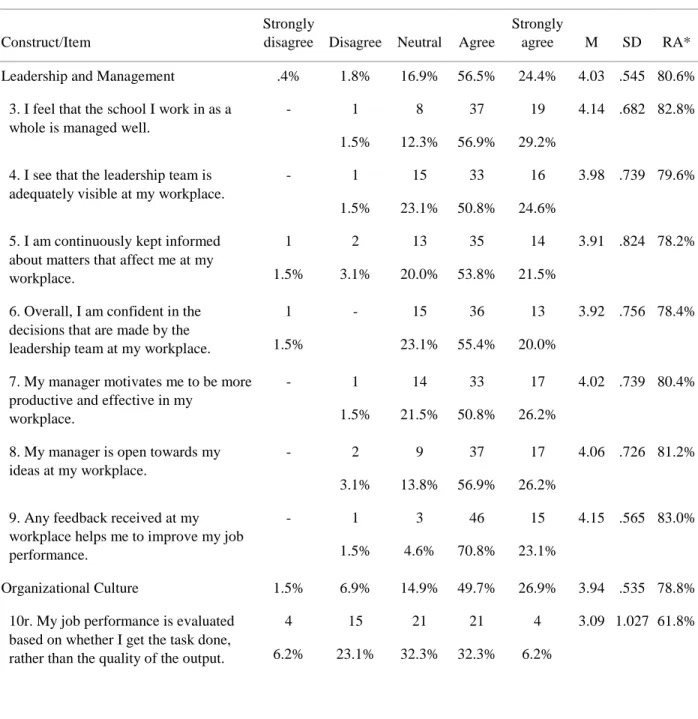
The author has also granted permission to the University to retain or make a digital copy for similar use and for the purpose of digitally preserving the work. Analysis of the well-being questionnaire data showed that most teachers were satisfied with their leadership and had a healthy lifestyle.
Background and Motivation
Well-being in life is measured by life satisfaction and global happiness. By finding a relationship between leadership practices and factors affecting teacher well-being, it is recommended that other studies examine the best practices on teacher well-being that leadership management should use to develop school performance. .
Problem Statement
Aim and Objectives
Research Questions
How do job satisfaction, organizational culture, teamwork, relationships, leadership management, remuneration, benefits and the working environment affect the well-being of teachers in one of the private schools in Dubai. What is the relationship between these practices and the well-being of teachers in the school?
Rationale of the study
Stress and anxiety in the workplace can have a negative effect on the teacher's well-being and mental health (Allen et al. 2018). Only a small amount of research has been done on how to cultivate teacher well-being in the workplace (Hattie & Yates 2014).
Dissertation Structure
The UAE National Agenda Vision 2021 is focused on promoting happiness as one of the pillars of the National Agenda to create a collective cohesive society. This chapter will also cover the analysis of factors affecting the well-being of teachers.
Overview of the Chapter
Conceptual Analysis
First, the economic well-being, supported by the economic and welfare well-being theories discussed in the theoretical framework, focuses on the financial well-being of the teacher and. The Leadership Feedback effect, supported by the LMX (Leader-Member Exchange) theory discussed in the theoretical framework, focuses on the relationship between the teacher and the leaders of the school, and whether the feedback and association positively or negatively affects their well-being influence .
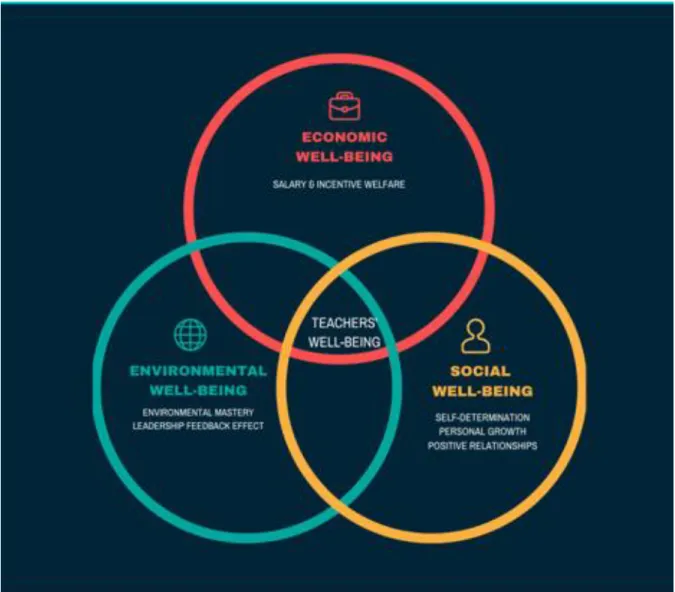
Theoretical Framework
- Social Cognitive Theory
- Subjective Well-being
- Self-determination Theory
- Economic and Welfare Theories of Well-being
- Positive Psychology
- Leader-Member Exchange theory
The subjective well-being theory (SWB) is the theory that revolves around the amount of contentment and positive emotions and moods they experience, identified as the positive effect, as well as the lack of negative emotions and moods present in that individual's dimension (negative affect ) (Diener & Ryan 2009). Wealth has also remained an essential factor in subjective well-being theory (Lijadi 2018).
