العود في Melatla و Peterla Razu Tadq ، "Emjal Sardalma" الرابع تحت Milaatla Medql Tadasher ممكن المشي في Tarlama. إنها أساسًا أساس سمك السردين ، نظرًا لظروف ذلك السردين. يساعدهم أسارد. ضع الحبل.
Background
In addition, many key stakeholders in the inclusive education sector are dissatisfied with the challenges they face (Anati 2013). While students with special needs can be included in the classroom, inclusion does not automatically mean that such students receive the right education to fulfill their potential.
Purpose and Rationale
The School for All initiative aims to promote inclusive education to better serve students with special needs. They pointed out that some stakeholders still act as "decision makers" for students with special needs.
Statement of the Problem
Families are not involved in the process and are reluctant to accept the unique needs of their children and pay for their care.
Research Questions (RQ)
Significance of Dissertation
Dissertation Structure
The concept of the 'social disability approach' (Shakespeare 2006) which underpins this research will be used as a framework for examining concerns about the effectiveness of and barriers faced in adopting inclusion policies. Conceptual and Theoretical Framework, Social Disability Approach, Inclusion in Education Global Perspectives, Inclusion Policy in UAE, Inclusion Team Members, Teachers' Attitude towards Inclusive Education, Parents' Involvement and Attitudes towards Inclusion, Professional Development and Inclusion, and School Culture Level of Inclusion.

Conceptual and Theoretical Framework
It provides students with age-appropriate activities that are tailored to the subjects and topics they are learning about. MAP: Assessments for Measuring Academic Progress (MAP) are computer-based adapted assessments given in the subjects of arithmetic, literature and verbal skills in schools.
Social Disability Approach
Inclusion in Education Global Prospective
13 However, an inclusive education system and its long-term sustainability depend on shifting the focus away from uniformity to diversity and inclusion as the primary measures of educational performance (Braunsteiner & Mariano 2014). In addition, it allows all learners to learn about and embrace human diversity, and to reduce the marginalization of disadvantaged individuals, by cultivating a school culture of mutual respect and inclusion.
Index for Inclusion
Furthermore, UAE society generally does not share this social perspective on disability, in which disability is seen as resulting from cultural barriers rather than being clinically inherent to the person. It is clear from the literature examples mentioned above, especially those related to the Middle East, that the main benefit of the index is its adaptability to contexts of different languages, cultures and academic outcomes.
Inclusion Policy in UAE
Inclusion Team Members
With the adoption of Federal Law 29/2006, the first law to protect the rights of people of determination and their inclusion in regular regular school environments, the UAE is trying to align its educational legislative framework with international standards and best practices regarding an inclusive education system (Gaad 2011). In addition, "headteachers, champion leaders, classroom teachers, teaching assistants, service managers, SEND and parents" make up the steering council for inclusive education systems, according to KHDA's (2017) policy framework four, "Supporting Inclusive Education".
Teachers’ Attitudes Towards Inclusion
Teachers are at the heart of it all, as they are expected to educate a wide range of academically diverse students. For example, compared to their elementary school peers, most middle school instructors often work with more than 125 students on a daily basis in situations in which instruction is often pedagogic, focused on large groups, and limited by the level of personal contact time. with guidance (Zigmond 1990). Furthermore, most secondary school educators are expected to be curriculum experts and are unlikely to make specific adjustments to students, such as use of alternative curricula, modified assessment/assessment, or alternative options.
In addition, many instructors today design and direct their instruction to the student, with grades calculated based on a baseline level of achievement (Schumm & Vaughn 1995).
Parents Perspective and Attitude Towards Inclusion
According to recent work by Abdat & Gaad (2022), parents expressed their fears about the limited implementation alternatives for their children's education and described their responsibilities as their children's supporters and guardians of their progress, emphasizing the need for external support. They also discovered that parents were offered minimal or no options when it came to their children's new schools. Furthermore, parents scaled up their reasoning by saying that their children's age and type of disability, such as autism, had an impact on the transition of young children to inclusive educational settings.
Furthermore, according to a 2017 UNESCO report, parents of children with special needs are often limited to only two choices: to meet the needs of their children in special education systems, or to enroll their children in the regular regular education system to ensure that they receive the same educational privileges as their peer group.
The Dubai Inclusive Educational Policy Framework
To help schools in Dubai implement the School for All project, a guide titled "Integrating Inclusive Education into the Classroom" has been created to assist them. Inclusive practices are challenging, diverse and constantly changing, depending on the educational context and community institutions, students, teachers and school officials involved in inclusive practices. This evolution is driven by the interaction between the school environment and the participants in inclusive classrooms.
Because of this, the objective should be to monitor and document the steps involved in the process of establishing the realism of inclusive education practices (Glesne 2006, p. 7). After factoring the qualitative method as the most appropriate for this specific research study, a triangulation of data collection methodologies was used to verify the reliability of its findings.
