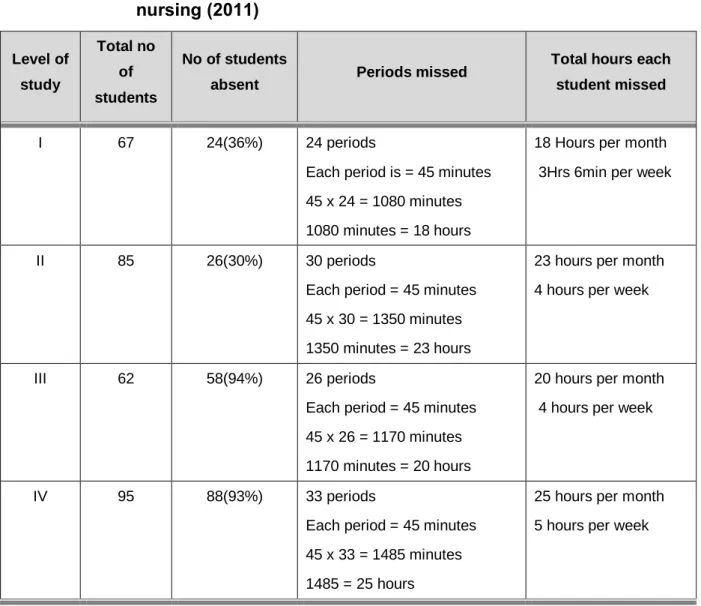
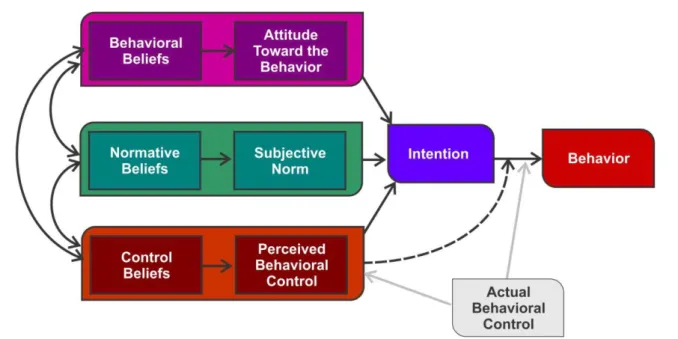
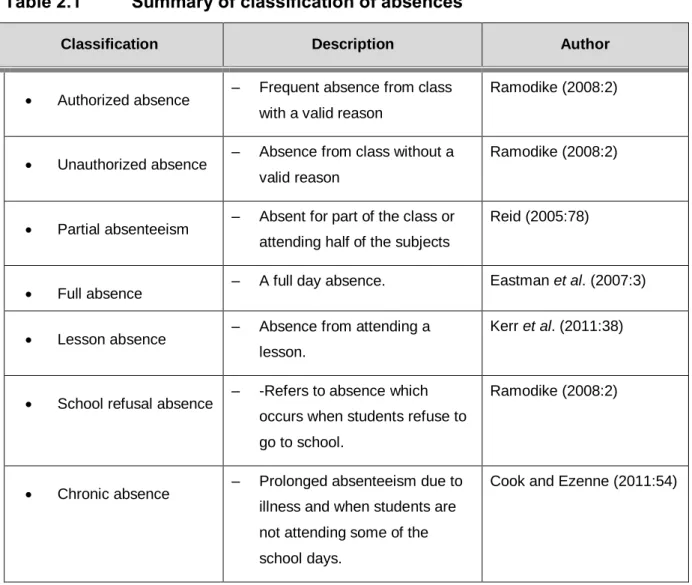
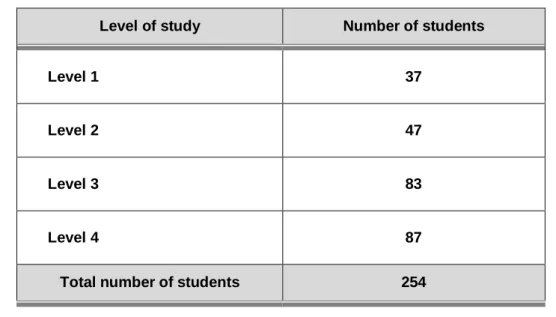
The sample included nursing students from I to IV. degrees (n=209) registered at the Faculty of Nursing in Limpopo Province. Regarding school-related factors, the majority of nursing students indicated that poor infrastructural facilities in the school were the cause of student absenteeism (39.2%; n=82).