Review of Related Literature
Glazzard and Rose (2019) conducted a different kind of research in this article to bring out the factors of a teacher's well-being. And for the school to take the responsibility to invest in the health and well-being of their staff.
Summary
Introduction
Research Paradigm
Focusing on what factors influence teacher well-being using the combined approach along with the focus on the educational field, the pragmatic paradigm is considered more appropriate and used by research paradigms. The use of the pragmatic approach in this study puts the research question and purpose at the center and tries to look at all the methods that can help in understanding the issue, thus being associated with the mixed method approach (Mackenzie & Knipe 2006). The pragmatic approach is generally placed between the research paradigm and its relation to methods, unlike postpositivism.
Research Approach
Mixed method approach
Qualitative research is a method that allows the researcher to place himself in the world (Creswell and Poth 2018). It is a collection of material and analytical applications that improve the worldview, starting with the creation of assumptions and the attachment of a theoretical framework through the study of a social problem that strongly considers individuals in the problem within (Creswell and Poth 2018). ). While the mixed method approach has not created as stable a footprint as quantitative and qualitative methods have separately, it will indeed become one of the most important approaches in research in many fields, including the field of education and studies.
Instrumentation
Using the mixed-method approach, a pathway will be created through the sample collection to discover different assumptions and beliefs, a pathway that is critical when discussing multiple characteristics that influence teacher well-being (Creswell 2013). A private school was chosen to provide a more closed analysis of teacher well-being by limiting the samples to a single school. The characteristics influencing the well-being of the teachers were appropriately derived from the survey and analyzed along with helping to find solutions to the problem.
Measurement Validation
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
- Number of Participants
- Sampling Adequacy
- Correlation
- Anti-image Correlation
- Commonalities
- Exploratory Factor Analysis Results
After rotation, the first component explained 40.5% of the variance, the second component explained 7.5%, the third component explained 6.2%, the fourth component explained 5.2%, the fifth component explained 4.9%, and the sixth component explained 4.2%, with total variance explained by 68.3%. In general, I trust the decisions made by the management team at my workplace. The EFA results show that the extracted factor solution is different from the factor structure proposed by the researcher.
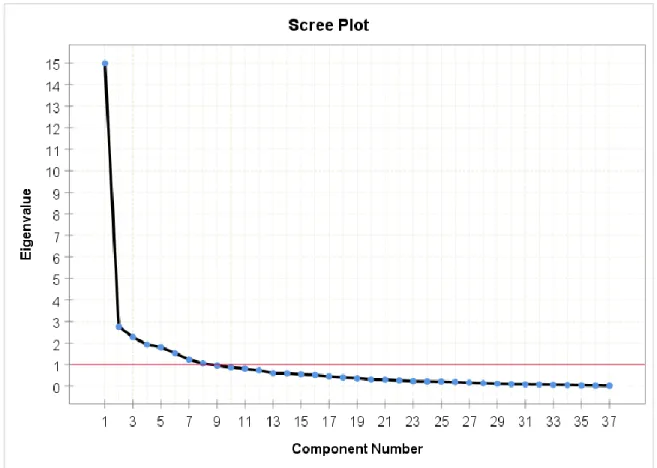
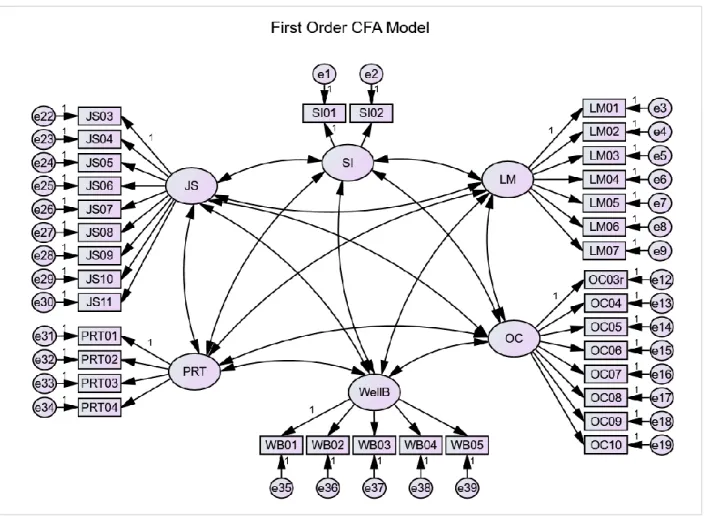
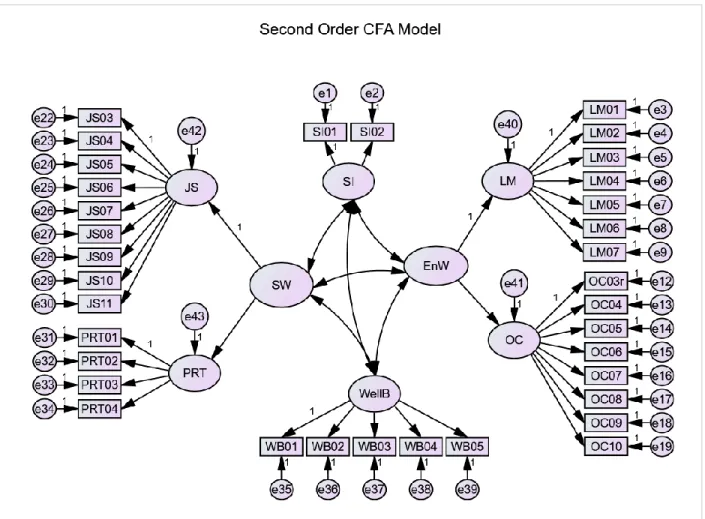
Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
Model Fit
However, the proposed factor structure will be retained as the grouping of items is more reasonable.
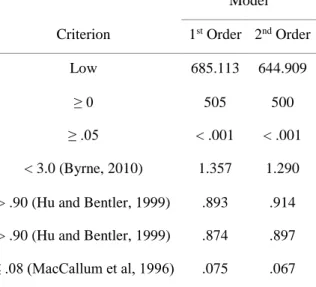
Psychometric Checks of the Model
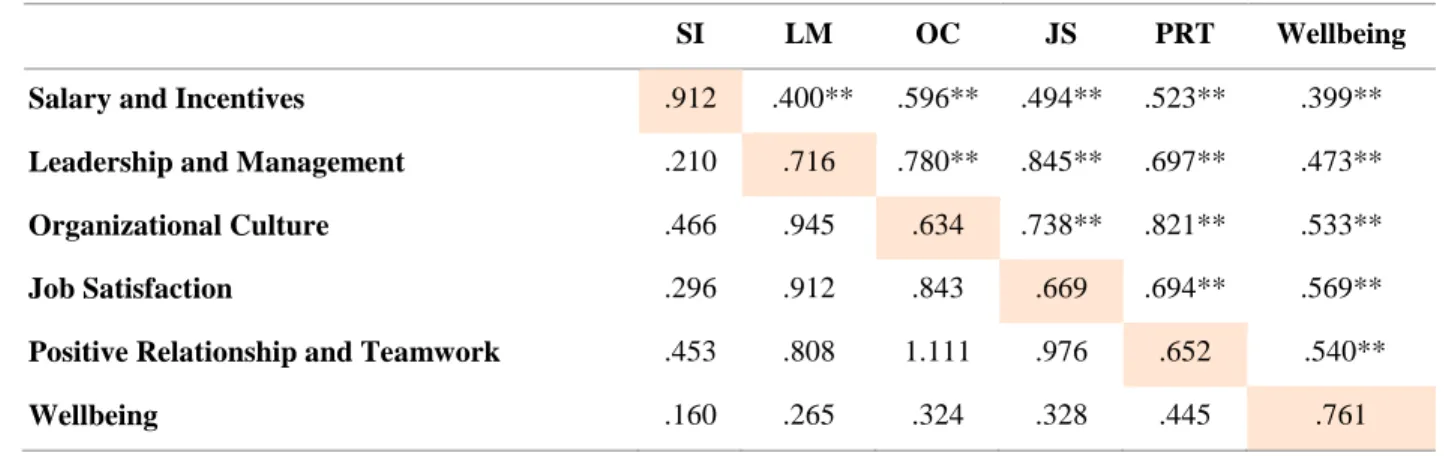
Overall, I am confident in the decisions made by the management team at my workplace .753 7. The model's discriminant validity was evidenced by AVE factors that were higher than the squared shared variance (SV) for all constructs (Fornell & Larcker, 1981 ). The interfactor correlation values for the dimensions were below 0.85 with a minimum value of 0.399 and a maximum value of 0.845, providing evidence for the discriminant validity of the model.
