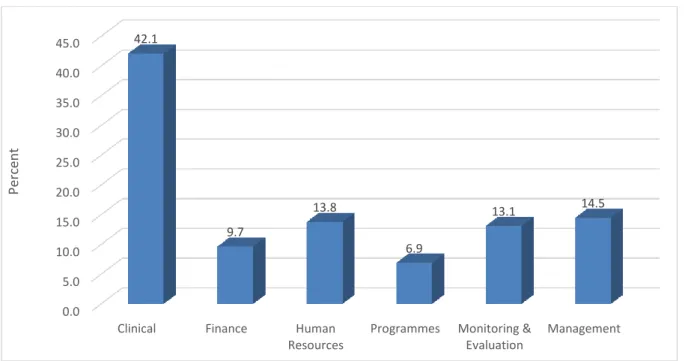
More than 80% of respondents had more than 5 years of work experience, and almost a quarter (24.0%) had more than 20 years of work experience. More than 80% of respondents believe that ethical behavior should be a key area of performance.
Introduction
There have been various complaints regarding unethical behavior by residents of the Ilembe Health District, which is part of the South African public health sector. Despite the availability of several articles by scholars and researchers on ethics, no research has been conducted regarding the knowledge, attitudes and experience of Ilembe Health District staff on ethics.
Background
This study was undertaken with the primary aim of examining the knowledge, attitudes and experience of employees of the Ilembe Health District, with the hope that this will help improve the health service environment. Public servants, including employees of Ilembe Health District, do not only work for Ilembe Health District, but also, and most importantly, serve the people of the district.
Research Questions
With this in mind, there is a need to strengthen the norms and values of the public sector, as newly hired public servants may have come to the service with values that differ from those of the public sector. The authors express concerns about hiring people from the private and other sectors, which may result in different ethical standards, which may need to be addressed through orientation and training on ethical standards in the public sector.
Objectives
Definitions of key terms
A code of practice is usually detailed and is usually used to protect employees and the status of employers. Most codes of conduct focus on detailed explicit activities in which staff may not engage (Gilman, 2005:16).
Delimitations of the study
Ethical considerations
Dissertation outline
This chapter provides an overview of the literature and theoretical framework related to ethics in the public sector. In this final chapter, the significant findings from the study will be made based on the research problem.
Summary
This chapter discusses the legislative and policy framework for ethics in the South African public sector. The population surveyed will be explained in relation to employees' knowledge, attitudes and experiences of workplace ethics, details of the questionnaire design, data collection method and sampling procedures.
Introduction
The Constitution of the Republic of South Africa
Civil servants' potential needs to be refined with good human resource management and career advancement practices. Public organizations should generally be demonstrative of the people of South Africa, with occupations and employee management practices based on merit, neutrality, fairness, and the requirement to redress historical inequalities to achieve comprehensive representation (South Africa, 1996:62).
The Public Service Act 103 of 1994
Everyone has the authority over physical and spiritual honor that entails the right to make educated decisions about reproductive health. Citizens of South Africa must be encouraged to participate in policy-making and attention must be paid to their needs.
The Code of Conduct - Public Service Regulations, 2001
White Paper on Transforming Public Service Delivery
The Patient’s Rights Charter
Health Professions Act (56 of 1974)
Nursing Act (50 of 1978)
The Public Finance Management Act (1 of 1999)
The Public Audit Act (25 of 2004)
The Protected Disclosures Act (26 of 2000)
The Nursing Council of South Africa deals with disciplining nurses for misconduct and unfair practice, promoting ethical behavior (South Africa.
Prevention and Combating of Corruption Activities Act (12 of 2004)
Summary
Introduction
The need for ethics in the public sector
This awareness is fueled by the citizenry and media, which have reported various unethical practices leading to the loss of public money. Public trust is essential in the field of public service which means that citizens must be treated fairly and public officials must handle public resources in a responsible manner that will inevitably inspire the citizen's trust and create a favorable environment.
Ethical culture in the public sector
There is an urgent need for the presence of ethical behavior in the public sector as it has a direct impact on the quality of life of all citizens, especially those who are vulnerable. Basically, the strength of ethical culture is measured by the priority placed on ethics in the organization.
