The paper-based version provides a more in-depth explanation of the concepts, while the computer version relies more on visual intuition. The paper-based version provides a more in-depth explanation of the concepts, while the computer version relies more on visual intuition.
The e-Bank balance sheet is a picture of the company at a certain date, which shows you the sources of funds (liabilities and shareholders' equity) and the use of funds (assets). A large part of the funds are deposits collected from customers and/or money borrowed from other banks.
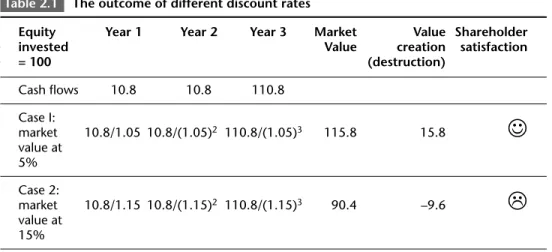
The cost of equity capital is the exchange rate used by the stock market to calculate the value of bank shares. The difference between the market value of the shares and the equity investment is called value creation.
Reading the income statement shows that profit after tax is the result of income from assets, cost of funds, level of operating expenses and corporate taxes. It is defined as the ratio of operating expenses divided by gross income (interest income plus fees minus interest expenses).
With these profit and equity allocations, we can calculate the return on equity for a specific profit center. Referring to step two, the golden rule of value creation requires that the RAROC of a profit center be greater than the cost of equity in e-Bank, the opportunity for returns available to investors in the financial markets.
Deposit and loan units will try to increase the net interest margin on deposits and loans. The net interest margin of a branch is the sum of the margin on deposits and the margin on loans.
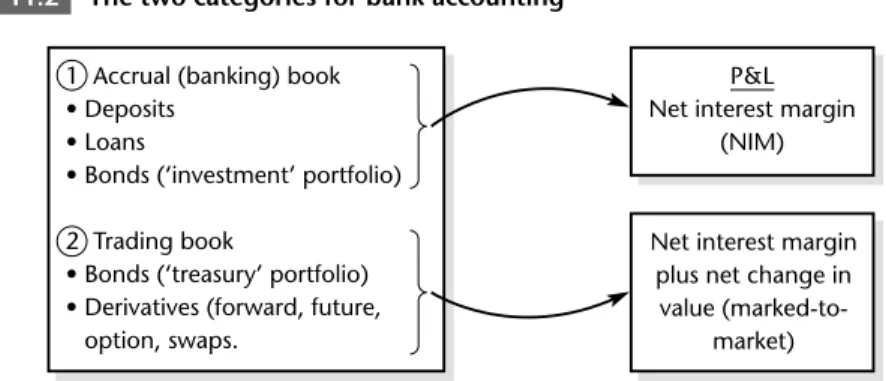
As discussed in Step 1, some bank transactions are off-balance sheet because, at their inception, they do not affect the asset or liability. Credit risk is the potential cost of the contract when the counterparty defaults.
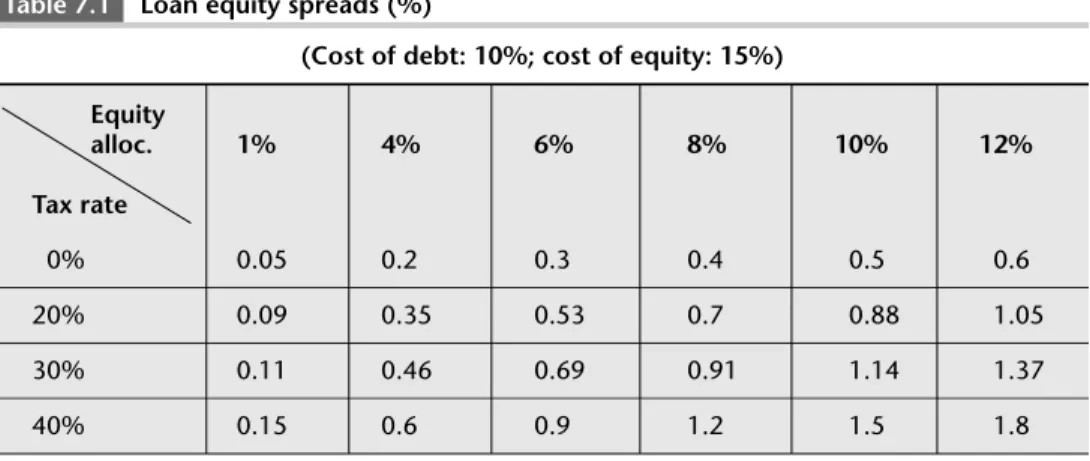
The discount rate R of 11.2% means that the present value of the loan transaction is exactly equal to 8, which is the capital invested by the shareholders. For example, the case discussed above of 8% equity with a tax rate of 40% leads to the required 'equity' spread of 1.2%. If you can convince your CFO that the credit risk is low and that 1% of equity is needed, you'll notice that the required 'equity' margin drops to 15 basis points (0.15%).