OVERVIEW AND RESEARCH AND PHILOSOPHICAL
INTRODUCTION
BACKGROUND AND RATIONALE FOR THE STUDY
- Classification of student absenteeism
- Causes of student absenteeism
- The impact of student absenteeism
- Strategies to reduce student absenteeism
PROBLEM STATEMENT
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
AIM AND OBJECTIVES
PARADIGMATIC PERSPECTIVE
- Meta-theoretical assumptions
- Man
- Health
- Environment
- Nursing
- Theoretical assumptions
- Central theoretical statement
- Conceptual definitions
- Methodological assumptions
RESEARCH DESIGN
RESEARCH METHOD
- Population
- Sample
- Probability was deleted random sampling written, was
- Sample size
- Pilot study
- Data collection
- Data collection method
- Data analysis
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
- Respect for others
- Relevance and value
- Scientific integrity
- Risk benefit ratio
- The right to freedom from harm and discomfort
- The right to protection from exploitation
- Respect for human dignity
- Informed consent
- Distributive justice
- Professional competence
- Privacy and confidentiality
- Publication of results
OUTLINE OF THE DISSERTATION
SUMMARY
LITERATURE REVIEW
INTRODUCTION
LITERATURE REVIEW
STUDENT ABSENTEEISM
- CLASSIFICATION OF ABSCENCES
CAUSES OF STUDENT ABSENTEEISM
- Student-centred factors
- Lack of personal interest in studies
- Socialisation and substance abuse among students
- Not understanding the subject
- Lack of study time
- Inability of students’ mental capacity to match the
- Inferiority complex among students
- Lengthy periods
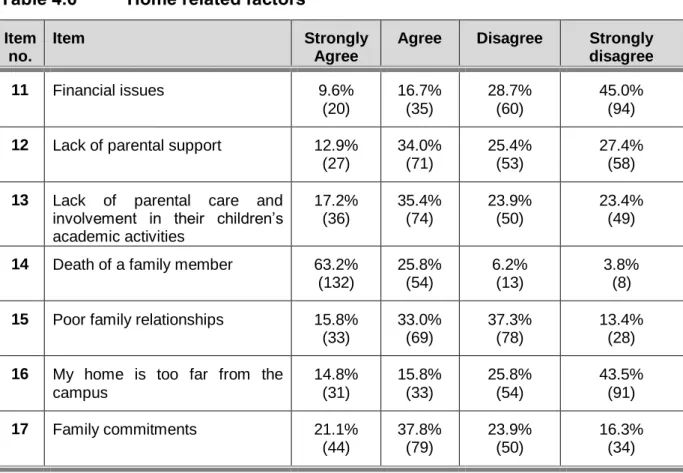
- Home-related factors
- A poor family relationship
- Death of a family member
- Family commitments
- Financial issues
- Travelling long distances to campus
- School-related factors
- Classroom environment not conducive to learning
- Poor lecturer-student relationship
- Inadequate orientation about school policies
- Excessive homework and projects for students
- Lack of recreational and allied activities
- Negative peer influence
- Poor infrastructural facilities in school
- Inclement weather
- Poor teaching skills of lecturers
- Lecturer not turning up for scheduled lecture
- Social factors
- Fear of students that bully
- Family commitments
- Low societal value for education
- Transportation problems
- Political activities
- Wealthy persons versus educated persons
- The belief that a lot of education is not required for
IMPACT OF STUDENT ABSENTEEISM
CONCLUSION
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
RESEARCH DESIGN
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory design
- Descriptive design
- Cross-sectional design
RESEARCH METHOD
- Population
- Sample and sampling procedure
- Sample
- Sampling
- Sample size
- Research setting
DATA COLLECTION
- Discussion of the instrument
- The Factors Influencing Absenteeism Questionnaire
- Data collection procedure
DATA ANALYSIS
VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF THE INSTRUMENT
- Validity
- Content validity
- Face validity
- Construct validity
- Reliability
CONCLUSION
RESULTS
INTRODUCTION
An overview of the statistical analysis process is provided and a discussion of the findings is given.
DATA COLLECTION
The population in this study consisted of nursing students from a selected campus of a Faculty of Nursing in Limpopo Province.