Data Analysis
Interfactor correlations are located above the diagonal, while the squared interfactor correlation values (also known as shared variance) are presented below the diagonal. The CFA was performed by the AMOS, while the EFA was performed by the SPSS. Regarding the interview, a private interview was conducted with the leadership at a private school in Dubai, in which the interviewees were asked both questions compatible with the topic and answers of the questionnaire participants.
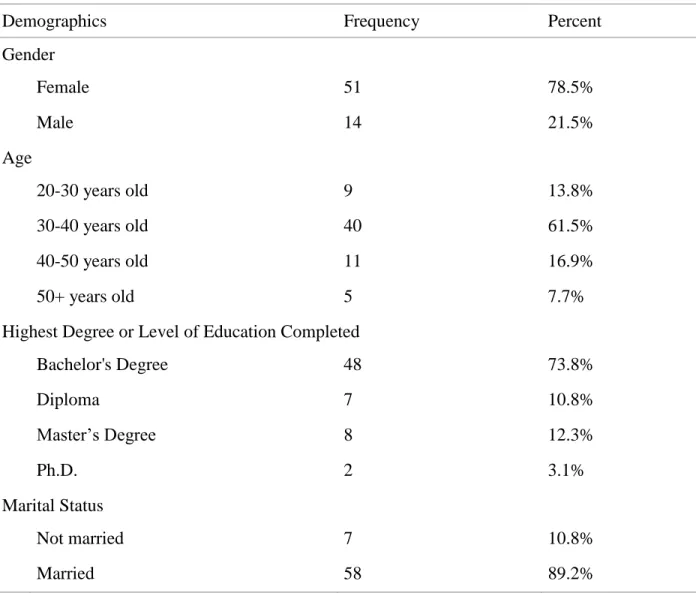
Sampling
Delimitation
The main focus of this study was teachers' well-being and which factors could attribute to their overall well-being. This also emphasizes why the interviews were only conducted with the management and leadership of the school, and not the teachers. By integrating management into the study, another side and factor of teachers' well-being will be more investigated, which supports the main goals and focus on teachers from a different angle.
Ethical Considerations
That being said, the survey was only distributed to the private school teachers in Dubai and not to the management of the school as they are the core and main subjects of the study. That's because the researchers wanted to elicit responses from leadership in reflection on the teachers' responses through the survey and to understand how a higher chain of command perceives this issue and what practices they adopt to ensure the well-being of their employees. Consent of all participants was given before participating in the study, with well-informed details about the goals and objectives of the paper, each in its own format, the interviewees well understood the purpose of the interview and were given the right to collaborate with the survey participants not to participate in the research to demonstrate the optional attribute in the research and the trustworthiness of the researcher (Connelly 2014).
Outline of the Chapter
Analysis of the Quantitative Data
Based on the statistical tests, only three hypotheses appeared to be supported: H1, H2 and H6, at p < 0.05.
Descriptive Analysis Participants’ Perceptions
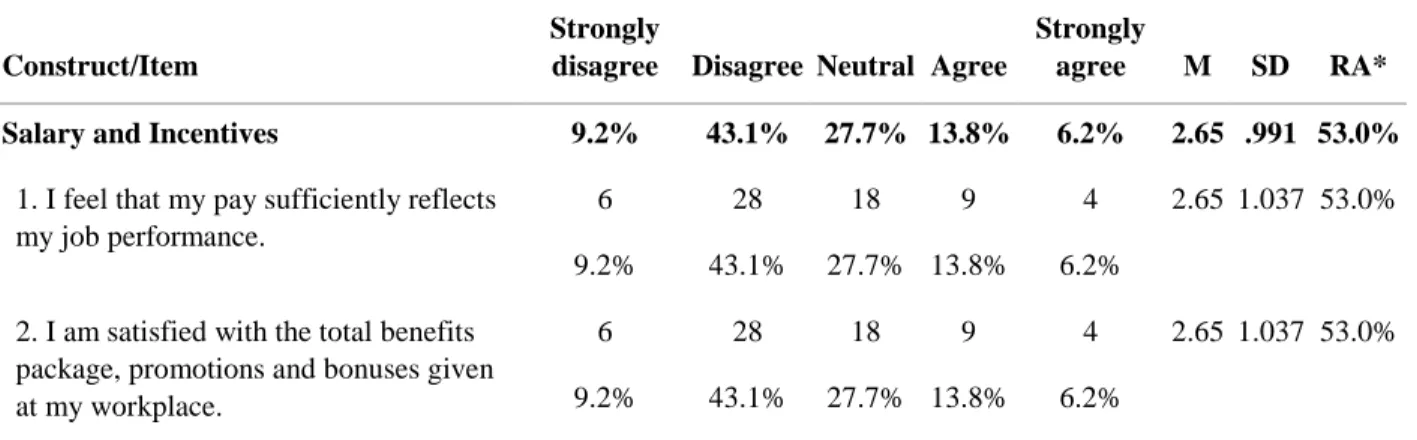
- Economic Well-being: Salary and Incentives
- Environmental Well-being
- Social Well-being
- Well-being
- Other Factors Negatively Affecting Teachers’ Well-being at Their Workplace
- Hypothesis 1
- Hypothesis 2
- Hypotheses 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7
- Hypothesis Testing Summary
- Summary of the Quantitative Data
A one-sample t-test was conducted to determine whether teachers' mean scores were above the neutral attitude, defined as a neutral attitude of 3.0. One-sample t-tests were also conducted to determine whether the mean score of teachers' attitudes toward wellness practices in terms of SI, LM, OC, JS, and PRT was above the neutral attitude, defined as a neutral attitude of 3.0. A one-sample t-test was conducted to determine whether the mean score of teachers' attitudes toward their personal well-being was above the neutral attitude, defined as a neutral attitude of 3.0.
Analysis of the Qualitative Data
Summary of Qualitative Data
The interviews with the leadership in general revealed that they strive to become a facilitator and a member of the team rather than a superior to their faculty. In addition, the interviewees revealed that their goals include developing their faculty's well-being through various workshops. Regarding salaries and incentives, the leadership has determined that they do not have central control over their distribution, but they seek to compensate by recognizing the achievements of the teachers, and focusing significantly on well-being.