Ethical attitudes
This supports the view that leaders in the public sector should use the organization's vision as a framework in the implementation of tasks so that citizens are best served without accepting good behavior. It is the general observation of citizens in South Africa that democracy is being diluted for the common good in exchange for public servants focusing on personal gains due to a culture that is unhealthy in the public sector.
Corruption in the South African public sector
Since 2001, South Africa has declined by 34 countries, with the largest decline being 17 which occurred since 2009. The dispute that corrupt behavior by office-bearers and administrative officials is influencing negative community perceptions on corruption in South Africa, is supported by research information.
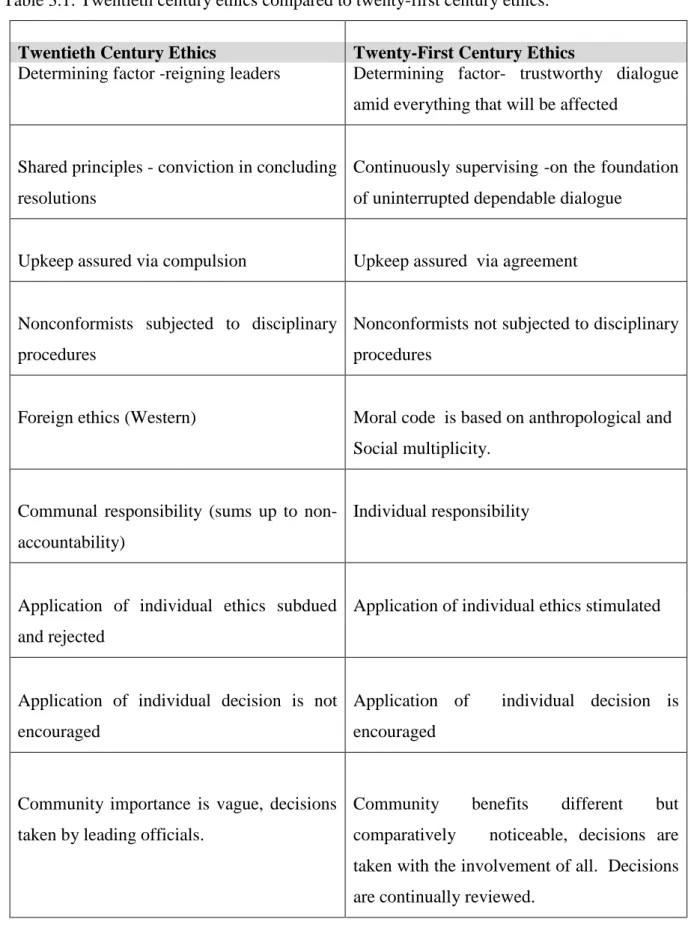
Comparison of public-sector ethics
Newham (2014:7) further reports that in addition to this trend, the current Afrobarometer report from 2013 shows that South Africa is one of the countries that has a marked escalation in public perception of worsening corruption, especially since 2008. South African legislation regarding corruption should be vigorously enforced, by rewarding public servants for good behavior and disciplining those officials who demonstrate unethical behavior.
Ethical leadership
Direct - public servants within government departments must show transparency in the resolutions and activities they take. It is clear that public leaders should apply these principles when leading other officials in the public sector, which will improve ethical behavior.
