An Ethnographic Study of Predictors of Hypertension and Its Preventive Strategies in a Rural Community in Delta State, Nigeria. Impact of Cultural and Traditional Practices on the Management and Prevention of Hypertension in Some Rural Settlements in Delta State, Nigeria” (addresses Research Objectives 5 and 6). Development of Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension in Rural Areas in Delta State, Nigeria” (addresses research objective 7.) Submitted to Cardiovascular Journal of Africa (Manuscript No. CVJSA-D-14-00153).
Introduction
- Introduction and background information
- Background to the study
- Hypertension and co-morbid conditions
- Cultural concepts relevant to an ethnographic study
- Motivation for the study
- Problem statement
- Research questions
- Study objectives
- Purpose of the study
- Specific objectives
- Significance of the study
- Definition of operational terms
- Format and outline of the thesis
What is the prevalence of high blood pressure (hypertension) in a selected rural community in Nigeria. What are the most appropriate strategies for the prevention and management of high blood pressure in a selected rural community in Delta State, Nigeria. Prevention Strategy: A Comprehensive Approach to Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure (Ofili & Ncama, 2014).
Strategies for prevention and control of hypertension in Nigeria rural communities
Hypertension in Rural Communities in Delta State, Nigeria: Prevalence, Risk Factors and
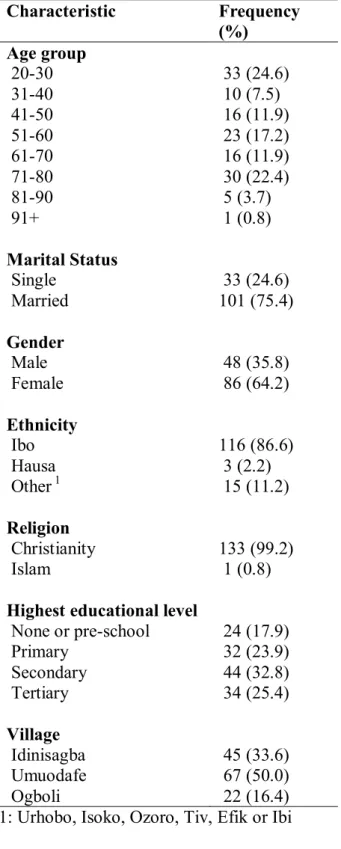
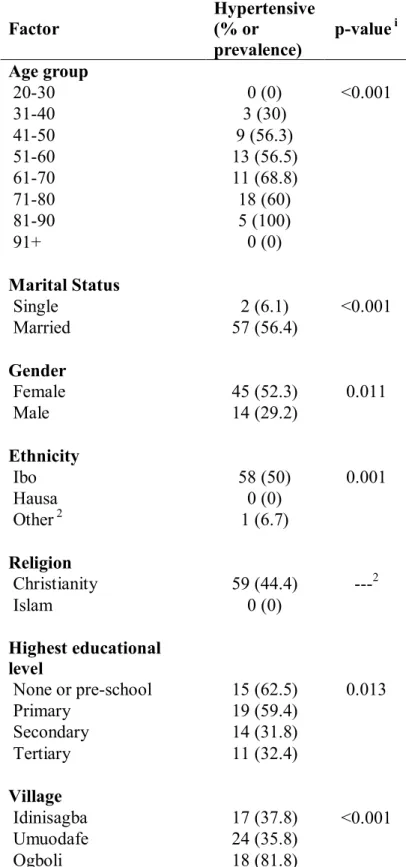
There was also a clearly increased risk of hypertension in Ogboli village compared to other villages. Since the overall prevalence of hypertension in rural areas ranges from 13.5% to 46.4% in the study country, the prevalence of hypertension is high (44%) in this rural community. Prevalence of hypertension in three rural communities of Ife North Local Government Area of Osun State, South West Nigeria.
Influence of Cultural and Traditional Practices on the Management and Prevention of
Many community-based models of high blood pressure management in rural settings are recommended. This study describes the experiences of a typical rural community in Delta State Nigeria regarding their various traditional and cultural practices and the impact these have on the management and prevention of high blood pressure in the community. High blood pressure is also managed by the use of drugs bought from chemists.
