 2-b4, and 2-i4). In addition to the special variables of each type and subtype of bows, there are some variables common to all.
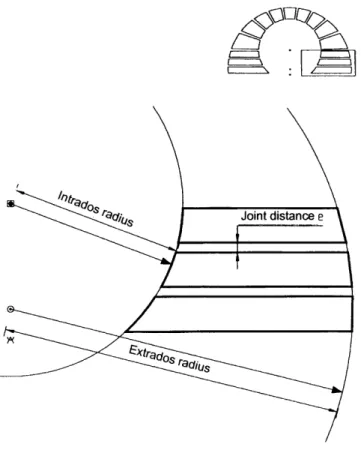
The effect it gives the bow can vary from unity (when equal to one) to extreme fragmentation. Joint Distance: Although the joint distance for a common bow varies from 1 to 2 cm, this variable can be used for modem decorative bows where it can be enlarged to exceed the width of the stones, giving different effects and sensations. The relationship between intrados and extrados (or the width of the stone): A very important variable that affects the durability and load-transfer capability of an arch.
An example of how each of these variables can affect the final output can be seen in Fig. The simplest round arch was taken as an example and in each case only one variable was changed and the other two fixed.

Module Design
I ELLIP I
It will not suffice to provide some drawing facilities along with the program and the more complex the additional features, the greater the load on the original program. Accordingly, there is a need for an environment that provides capabilities to draw the other necessary parts and allows the arch-creating program to operate in a compatible manner within its constraints. Contact the author at myagham@hotmai1.com myagham@ksu.edu.sa or the department address to obtain a copy of the archive creation software.
Once the command has been initiated, a series of questions are asked, and the answer to them can be a mixture of the previous four methods. Thus, the an commands can be accessed from the command line or any of the various menus. After the command sequence (representing an arc type) completes, the program returns control to AutoCAD.
This mechanism is required and cannot be implemented by AutoCAD's scale command. Purely scaling an arc will cause each facet of the arc to scale in a proportional manner. The ASCII save capability allows the user to recall any saved arc and place it within the drawing according to the current joint distance defined by the user. The command sequence shown in the figure is the sequence that appears when using the standard AutoCAD "command line".
He can enter any value, even if he does not understand the meaning of the prompt, because the program will check the validity of the data and ask f(. 26, the sequence of the prompts is very similar to the normal AutoCAD command. the arc lost its structural importance in architecture, it is still a valuable element in the formal body position.
Second, it broke up the bow types into parts, defying the parts common to more than one type and those restricted to a single type. The language of the program was chosen to be AutoLISP (the programming language of AutoCAD software). This choice was based on the nature of the arc which is not a fmal output in itself, but it is usually part of an elevation, and AutoCAD provides the ability to produce all other elements without using it as a burden on the arch to have software if it were to be a stand-alone package.
A user manual (from which some of the drawings of this paper are taken) has been prepared, and the program can be easily used by professionals, educators and students. A three-dimensional version of the porgram, to which more arc types can be added, will be the next step in the line of this research.