The majority of social innovations included in the survey were service innovations. It was founded by a Swedish association that is mainly active in the Stockholm region (see: Nordfeldt et al. in this chapter).
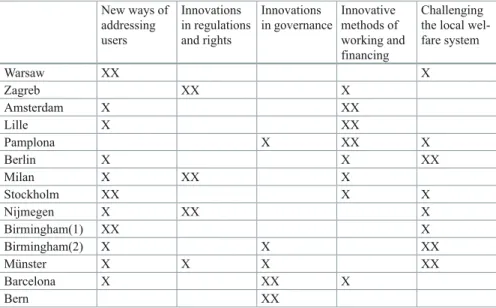
Sending and Receiving—the Diffusion of Social Innovations
Therefore, the question of motivation (or lack thereof) is important in the analysis of the diffusion of social innovations. They may have a predominantly bottom-up character, promoted by third sector organizations and the cultural orientations of the specific environment they come from (see, for example, the cases from Sweden and France in this chapter).
Conclusions
In the debates about persistent hierarchy (Lynn 2011) and new forms of governance sensible to this challenge, some have labeled such an approach “democratic experimentalism” (Sabel 2012). Implicitly, it overestimates the role of organizations involved in the direct transfer of innovations (especially professional networks) and underestimates the role of actors involved in the wider process of local transformation, including citizens and voluntary organisations.
179 Open Access This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any non-commercial use, duplication, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in in any medium or format, as long as the original author(s) and source are properly credited, a link to the Creative Commons license is provided, and any changes made are noted. Images or other third-party material in this chapter are licensed under a Creative Commons Work License unless otherwise noted in the credit line; if such material is not covered by a Creative Commons license for the work and such action is not permitted by law, users will need to obtain permission from the licensee to duplicate, adapt or reproduce the material.
Warsaw: Paving New Ways for Participation of Mothers, Fathers, and Children in Local Public
- Introduction
- Warsaw As a Context of Innovation
- The Foundation
- Types of Services and Ways of Addressing Users
- Internal Organization and Modes of Working
- Embeddedness in the Local Welfare System
- Conclusions
Mothers’ Art” - the exhibition of modern art created by mothers; "MaMa Perform"—performative workshops for mothers; publication of books for adults (such as the anthology "What does it mean to be a mother in Poland") and stories for children;. MaMa Foundation's activities are followed with interest by organizations and institutions in other Polish cities as well as abroad.
Zagreb: Parents in Action—Innovative Ways of Support and Policies for Children, Women and
Introduction
This chapter presents the case of the CSO Roditelji u akciji–Parents in Action (RODA), which is seen as innovative in the field of childcare. According to the National Strategy for Family Policy (2003), an increase in the number of childcare facilities and an increase in the number of children receiving organized pre-school care and education was one of the priority areas for family policy development.
RODA
- Internal Organisation and Modes of Working
- Concepts and Ways of Addressing Users
- Interaction with the Local Welfare System
The association's activities are mainly financed through state and city programs that support civil society. They also distribute a kind of anti-award to those who stand out in their negative approach to the association's vision.
Conclusions
Hamdouch (Eds.), International handbook on social innovation: Collective action, social learning, and transdisciplinary research (pp. 412–423). Hamdouch (Eds.), International handbook on social innovation: Collective action, social learning, and transdisciplinary research (pp. 442–453).
Amsterdam: Neighbourhood Stores for
Department of Political Science and Public Administration, Institute for Management Research, Radboud University Nijmegen, PO Box HK Nijmegen, The Netherlands e-mail: t.brandsen@fm.ru.nl.
Education, Research, and Talent Development—
The BOOT Project
Introduction
At the same time, wijkaanpak encourages different actors who are involved in the provision of welfare services at the local level to engage in new partnerships with other actors operating in the same neighbourhoods. Neighborhood shops for education, research and talent development (Burtwinkels voor Onderzoek, Onderwijs en Talentontwikkeling, or BOOT) can be seen as a combination of these developments, a national push towards more collaboration and a local evolution towards pragmatic, tailored solutions for the problems of special fields.