One of the participants indicated that he uses the local gin unrefined, which is a major risk factor for high blood pressure. In this study, the traditional and cultural practices identified for the treatment of hypertension were divided into drug and non-drug therapies, which reflect symptom management. Further studies on the sociological aspects of hypertension are recommended to identify reasons for the simultaneous use of traditional and Western medicine in relation to developing models for community-based management of hypertension in rural settings.
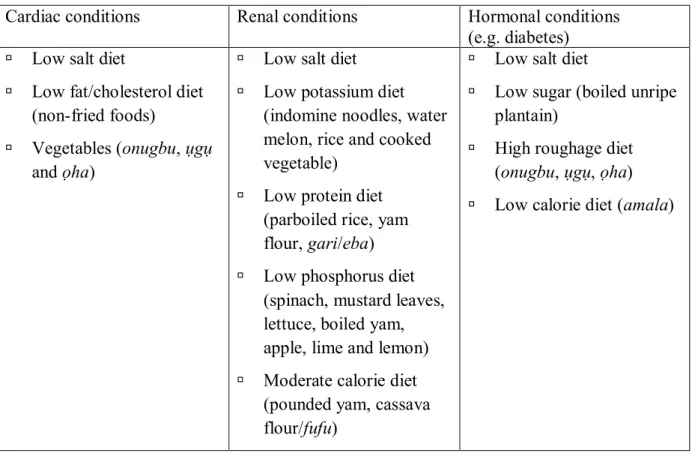
Non-pharmacological measures for the control of hypertension (lifestyle modification and elimination of stressors/predisposing factors). Salt reduction: Reducing the amount of sodium (salt) in the diet can help lower blood pressure, especially in hypertensive patients. Different preventive measures for high blood pressure versus primary (including screening programs), secondary and tertiary measures.
Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7 ed.). In the Idikan community of Ibadan, Southwestern Nigeria, patients visiting the hospital for medical care also used traditional medicine and patent medicine vendors to manage and prevent high blood pressure (Osamor, 2011).
Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure.
Other means used alongside with the traditional and cultural practices
Remedies employed on failure of the traditional and cultural practices to do its work
Development of Guidelines for Management of Hypertension in Rural Areas in Delta State,
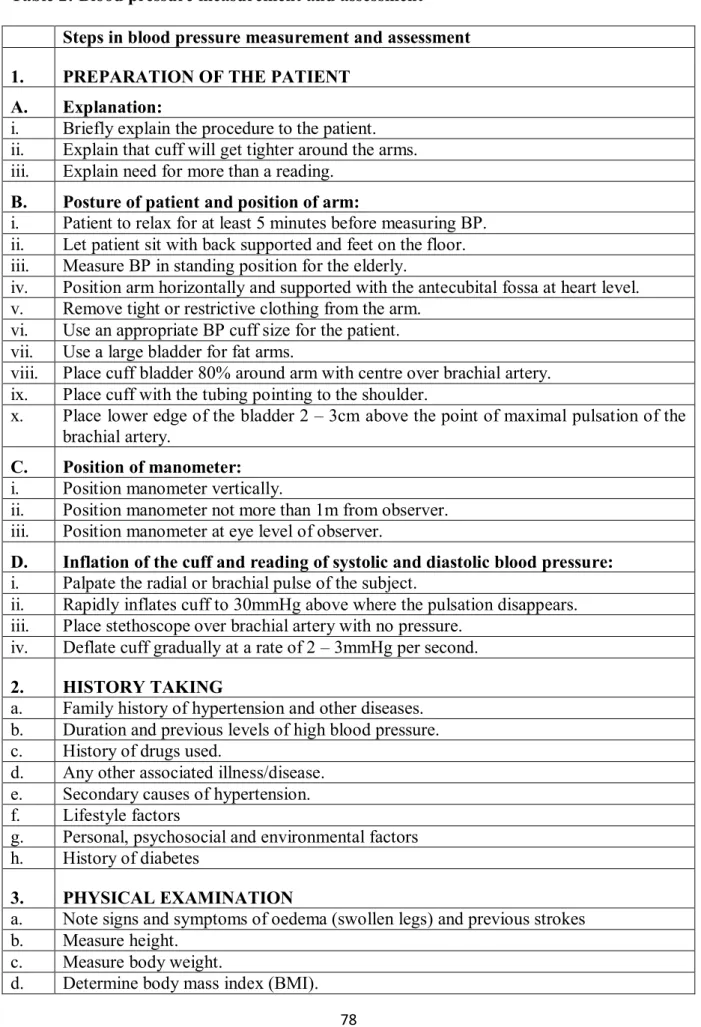
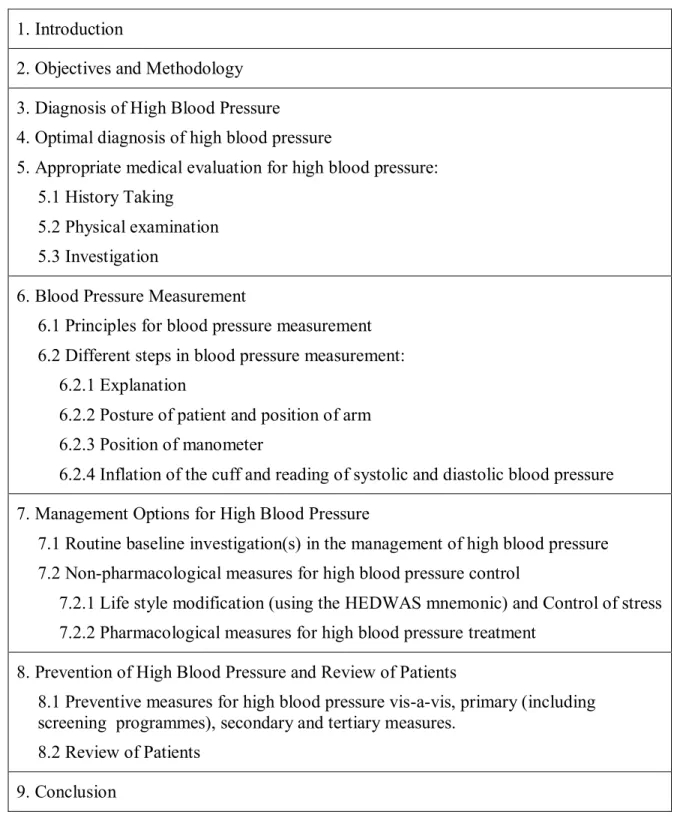
Major concepts covered include the optimal diagnosis and appropriate medical evaluation of high blood pressure, the principles of blood pressure measurement, and the various steps in blood pressure measurement. First-line medications for high blood pressure include diuretics, calcium channel blockers (eg, nifedipine and amlodipine), and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. This takes into account facilities, social and environmental factors and other issues affecting the development of high blood pressure in rural settings in Delta State, Nigeria.