DATA ANALYSIS
The Bartlett test refers to a test in statistics to determine whether there is sufficient correlation between items. According to Polit and Beck, internal consistency is the degree to which the sub-sections of a composite scale all measure the same attribute as a measure of scale reliability. Cronbach's alpha coefficient refers to a test most often used to assess internal consistency (Brink et al.
Spearman's rank order correlation coefficient refers to the correlation coefficient used when one or more variables are measured on an ordinal scale (Jackson, 2009: 423). According to Jackson, the independent sample t-test refers to a parametric inferential statistical test of the null hypothesis for a single sample in which the population variance is unknown.
RESULTS
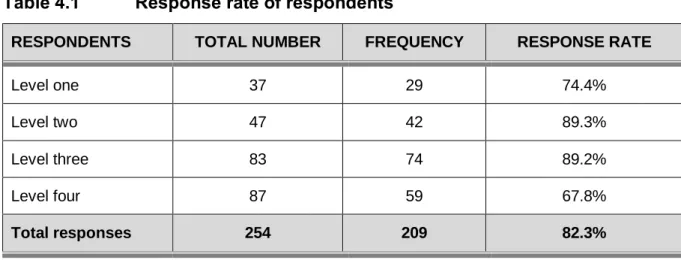
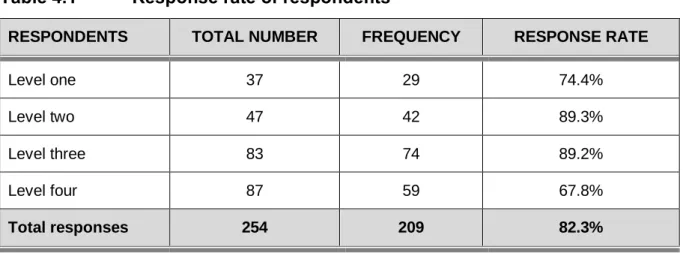
- Response rate
- Demographic profile
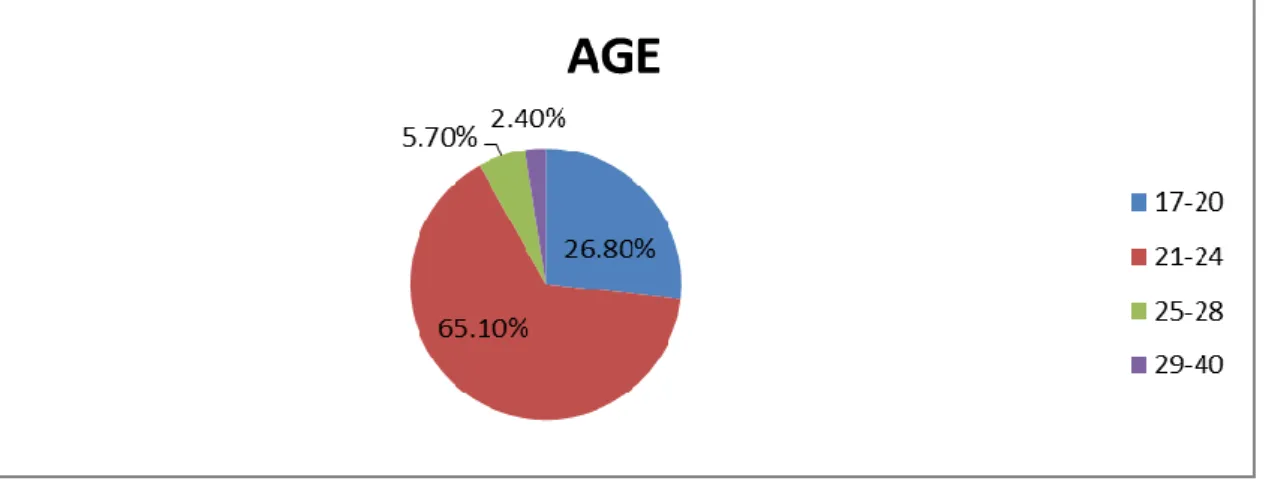
- Age
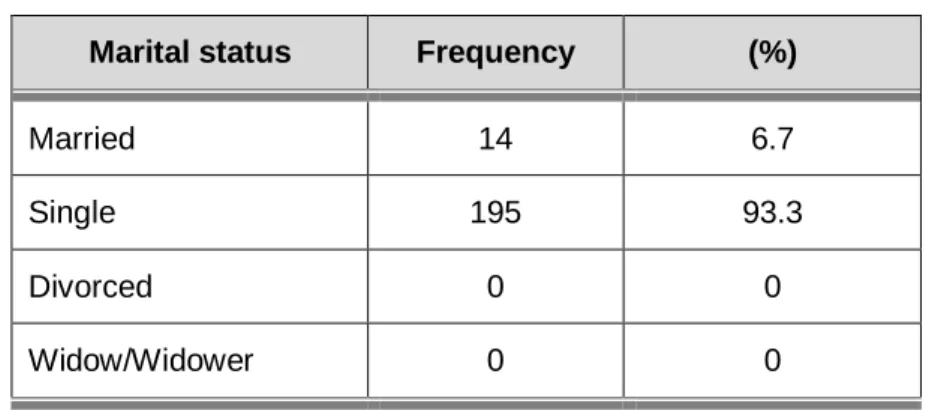
- Marital status
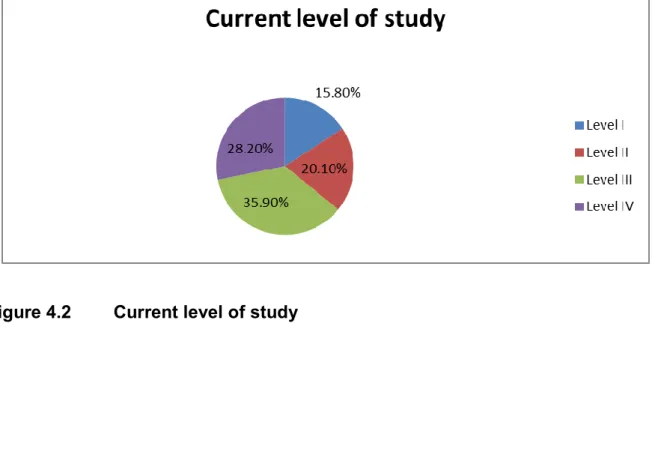
- Current level of study
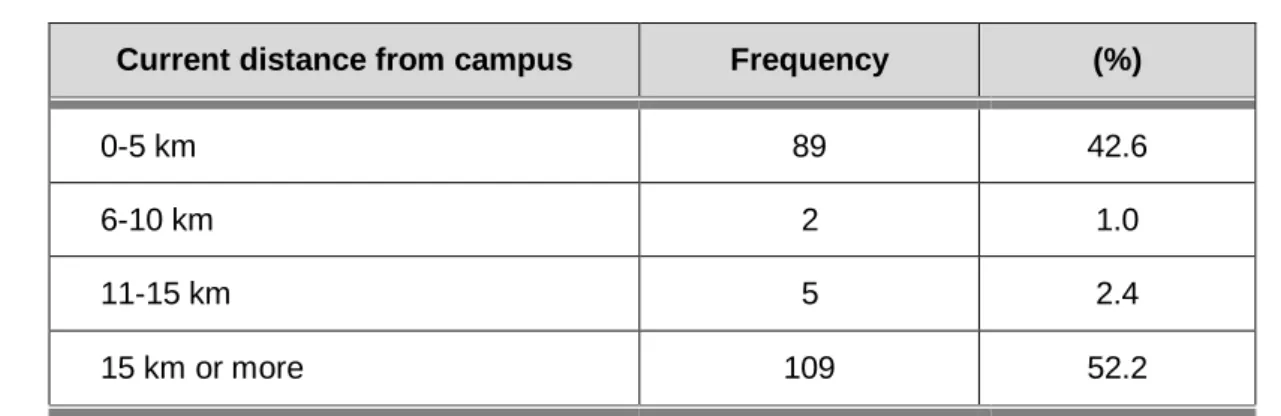
- Distance from campus
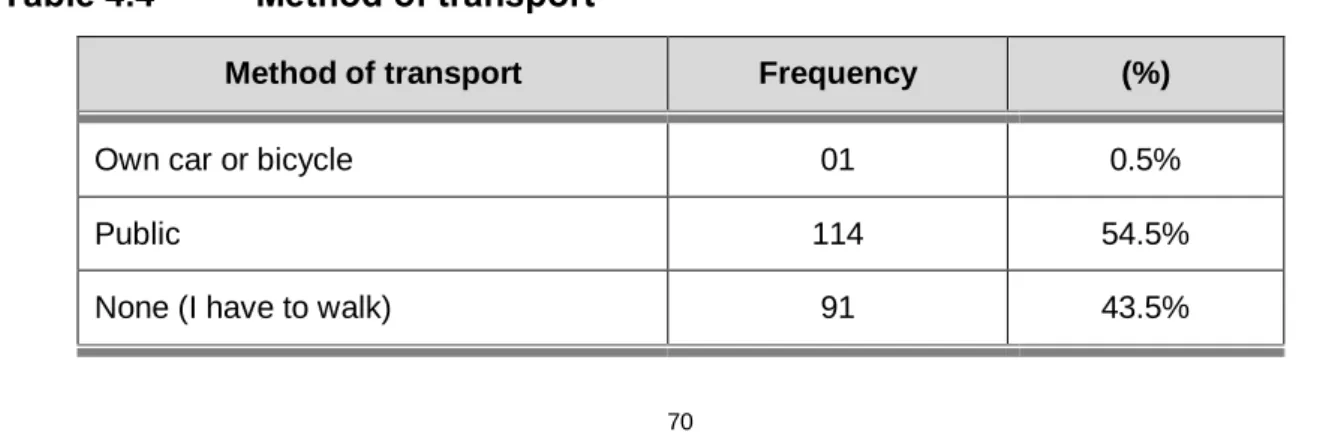
- Method of transport
The data was collected at a college of nursing in the Limpopo Province and there were 254 (N=254) registered nursing students. The following demographic data are discussed: the age of the nursing students, the marital status, the current level