Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Business and Law for the completion of the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT. The author has also granted permission to the University to retain or make a digital copy for similar use and for the purposes of digital preservation of the work.
DEVELOPING THE RESEARCH AGENDA/INTRODUCTION
Introduction
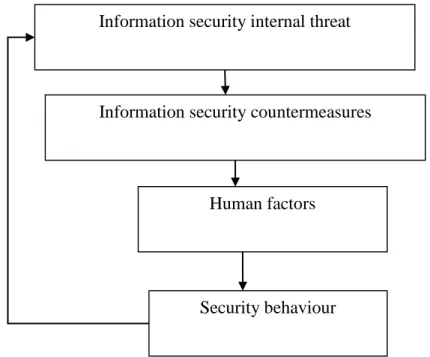
A portion of information security breaches are due to human factor issues which remain unresolved (Maass et al., 2018). Mamonov and Benbunan-Fich (2018) argued that information security is required to focus on human behaviors to mitigate risks and issues.
Research Background
- Human Factors in Information Security
The results showed that the organizational culture influences the investigated principles of the information security. Training as well as awareness is necessary for people to thrive in the culture of information security.
Research Problem Statement
The researcher can understand the drivers as well as the limitations of forces related to human issues with obstacles to information security in public organizations. The main aim is to explore and identify the information security countermeasures and provide a framework to improve the information security.
Research Questions
There are certain main implications of the role of human factors and challenges in the process of information security Moody et al. What are the information security countermeasures that can influence the human risky cyber security behavioral practices in public organizations.
Research Aim
What are the users' addictive behavior that can lead to an increase in risky cyber security behavioral practices. Hadlington (2017) investigated human factors in cybersecurity and examined the relationship between Internet addiction, impulsivity, attitudes toward cybersecurity, and risky cybersecurity behaviors.
Research Objectives
Research Scope and Significance
Cyber security strategies are used to design a framework of information security countermeasures related to human behavior. Information security countermeasure constructs help inform security culture policies (Pearlson et al., 2016).
Research Hypotheses
The conceptual framework of this particular study is based on strategic planning regarding information security policies, employee training and awareness, and appropriate countermeasures, along with structure and operations in the IT services. Previous studies on the information security domain are broad in nature, providing a general overview of information security research (Martins et al., 2014).
Thesis Structure
This particular section both presents and discusses the primary method for answering the research questions. These steps are important to find out the population's opinions that can add value to the research topic.
Summary
LITERATURE REVIEW
Introduction
- Information Systems
- What is Information Security?
- Threats to Information Security
- Information Security Behaviour
- Information Security Principles
- Relevant Theories and Methods
- Threats to Information Security: Human Behaviour is a Constant Risk
- Threats to Information Security
- Human Behaviour as an Aspect of Information Security
- How Human Behaviour can be influenced by Standards, Guidelines and COBIT
- COBIT
- Human Factors and End User’s Behaviour
- Human Behaviour Risks Related to Information Security
- Public Organisation Information Security Culture
- Organisational Culture
- Information Security Culture
- Cultural Change
- Cultural Impact on Human Behaviour
- Significance of IS across Public Organisations
- Factors Influencing IS
- Impact of the Factors Affecting IS
- Additional Factors
- Information Security Policy
- What is an Information Security Policy?