Procedures and activities that were not feasible included blood pressure measurement and assessment, physical examination (examination of the cardiovascular system for heart size, enlarged heart, optic fundi, and nervous system for signs of hypertensive retinopathy), and routine baseline examinations (serum urea, creatine, and electrolytes for assessment of kidney function, lipid profile to assess cholesterol levels, echocardiogram and chest X-ray to assess cardiac enlargement). This will be discussed in relation to optimal diagnosis of hypertension and appropriate medical assessment for hypertension. Blood pressure must be checked again in 2 weeks if it is mild, moderate and in case of target organ damage.
Alcohol reduction: Drinking too much alcohol can raise your blood pressure and make it harder to treat high blood pressure. The blood pressure measurement procedures and the pharmacological measures for the treatment of high blood pressure must be updated from time to time as new skills emerge in practice. Non-pharmacological measures for high blood pressure control (such as the HEDWAS regimen) will have a strong impact on health, quality of life and mortality among rural communities in Nigeria.
Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National High Blood Pressure Education Program.
Theoretical Development of Guidelines for Management and Prevention of Hypertension in
- Introduction
- Purpose and objectives of the Guidelines
- Scope of the guidelines
- Target group for the Guidelines
- Disease/condition(s) included in Guidelines
- Guidelines categories
- Strategies, interventions and practices considered in formulating the Guidelines
- Expected outcomes
- Essentials of the Guidelines
- Context of the Guidelines
- Principal concepts in the three hypertension prevention and management strategies
- Concepts in the combined HEDWAPS approach
- Enabling hypertension management strategies through HBM/SCT theories
- Conclusion
Prevention and control of high blood pressure will undoubtedly have a strong impact on health, quality of life and mortality among rural Nigerians. These strategies must address behavioral and environmental factors associated with the prevention and control of high blood pressure to achieve three sub-goals: prevention, early detection and control of hypertension. Reduced target blood pressure (systolic <140 mmHg and diastolic <90 mmHg) with minimal or no drug side effects.
