The effect of exclusive olive oil consumption on successful aging: a combined analysis of the epidemiological studies of ATTICA and MEDIS. She is the founder of the "Research Center of Olive Cultivation and Olive Oil Industry" at the University of Bari.
Varietal Authentication of Extra Virgin Olive Oils by Triacylglycerols and Volatiles Analysis
- Introduction
- Materials and Methods 1. Materials and Chemicals
- Results and Discussion 1. Triacylglycerol Fraction
- Conclusions
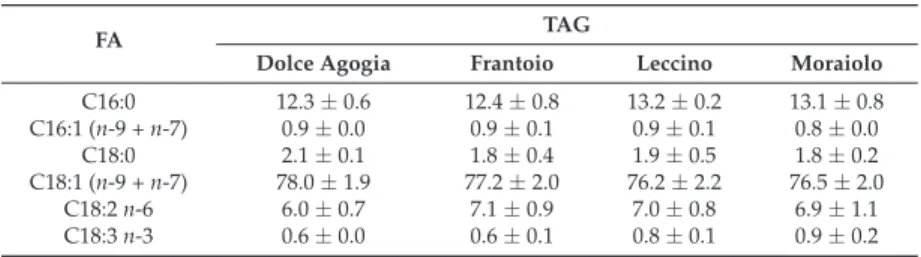
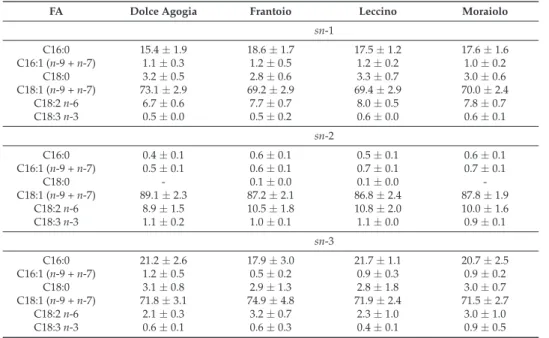
Table 1 shows data on the acid compositions of the total TAG percentage composition of EVOO monovariety samples. Figure 1 shows the chromatographic profile of volatile compounds of a monovarietal sample of EVOO (Dolce Agogia).
1 H NMR and Multivariate Analysis for Geographic Characterization of Commercial Extra Virgin Olive
Materials and Methods 1. Samples
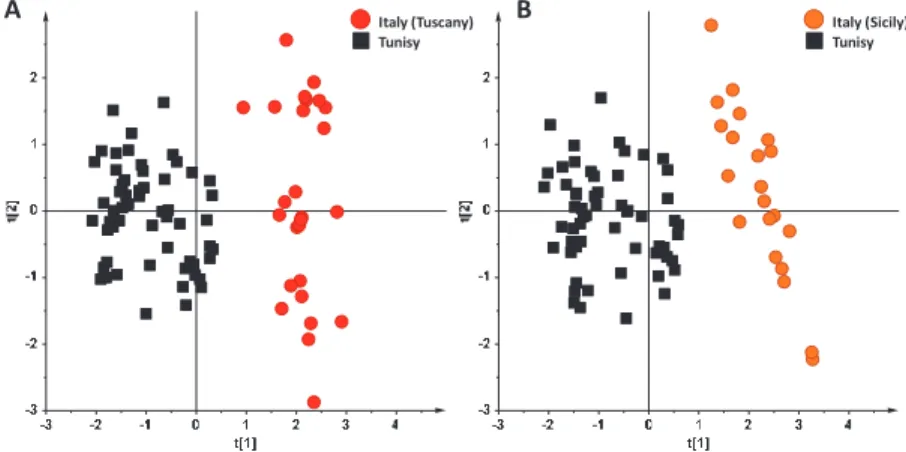
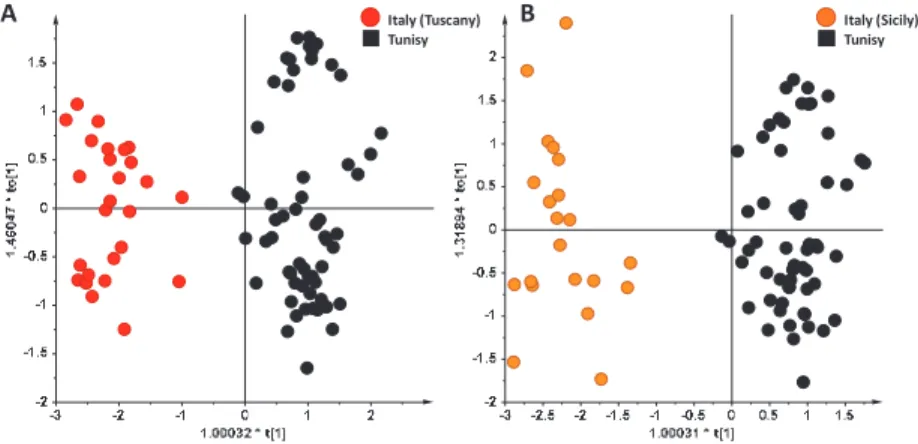
The R2(cum) and Q2(cum) are the two parameters used to describe the goodness of the model at the minimum number of components cumulatively required (cum) to best account for data variability. The R2 accounts for the total variations in the data and provides a quantitative measure of the goodness of the fit.