- User Behaviour Related to the Information Security Policy
- Compliance with the Information Security Policy
- Human Computer Interaction (HCI) and Behaviour Change
- Insider Threats Behaviour
- Modelling Human Behaviour to Anticipate Insider Attacks
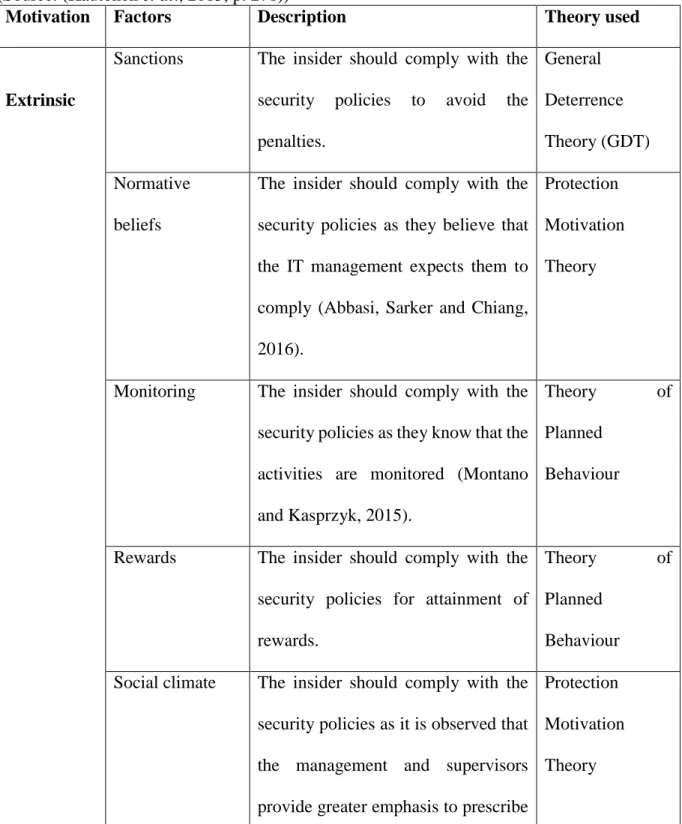
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivators in Information Security Behaviour
- Insider Misuse and Incident Responses
- Conclusion
It is defined as the compliance of the users with the security policies of the organization. That this theory is an adaptation of the theory of reasoned action in the field of information security. Staff are not aware of the information security policies; therefore they share information with others.
Information security culture is part of the organizational culture, as information security is an organizational function. 2016) defined the information security culture as the totality of the human characteristics such as behavior and attitudes as well as the beliefs held by the organization. Inadequate use of technology can have a huge impact on IS countermeasures as well as on employee behavior (Cheng et al., 2014).
Information security culture is part of organizational culture, as information security has become an organizational function.
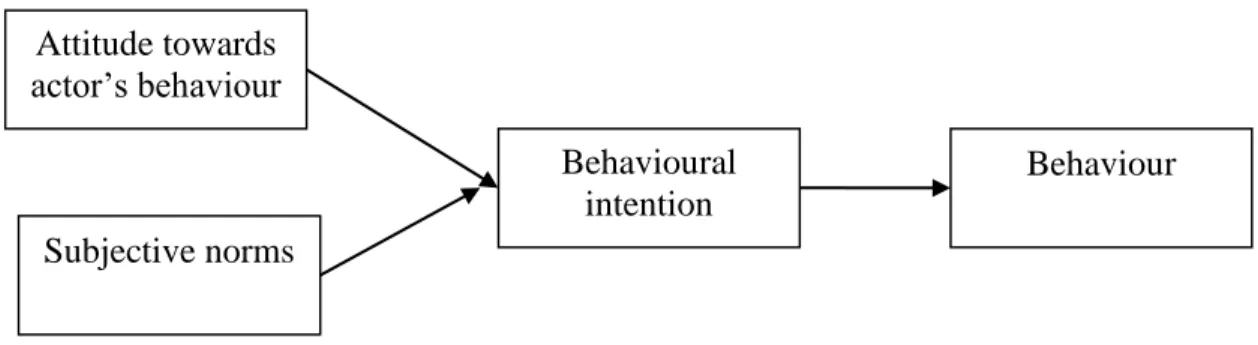
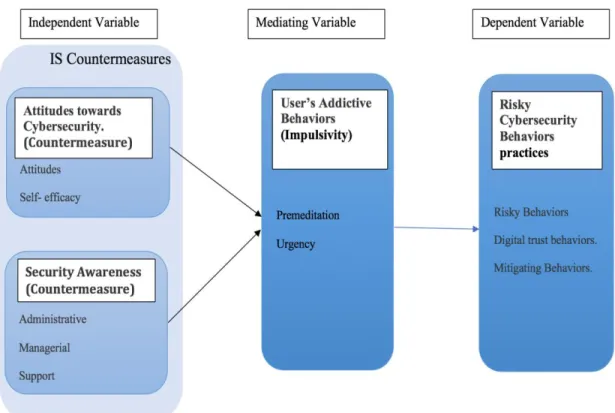
RESEARCH CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Introduction
Theoretical Development
- Security Awareness Countermeasures
- Attitudes towards Cybersecurity Countermeasures
- Users’ Addictive Behaviours
- Information Security Countermeasures
- People’s Addictive Behaviour and the Information Security System
- Risky Cybersecurity Behaviour Practices
Proposed Conceptual Framework of the Research Study
Conclusion
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Introduction
Research methodology is the technique or approach used to conduct research (Kumar, 2018). The purpose of this chapter is to describe the research methodology used in this thesis. There are two sections, which describe the purpose of the research along with the research approaches (Clark and Creswell, 2014).