Involve the non-health sector in creating healthy policies, programs and services to support healthy lifestyles and the detection and control of high blood pressure. Provide education on healthy lifestyles and prevention and control of high blood pressure, using a variety of methods, as part of primary care for everyone of all ages. Provide intensive lifestyle education to individuals with high blood pressure as an essential part of controlling high blood pressure management.
Develop and deliver educational resources on healthy behaviors and the prevention and treatment of high blood pressure to individuals, families and health care providers. Conduct surveillance, research, and program evaluation to provide the evidence base for the high blood pressure prevention and control program. Understanding the cognitive-attitudinal and affective-motivational constructs that support individual behavior change has been useful in the development of intervention programs (Ralph, Richard, & Michelle, 2002)—as in the case of the hypertension prevention and control guidelines. pressure in a rural area, which is proposed in this study.
Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Heart Lung Blood Institute, and the National High Blood Pressure Education Program.
Discussion, Limitations, Recommendations and Conclusion
- Introduction
- Principal findings
- Discussion
- Recommendations
- Recommendations for practice
- Recommendations for education
- Recommendations for further research
- Study limitations
- Conclusion
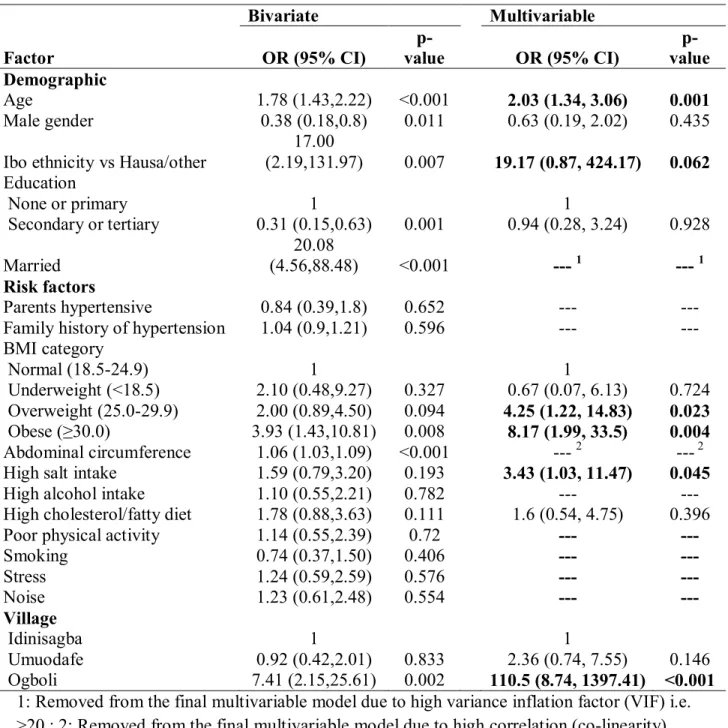
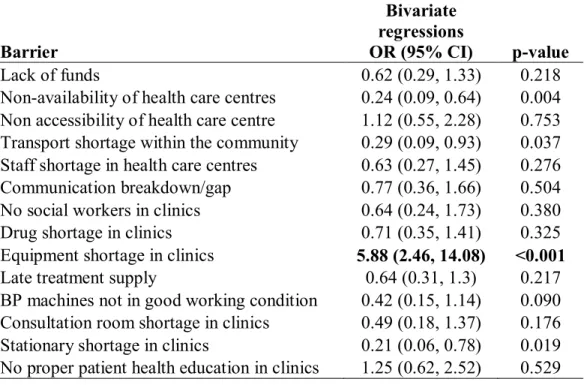
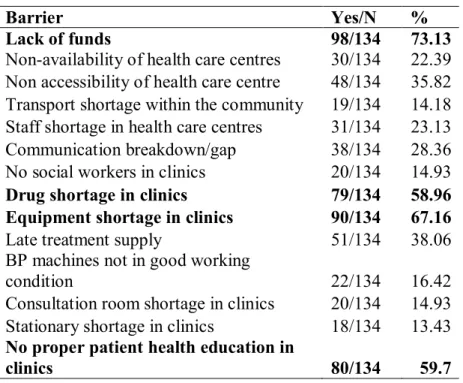
A significantly higher risk of hypertension was also found in Ogboli village compared to other locations. Compared to other well-known risk factors for the development of hypertension such as gender, age, BMI and certain lifestyle factors, this study found a higher prevalence of hypertension in women than in men (men 29.2%; women 52.3%), in contrast to other studies, globally and within the study country, which have shown higher prevalence of hypertension in men than in women (Adebayo, et al., 2013; Agyemang, 2006; Alikor, et al., 2013). In comparison, the main barriers to managing hypertension in community health centers reported in studies conducted in South-Eastern Nigeria and Limpopo Province in South Africa were financial constraints (Okwuonu, et al., 2014) and non-adherence to treatment, lack of transport, lack of staff, shortage of medicines respectively and late provision of treatment by hospital dispensary (Sekokotla, et al., 2003).
