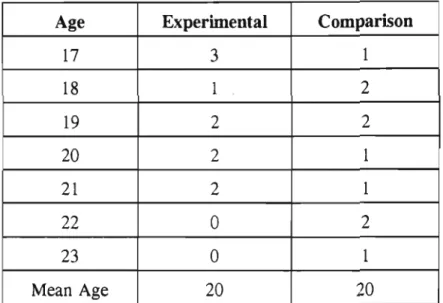
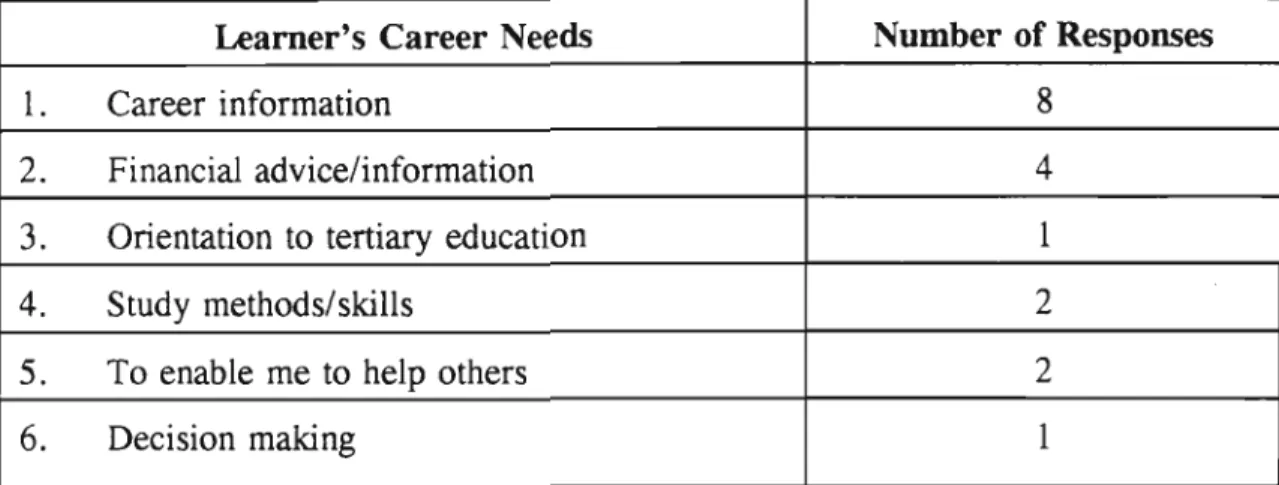
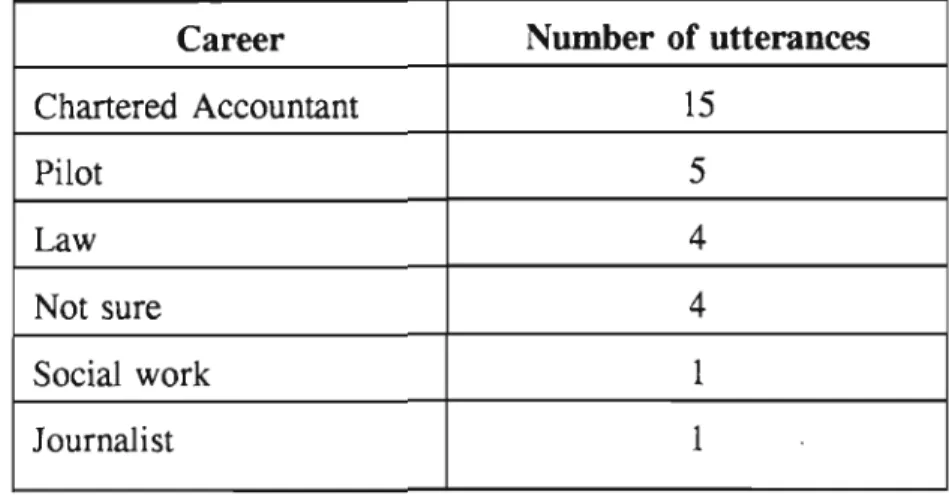
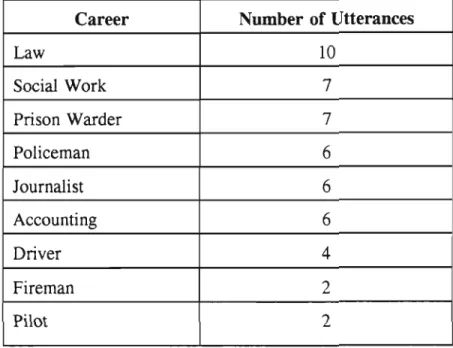
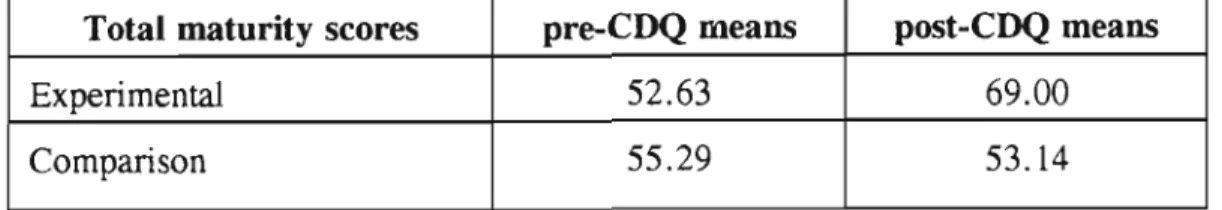
A quantitative and qualitative analysis of the data collected was conducted to determine the effect of the focus group discussions on the career maturity levels of the students. The analysis showed a clear improvement in the experimental group's overall career maturity scores, as measured by the Career Development Questionnaire.