The main objective of research methodology is to identify and justify possible methods, data collection methods, research sample and questionnaire using an online survey. This particular section presents and discusses the main methods used to answer the research questions.
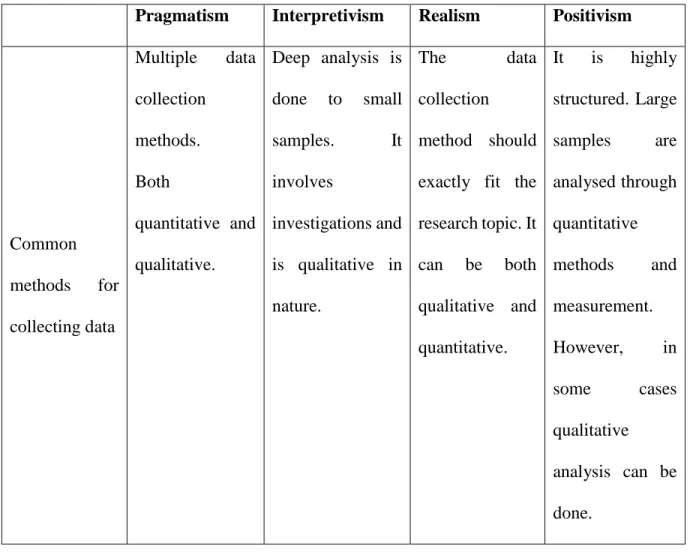
Research Philosophy
At the end of this specific chapter, the research data are collected and analyzed using the methods described. This means that the first step in any research methodology should be to identify the research philosophy to be used. Assumptions about the nature and source of knowledge define each stage of the research process.
The type of research philosophy depends on the scope and purpose of the research (Webster, 2017). Interpretivism uses smaller samples which provide an in-depth analysis of the research study (Neuman and Robson, 2014).
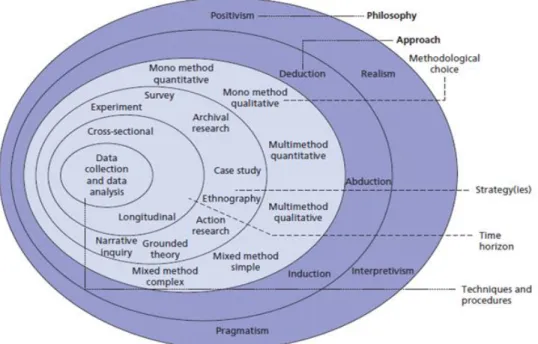
Research Approach
An inductive research approach is useful if there is no hypothesis, and the research begins only with a goal, objective, and research question. A research approach is the plan and procedure for how the research will be conducted (Tuffour, 2017). The first step of the research was to identify the population to be used for the research.
The researcher reads the existing theories of the research phenomenon, while checking the research hypothesis from the theories. Viswanadham (2017) stated that the deductive approach deals with the deduction of conclusions in order to find research patterns with them.
