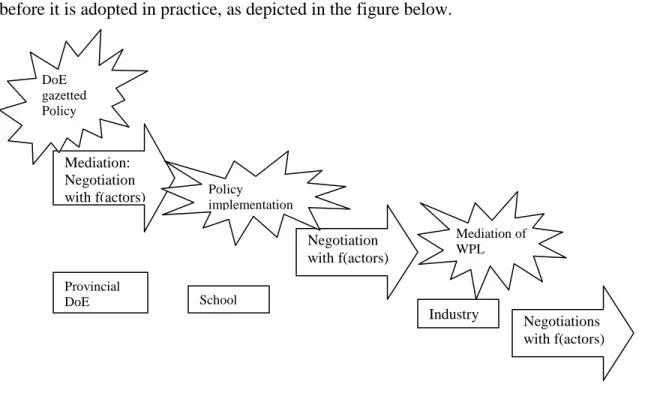
The trajectory of the NCF-FET Life Sciences Policy is traced during the practice of mediation of policy, implementation of policy and mediation of workplace learning. Furthermore, contradictions in the constitution of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy are highlighted: it supports constructivist principles and has a social transformative agenda, but its construction is guided by behaviourist and cognitivist principles.
LIST OF TABLES
NOTE TO THE READER
This led me to conduct the main research, which examines, firstly, how policies are constructed and translated into practice, and which SKAV are formed in practice at the intersection of DoE, schools and industry, and secondly, whether there is an interface exists between the nodes in terms of policy construction and SKAV development, and if so, what the nature of the interface is. The concepts offered by ANT are used to identify the uncertainties and controversies between the nodes of our research, namely DoE, schools and industry.
CHAPTER ONE
CARTESIAN GRID: MAPPING THE TOPOGRAPHY
- Introduction
- Mapping NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy’s link to Biotechnology
- Mapping the conceptualisation of Biotechnology within the NBSD
- Second generation - use of cells or tissue cultures to
- Third generation - commonly known as modern biotechnology, is associated with recombinant DNA technology
- Mapping the conceptualization of Biotechnology within the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy
- Mapping the preliminary study
- Mapping the use of Actor Network Theory
- Mapping the stage for the dissertation
- Mapping ANT’s terminology
- Conclusion
The DoE accepted the DST's request and included aspects of biotechnology in the NCS-FET curriculum for life sciences. How NCS-FET's life sciences policy conceptualises biotechnology is presented in the next section.
CHAPTER TWO
MAPPING THE THEORETICAL TERRAIN AND LITERATURE REVIEW
Introduction
Mapping the search for a theoretical framework
All the above frameworks do not allow policy to be considered as an actor; they favor human actors over non-human actors. Its distinctive principles and conceptual resources enable curriculum reform to be considered a network activity.
Mapping the distinctive theoretical tenets of ANT
9 Network: (a term I use to describe the interconnectedness of the many associations formed between actors in a network. To discover materials, we must follow the growth of the network (Latour, 2005).
Resolving uncertainties
These ties allow me to see aspects of the social impact on the actors' actions. In the next section, I highlight the spokespersons regarding the research nodes.
Conclusion
At the DoE node the spokesperson is the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy (published policy and mediated policy) and subject advisors, while at the school node it is the Life Sciences teachers and policy as they are responsible for delivering the curriculum . When the group's spokesperson warns us about the tensions within the group, the optical density (composition) of the media through which the policy beam passes comes to the fore.
Introduction
Review of scripts
- The policy canopy in South Africa
- Uncertainties of the roles of schools in society
- Mismatches in the preparedness of learners for the world of work
- Networks between the school science curriculum and industry
- Overview of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy
- Constitution of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy
- Conclusion
Prior to the formulation of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy, the DST prepared the NBSD. At each node I indicate how the flow of the NCS-FET Life Science Policy document follows.
CHAPTER THREE
MAPPING THE METHODOLOGY
Mapping the writing of an ANT report
This included all correspondence sent and received relating to the study, namely emails sent to scholars in the field (Mouton12, Benswick13 and Mensha14. Is there an interface in terms of policy making and development of SKAV between the hubs – and if so, what was observed am how alliance networks are responsible for fracture at the interface point to describe the nature of the interface.
The response of the visible actor to the network actor was observed to determine how the practice is carried out.
