This dissertation is submitted to the School of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences at the University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban in partial fulfillment of the degree, Masters in Nursing Management / Administration. Thanks to the Ministry of Health Rwanda, your partnership with Belgian Technical Cooperation (BTC) through their Education Project, you gave me the financial support throughout the course time. Pie Chart 1 Reasons for Changing Employment Status 53 Pie Chart 2 Motivation to Leave Former Health Care Facility 54 Pie Chart 3 Factors Improving Nurse Retention 55 .
BACKGROUND
The high turnover of nurses compromises patient care and increases health care costs and negatively affects care. When nurses leave healthcare institutions, the quality of nursing care declines due to the loss of their expertise. The profession was strengthened by the creation of a nursing office in the Ministry of Health to look into matters relating to the nursing profession and to initiate the draft bill for a Nursing Council.
RESEARCH PROBLEM
Recruitment and deployment of nurses was in the hands of the public service in collaboration with the Ministry of Health's personnel office. The process of establishing the Rwanda Nursing and Midwifery Council has been ongoing since February 2006; therefore it is hoped that a proper record will be kept of the nurses' movements. Despite all these retention strategies, there is still a high turnover of nurses from the health sector to other organizations for non-nursing tasks.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
It is therefore not known why nurses change their employment status and change careers. This will be the first study to explore the reason(s) why the Rwandan nurses change their employment status.
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES The objectives of the study are
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
OPERATIONAL DEFINITIONS
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK Introduction
Extrinsic or hygiene or maintenance needs are related to aspects such as satisfactory pay, adequate supervision, job promotions, special fringe benefits, enlightened policy and administration, good working conditions and job security. According to Owens (2004,p.379), the criticism of Herzberg's two-factor theory of motivation was based on the fact that it was developed through research in which people were asked to describe critical incidents in their working lives that involved motivation and job satisfaction. . Of all the motivational theories, the two-factor theory remains a powerful explanation of motivation in the workplace (Owens, 2004, p.379).
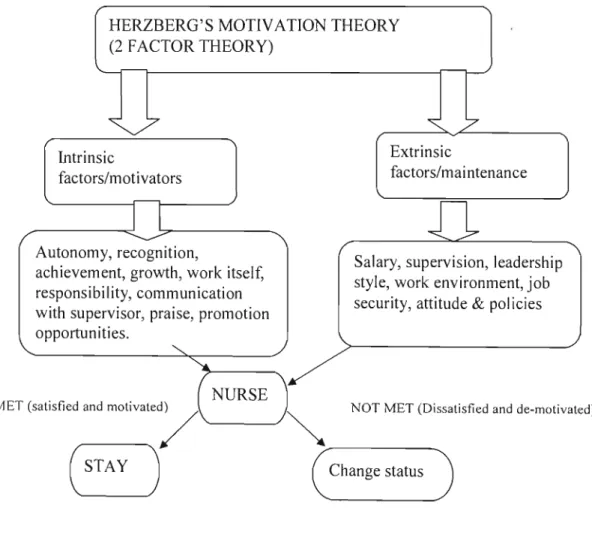
INTRODUCTION
JOB SATISFACTION
MOTIVATION
Some other factors such as organizational commitment also play an important role in nurses' job satisfaction and their retention (Khowaja et al. 2005, p.34). Staff development has been identified in the literature as an important factor in job satisfaction. All the mentioned studies provide support for the beneficial role of the nurse manager who has been referred to as "a chief retention officer" (Anthony et al. 2005, p.147).
WORKING CONDITIONS
It is the role of the nurse manager and the nurse manager to establish a working environment that supports professional practice. The author further advises that it is also important that nurses play an active role in shaping their environment. It is likely that they can improve the satisfaction and retention of critically needed managers and improve the development of future managers in nursing (Wilson 2005, p.144).
COMMUNICATION
Skilled Communication: Nurses must be as skilled in communication skills as they are in clinical skills. Efficient decision making: Nurses must be valued and committed partners in creating policy, directing and evaluating clinical care, and leading organizational activities. Meaningful Recognition: Nurses should be recognized and recognize others for the value each of them brings to the organization's workplace.
ENVIRONMENT
It is believed that those who don't start well don't stick around for long, and furthermore, employee turnover takes a high toll on the morale of those who do stay behind. When people leave the organization, those left behind begin to wonder whether they should also look for new work. The author went on to suggest other strategies to promote retention, such as developing a portfolio of skills for each member, helping individual staff grow and explore other alternative career options, utilizing nurse leaders to portraying the image of the nursing profession and training young nurses. and to protect the profession from intimidation, verbal and physical abuse and subsequently to tackle the problem of workload.