Research Design
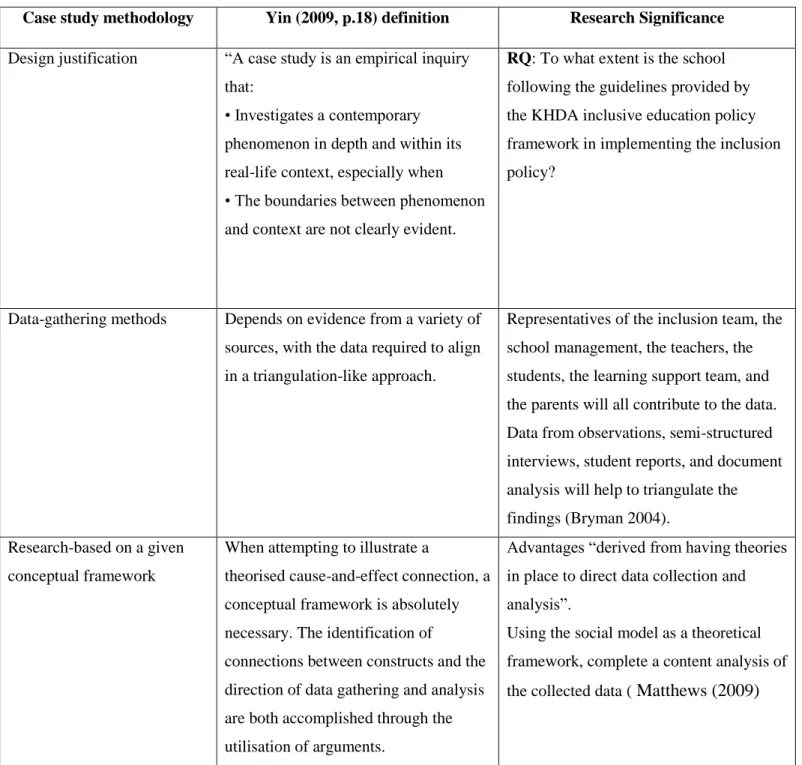
This qualitative study was motivated by the following table, which is related to the main research objectives stated in the introduction. Case study methodology Yin (2009, p. 18) definition Research significance Design rationale “A case study is an empirical investigation. RQ: To what extent does the school follow the guidelines of the KHDA inclusive education policy framework when implementing the inclusion policy.
Data collection methods Rely on evidence from a variety of sources, with data needed to be reconciled in a triangulation-like approach. Representatives of the inclusion team, school management, teachers, students, learning support team and parents will contribute to the data.
Site Selection
In the UAE, researchers have previously studied the educational experiences of students with disabilities (Alghazo & Gaad 2004; Arif & Gaad 2008). Equity and diversity” was ensured in the participant screening and application procedures used in the school (Yazan 2015).
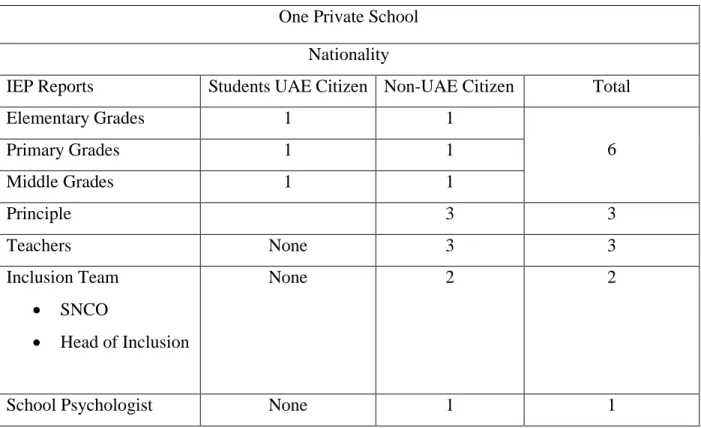
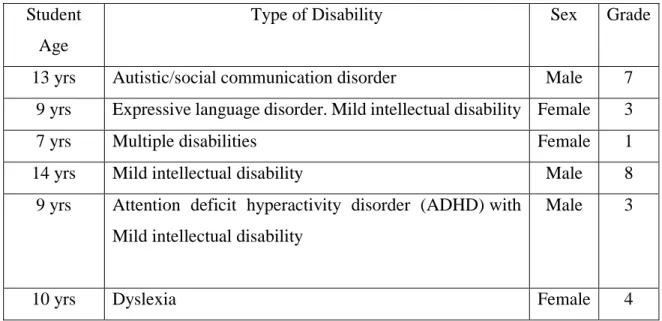
Study Participants
Ethical Consideration
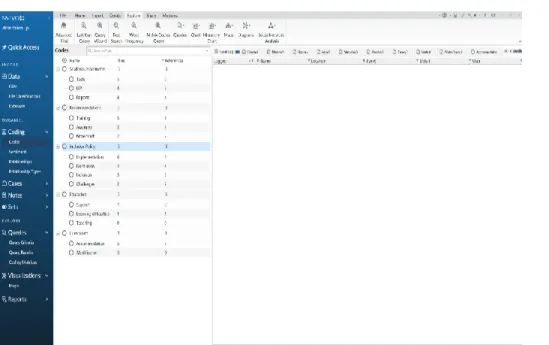
Data Collection Method Analysis
After the approval of the research project proposal, the design, preparation and pilot testing of the instruments were carried out to increase the reliability of these instruments. As a result, this researcher was able to single out one school that met the site selection criteria, allowing the instrument recommendations to be piloted and providing direct knowledge of the application of the inclusive standards that were the subject of this research. After the pilot survey, data collection began by obtaining letters of consent from each school's administrative staff.