of study, the current distance that the nursing students travel from the campus and the mode of transport they use. According to the South African Nursing Council's age analyses, the age of the nursing students enrolled in the R425 program varies from 17-53 years (SARV, 2014).
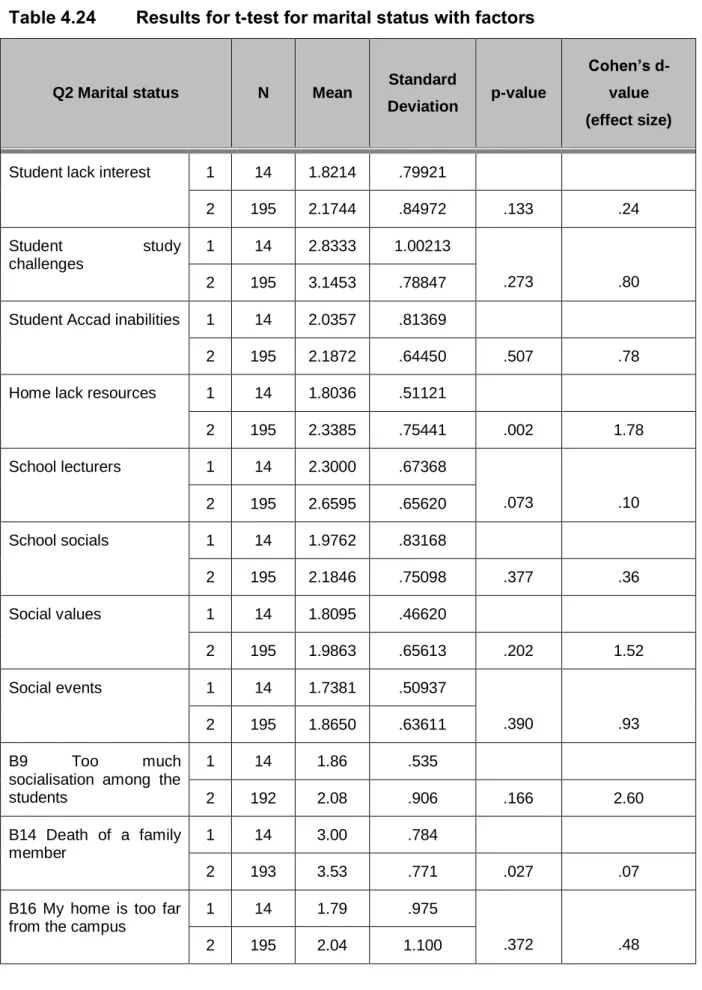
According to the respondents' answers to the question about marital status, the largest proportion of the respondents (93.3%; n=195) indicated that they were single (unmarried) and the respondents who were married 6.7% (n=14) of the respondents. The respondents were also asked about the method of transport they use to travel to campus. n=1) of the respondents used his/her own transport (car or bicycle).