In a study by Hensinger, Mineath, Pary, & Robertson (2004, p. 268), which addressed the issue of nursing shortages in the healthcare industry it was noted that; in addition to administrators' desire to retain nurses; by keeping them committed to their workplace for better nursing outcomes, and the savings realized from lower recruitment and orientation costs, staff retention also enhances the institutional identity and pride that is built with a stable staff . Environments that ignore the demands of nurses often suffer the consequences of high nurse turnover and persistent nurse vacancies. The author's conclusion is that effective retention programs are those that create supportive, challenging, and rewarding work environments.
Professional burnout is a syndrome characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization and reduction of personal achievements (Kennedy, 2005, p.382). Prolonged work stress has negative effects on the quality of work life for nurses and patients, in addition, burnout results in increased sick time, tardiness, more workers' compensation claims, greater workplace conflict, violence and substance abuse (Lasch inger, Finegan, Shamian, & Wilk, 2001). It is on this note that the author recommends that nurse managers in long-term care settings should assess and manage.
CONCLUSION
Introduction
Research Design
There are three referral hospitals, three district hospitals, several health centers, private hospitals, clinics and ambulances, owned by the public and private sectors.
Population
The researcher used purposive sampling method and snowball method, both of which belong to the non-probability sampling techniques. According to Brink (2006, p. 133), the purposive sampling technique is based on the researcher's judgment about subjects or objects who are typical or representative of the research phenomenon, or who are particularly knowledgeable about the question at hand, and facilitates quickly reaching the target group . The technique will make it easier for the researcher to access those working in these organizations as nurses are part of the overall workforce working in these organizations and not all of them are known to the researcher.
Brink (2006) suggests that the snowball sampling method involves assisting the study subjects in obtaining other potential subjects, especially when it is difficult for the researcher to access the population, however there are limitations to this type of study, fmdings carmot be generalized to the entire population. After receiving permission from the selected organizations, the researcher held a short meeting with the identified nurses in the mentioned institution to make the first contact and introduce the study, to inform them of their rights, the issues of anonymity and confidentiality regarding the study. . The researcher met those who were willing to participate in the study after office hours to sign the declaration form and provide them.
Participants were asked to return the questionnaire within three days; otherwise, it would take the participant 20 minutes to complete the questionnaire.
Data Collection Instrument
Ethical consideration
Validity
Reliability
Distribution by Gender
Distribution of respondents by marital status
This could be explained by the fact that the nursing profession still attracts a large number of women (Edwards, 1997). The highest number of respondents according to their qualification were registered nurses n=74, equivalent to 84.1%, followed by registered nurses (n=l3) equal to 14.8%, and others, equivalent to 1.1 %. The researcher believes that registered nurses achieve the highest number because there are more nurses in this category than in any other category.
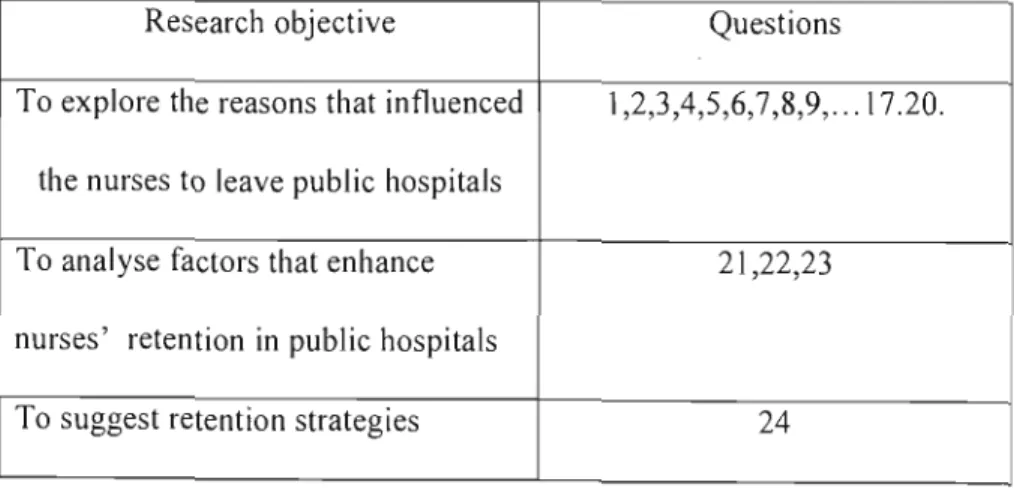
Respondents by their level of education
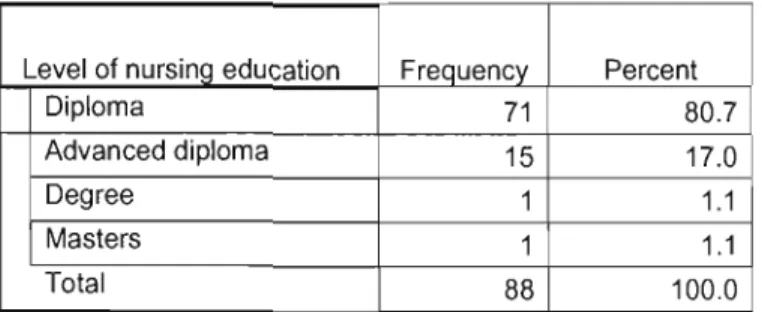
Respondents by the type of health care facility in which they worked
This table shows the free movement of nurses and multiple work areas in which nurses work.