Research Design
It should define the techniques that will be used in collecting and analyzing the research. It must determine the time frame in which the research will be carried out. f) The research environment must be defined. An exploratory research design provides insight and understanding of research questions along with situations (Flick, 2015).
It answers the research questions and, based on one of the research designs for the current study, it is required to gauge different projects. The choice of the research design depends on the research problem being addressed and not the other way around (Leavy, 2017).
Data Collection Process
- Data Sources
- Data Analysis
- Data Interpretation
- Data Presentation
Using the data collection tools, it is necessary to transfer facts from the field into data as well as tables. On the other hand, quantitative analysis is where a general view of the research topic is created (Jacobi et al., 2016). The purpose of quantitative analysis is referred to new research methodological developments with systematic integration.
The purpose of data interpretation is to find out the outcome of the research in relation to the research question. In this thesis, the researcher developed a conclusive report on the findings of the study (Fetters and Molina-Azorin, 2019).
Sample and Sampling Method
The reports can be submitted directly to the specific organization or made available online for multiple organizations. If the research results are not presented but remain with the researcher, the research can be considered worthless (Viswanadham, 2018). It benefits the researcher when there are limited costs and time to conduct the research.
Employees in the services of public organizations of the UAE are considered a model for this work. The research accepts 8% as the margin of error, 90% as the confidence level and 0.5 as the standard deviation.
Validation and Verification
Area of Concern Research Stage Solutions to increase the validation and verification in the research study. Testing the research hypothesis using survey research will enable the researcher to compare results from quantitative research. Various perceptions of the author and research participants will improve the validation of the research data (Vaioleti, 2006).
In the research that was conducted, validation took place by ensuring that the research was conducted according to the research objectives as defined in the research design (Magazzeni, Mcburney, and Nash, 2017). Since the results of the study were in line with the research questions and objectives, the study can be considered valid.
Ethical Considerations
Summary
The entire research study is mainly based on the primary data collection method, where all the data is collected through the use of an online survey, and the participants – those who are interested in the study – are only considered to give their feedback based on the questionnaire. . The data collection process aims to provide raw data as well as information that helps develop the information security model culture.
RESEARCH FINDINGS
Introduction
Data Analysis Types and Tools
Rapid Miner is one of the most popular data science platforms and is very useful for analyzing any kind of data in real time. Knime is also considered as one of the greatest data tools which is very useful to interpret any data using visual programming (Lewis, 2016). Creating the output file from the data is one of the advantages associated with using this tool (Paulus and Bennett, 2017).
On the other hand, there are also a few limitations associated with SPSS, such as the quality of the graphics that are automatically generated from this software. Descriptive statistics are an integral part of the data analysis method and were performed using SPSS (Wang and Zhang, 2019).
Data Collection Analysis
- Sample Size
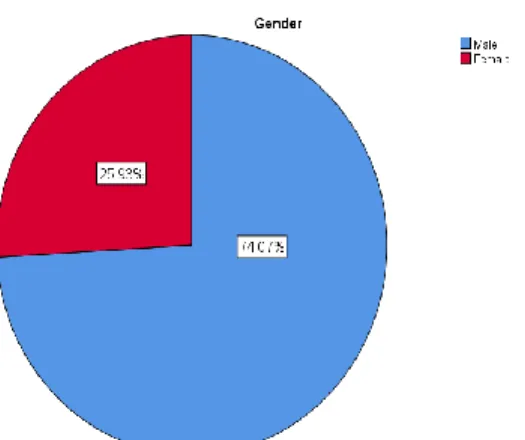
- Gender
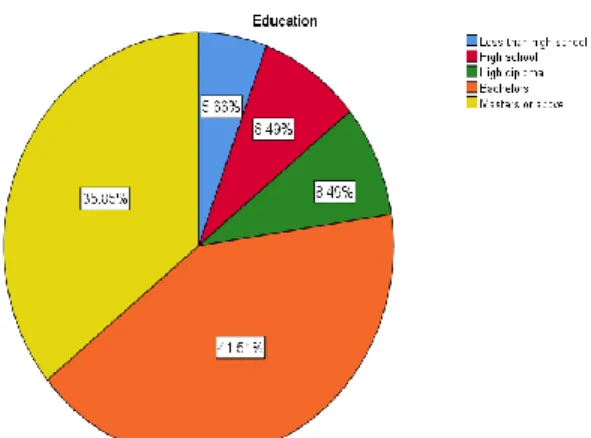
- Education
- Training to UG/PG level
- IT-Related Training Courses
- Years Working in Current Position
- Position Held at Work
- Nature of Task Performed in the Workplace
- Common Method Variance (CMV)
Thus, based on the above, it can be understood that the majority of the population of this sample is male. This demographic question will be very useful to understand the basic IT knowledge of the participants who have stated their opinion in the online survey. Thus, out of 124, 28 of them have not undergone any training course related to IT and the rest have.