Results and Discussion NMR Spectroscopy and MVA
Higher differences in average precipitation and temperature generally resulted in a more constant discriminative ability of the investigated OPLS-DA models. Application of stable isotope ratio analysis to characterize the geographical origin of olive oils.
![Figure 1. (A) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) (t[1]/t[2] scoreplot for the whole Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) dataset of extravirgin olive oils (EVOOs) (six components give R2X(cum) = 0.925 and Q2(cum) = 0.822)](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9200910.0/28.723.139.583.106.330/principal-component-analysis-scoreplot-magnetic-resonance-extravirgin-components.webp)
Determination of Pigments in Virgin and Extra-Virgin Olive Oils: A Comparison between Two Near UV-Vis
Materials and Methods
The UV-vis absorption spectra of the olive oil samples were obtained using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (Jasco V-550), at room temperature, using quartz cells with an optical path of 1 cm (first method) or 0.5 cm (second method). Both experimental spectra of the olive oil samples in bulk and diluted in cyclohexane were collected in the range between 220 and 800 nm.
Results and Discussion
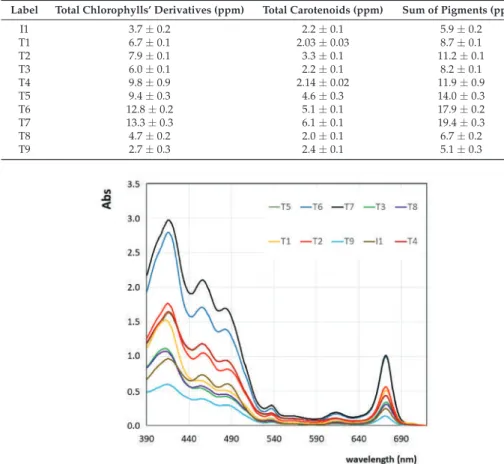
Plot of the sum of pigments (ppm) for the investigated olive oil samples as obtained from the two spectroscopic methods: Values obtained with the method used by Mínguez-Mosquera et al. The calculation of the total amount of carotenoids and the total amount of chlorophylls' derivatives from the main pigments' content obtained by the method proposed by Domenici et al.
Polar Lipids from Olives and Olive Oil: A Review on Their Identification, Significance and Potential
Biotechnological Applications
Identification of Polar Lipids from Olives, Olive Oil, and Their Industrial By-Products The identification of polar lipids in olives and olive oil is a difficult task since they are minor
Schematic presentation of methodological approaches used for the study of polar lipids from olives and olive oil. Liquid/liquid extraction (LLE) has been used to extract polar lipids from olives and olive oil. Chemical structures of glycerophospholipid and glycolipid classes identified in olives and olive oil.

Potential Biotechnological Uses of Polar Lipids from Olives’ and Olive Oil’s Industrial By-Products
There is some scientific evidence that the polar lipid fraction of olive oil and olive pulp possesses antithrombotic and antiatherosclerotic activity mediated by PAF. Nevertheless, more studies are needed to elucidate the chemical structure of the bioactive lipids to understand the mechanisms of action and to determine the concentration of these compounds in olive oil or olive pulp to observe an in vivo effect in humans. The potential biotechnological applications of the olive-derived by-products highlight the valuable alternatives that underpin the table olive and olive oil industries.