Practice(s) to be trailed at each node
- DoE node
- Schools node
- Industry node
At the school's hub Life Sciences, teachers are involved in the implementation of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy. They were engaged in the teaching of biology prior to the implementation of the NCS-FET Life Science Policy in schools in 2006. The Chief Education Officer is assisted in the supervision of the workplace learning program by three mentors (qualified pharmacists) who are responsible for imparting learning at work.
They taught in the Phoenix-North region and forged a link between the schools and industry node regarding the network of SKAV development.
Mapping the “objectfullness” of data constituted
As mentioned earlier (in section 3.1), the methodological implication is that the role of the researcher is redefined in an ANT study. In an ANT study, the role of the researcher contributes to the objectivity of the data generated (elaborated in the next section). The researcher is required to pay attention to what actors say or do in order to provide a complete account of events as they occur, without adding his or her own interpretation to the actors' narratives (Latour, 2005).
This means that in an ANT study, the lived experiences of actors take precedence.
Mapping the research design of the study
- Mapping gaining of access
- Mapping how data are constituted
Permission was also obtained from the subject advisor to observe the mediation of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy document. Teachers were purposively selected and had to engage in the implementation of the NCS-FET Life Sciences Policy. While delivering the questionnaire to the first life science teacher, I was struck by anecdotal incidents about life science teachers in this region.
Regarding the life sciences lessons observed, only one lesson per teacher (of one hour) was videotaped and transcribed.
Mapping the design for analysis
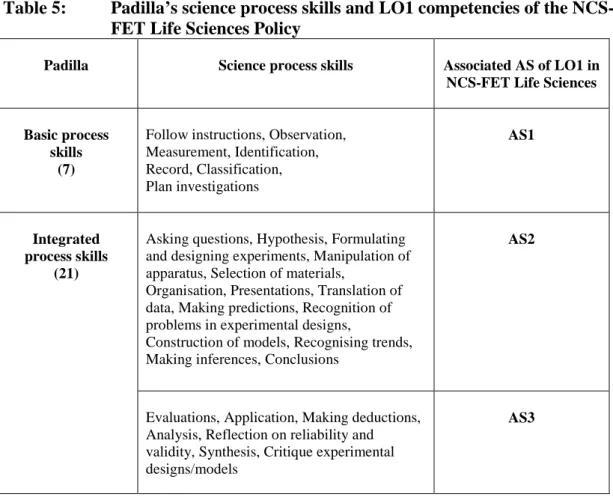
During the observation of mediation in workplace learning, a cross was placed for each of the 33 SKAV in the relevant column for the six observed NTEW. All the traces created by the striking actors were woven together through repeated reading and viewing of the transcripts. The construction of policy thus emerges from or from the set of sociomaterial actors.
In order to empirically identify the SKAV created at the DoE and school nodes, close attention has been paid to the nature of the activity involved.
Conclusion
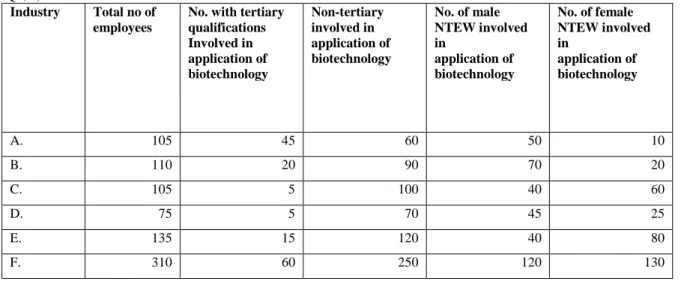
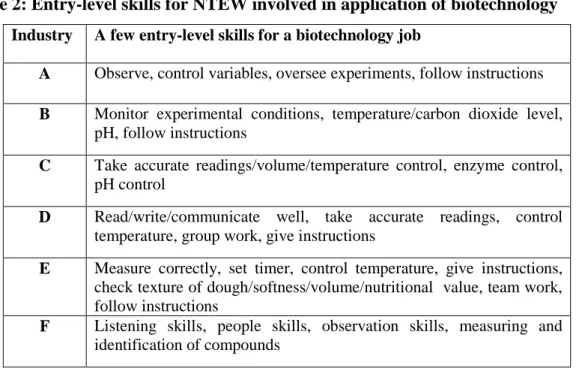
SKAV formed during mediation of workplace learning at the industry node, the list of identifying characteristics of SKAV provided by the evaluation agency was used. At the cross-nodal level, data collected at the DoE, schools and industry nodes were (re)compiled. I noted all the f(actors) that changed the optical density of each node from the nodal networks.