Neighbourhood Stores for Education, Research, and Talent Development (Buurtwinkels voor Onderzoek,
- Conceptions and Ways of Addressing Users
- Internal Organization and Modes of Working
- Interaction with the Local Welfare System
- Future Developments
So there are also other BOOT concepts in other parts of the Netherlands that do it their own way. And this is a trend that you see throughout the Netherlands, even in Europe (Manager BOOT).
Conclusion
Lille Metropolis: Co-production of Housing in a Major Urban Renewal District
- Introduction
- The Ilot Stephenson Rehabilitation
- Approaches and Ways of Addressing Users
- Internal Organisation and Working Methods
- Embeddedness in the Local Welfare System
The Ilot Stephenson project also inspired and strengthened the management of the entire urban renewal planning process. Concretely, a part of the architectural firm is established in the district, which is considered a workplace.
Pamplona: Neighbourhood Children
Services—A Grassroots and Local Council Initiative
- Introduction
- The Context
- The Development of Neighbourhood Children’s Services in Pamplona
- Conceptions and Ways of Addressing Users
- Organisation and Modes of Working
- Governance
- Conclusions
The concept of working to promote children's rights seems to be linked to the concept of project autonomy, even if they belong to local government. The triangle consisting of the local council (responsible for the service as a whole), associations (which have a legal contract with the local council for implementation) and contractors (who are employed by the association but are in practice integrated into the local organization of social services) enables the previously mentioned project autonomy.
Berlin: Kreuzberg Acts—Entrepreneurship in the District
Introduction
Kreuzberg Acts: The Innovation
- Types of Services and Ways of Addressing Users
- Internal Organization and Modes of Working
- Embeddedness of the Project in the Local Welfare System
Measured in terms of cooperation with local and state authorities, Lok.a.Motion is a fairly well-embedded partner. Despite these shortcomings in terms of institutional support, Lok.a.Motion developed strategies to use the local welfare system for its own goals.
Conclusion
For example, convincing the district mayor or the manager of the job center of a specific project proved more successful than trying to break routine patterns of vocational training all at once. Co-op: A revolutionary mindset that combines competition and cooperation: The game theory strategy that is changing the game of business.
Milan: “We Help You to Help Yourself”—The Project of the Fondazione Welfare Ambrosiano
- Milan and the Context of Innovation in Welfare Policies
- Fondazione Welfare Ambrosiano: Basic Features
- The Core Activity: Micro-credit Guarantees, a New Welfare Instrument
- New Frontiers: FWA as an Innovator in the Local Welfare System
Two fundamental characteristics of the foundation's actions are an active approach and rotation in the use of funds. Created as an anti-crisis initiative, the FWA currently envisages its role also after the end of the recession.
Stockholm: Innovative Ways of Supporting Children of Single (Lone) Mothers
Introduction
An "agreement" was drawn up and agreed upon between the local administration and civil society organizations (CSOs) working in the field of social welfare. There are strong expectations that civil society will actively participate in the renewal of social welfare (Segnestam Larsson and Carrigan 2013).
Children of Single (Lone) Mothers (Barn till Ensamma Mammor)
- Internal Characteristics
- Dealing with Local Context
This part of the project is costly and the three people working on the project have devised a special way of fundraising. Much still needs to be done to make people recognize the problems of these children”, says the project leader (interview).
Concluding Remarks
By making this group visible, there is an ambition in the project to contribute to long-term changes for the target group, both children and mothers. The project has undergone some diffusion, which is also in line with Fryshuset's ambitions.
Nijmegen: Work Corporations—for the Unemployed, by the Unemployed
- Introduction
- Work Corporations
- Internal Organisation
- Ways of Addressing Users
- Interaction with the Local Welfare System
- Future Developments
- Conclusion
Almost all users of the employment agencies have to have an interview or sometimes even a formal job application. In short, there should be a more intensive relationship between the municipality and the labor companies than anticipated.