CHAPTER ONE
- Background to the study
- Definition of tenns
- Conventions to be followed and abbreviations used
- Aims of this research
- Chapter summary
Instead, although guidance was intended to be part of the school curriculum in Kwa-Zulu Natal (KZN), there was no provision for career education in many schools, especially in the ex-DEC schools (Mtolo, 1996). It was often assumed that the black learners' needs were the same, regardless of the schools they attended.
CHAPTER TWO
LITERATURE REVIEW
Super's theory of career maturity
The development of the Career Development Inventory has culminated in the development of context-based career-based instruments. For example, the applicability of the majority of these theories in the South African context is debatable.
Developmental-contextual theories
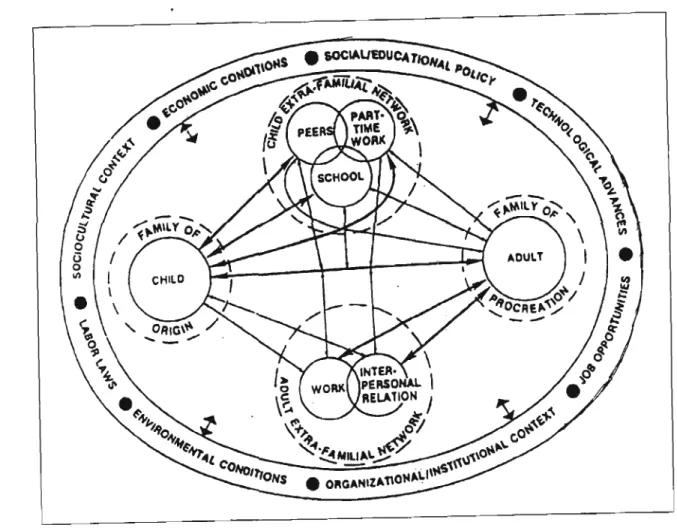
- Bronfenbrenner's ecological modd of humim development
- The microsystem
- The mesosystem
- The exosystem
The school is seen as the second most important microsystem after the family, because it has a strong influence on the child's career development (Vondracek et al., 1986). 1986) lists environmental conditions as one of the macrosystems that influence individuals' career development.
Career education research in South African black secondary schools
Its results highlighted the need to improve the level of career maturity and career development throughout the career. His findings were similar to those of Benjamin (1995) and Sedibe (1995) in that he identified contextual factors that influence career development. Like Benjamin (1995), he recommends that deficiencies in career development for Black students should be addressed.
He further recommends that career development programs that use self-exploratory measurement instruments should be validated.
CHAPTER THREE
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY
- A quasi-experimental design: the non-equivalent comparison group design
- Qualitative approaches used
- Questionnaires
- Observational methods
- Focus groups
- Quantitative methods used
- The Career Development Questionnaire
- Research participants
- Ethical issues
- Conclusion
In the following sections, the researcher discusses some of the criticisms made by quantitative researchers and qualitative researchers' responses. However, the CDQ was administered first because the researcher wanted to discuss the career information in detail with each of the participants. The researcher, the research assistant and the two teachers involved in the research took turns facilitating the sessions. a) The research assistant was employed in this study to co-facilitate the first and second focus group sessions.
Both qualitative and quantitative data were collected from the experimental group and the rest of the data was from the reflections of the researcher and the research assistants.