DISCUSSION OF THE DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
- Student-centred factors
- Home-related factors
- School-related factors
- Social factors
The majority of the respondents (31.6%; n=66) strongly disagree and 31.6% (n=66) disagree that they are absent from class due to a lack of interest in school subjects or courses (item 1). Most of the respondents, 41.6% (n=87), disagreed and 25.4% (n=53) agreed that they are absent from class when the teacher does not show up for a scheduled lecture (item 21). The majority of respondents (38.8% (n=81)) disagreed and 22.0% (n=46) strongly disagreed that they were absent due to a lack of recreational and related activities (item 23).
The largest share of respondents, 51.6% (n=108), do not agree, and 27.8% (n=58) do not agree at all that the wealthy are considered more than the educated (item 31). The largest proportion of respondents, 29.7% (n=62), do not agree at all, and 26.8% (n=56) do not agree that they are absent themselves when they are afraid of students who bully (item 36).
MEASURES TO REDUCE STUDENTS’
- Orientation program
- Established policy for controlling student absenteeism
- Systematic student absenteeism monitoring tool
- Motivating program
- Prize giving ceremony
- Friendly mutual student-lecturer relationship
Regarding program improvement, 67.9% (n=142) of respondents indicated that they needed to improve the current program. According to 41.1% (n=86) of respondents, they do not have a monitoring program, and 33.0% (n=69) of respondents indicated the need to establish a program. According to 43.5% (n=91) of the respondents, there is a motivational program on campus, and 36.4% (n=76) stated that they want to improve the current program.
The largest share (56.5%) of respondents (n=118) stated that they do not have a motivational program that emphasizes the benefits of attending classes. The largest share (50.7%) of respondents (n=106) stated that they do not have a friendly and mutual relationship program between lecturer and student on campus.
FACTOR ANALYSIS
- Exploratory factor analysis
- Student-centred factors
- School-related factors
- Home-related factors
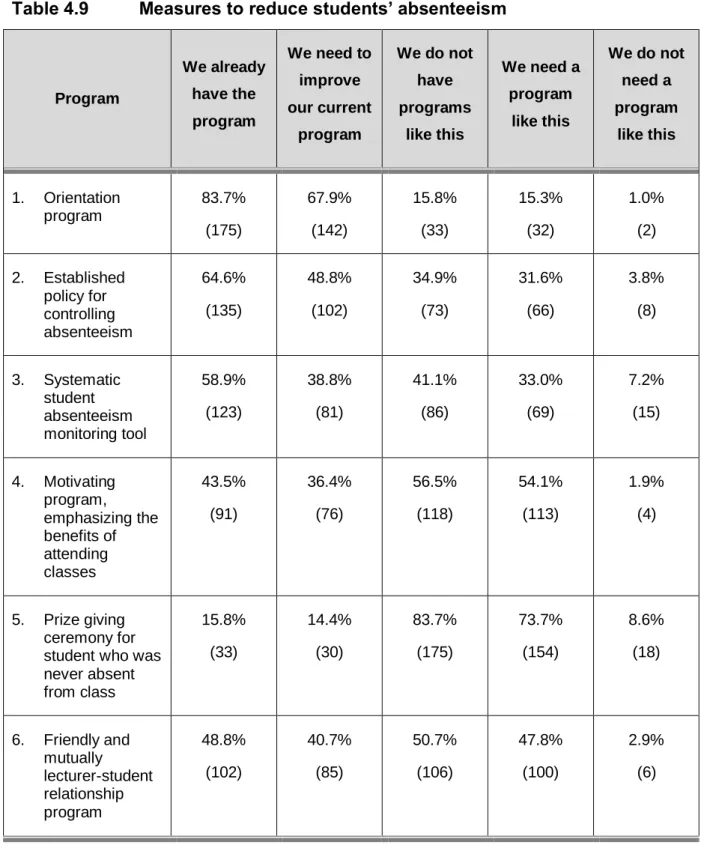
Grouping of items was satisfactory with four-factor analysis; therefore, it was discussed and agreed that this could form the final product. The results of the KMO value and the Bartlett test for the school-related factor analysis were 0.745 and a total variance of 53.684% was explained; these results are sufficient. Table 4.12 shows the subscales of factor three analysis and the items they represent.