While chapter three demonstrated how to trace the tracks left by an actor, chapter four involves the collection of the trails.
CHAPTER FOUR
MAPPING THE SOCIAL CONTEXT
Introduction
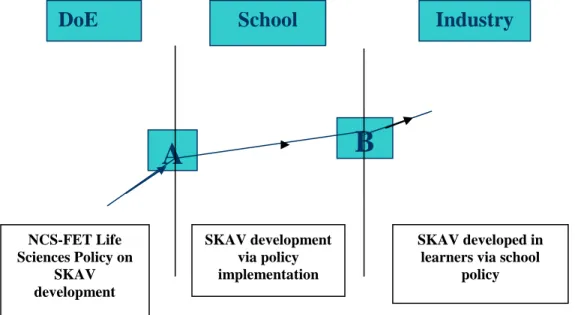
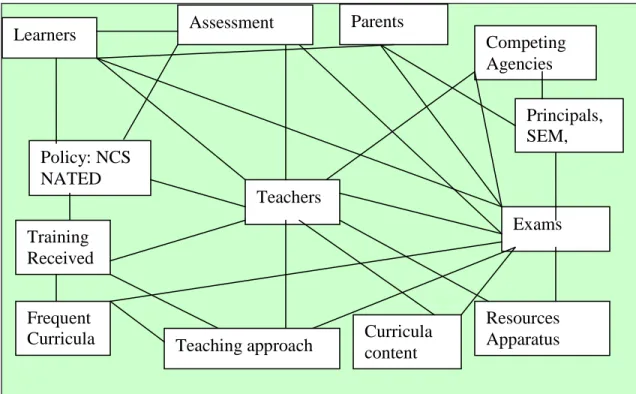
In this chapter I bring together the networks created by the prominent actors in the three nodes of the study. A functional sketch of the actors enrolled in the network was created for each node (see Figures II, III and IV in this chapter). Therefore, the associations of actors are examined in the analysis for their contribution to the structure and stability of the created network.
The final section concludes the chapter by highlighting the socio-material context, reality or ontology of the node networks.
Mapping the presentation of findings
- DoE node
- Practice gets performed as negotiable moments of obedience seeking
- SKAV constituted in practice
- Schools node
- Industry node
Good NSC exam results distract the dissemination of the policy from the intentions of the published policy. The construction of politics as an obstacle reveals the alliance formed with good NSC exam results and teachers. The alliance formed with good NSC exam results undermines policy regarding teaching approach ("use a practice method"), student image ("practice makes perfect") and assessment practices ("master testable competencies"), but confirms policy regarding curriculum content.
Constructing politics as a barrier illuminates teachers' dissatisfaction and frustration with the mediation of politics (“tell us what to do”, “poor training”), long curriculum content, difficult exam papers and their lack of involvement in politics . formulation process.
Conclusion
The alliances that are formed change the "optical density" of the node and affect how exercise is performed. At the DoE node, good NSC exam results are placed at the fore in every construction of policy. Good NSC exam results become a mediator that changes the optical density of the DoE node.
NSC exams turn into an intermediary and change the optical density of the school node through the many associations they form in the network of school actors.
CHAPTER FIVE
EMERGENT EFFECT OF CURRICULUM POLICY REFORM
Is there an interface?
