I understand that a copy of my research will be deposited in the University Library for permanent safekeeping. I understand that the British University in Dubai may make a digital copy available in the institutional repository. Essential recommendations are encapsulated to improve the quality of the IEPs in the school and set significant directions for further research to contribute to UAE perspectives.
42 Table 11: Teachers' responses to the question 'What are your recommendations to improve the quality of IEP development and implementation in the school?'.
INTRODUCTION
- Introduction
- Definitions of Key Terms
- Background and Rationale of the Study
- Study Purpose and Research Questions
- Significance of the Study
- Study Objectives
- Organisation of Chapters
The study focuses on three critical aspects: the current attitudes of teachers towards adopting and implementing IEPs, the impact of teachers' attitudes towards adopting and implementing IEPs on the inclusion of determined students in a mainstream classroom setting and their knowledge to support them effectively. and essential recommendations to improve the quality of IEP development and implementation in the school. What is the effectiveness of developing and implementing the Individual Education Plan for students with determination in a private school in Dubai and its impact on their inclusiveness in the mainstream classroom environment?'. Q4: What are the recommendations to improve the quality of IEP development and implementation in the school?
To propose significant recommendations to improve the quality of IEP development and implementation in the school.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Inclusive Education in UAE
- Understanding Individual Education Plans (IEPs)
- Characteristics of High-Quality IEP Goals
- Perception of Individual Education Plan (IEP) Process
- Teachers’ Attitudes Toward IEP
- The Influence of Teachers’ Professional Development on the Quality of IEP
- Teachers’ Challenges of Effective IEP Implementation
- Best Practice of Developing and Implementing IEPs
In summary, the IEP is the foundation of inclusive education for students with special needs (Jachova, Kovačević & Hasanbegović 2018). Therefore, each member of the IEP team must demonstrate essential experience and knowledge to develop and implement a high-quality IEP for students with special educational needs (İlik & Sarı 2017). However, when teachers use the IEP process as a key tool, they can create customized plans for students with special needs (Mereoiu, Abercrombie & Murray 2016).
Teachers play a critical role in implementing the IEP for students with special needs in the regular classroom setting (Rotter 2014).
METHODOLOGY
- Introduction
- Research Site and Access
- Data Collection Tools
- Interview
- Official and Confidential Documents
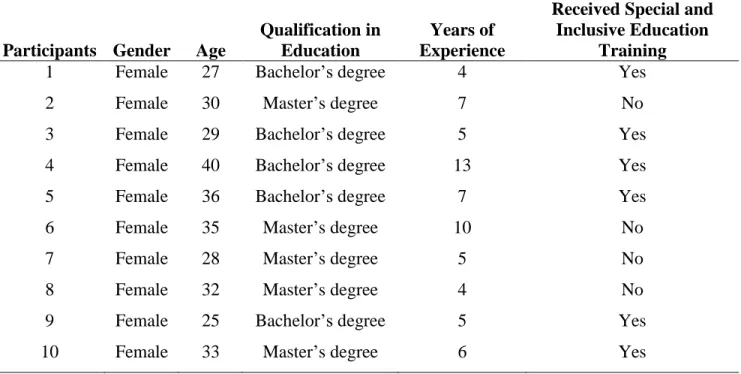
- Participants
- Data Analysis
- Semi-Structured Interviews Analysis
- Official and Confidential Documents Analysis
- Reliability and Validity
- Ethical Considerations
- Permission to Conduct the Study
- Confidentiality and Anonymity
- Consent Letter
Q3) To what extent parents participate in the development and implementation of the IEP. Q4) What are the recommendations for improving the quality of IEP development and implementation at school. The first chapter is the Introduction, dealing with the background of the study, definitions of key terms, purpose of the study and research questions, objectives of the study and an overview of the methodology the researcher followed in conducting the study. The second chapter is the literature review of previous studies related to this topic.
Chapter Four presents the findings, describes and analyzes the results of the data collected from interviews and official and confidential documents. Finally, Chapter Six provides the essential recommendations for improving the quality of the IEP development and implementation in the school, as well as the recommendations for further research. In addition to their background and knowledge of the IEP, each interview lasted ten minutes.
Q8 What are your recommendations to improve the quality of IEP development and implementation in the school. Since teachers are one of the most important elements influencing the success of inclusive education in schools, this study focused only on teachers. The second tool used for data collection was the school's inclusion policy document, which includes essential guidelines to apply inclusive education in school and the Dubai Inclusive Education Policy Framework 2017, which aims to empower service providers education, government and local regulations across Dubai. to promote inclusive education by comparing and contrasting the two documents in order to examine whether the school effectively follows and implements the guidelines provided in the framework.
Therefore, before and after data collection, the researcher must ensure the validity of the research instrument, which focuses on what can be measured and how accurately it is measured. The researcher had to complete the BUiD ethics form (Appendix A) to obtain permission to conduct the research from the university's research ethics committee to allow for the ideal conduct of the research according to the guidelines outlined in the guide.