Table 4.13 sets out the subscales of the factor three analysis and the items displayed. Home-related factors consisted of seven items. The researcher and statistician discussed and agreed on a two-factor analysis for grouping the items.
RELIABILITY
- Student-centred factors
- School-related factors
- Social factors
- Home-related factors
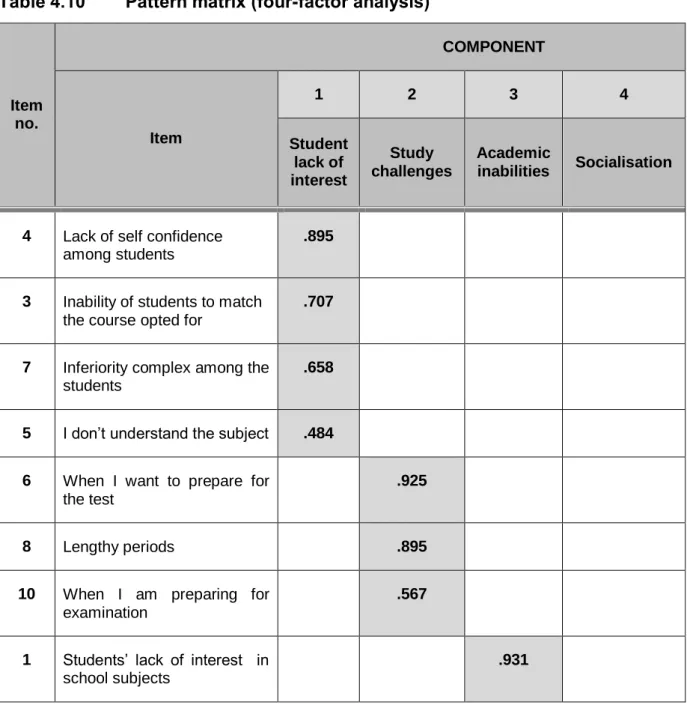
Study challenges were seen as the biggest problem (M=3.12), while academic incompetence and lack of student interest were lesser problems. The topic of social impoverishment was given to the following articles; point 23 – lack of recreational and accompanying activities such as sports programs; point 24 - lack of cooler or farewell holidays; and point 25 – inadequate orientation for training hours. The results obtained for dissatisfaction with lecturers are considered acceptable and show that this aspect has a great impact on student absenteeism.
Lack of resources was the theme of item 11 – financial issues; item 12 – lack of parental support; item 13 – lack of parental care; and item 14 – involvement in their children's academic activities and poor family relationships. From the home-related factors, lack of resources was the ultimate reason for student absenteeism.
CORRELATIONS
- Correlation between the factors and ordered
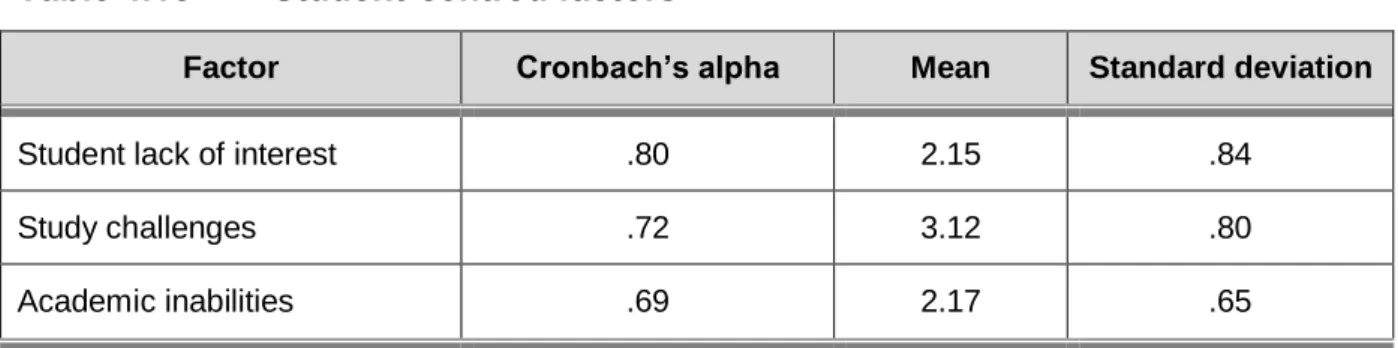
A moderately positive correlation (r=.401) is shown between the school teachers and the students' lack of interest, which means that students who experience dissatisfaction with school teachers may experience a lack of interest in their studies. There was a moderate positive correlation between school teachers (r=.265) and home deprivation, which may mean that students who lack home resources may experience dissatisfaction with their teachers. Home lacks resources and social values had a moderate positive correlation (r=.335), indicating that students who lack home resources may value social life more than their studies.