Conclusions and Future Perspectives
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry detection of extra virgin olive oil adulteration with hazelnut oil by analysis of phospholipids using an ionic liquid as matrix and extraction solvent.Food Chem. Antithrombotic and antiatherosclerotic properties of olive oil and polar extracts of olive press in rabbits. Med. Optimization of a solid-phase extraction method and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry for the determination of phospholipids in virgin olive oil.Food Res.
Industrial Ultrasound Applications in the
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Extraction Process: History, Approaches, and Key Questions
The Olive Oil Sector and the Evolution of the Oil Miller Profession
This is because from olive grove management to the bottling phase there are hundreds of decisions that must be made consciously. In fact, during all operations, ranging from crushing, to malaxation and to the centrifugal separation [4-7], complex phenomena of a physical, chemical and biochemical nature are established. The role of research in innovation: history and approaches regarding the implementation of ultrasound in the virgin olive oil extraction process.
The Role of Research in Innovation: History and Approaches Relative to the Implementation of Ultrasound in the Virgin Olive Oil Extraction Process
Effective management of bottlenecks in the olive oil extraction stage can lead to great advantages in terms of efficiency (higher oil yield, more phenolic compounds and a pleasant and harmonious sensory profile) and process efficiency (less time, less cost, less energy). End-user validation of an industrial ultrasonic application in the extraction process of extra virgin olive oil. It determines the desired radical change in the value of the product (healthier) and the improvement of producers' income (a larger quantity of a higher value product).

An Innovation That Looks to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
Two companies, Pieralisi, market leader in oil machines (Italy), and Cedrat Technologies, market leader in ultrasonic devices (France); they designed and produced prototypes (500 and 4000 kg/h); and finally. In particular, it is difficult to have complete control over the factors (oxygen concentration, temperature, etc.) that affect the activation of desired enzymatic reactions (synthesis of volatile compounds via the lipoxygenase pathway) and the inhibition of undesirable enzymatic reactions (oxidation of polyphenols by peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase) [3]. Considering the experimental evidence that showed that the innovative technology developed did not compromise the synthesis of aromas, and considering the different enzyme kinetics, which sees the lipoxygenase pathway preferentially in terms of time compared to oxidative enzymes that require long activation times in process conditions, it can be concluded that, contrary to what happens in other food industries, no degradation reaction can be attributed to the use of ultrasound [31].
Key Questions on Industrial Ultrasound Applications in the Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Extraction Process
The first step of this research was represented by an overview of the potential application of emerging technologies in the pure olive oil extraction process. Starting from the development of the idea (TRL 0) and the investigation of the principles postulated and observed without any experimental evidence available (TRL 1), the potential of a group of emerging technologies (ultrasound, microwaves and pulsed electric fields) was analyzed to improve the pure olive oil extraction process. The final part of these first steps was concluded with the formulation of a hypothesis of the application of ultrasound technology to the pure olive oil extraction process (TRL 2).

The Role of Patents and Open Innovation in Accelerating Scientific Innovation
Influence of different centrifugal extraction systems on antioxidant content and stability of virgin olive oil. Working towards the development of innovative ultrasound equipment for the extraction of virgin olive oil. Ultrasound. A review of emerging techniques in the extraction process of virgin olive oil: Strategies in the development of innovative plants.J.
Pharma-Nutritional Properties of Olive Oil Phenols
Transfer of New Findings to Human Nutrition
Molecular Insights into Mechanisms of Action
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are important inflammatory effectors that contribute to the elimination of invading pathogens and support tissue repair, which accelerates the resolution of inflammation. However, ROS/RNS can cause the generation of inflammatory initiators (eg inflammatory cytokines) and damage macromolecules such as lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. In particular, olive oil and its phenolic compounds exert beneficial health effects that include anti-inflammatory and antioxidant (direct or indirect) mechanisms, as reflected in many reviews [47-51].
Cardiovascular Disease, Metabolic Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes
The protective action of HT, tyrosol (Tyr) and other phenolic compounds present in olive oil against oxidative damage and inflammatory response has been repeatedly demonstrated in vitro and in vivo [81]. Recently, in the context of inflammatory response in immune blood cells, pure HT, Tyr and homovanillic alcohol (HVA) at physiologically relevant concentrations (0.25-1μM) were able to inhibit oxysterol-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1βANT, PK, MIF, MIF, MIF and RIDOS). JNK, p38) [82]. Fewer studies in healthy [91] and hyperlipidemic subjects [92] reported an absence of effect in surrogate markers of CVD, including lipid profile, inflammation and oxidation, after supplementation with olive oil biophenols.