Whistle blowing and ethics
The whistleblowing process is depicted in Figure 3.1, which demonstrates the breakdown of authority to comply with to report the breach and the steps to be taken by each superior. It is essential that all whistleblowers are adequately protected and the stigma surrounding whistleblowing must be addressed by the public sector because other officials who intend to expose unethical behavior will choose not to report for fear of victimization become
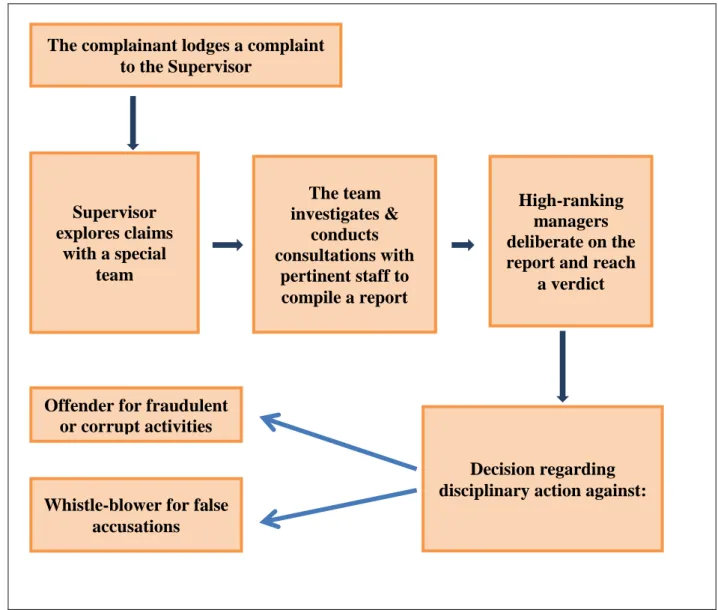
Code of conduct and ethics implementation
The much-needed reporting of those who engage in unethical behavior will help in monitoring and evaluating the legal prescriptions. The South African government has solid legal guidance for all public officials, although there seems to be a loophole in the monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of the directives and guidelines.
Principal theories upon which the research project will be constructed
TELEOLOGICAL AND ONTOLOGICAL THEORIES
- Teleological theories (utilitarianism)
- Strengths and weaknesses of teleological theories
- Deontological theories (Kantian Ethics)
- Strengths and weaknesses of deontological theories
The weakness of teleological theories is that ordinary moral reasoning collides with the teleological principle that the rightness of actions is judged solely on the basis of the goodness of the consequence. Teleological theories can also conflict with the view of justice, as society usually expects justice to happen regardless of the consequences (Browne, 2003:6).
Summary
Introduction
Research design and methodology
The correlation value between "the whistleblowers should not be protected" and the ethical reputation of an organization is not important is .320. 2008. The nuts and bolts of ethics, accountability and professionalism in the public sector: An ethical leadership perspective.
Research setting
Study population
Employees who met the described criteria were selected from the target group as a smaller group. 2010:n.p) “the use of probability sampling in quantitative research reduces errors and biases in research. Sampling is the process by which researchers select a portion of the target population, as the study population, to represent the entire unit.” The.
Sample size
Research methods
- Data collection
- Questionnaire
- Validity
- Reliability
- Reliability and validity of the research process
It is related to the theoretical data of the idea to be measured. According to Anon, citing Robson (2007:n.p), the ability to produce the same information when presented again under the same conditions.
Data analysis and interpretation
The use of simple language to formulate the questionnaire allowed the study participants to give appropriate answers, thereby preventing the results from being distorted.
Summary
Introduction
The sample
The research instrument
Reliability statistics
Factor analysis
Importance of factor analysis
A separate use of factor analysis is in survey research, where a researcher wants to characterize a number of questions with a small number of theoretical factors.
Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin and Bartlett's Test
Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity
A significant value of less than 0.05 means that we can safely proceed with the factor analysis.
Rotated Component Matrix
Factor analysis is commonly used in survey research when a researcher wishes to represent a set of questions with a smaller number of hypothetical factors as explained in 5.5. An investigation of item content loadings at or above 0.5 (and from higher or higher loadings in cases where cross-loading items is higher) measures success along with several components.
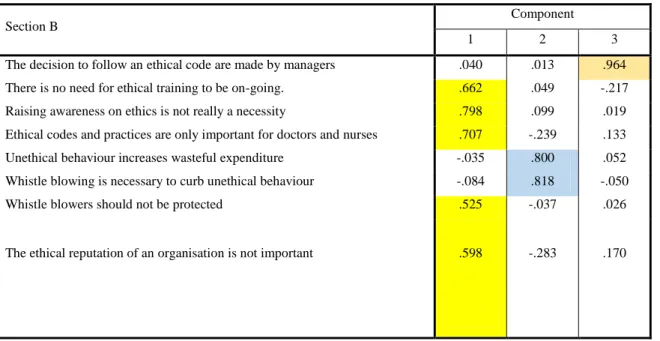
Themes identified
Importantly, the variables that created the sections are divided into 3, 2, and 5 subtopics, respectively (as indicated by the color coding). This coincidence means that the respondents have recognized sub-themes which may have been due to the method of construction of the questionnaire in terms of negative statements.