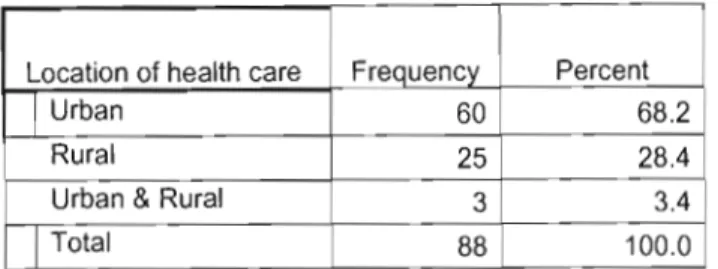
Responses by the location of the health care facility
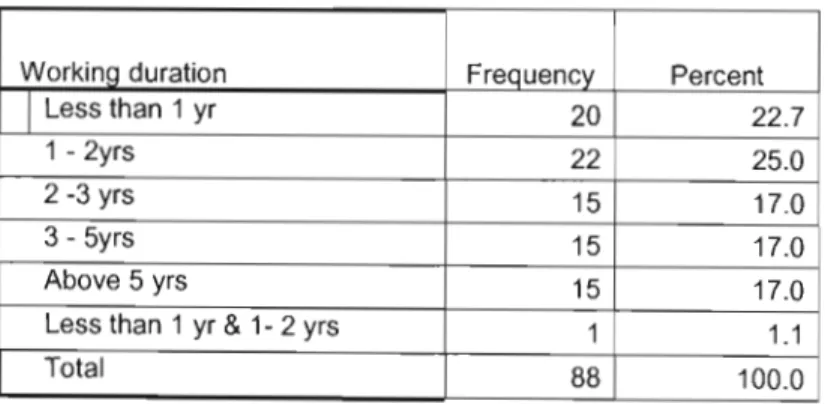
Working experiences of nurses in their former health care facilities was described and shown in the table
As regards the intrinsic motivating factors, the following responses were obtained
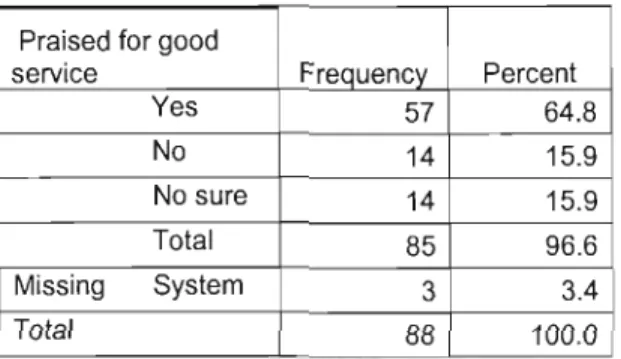
Asked whether nurses were praised for any good services rendered
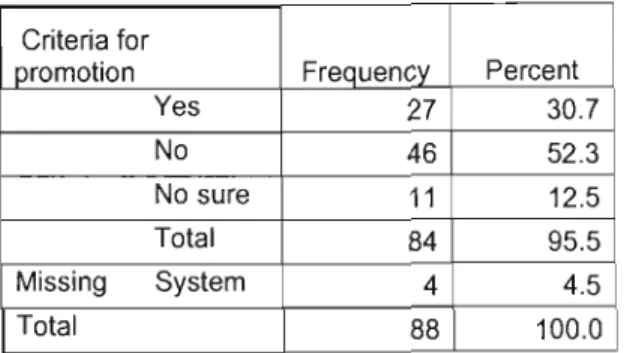
When respondents were asked about the existence of promotion criteria in their former health care facilities
When asked about their relationships with their former immediate supervisors
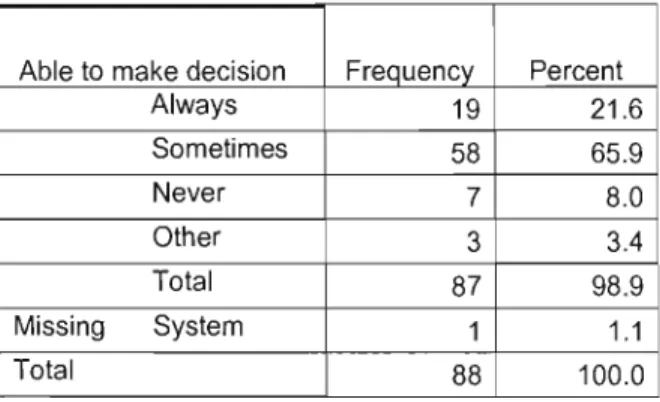
When asked whether they had autonomy in decision-making as regards the planning and implementation of patient care, the responses were as follows
Presence of team work was also investigated in their former health care facilities, and the following were the responses
Respondents were asked whether they enjoyed teamwork; the responses were as follows
Respondents were asked whether they had experienced an orientation period
When asked who was responsible for their orientation at their former health facility, the responses were as follows
When asked about the posts they occupied in their former health care settings the responses were as follows
Regarding the Extrinsic motivating factors the following responses were as follows;
When asked to give opinions on the staffing in their former health facility the following were the findings
When respondents were asked about collaboration with the physicians the following information was revealed
Were you informed ofthe retirement plan?
Did the health care facility experience any shortages of essential drugs and materials?
Did you attend any in-service course(s) while you were still employed with your former institution?
Did your former institution have regulations to guide your actions?
Did your former institution have policies and procedures to guide you? The following were the responses
How would you rate your salary scale in relation to other professionals' salaries in other organisations?
Was the salary paid on time?
Did you like being a professional nurse?
When asked to explain why they didn't like nursing the responses were
For open-ended questions, responses were written down and Pie charts were used to illustrate the responses in percentages
Reasons for changing employment status were expressed differently as follows
What motivated you to leave your former health facility?
Factors that nurses believe would enhance retention Increase in salary