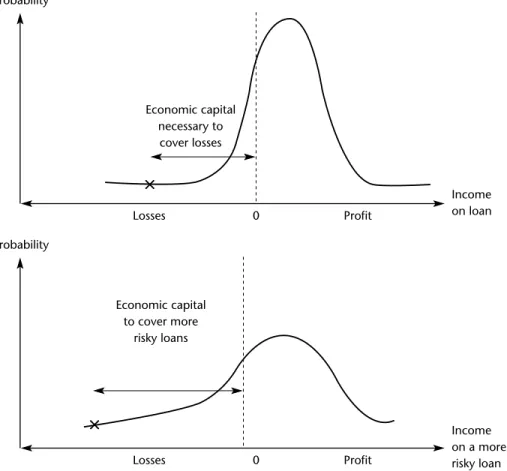
The breakeven rate on a loan is the rate at which there is no value creation. Economic capital is the capital needed to cover potential loan losses (also referred to as risk-based capital). Calculate the bottom line loan rate and the 'equity' spread on a $100 loan from one year to maturity.
At the end of the first year, when the loan interest rate is paid, should e-Bank recognize the interest received as full income, or should the bank create a provision for credit risk for potential future losses. If the interest income earned on the loan at the end of the first year was considered a profit, there would be great incentives for lenders to make high-margin (and often high-risk) long-maturity loans with the goal of showing a very large profit in the early years. If this lending strategy was good for the loan manager's year-end performance and bonus, it could hurt the bank in the future when loan losses show up.
So a loan department's profit should include the net interest margin received plus any change in the net value of the loan (loans minus debt). This exercise concerns a loan with two years to maturity. today it is about deciding whether a loan proposal creates value for the bank;. a year later, an interest margin has been earned and the question is how much profit should accrue to the loan department. At the end of the first year, the loan department has obtained an interest margin on the loan and has a loan and a debt with one more year to maturity.
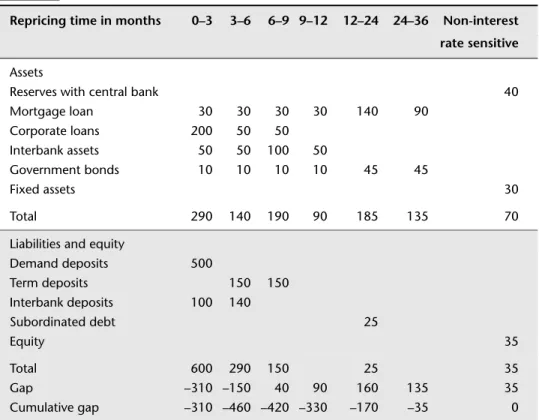
Those who cannot remember the past are doomed to repeat it.” A bank's management must be informed of the impact of a rare large change in interest rates on the bank's net interest margin. 1 With regard to the net interest margin for the coming quarter (0-3 months): will it improve if interest rates rise? 2 Regarding the net interest margin of the second quarter (3-6 months), will it improve if interest rates rise?
To measure the risk, the bank must choose a relevant interest rate change that covers most cases. The second measure of interest rate risk looks at the impact of solvency and interest rates on the value of assets and deposits, that is, the value of the bank's equity. Duration is an indicator of the impact of interest rates on the value of an asset.
2. Estimate the percentage change in the value of the bank's equity if interest rates move by 2%. The methodology for managing liquidity risk is similar to that of interest rate risk management.

At the beginning of the ALM program you read the introduction and a screen with an explanation of the navigation tools. The program will show you how to navigate as the different navigation icons are presented in the introduction. Immediately after the introduction you will find a roadmap with the 17 phases of the program.