It can therefore be understood that most of the survey participants work in a managerial role in their respective organizations. The nature of the work performed by each of the survey participants can be understood from this demographic question.
Reliability Analysis
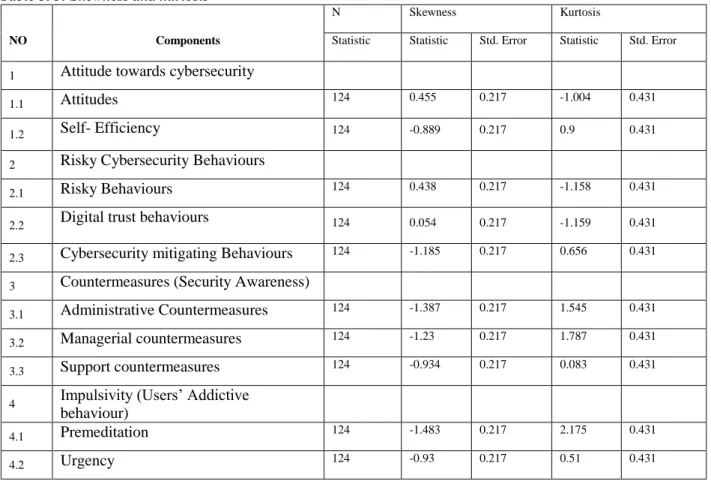
Normality Test for the Dependent and Independent Variables
A normality test such as the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test can be very useful for analyzing research with fewer components. Interpretation of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test must be performed in an accurate order, while the null hypothesis can be performed using Shapiro-Wilk tests. Based on the table above, it can be stated that none of the research components violates the acceptance standards set in the previous section.
Frequency Analysis
- Attitudes towards Cybersecurity Countermeasures
- Risky Cybersecurity Behaviour Practices
- Countermeasures
- Impulsivity (Users’ addictive behaviours)
However, 9% of the population neither agreed nor disagreed, 20% somewhat agreed with it, while 31% agreed and the rest (16%) strongly agreed. However, 16% agreed that they click on links from unsolicited emails, and the rest (9%) of the population strongly agreed with this statement. Regarding email security, 6% strongly disagreed that they check the security of an email with an attachment, 6% disagreed with this discussion topic, 4% of people somewhat disagreed, and 4% were neither agree nor disagree.
9% of online survey respondents strongly disagreed that their organization organized safety meetings and training, 4% disagreed with this statement and 7%. However, 3% disagreed or disagreed with this topic of conversation, while 34% of the population somewhat agreed with the selected discussion, 27% of them agreed and the rest (18%) strongly agreed.