FINDINGS
- Information of the Study Site
- Information of the Study Participants
- Official and Confidential Documents
- Dubai Inclusive Education Policy Framework
- School’s Inclusion Policy
- Individual Education Plan (IEP) and Assessments
- Interview Findings
- Evaluating Knowledge of the Individual Education Plan by Opinion of Teachers
Providing essential motivation for teachers and other support team members to improve inclusive education over a long period of time (KHDA 2017). Table 3, which refers to the confidential data of school students, summarizes the different categories of disabilities. Additionally, IEP team members are referenced in each IEP, which includes the names and signatures of the teachers who teach the student.
In addition, all of the standards covered by the assessments are documented in the IEP for each student. As a result, the development and implementation of the IEP effectively achieves its goals, which are to support student determination and make each student feel valued and welcome in the school community. Finally, the interview explored the impact of IEPs on the inclusion of determined students in the mainstream classroom.
Actually, I am a member of the IEP committee, but I don't know what my roles and responsibilities are to support the students of determination.'. It is clearly shown that 60% of the teachers were never invited to the IEP meetings throughout the academic year, which indicates a lack of communication between teachers and the. In contrast, only 3/10 of the teachers were invited to the IEP meeting, while 1/10 showed a lack of participation due to a heavy workload.
I speak weekly with the Head of Inclusion and support the teacher to discuss the progress of the student.'. The table above shows that 50% of teachers stated that parents are essential to participate in IEP meetings and play an important role in their child's progress. Involving the teachers in the process, increasing the number of learning support teachers and providing more visual and practical aids.
To inform teachers in more detail about the elements of the IEP and what is expected of the teachers.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
In addition, their participation in the IEP process was limited due to a breakdown in communication between them and the inclusion department. For example, one teacher reported that the inclusion department developed the IEP without her involvement and that she was only responsible for implementing the accommodations included in the IEP to meet the student's individualized goals, indicating a lack of understanding of her key role in setting Annual Goals IEP for her student. Due to a misunderstanding of the essential role of students in the IEP process, participants did not know whether students were participating in the IEP or not.
As a result, they are unaware of their essential duties in the IEP process and lesson planning for their students, which should be communicated to them through effective collaboration between teachers and the inclusion support team and other professionals working with determined students. In addition, the answers of the interviewed teachers regarding the participation of the parents in the IEP meetings fluctuated among themselves; most teachers said that parents should participate in the IEP meetings and play an important role in their children's progress. However, the collected data indicated that the school did not provide the teachers with the required knowledge of the IEP process, the IEP components, adaptations and curriculum adaptation and most of them depended on their personal and previous experiences to encourage the students' determination. support without their individualized goals.
The individualized support provided to students with determination to implement their individualized goals was limited due to the low number of learning support teachers and special education teachers in the school, while IEP progress monitoring was unclear and no records were found as evidence . In addition, all of the teachers recommended that the school hold regular meetings with the IEP committee to develop the IEP for each determined student and allow them to become influential members of the IEP process. Regarding the IEP structure, it has been noted that the school effectively developed the IEP template.
However, the lack of teacher training to effectively implement the interventions for students with determination affects student performance and achievement in school. Meanwhile, behaviorally, there is no evidence that the school includes social and behavioral goals in the IEP to support students with behavioral disorders, which mainly affect the inclusiveness of students' determination in the classroom.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Recommendations to Improve the Quality of IEP and Inclusive Education
Developing annual Continuing Professional Development (CPD) plans for all teachers and Learning Support Assistants (LSAs) across the school to increase their knowledge of inclusive education. i) Increase teachers' awareness of the importance of the role of the inclusion department and the collaboration between teachers and the inclusion team;. j) Ensure that all teachers receive the support they need so that inclusive approaches to teaching and learning are embedded in their practice. k) To provide all members of the IEP Committee with a signed copy of the IEP at all times as a working document. In conclusion, to achieve high standards of inclusive education best practice, schools need to understand current teachers' attitudes towards inclusion and provide ongoing professional development for new and experienced teachers about inclusion and how best to create and implement IEPs for students with determination in a regular classroom to help them succeed in life and encourage them to become influential members of society. The researcher has thus prepared a proposed action plan that must be taken into account in order to achieve the best inclusive teaching practices as a consequence of IEP development and implementation at the school (Appendix M).
Recommendations for Further Research
The relationship between teacher knowledge and skills and teacher attitudes toward students with special needs among elementary, middle, and high school teachers in rural Texas schools. The Individualized Education Plan (IEP) Process for Students with Intellectual Disabilities in Saudi Arabia: Challenges and Solutions. Accessing the Common Core Standards for Students with Learning Disabilities: Strategies for Writing Standards-Based IEP Goals.
Primary mainstream teachers' attitudes towards the inclusion of pupils with special educational needs in the private sector: A perspective from. Culturally responsive special education referrals of English learners in a rural school district: Pilot project. The Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) training program: Its effect on how inclusive education teachers perceive their competencies to design IEPs.
COVID and the Classroom: The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Special Education and Policy Implementation. Implementing children's rights: what is in the 'best interests of the child' in relation to the Individual Education Plan (IEP) process for students with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Co-teaching during teacher training periods: experiences of Finnish special education and general education teachers.