CHAPTER FOUR
RESULTS
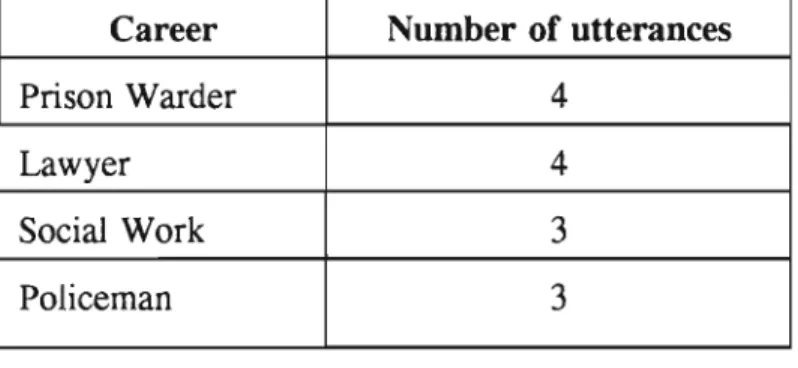
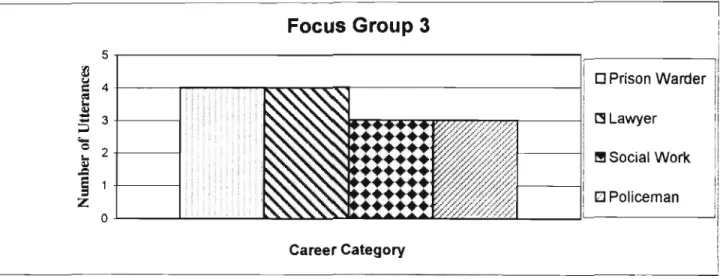
Focus group 3
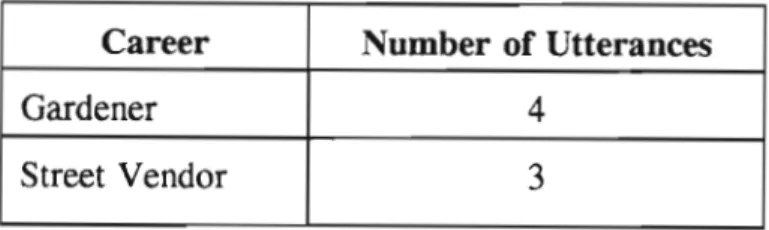
34;Most of us come from poor backgrounds. We are so poor that sometimes we cannot afford a simple thing like calling." 34;Some of us come from poor families, where calling can be considered a luxury if there is bread to think about." Our parents just can't afford it." After thinking about the different careers the students had discussed in the previous focus groups, the researcher, in consultation with the research assistant, decided to shift the focus group discussions to a session on entrepreneurship. This concludes corresponds to one of the research objectives, namely investigating part of the career of students.
After the preceding focus group discussions, it appeared that the learners mainly focused on professions and work in the formal sector, especially the government, and did not look at self-employment as an option.
Focus group 5
Descriptive summary of focus group process
- Changes in career exploration
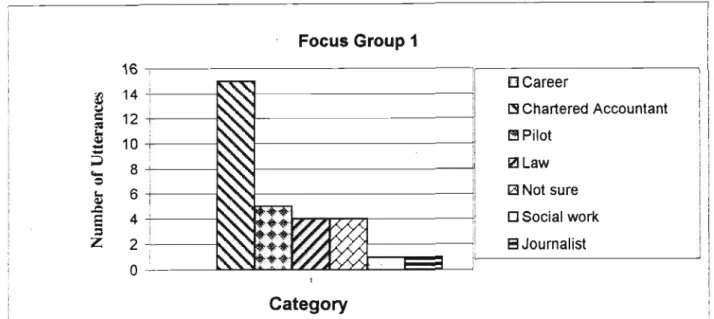
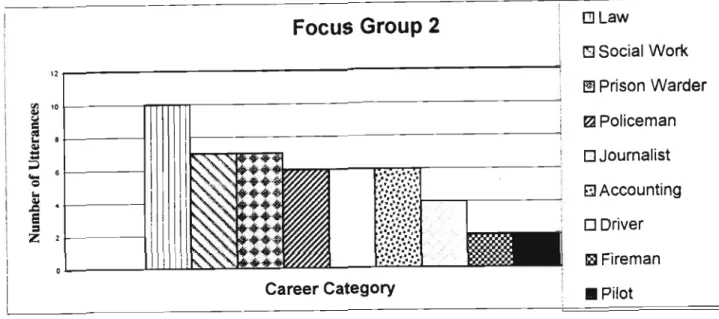
The four graphs above show that there has been a significant shift in focus in the focus group discussions from occupations that require high qualifications and are consequently difficult to access to occupations that are easier to access. Students demonstrated a lack of insight into the availability of non-vocational careers, but in recent sessions there has been a shift towards lower-level careers in the informal sector, particularly self-employment. In the first group meeting, more direct than indirect questions were used, as were open-ended questions, and the number of responses from the group was limited, as shown in the graph below.
The use of open-ended questions encouraged participation in subsequent groups as illustrated in Figure 4.5 below.