You can select the level you want to work on by clicking on it (our advice is to select them in a logical order). The program is divided into two main and distinct parts: value creation with levels from one to ten and risk management with levels from eleven to seventeen). If you click on the 'light bulb', the computer will show you how to calculate the correct answer with an animated explanation. You can print any page of the program by activating that page and then clicking the print icon.
If the interest rate rises, the net interest margin in the first quarter will decrease because the cost of funds will be higher then. This means that if the interest rate rises and stays higher, the second quarter interest margin will be affected by the repricing of deposits from the first quarter (-20), the repricing of +50 net assets into the second quarter creates a total (cumulative) gap of +30, which is important for the interest margin. If interest rates rise, second quarter net interest margin will increase because revenues will increase.
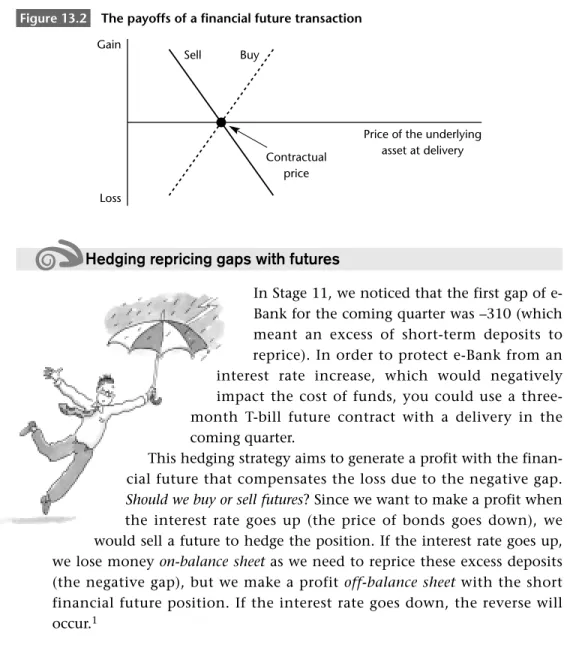
In the case of a positive spread, where the assets available for repricing are greater than the debt being repriced, an increase in interest rate levels will be good for you because the additional interest income will exceed the additional interest expense. In the case of a negative gap where the deposits to be revalued are greater than the asset being revalued, an increase in interest rate levels will be bad for you as the additional interest expense will exceed the additional interest income. One way to improve your first week's liquidity is to borrow 10,000 with a one-year maturity and buy a one-week bond.
COD: cost of debt is one of the drivers of return on equity (ROE). It is defined as total interest expenses divided by the total debt of the bank. It is often estimated as the sum of the current interest rate on risk-free government bonds plus a risk premium to recognize the riskiness of stocks.
It is defined as the sum of each year in which a cash flow is received, weighted by the relative importance of the discounted cash flows in that year. Interest rate risk: refers to the impact of an unexpected change in the interest rate on the bank's profit or on the economic value of equity capital. RWA: Risk-adjusted asset defined as the book value of assets multiplied by a weight that reflects the riskiness of the asset.
Standard Deviation: A statistical measure of the average degree of variation of a random variable from its mean value. Systemic risk: the risk that bankruptcy will cause widespread problems in the financial system as a whole. Zero Coupon Bond: A bond that pays a single payment on the maturity date of the bond.
- GENERAL
- GRANT OF LICENCE
- PROPRIETARY RIGHTS IN THE PRODUCT
- OTHER RESTRICTIONS The Licensee may not
- WARRANTY
- LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
- TERMINATION
For the purposes of this Agreement: 'the Product' means the contents of the Asset and Liability Management CD-ROM ordered by the Licensee, the .. software that enables the search and retrieval of information on the CD-ROM and the accompanying enable manuals; . This Agreement permits Licensee to use only one copy of the Product on a single computer for search and retrieval purposes. The Licensee may not copy the content or any part of the Product from the Product to a computer hard drive or any other permanent electronic storage device (except as occurs when the Licensee runs the setup/installer program or uses other features of the Product on a single computer).
For the avoidance of doubt, the Product remains the exclusive property of the Publishers at all times. The Publishers do not warrant that Licensee's use of the product will be uninterrupted or error-free. Any implied warranties on the Product are limited to 30 days from the date of receipt.