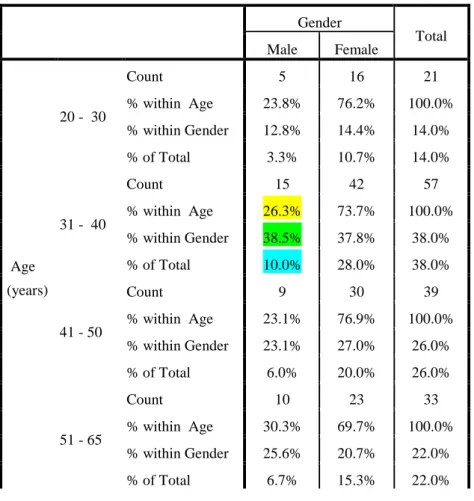
SECTION A - Demographic data
Section Analysis
The following section analyzes the respondents' scoring patterns per variable per section. The results are first presented using summarized percentages for the variables that make up each section.
SECTION B – Knowledge
Themes identified
The themes that emerged from this section are the need for ethics committees to be in place, the involvement of trade unions in creating an ethical culture, the need for ongoing training on ethical codes, the negative attitude of respondents to the implementation of ethical codes and to that of the protection of whistleblowers. Is it considered unethical for someone to harass another person Unions should be involved in creating an ethical culture Romantic involvement between supervisor and subordinate to task-related or.
SECTION C - Attitude
More than 90% of respondents felt that all employees should be able to identify unethical behavior and that it is important to be an ethical role model. All employees must be able to identify unethical behavior. The responsibility of making ethical decisions is time-consuming.
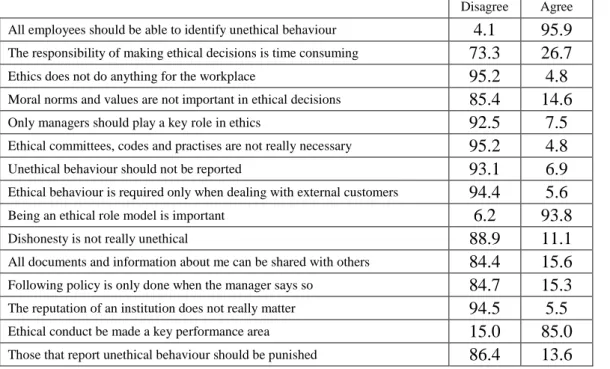
SECTION D – Experience
Themes identified
Themes that emerged are the need to develop ethics committees, the need for ethics training updates and orientation, the need to prioritize ethics in the workplace, the need for monitoring and enforcement of ethical codes of conduct, romantic relationships between supervisors and subordinates. and negative attitudes toward whistleblowing.
The chi-square tests
Hypothesis testing
All other values highlighted in yellow mean significant differences (See Table 5.4.15). that ethical auditing involves investigating whether any unethical values and behaviors are evident in the organization. The direction of the points can be obtained from the frequency tables in the appendix.
Correlations
The correlation value between "It is appropriate to control unethical behavior" and "There is no need for ongoing ethics education" is -0.337. The correlation value between "Romantic contact between superior and subordinate is acceptable to gain favor in relation to tasks or career" and "All employees should be able to recognize unethical behavior" is -0.240.
Summary
Introduction
Discussion of major findings
- SECTION A- Demographics
- SECTION B – Knowledge
- Themes identified
- SECTION C – Attitude
- SECTION D – Experience
- Themes identified
More than two-thirds (78.4%) of respondents have not received updates or training since employment. More than a third (35.5%) of respondents disagreed with discouraging reporting romantic relationships between supervisors and subordinates.
Limitations
Almost half (45.6%) of respondents disagree that their supervisors and colleagues are role models who display ethical behavior. Almost a third (31.6%) of respondents agree that colleagues or witnesses have been reprimanded for whistleblowing.
Recommendations
Recommendations for practice
Recommendations for further research
Conclusion
Understanding and maintaining ethical values in the public sector through a holistic approach to leadership. The critical need for ethical leadership to curb corruption and promote good governance in the South African public sector.