Neurodegenerative Diseases
Recent studies suggest that olive oil phenolic compounds are processed by the body as xenobiotics via the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling axis and exert their protective action through the induction of these enzymes. In summary, in vitro and in vitro neuroprotective activities attributed to olive oil phenols include interference with amyloid and tau protein aggregation, and reduction of Aβ deposition, production, and induced inflammation, as well as enhanced Aβ clearance, decreased inflammatory biomarkers, oxidative stress, and apoptosis, reduction of cerebral infarct volume and damage following induced injury, and attenuation of insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ATP depletion. On the other hand, human evidence on the neuroprotective activity of olive oil phenols derived from clinical trials is sparse (Table 1, Figure 1).
Hepatic Dysfunction
Tyr, OLE and PEOP significantly reduced the triglyceride (TG) content in relation to steatotic cells. Human evidence on hepatoprotective actions of olive oil phenols from clinical trials is scarce and inconclusive (Table 1). However, other studies where extracts of phenolic compounds from olive oil were supplemented in healthy and hyperlipidemic subjects reported an absence of effect on liver function.
Cancer
Modulation of the inflammatory phenotype associated with aging has been suggested to be an important mechanism of action of olive oil phenol. 107] in healthy men and postmenopausal women, respectively, have reported reduced oxidative DNA damage after short-term ingestion of phenol-rich olive oil. Recently, the PREDIMED trial reported a reduction in the incidence of breast cancer after long-term consumption of a Mediterranean diet rich in phenolic olive oil, compared to a low-fat control diet [22].
Rheumatic Diseases
In addition, pretreatment with these phenolic compounds prevented TNF-α-induced inflammatory effects in these cells [ 181 ]. In the same mouse model, consumption of an HT-acetate-supplemented diet significantly prevented the development of arthritis and reduced serum IgG1 and IgG2a, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), and metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) levels, as well as pro-inflammatory, TNF, TNF, TNF, TNF, and TNF levels. IL-6 and IL-17A). The results show that maternal consumption of different types of oils affects miR expression and may epigenetically explain the long-term phenotypic changes of the offspring [204].
Conclusions
Extra virgin olive oil attenuates amyloid-beta and tau pathologies in the brain of tgswdi mice.J. In vitro effects of extracts of extra virgin olive oil on human colon cancer cells.Nutr. Anti-inflammatory and joint protective effects of extra virgin olive oil polyphenol extract in experimental arthritis.J.
The Effect of Exclusive Olive Oil Consumption on Successful Aging: A Combined Analysis of the
Results
Results of linear regression models (b±SE) that evaluated the association between (a) the category "Non-exclusive culinary use of olive oil" compared to the category "No culinary use of olive oil" (independent variable) or (b) the category "Exclusive culinary use of olive oil" compared to the category "No culinary use of olive oil" (independent variable) and the index of successful aging (dependent outcome).
Discussion
As a result, such strategies that encourage the exclusive use of olive oil as a preparatory (unheated) and cooking oil can help improve the sustainability of both populations and public health systems. According to the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture), extra virgin olive oil, the most popular culinary type of olive oil, contains 73,330 g of monounsaturated fatty acids, 13,330 g of saturated fatty acids, and 6,670 g of polyunsaturated fatty acids per 100 ml [34], and can be considered the best oil for consumption [35]. In addition, the type of olive oil consumed was not stated; however, the effect of olive oil - regardless of the specific type - on human health has been established [36].
Conclusions
Monounsaturated fatty acids, olive oil and health status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Lipids Health Dis. Role of olive oil and monounsaturated fatty acids in mitochondrial oxidative stress and aging.Nutr. Beneficial effects of olive oil phenols on the aging process: Experimental evidence and possible mechanisms of action. Nutr.
MDPI

![Figure 2. (A) PCA (t[1]/t[3] scoreplot for the whole NMR dataset of EVOOs (six components give R2X(cum) = 0.939 and Q2(cum) = 0.859)](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9200910.0/28.723.129.596.622.851/figure-pca-scoreplot-nmr-dataset-evoos-components-cum.webp)