Triangulation
A discussion was given about the implemented practice to maintain well-being in the school, which included the formation of a teachers' union to help relieve the burden on their faculty. While environmental well-being has declined, leaders are working to help and help increase teacher well-being. In response, leaders do understand their limitations, but they recognize a higher authority that controls distribution, serves an alternative that they can control by validating teachers' job performance achievements, and supporting them to help offset the decline in economic prosperity. - to be.
Overview of Chapter
Summary of the Study
They also found that work-related stress due to various activities and tasks also affects teachers' well-being. 2018) takes the concept of clarifying how "education actors" can apply to oversee and develop the well-being of teachers in their organizations, showing how 61% of educators consider stressful work as one of the findings (Cox et al. 2018). In general, teachers felt positive about well-being practices presented by leadership and management, organizational culture and job satisfaction, and responded negatively to pay and incentives, but considered job and personal satisfaction as determinants of good well-being, this actually brought as a surprise to realize how a small amount of factors have a large effect on the well-being of teachers.
Key Findings
Many of the teachers were consumed in feelings of stress and burnout in their workplace, which caused a decrease in overall well-being. Teachers were relatively good with his leadership, management and organizational cultures, concluding that their leadership as a whole has less effect on well-being. Leadership at the school recognizes the teachers' well-being and aims to develop and improve it through councils and workshops.
Implications
The school leadership recognizes the effect of economic factors on the well-being of teachers, but has no central control of the issue, as it has been handed over to a higher entity. The overall happiness of the teachers in the study indicates the possibility of an improvement in the well-being of teachers in the education sector, especially in Dubai, as studies such as Jonathan and Andrea (2019) may have implied otherwise when discussing the effect of well-being. being in job performance. This provides the opportunity to further elaborate the factors that cause positive well-being within teachers, away from the general discussion of factors that affect teachers as a whole, as is done in the paper.
Recommendations
Limitations
Overall, the study could have used additional qualitative measures to clarify the findings and extend the mixed method approach (Fetters & . Creswell 2013). Overall, although the findings of the study cannot be generalized due to its focus on a private school in Dubai, the study provides a way to understand what factors influence teachers.
Scope of Further Study
Concluding Note
The impact of teacher well-being and mental health on pupil progress in primary schools. Teachers at work: Factors influencing satisfaction, retention, and the professional well-being of elementary and secondary educators. Best news yet about the six-factor model of wellness. https://getatomi.com/staffroom/dealing-with-teacher-wellbeing [Accessed 16 Nov.
Survey Question for Teachers
Interview Questions for Leadership
School’s Consent Form