Change in Spontaneity of Expression
Interactions with peers
The students presented their ideas to the moderator and seemed interested in what she had to say in response to what they had said, they seemed to be caught up in the idea discussed above that the educator has all the answers. To encourage full participation, students were grouped together for their career research projects and in presenting their findings they sat as groups that had worked together, so interaction was further enhanced and gender segregation was discouraged. For example, when one of the students said she wanted to be a journalist, some of the students challenged her and said she was too shy to be a journalist and further suggested that she investigate other careers.
This was a good indication that students were moving from their preconceived ideas that the educator is there to provide information to sharing information, challenging each other's ideas and supporting each other regardless of gender.
Evaluation of the focus group method
- Quantitative programme evaluation
- Qualitative programme evaluation
- Participants' evaluation of the programme
Inspection of the means in Table 4.12 would indicate that the source of this was the higher post-test score in the experimental group. It seems that about 78% of the students did not benefit from the focus group discussion on entrepreneurship. They report that students are well motivated, take initiative and are self-disciplined compared to the rest of the matric class.
The students may have modeled some of these and therefore the teachers reported this group as 'different' from the rest of the students in the school.
Summary of results
Furthermore, they are listed as actively involved in classroom activities and using the time slot we had used for research for study purposes.
CHAPTER FIVE
DISCUSSION
Contextual factors that came out of the focus group discussions
- The child's family of origin and cultural issues
- Child's extra familial network
- Family of procreation-adult
- Macrosystems
- Educational policy
- Technological advances
- Job opportunities
Career guidance counselors do not exist and students depend on their subject teachers for career information. Skuy et al., (1985); De Haas (1991) and Haffajee (1991) found that parents had more influence on students' career decisions than their guiding teachers. This illustrates that the students viewed the role of the white researcher as superior to that of the black researcher.
The evaluation of the intervention indicated that the students had become aware of career information sources and that they knew a lot about careers available to them.
Career education research with black participants
This indicates that students' career information has increased significantly and it also highlights the value of short-term career education interventions in improving career development (Benjamin, 1995; Katranas, 1999; Spencer, 1999). The results as measured by the CDQ illustrate that career development may have been facilitated. The studies conducted focus on ways to improve the career development of Black students who have not received formal and structured career guidance.
This type of research in black schools raises questions about the inequities that still exist in black education and how they impact students' career development.
Limitations of this study
One of the more subtle goals of this research was to empower educators observing focus group discussions with the skills needed to conduct career-related focus groups. This could have allowed the researcher to ascertain whether they could handle the presentations themselves and the content of the presentations. Although this is obviously one of the issues that the researcher had to consider to ensure that there is continued cooperation and understanding, the educators were constantly there to observe and contribute to the direction of the group.
Ethically, it would have been advisable to offer the comparison group the same treatment as was offered to the experimental group, but due to pragmatic limitations, for example the unavailability of the learners for exams, meant that the researcher could not give them the same treatment.
CHAPTER SIX
Recommendations for further research
In light of the above discussion, there are several recommendations that can be made. The generalizability of the present findings could be extended by conducting research on a larger scale with a sample that is more representative of the resource-poor population of this country. This may impose restrictions on matched samples for comparative analysis with respect to student geographic location.
A developmental contextual approach to career education as conceptualized by this study can inform these vocational education programs and thus have a valued impact on the career development of the learners and the economy of this country.
Indian high school students' and teachers' perceptions of the school counselor as the most appropriate helper. Cognitive processes and career decision making: A pilot evaluation of an intervention in a black high school.
BIOGRAPHICAL QUESTIONNAIRE
We'd like you to have a say in the Career Education Program we'll be running with you. WHAT KIND OF TRAINING WOULD YOU NEED TO DO THE CAREER OR JOBS YOU MENTIONED.
CONSENT FORMS - FOR PARTICIPANTS AND PARENTS
CONSENT FORM FOR PARTICIPANTS
LETTERS TO THE SUPERINTENDENT
OF EDUCAT10N MANAGEMENT, KWAZULU-NATAL, DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION AND CULTURE
THE PRINCIPAL OF PHAYIPHINI HIGH SCHOOL, KWA-MPUMUZA
REQUESTING PERMISSION FOR THIS STUDY
Participation of 12th grade students is voluntary and confidentiality regarding student identity will be maintained. I would like to request permission from the KwaZulu-Natal Department of Education and Culture to conduct this research. Educational Psychology) at the School of Psychology at the University of Natal (Pietermaritzburg), I want to carry out a research project in career education at your school.
Participation by the grade 12 learners is voluntary and confidentiality regarding the identity of the participants will be maintained.
FOCUS GROUPS
Because one of the most important goals of the project is to encourage students to be open-minded and to prioritize from their list of expectations what they think can be done given the time constraints. Pupils (in groups) tell in full how they went about searching for information. Students consult with experts in their chosen fields and also reflect on entrepreneurial skills they may possess.
Finding the reason why students consult their teachers instead of professionals for career information.
EVALUATION QUESTIONNAIRE