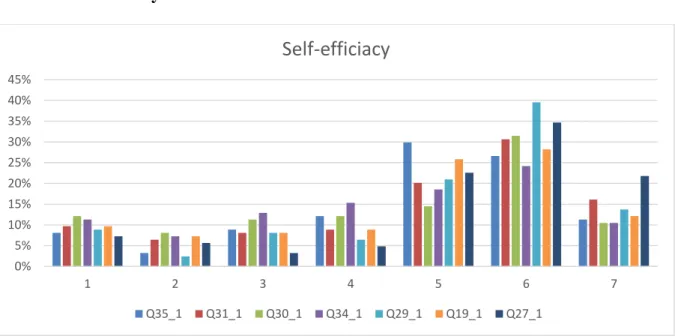
Dependent and Independent Variables
The standard deviation and mean of this thesis variable can be deduced from descriptive statistics; it can be understood that the minimum ratio is 1.00 while the maximum ratio is 7.00. The minimum value of the dependent variable is 1.00 and the maximum value of the dependent variable is 7.00. The standard deviation of the dependent variable is 1.92379, as the resulting mean is 3.4901.
Therefore, the mean of the information countermeasures is 5.2687 and the standard deviation was found to be 1.45260. Considering the broker, the minimum value is 1.00, while the maximum value was found at 7.00.
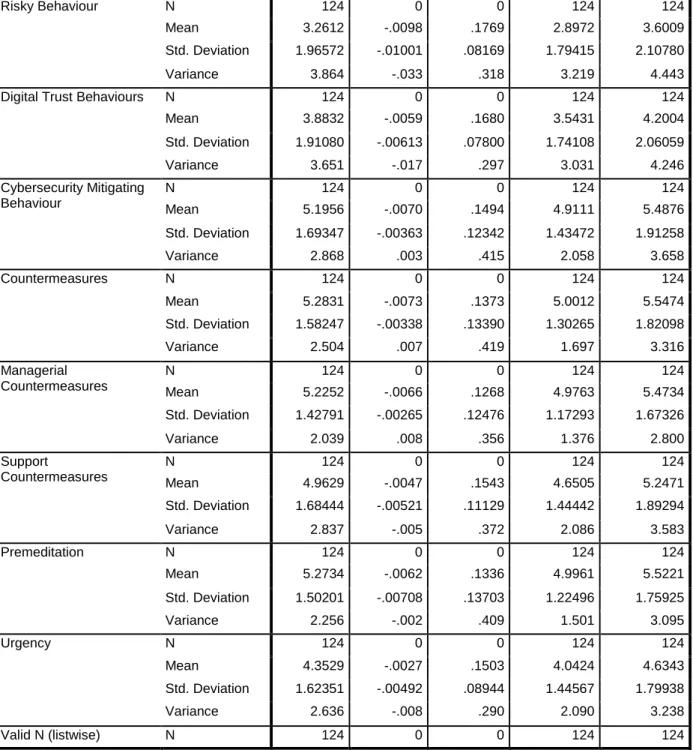
DATA ANALYSIS
Introduction
Correlation Test (Pearson)
Correlation Results Summary
Regression Analysis
- The Result for the First Hypothesis
- The Result for the Second Hypothesis
- The Result for the Third Hypothesis
- The Result for the Fourth Hypothesis
- The Result for the Fifth Hypothesis
- The Result for the Sixth Hypothesis
Confirming the Research Constructs Association
- Relationship between Dependent and Independent Constructs
- Mediation Analysis Results
The Discussion of the Indirect Influence
- The Mediating Effect of Impulsivity
- The Mediating Effect of Premeditation
- The Mediating Effect of Urgency
Summary of Data Analysis
DISCUSSION
Introduction
Overview of the Research Questions
Descriptive Analysis Findings Discussion
Frequency Discussion of the Research Constructs
Association of Findings Discussion and Contribution to Knowledge
Regression Analysis Contribution to Knowledge
Conclusion
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Research Overview
Meeting the Aim and Objectives of this Thesis
Key Findings of this Thesis
Research Novelty and Contribution to Knowledge
Research Implications
Implications for Research/Theory
Implications for Practice/Managers
- Hypothesis 1
- Hypothesis 2
- Hypothesis 3
- Hypothesis 4
- Hypothesis 5
- Hypothesis 6
Research Limitations
Future Research Recommendations
2: Direct effect
3: Moderator effect
4: Mediator effect