The school agreed to receive participants' consent and the aims of this study were clarified before the observation or interview. The school was visited every day for four weeks of the study period, during which a total of 25 interviews and 10 observation sessions were conducted, and school teachers' qualifications such as student IEPs, homework, teacher forms, SEND lesson plans were collected.
Semi-structured Interview
Pilot Study
Role of Researcher
- First Theme: Effectives of Inclusion Policy Implementation
- Second Theme: Identifying Students with Special Educational Needs
- Third Theme: Monitoring and Following Up on SEND Progress
- Fourth Theme: Curricula Modification
The analysis of the documents showed that the school follows the relevant KHDA framework requirements in its implementation of the MoE's inclusion policy. They also constantly adjust and adapt the academic goals of the classroom to the individuality of the students enrolled. All the procedures used by the school were adapted from KHDA's inclusive framework through the involvement of the principal and inclusion manager at the school.
The school adheres to the standards from the KHDA framework throughout the enrollment process to identify the children who have special needs and construct the IEP through the first two weeks after admission (KHDA 2017). The results of this study conducted to assess the effectiveness of the implementation of the inclusion policy in the school environment will now be cross-analyzed and synchronized.
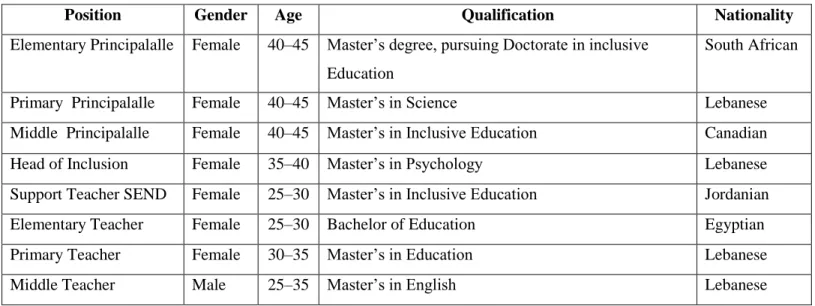
Discussion of the Main Research Question
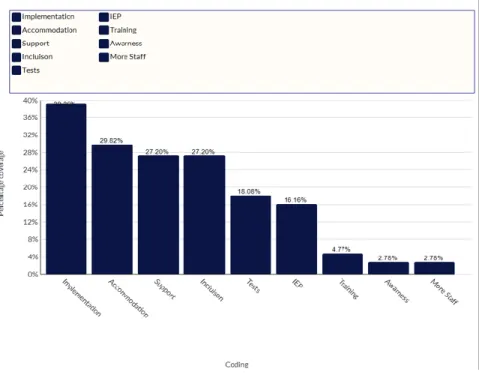
According to Matthews (2009), good adoption of the social model occurs when students are not categorized or labeled in any way and they receive the same treatment as the other students in the class, regardless of their abilities. All teachers believed that the efficiency of inclusion depended on the nature and degree of the student's condition. According to the researcher's findings, the challenges the school faced were related to the insufficient number of qualified teachers and inadequate teacher training.
In several classrooms, for example, additional tiles and handles for the stairs allow easier and more independent movement within the building. Often, curriculum changes were limited to assessments, tests, and exams and did not address SEND among the whole class.
Discussion of the Sub-research Questions
However, a paradox arises from the fact that one must be aware of the special conditions in the inclusion policy as well as the characteristics of a student. General education teachers in the United Arab Emirates and their acceptance of the inclusion of students with disabilities. The Dubai Inclusive Framework provides clear rules for school leaders and teachers on how to implement best practices for inclusive education and provides a clear job description for each member of the IEP committee.
A framework provides clear rules for school leaders and teachers on how best practices for inclusive education can be implemented and establishes a clear job description for each member of the IEP committee. A framework provides clear rules for school leaders and teachers on how best practices for inclusive education can be implemented and provides a clear job description for each member of the IEP committee. What recommendations do you propose to improve the implementation of inclusion policies in your school?
Of course, the role I play on the committee has been communicated to me by the inclusion team and the principal of each school should be part of the committee.