There was a moderate positive relationship between distance from campus and home being too far from campus (r=.301). However, a moderate positive relationship was found between transportation difficulties and distance from campus (r = 0.372).
ASSOCIATION OF FACTORS WITH BIOGRAPHICAL
- Marital status
- Method of transport
Great practical importance was also seen in social events among single students (M=1.86) and married students (M=1.73). Single students (M=2.08) experienced more student socialization than married students (M=1.86) and a high practical significance was seen. For single students (M=2.04) my house is too far from campus was a bigger problem than for married students (M=1.79); medium significance was reported.
Single students (M=2.11) were found to have more transportation problems than married students (M=1.64) and medium significance was evident. In addition, single students are more afraid of students who bully (M=2.37) than married students (M=1.79), as indicated by high significance.
CONCLUSION
SUMMARY
EVALUATION OF THE STUDY, LIMITATIONS AND
INTRODUCTION
EVALUATION OF THE STUDY
Regarding the study's objective 1, which is to explore and describe the reasons for student absenteeism, the results indicated that students absent from classes due to student-centered factors, for example, when they want to prepare for exams, the largest proportion of respondents ( 53.1%, n=111) strongly agreed with this point. Regarding the statistically significant relationship between the variables demonstrated by the correlation coefficients, there is no relationship between socialization and student absenteeism. Based on the results, most of the respondents disagreed with factors such as lack of entertainment options around campus as a reason for absenteeism.
Regarding measures to reduce student absenteeism, most of the respondents, 73.7% (n=154), indicated the need for an award ceremony to honor students who were never absent from class. The requirements of objective 1, describing the reasons for student absenteeism, and objective 2, formulating strategies to reduce student absenteeism, have been met. Consequently, the study contributed to the knowledge base of nursing in South Africa.
LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
Implementation of a student orientation program focusing on the consequences of student absenteeism, which is implemented at least twice a year; in the first and second semesters. Additionally, nursing students who are only available on campus during exams (direct enrollments) were not part of the study as they were not available at the time of data collection. Mediator collected data at a selected nursing college campus in Limpopo province, so the results cannot be generalized to other nursing colleges in South Africa.
However, despite the limitations, the study provided important information about the factors that contribute to student absenteeism. The identified factors were useful in developing strategies that could reduce student absenteeism.
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Nursing education
- Practice
- Further research
- Policy development
College management should encourage the improvement of infrastructure such as well-equipped libraries and laboratories to develop the knowledge and skills of nursing students. The management of the higher education institution should ensure that there will be professional development for the lecturers, which will include topics such as class management, promoting the student-lecturer relationship and providing moral support to the students. Replication of the same study at different nursing campuses to compare the findings and see if different findings can be obtained as the nursing educational environment is different.
An investigation of the factors that contribute to student absenteeism as seen by nurse educators using a qualitative approach. It is recommended to develop a policy that will address student absenteeism in a nursing college in Limpopo province, which will be monitored systematically.
CONCLUSION
Continuation of the study, using a qualitative approach to explore and describe in more depth the identified factors influencing student absenteeism to obtain richer data. The college management should develop an orientation program policy that will address the consequences of class absence.
SUMMARY
The impact of student and teacher absenteeism on student achievement in secondary school: the case of Kumali-Metro school district. Cross-institutional study of the causes of absenteeism among university students in Barbados and Nigeria. Improving student attendance in Indiana schools: synthesis of existing research related to student absenteeism and effective, research-based interventions.
Student absenteeism: interventions and programs to reduce chronic absenteeism and truancy St. The paradise Unified school parent-student handbook. World Health Organization Official, No. 2.) http://www.who.Into/suggestions/fag/en Date accessed: 30 November 2010.