People should be given the opportunity to choose a career in nursing instead of the government just sending them to nursing schools where the entry requirement is based on the grades achieved in the final exams. In the survey, nurses reported that they never decide to become a nurse and this was one of the reasons that influenced the change in employment status. The government should strengthen the profession by raising the level of nursing education to a diploma program and increasing post-graduate study opportunities as with all other professions in the country.
The study found that nurses change employment status due to late salary payments. Staffing levels in healthcare facilities should be a government concern that needs to be addressed as understaffing leads to staff turnover and poor patient outcomes. As a result, the problem of long working hours is reported by the nurses, along with relevant compensation for extra hours. The study found that one of the reasons nurses left was because they were afraid of becoming infected with chronic diseases.
The findings of the study cannot be generalized because the sample size is small for a quantitative study. In addition, the respondents were purposively selected, so there is no representation of the population. The lack of nursing data on changes in employment status remains an obstacle in determining the rate of turnover for nurses in the Rwandan health care industry.
Therefore, it is important for managers to understand what motivates employees and incorporate this into the reward system Linden, (1998).
ANNEX A
Type of healthcare institution where you worked. a) Tertiary hospital 0 (b) District hospital 0 c) Health centers 0. How do you think the staff at your previous workplace was a) Adequate 0 b) Inadequate 0 c) Very insufficient 0. How did you fare? with the doctors in your department about the planning and implementation of care.
Q15.Did you take any further training course(s) while still working at your former institution?
ANNEX B
L’établissement de santé manquait-il de stocks de médicaments et de matériels essentiels ? Selon vous, quels facteurs aident les infirmières à rester dans leur domaine ?
ANNEX C
Reimbursement of expenses, the participants will be reimbursed for the transportation they spent on getting to the meeting place and home, and a snack will be served, since the lecture will be after work.
ANNEX D
ANNEX E
AUGUST 2006
UNIVERSITY OF
KWAZULU - NATAL
ANNEX F
ANNEX G
KWAZUlU-NATAl
So you are now allowed to have free access to any information related to your case study. For any problem related to this topic, please contact the CAMERWA Administrative Service.
ANNEX I