In developing these guidelines, facilities available in the area, together with social and environmental factors influencing the development of hypertension in rural settings, were specifically taken into account. Future guidelines should address the needs of special population individuals to include hypertension in pregnancy, the elderly and adolescents, hypertension in persons living with HIV/AIDS, and persons with comorbid conditions. In addition, the guidelines did not cover hypertension prevention and management for special populations—which include hypertension in pregnancy, the elderly and adolescents, hypertension in persons living with HIV/AIDS, and people with comorbid conditions.
Hypertension in a rural community in Rivers State, Niger Delta Region of Nigeria: prevalence and risk factors. Relationship between body weight and prevalence of isolated systolic hypertension in elderly subjects. Financial burden of hypertension treatment in African countries: a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing two approaches to hypertension treatment in cardiovascular disease prevention.
Forekomst og determinanter for hypertension i Abia State Nigeria: resultater fra Abia State Non-Communicable Diseases and Cardiovascular Risk Factors Survey.
Questionnaire & ethics consent form / participant info (English version)
What are the lifestyle factors associated with high blood pressure (i) High salt intake Mentioned ( ) Not mentioned ( ). ii) High alcohol intake Mentioned ( ) Not mentioned ( ). iii) Overweight/Obesity Mentioned ( ) Not Mentioned ( ) (iv) High Cholesterol/Fat Diet Mentioned ( ) Not Mentioned ( ) (v) Poor Physical Activity Mentioned ( ) Not Mentioned ( ) (vi) Drinking tobacco mentioned ( ) Not mentioned ( ). ix) Family history of hypertension Mentioned ( ) Not mentioned. What are the health care barriers to managing hypertension (please indicate by ticking the barriers that apply to you).
Questionnaire & ethics consent form / participant info (local language version)
Abụ m ..(aha onye so na ya) kwupụta na m ghọtara ọdịnaya nke akwụkwọ a na ụdị nyocha a. Aghọtakwara m na m nwere ike ịpụ na nyocha a mgbe ọ bụla m chọrọ, ma ọ bụrụ na achọrọ m ịpụ. Ego ole ka ị na-ese n'otu ụbọchị? Afọ ole ka ị malitere ise siga?
Kedu oge ị na-ehi ụra n'ehihie? i) site na elekere otu rue elekere ato ( ) (ii) site na elekere anọ rue elekere isii ( ) (iii) site na elekere asaa rue elekere itoolu ( ) (iv) site na iri o elekere gawa n'ihu. Kedu ndị bụ ihe mgbochi na ahụike metụtara ibelata ọbara mgbali elu (Biko gosi otu mgbochi a si emetụta gị). Agụghị ndị ọrịa n'ụzọ ha ga-esi mara ihe ha ga-eme iji belata ọrịa ha.
In-depth interviews (English version)
In-depth interviews (local language version)
Sample in-depth interview transcript
Are there any other tools/articles that you use related to traditional and cultural practices for the prevention and treatment of hypertension in your community. What are the barriers to the use of these traditional and cultural practices in the prevention and management of hypertension. Answer - Barriers include outcasts or excluded individuals who are not allowed to use various traditional and cultural practices in the community, festive periods/moments.
Research ethics approval
Amendment research ethics approval
Gatekeeper’s permission
Statistical letter of certification
Letter re editing help
Acknowledgement of role played by student in the research study
Instructions to authors- Cardiovascular Journal of Africa
Proof of submission of manuscripts online (Article 3
Proof of submission of manuscripts online (Article 4)
Proof of payment documentation (publication fees)
![Fig 2: Reported barriers for management of HT [descending order]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/pubpdfnet/10640585.0/49.893.123.741.164.707/fig-2-reported-barriers-management-ht-descending-order.webp)