Birmingham: The Youth Employment and Enterprise Rehearsal Project
Introduction
However, because Birmingham contains some of the most deprived areas with the highest levels of unemployment in England, various central government initiatives have been implemented locally through the city council since 2000. The city was allocated £118 million over 3 years from 2008, and almost half of WNF's resources specifically targeted unemployment (unemployment is a broader term than unemployment as it includes everyone of working age who is not working regardless of their circumstances).
YEER Project
- Context
There were a number of key contextual factors that enabled the existence of the YEER project in Birmingham. It also linked to the move towards working in partnership and a desire to increase the involvement of the third sector.
Conclusion
Personal Social Services Research Unit, Cornwallis Building, University of Kent, Canterbury CT2 7NF, Kent, UK. School of Social Policy, Sociology and Social Research, Cornwallis Building, University of Kent, Canterbury CT2 7NF, Kent, UK.
Birmingham: A “Locality Approach” to Combating Worklessness
Introduction
Bespoke/tailored programs that match skills needs to job content/skills demand, addressing barriers to employment and including post-employment support for the individual and employer.
A Locality Approach to Unemployment .1 Internal Organisation
- Interaction with Users
- Context
The approach also supported partnership working, which was a characteristic of the local welfare system emphasized by local government. Private sector providers also felt that their relationships with many community and third sector groups had improved during the delivery phase of the employment and skills plans.
Conclusion
The locality approach has had problems with sustainability and is currently not working in some of the original areas where it was implemented or not in the way it was originally intended. This was primarily seen as a knock-on effect of the loss of neighborhood management resources which supported the process.
Münster: How Prevention Visits Improve Local Child Protection
Münster—City Context and the Field of Local Childcare Policy
In summary, adequate childcare provision and increased flexibility, as well as increasing quality standards, appear to be important for the well-being of individuals and for improving the attractiveness of the city as a whole. In general, it is possible to recognize a broad consensus among relevant actors from local politics and public administration and organized civil society on the promotion of childcare policy.
- Internal Organisation and Modes of Working
- Context of the Innovation—Interaction with the Local Welfare System
The actors of the Youth Office adapted the concept to the situation in Münster. 4 The description of the parents' letters is based on the website of the Youth Office.
Conclusion
In addition to this, the evaluation of prevention visits in different cities underlines the positive effects of the specific Münster model: Parents participating in the study emphasize the positive effects of both the work with employees of the Youth Office as well as the visit of all parents in the city (Frese and Günther 2012). The analysis of the prevention visits in Münster demonstrates the necessity of innovators to join locally prevailing norms and values.
Newspaper Articles
Interviews
Internet
Barcelona: A Citizen’s Agreement for an Inclusive City
Barcelona’s Sociopolitical Structure
In this way, policy makers in the Social Welfare Department set themselves a basic goal of building a social services model that was participatory. Meanwhile, the search for a "Barcelona model" has continued more seriously in various political arenas, and cooperation with civil society in social welfare matters has also increased significantly, representing a force for social innovation in the city.
The Programme “Citizen’s Agreement for an Inclusive Barcelona”
- The Programme
- Impact of the Programme
It also promotes projects in which collaboration between diverse entities and organizations in the city is key. The importance of the CA in the city's social welfare system can also be measured with the change in the municipal government.
Conclusions
- The CA Programme
- The Action Networks
It is the Social Economy Network (previously the Network for Social Integration and Labor Market Integration), which is managed by the Barcelona Activa municipal institution. This is one of the issues that the entities running the CA have on the table for future discussion.
Bern: Integration Guidelines
- Introduction
- The Context
- Integration Guidelines
- Internal Organization and Mode of Working
- Conception and Ways of Addressing Users
- Interaction with the Governance System
- Conclusion
First, through the development of the guidelines and the consultation process, experts and stakeholders (sometimes not considered stakeholders or previously not considered themselves stakeholders) are involved and encouraged to participate in the city's integration policies. On the other hand, the guidelines can be seen as a recognition of the eminently political nature of integration policies.