- Nodal overview of policy construction
- DoE-schools -industry interface
- Nodal overview of SKAV constitution
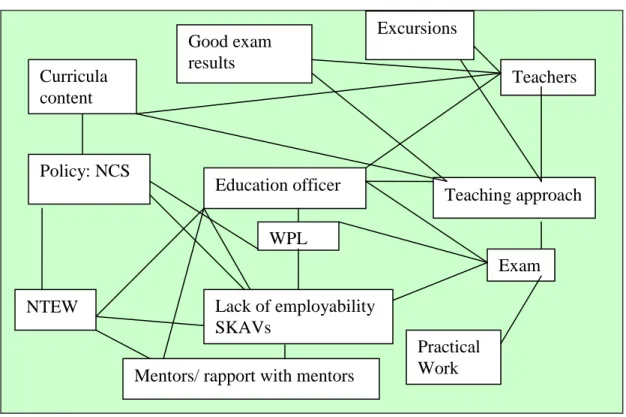
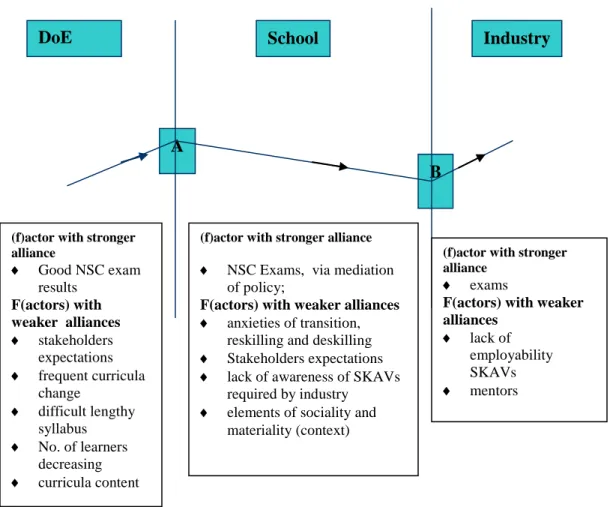
The key to the figure indicates the points of convergence and points of divergence regarding the construction of policy at the points of convergence. The interface(s) regarding the construction of policy can be mapped in the four possible combinations, viz. The schools-industry interface highlights the construction of policy as a barrier in terms of the difficult, lengthy content and lack of SKAV for employability (see Chapter Four).
There is a minuscule DoE-school-industry interface in terms of SKAV development that takes place during policy mediation.
The nature of the interface
Multiple coalitions with good NSC exam results in the DoE node are strong and stable. It is interesting to note that the merged alliance formed with good NSC exam results at the DoE node is restructured and emerges as an exam alliance at the schools and industry node. This means that the alliance network of good NSC exam results initiated in the DoE node comes under adaptive pressure in the schools and the industry node.
The above discussion on (re)joining traced networks captures the "interiority" of each node and at the internodal level reflects the interface and network of actors of this study.
Unveiling the emergent effects of curriculum policy reform
- Curiculum policy reform as bricolage
- Espoused policy slippage vis-à-vis enacted policy
- Heroic performance of a human actor vis-à-vis multiple actors
- Gaps within the curriculum policy reform process
- Reflections on the use of ANT
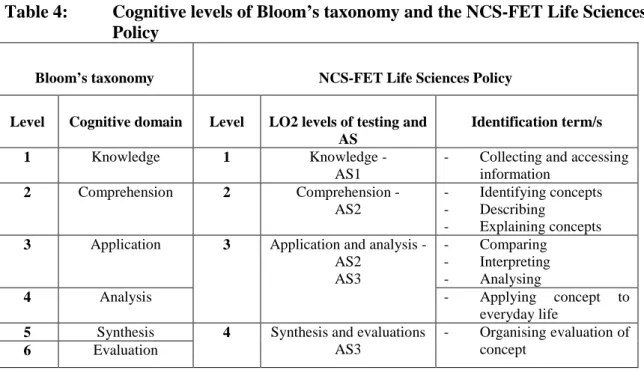
In light of the above, curriculum policy reform is a complex and networked process involving many actors. I used the metaphor of a dynamic ecosystem to capture the fluidity and heterogeneity of the curriculum policy reform process (Heath, 2000). During policy mediation, the gazetted policy evolves in terms of foregrounding SKAV and policy construction at the juncture of DoE and schools (as seen in Figures VI and VII).
For example, the construction of politics as alienated and the results of the preliminary study show the lack of teachers and industrialists.
Conclusion
Interface shows the permeability of the media at the point of convergence and shows new effects. The emergent ray emerging from the interface point shows the emergent effects of the actor network. Report of the Curriculum Review Committee 2005: A South African Curriculum for the 21st Century.
Using local industries to make science real: A critical analysis of the relevance of examples used in the school science curriculum.
DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION NODE
A4 Schedule showing duration of FET training session 169 A5 Permission from industry to conduct research 170 B PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION.
SCHOOL NODE
INDUSTRY NODE
What suggestions have you made about the NCS-FET Life Sciences curriculum/ policy goals or. You have been deliberately selected because of your involvement in the development of the NCS-FET Life Sciences curriculum. How is partnership with industries/educators/employees negotiated with regard to SKAV's development and the goals of the NCS -FET Life Sciences curriculum.
At the curriculum implementation level, curriculum developers and subject advisors trained teachers to implement the NCS -FET Life Sciences curriculum.