You may use the work for your own non-commercial and personal use; any other use of the work is strictly prohibited. This book will discuss some of the mechanics of corporate valuation and examine the context and environment of valuation. This is unfortunate, as a professional who understands valuation can contribute to the accuracy of the process.
Additionally, some of the tables are long, and the print will be larger and easier to read on a letter-sized page, rather than the way they will appear in the book. I have been a major innovator in the business valuation profession having published significant research touching on many of the key valuation areas. If you own one of the 8 million small businesses in the United States, you must be very curious what your business is worth.
In order to keep the first part - the evaluation of the "core" of the book -. relatively short, so you will read it and use it. Once a business owner understands the valuation process, they become an invaluable part of the process.
BUSINESS VALUATION
POR 1
We can combine this expression with growth in the first few years as long-term growth, since both terms increase the company's value – one in the numerator in equation 9.5 and one in the denominator. This is a bird's eye view of the value of your business in the future and nothing else will affect the value. The purpose of the previous section was to identify the variables over which you have control, which may affect the valuation of your business.
To uncover each of the above four5 points in the future valuation equation, from the growth rate to the discount rate, with some interactions between items that might otherwise appear independent. The previous discussion established the very large impact of the discount rate on valuation. There are two types of risk: risk associated with the business and risk for the buyer in being able to ascertain the honesty of the seller.
Operational risk factors are the risks inherent to the nature of the business. They include industry business cycles, fixed costs and owner dependence. On the other hand, any part of the cyclical nature of the business that you can control and “smooth out” should increase the value of your business.
The right side of the balance sheet will be debt with interest plus equity (again ignoring miscellaneous items). The first measure is the percentage on the right-hand side of the balance sheet that comes from interest-bearing debt, which is debt divided by debt and equity. Therefore, the presence of debt lowers ROE below the ROE of a company without debt (Company A) if the scenario is bad enough.
Beta is a measure of the volatility of a given stock relative to the volatility of the market. The presence of debt increases the beta of the stock, which is known as the equity beta. Some researchers will also provide an asset beta of the stock, which is the beta of the stock with the effect of debt removed, i.e. assuming the company is debt-free.
![TABLE 9.2 Effect of Financial Leverage on Returns & Volatility—75% Variable Expense Skeleton RHS of Balance Sheet [1]Firm AFirm B Interest-Bearing$0$8,000,000 Debt Equity$10,000,000$2,000,000 Total Debt &$10,000,000$10,000,000 Equity Total Assets F](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/azpdfco/10629530.0/180.648.143.588.119.875/financial-leverage-returns-volatility-variable-expense-skeleton-balance.webp)
THE SALE AND FINANCING OF
A BUSINESS
If the VC commits to providing you with $1 million in funding and you give him or her 40 percent of the company, you have just implicitly valued your company at $1 million, 40%$2.5 million. It contains a lot of information, and the frustrating but understandable aspect of it, given the complexity of the tax law, is that you will not go through this chapter with a detailed knowledge of the tax law that will enable you to be your own tax attorney. If she paid all that in cash, then that is also the actual sales price of the company.
If the note requires payment of an interest rate equal to what a bank would charge for a loan of the same risk, then the fair market value of the note is equal to its face amount and the nominal selling price of the business. equates to the actual selling price. The only difference between nominal and real ADF is that in the former, we use the nominal interest rate of the loan, which is fixed for the life of the loan, while in the latter, we use the current market rate that a bank would charge this loan, which changes almost constantly. If the discount rate were zero, then the present value of the loan would equal the total payments of $1.00 per month 84 months, $84.00.
Now we can calculate the ratio between the real selling price and the nominal selling price and thus the discount percentage. If the loan were 100 percent funded, the real present value of the loan is only The discount percentage depends only on the length of the loan, the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate.
On the other hand, if the buyer secures the note of sale of the business with a piece of commercial real estate worth $5 million, net of the mortgage, then the risk of the loan is significantly reduced. An earn-out is that part of a company's sales price that is conditional. The earn-out is not a certainty and therefore that part of the sales price must be reduced to the expected value in order to calculate the actual sales price.
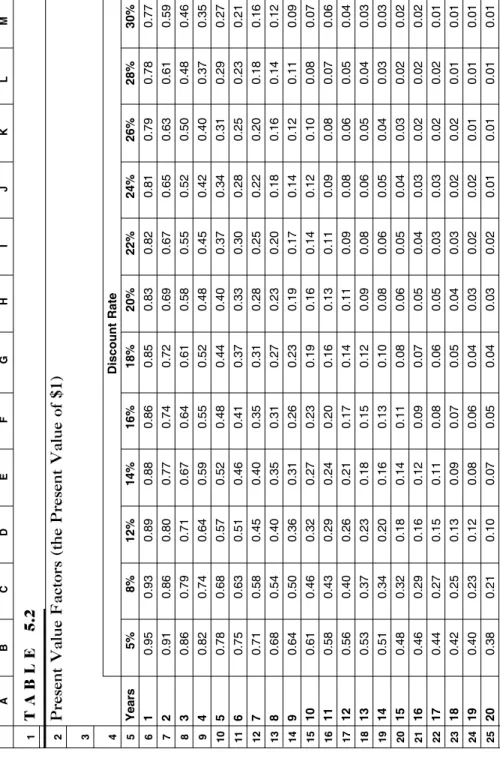
Since we have already reduced the earnings to their expected value from the end of Year Three, we must discount them to present value at a business rate.3 Assuming 20 percent is the appropriate rate, the present value factor (review Chapter 5 if you feeling rusty) is 0.5787. So what looked like an additional $1 million to the seller in the form of earnings was just less than 40 percent of his nominal amount. The importance of the preceding discussion is that you should be careful when buying or selling a business, and understand the real value of what you are buying or selling.
![TABLE 6.1 Gordon Model Multiples Section 1 [1]Section 2: GMMs (Midyear) AvgConstant Growth Rateg Mkt CapFMVReturn2%1%0%1%2%3%4%5%6%7%8% $10,000,000,00013.7%6.87.37.88.49.110.011.012.313.916.018.8 1,000,000,00016.0%6.06.46.87.27.78.39.09.810.812.013.5 100,0](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/azpdfco/10629530.0/127.648.91.570.84.875/gordon-multiples-section-section-midyear-avgconstant-growth-capfmvreturn2.webp)
![TABLE 9.3 Effect of Financial Leverage on Returns & Volatility—85% Variable Expense Skeleton RHS of Balance Sheet [1]Firm AFirm B Interest-Bearing$0$8,000,000 Debt Equity$10,000,000$2,000,000 Total Debt &$10,000,000$10,000,000 Equity Total Assets F](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/azpdfco/10629530.0/184.648.145.589.118.879/financial-leverage-returns-volatility-variable-expense-skeleton-balance.webp)
![TABLE 9.4 Effect of Financial Leverage on Returns & Volatility—90% Variable Expense Skeleton RHS of Balance Sheet [1]Firm AFirm B Interest-Bearing$0$8,000,000 Debt Equity$10,000,000$2,000,000 Total Debt &$10,000,000$10,000,000 Equity Total Assets F](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/azpdfco/10629530.0/186.648.144.589.119.878/financial-leverage-returns-volatility-variable-expense-skeleton-balance.webp)