Therefore, the purpose of this study was to analyze the scope-agility paradox within the context of project portfolio management (PPM). This was done by analyzing the relationships between agility, PPM strategic alignment and the organization's ability to achieve its strategic goals.
Introduction and description of the problem
Because of this changing environment, strategic implementation is an emergent process, requiring agility and adaptability (Mitchell, 2018). If the original strategy is flawed due to bounded rationality, and PPM conforms to this strategy as argued by the strategic alignment literature, the argument for bottom-up strategic agility finds support.
Purpose and scope of the research
Research problem
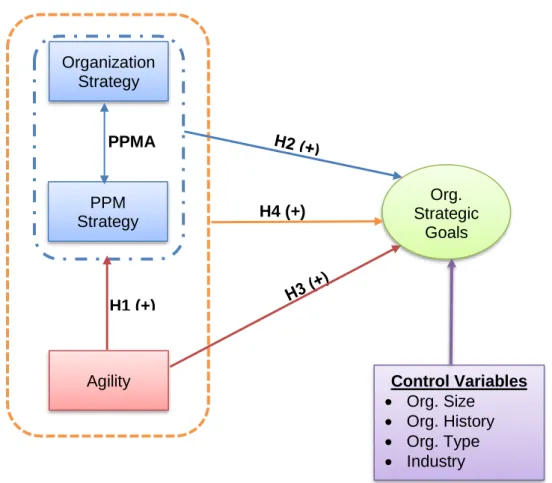
Therefore, the goal of the research is to understand the relationship between strategic alignment and agility and how this relationship affects the achievement of the organization's strategic goals. This conceptual model suggests a hypothesized relationship between PPM, agility, strategic alignment, and an organization's strategic goals.
Theoretical and business needs
This study extends knowledge to the project portfolio management field in a different context to assess whether similar conclusions are applicable. In order to guide the understanding and testing of the hypotheses, a conceptual model has also been developed in chapter three.
Research structure
Introduction
Project portfolio management theory
Although project management is a critical tool for organizations to achieve their strategic goals (Alexander Lord, 1993; Killen, 2017), the relationship between the project and the organization is complex (Musawir et al., 2017). This makes the project selection criterion the best mediator to ensure alignment of project portfolios to strategic goals (Kaiser et al., 2015).
Strategic alignment theory
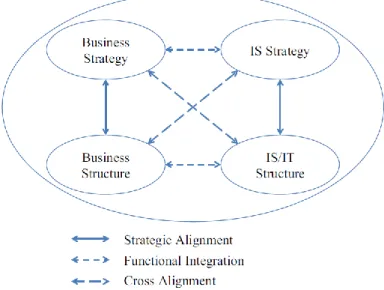
Strategic alignment model
The concept of strategic alignment originates from the strategic management literature before being used in IS literature and SAM development (Renaud et al., 2016). Additionally, most alignment models are based on the four elements of the SAM that must be aligned (Luftman et al., 2017).
PPM strategic alignment
Moreover, it is possible that a project may fail in achieving the internal project goals, but still create value and benefits for the company (Musawir et al., 2017). Conversely, a project may achieve its internal goals and yet fail to create the required business value (Musawir et al., 2017).
The theory of agility
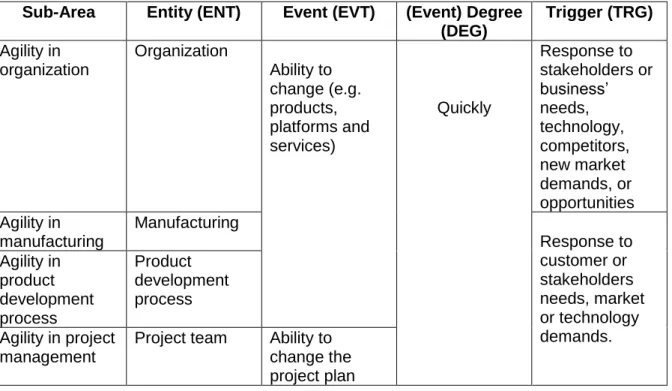
- Defining agility
- Agility as a dynamic capability
- The antecedents/dimensions of agility
- Bottom-up agility
- Agile project management
- Workforce agility
Agility is conceptualized from the strategic management theory of dynamic capabilities (Park et al., 2017). Furthermore, three dimensions are identified, namely: (i) the acquisition of customer agility, (ii) partnership agility and (ii) operational agility (Felipe et al., 2016).
Alignment-agility paradox
However, Shin et al., (2015) noted that researchers in the IT field found that high levels of customization can inhibit organizational agility. This is similar to what Zhou et al. 2018) found and called this phenomenon the "alignment-agility" paradox.
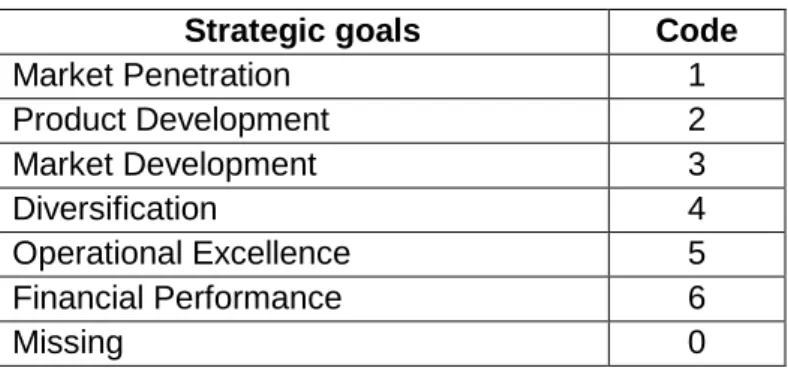
Strategic goals
Moreover, Ilmudene (2019) supported this view, stating that strategic alignment is a predictor of business success, therefore a better strategic alignment is expected to increase business success. Sabherwal, Sabherwal, Havakhor, and Steelman (2019) also found that although IS researchers and senior executives agree that strategic alignment between business and IT is important, there are researchers who have argued that alignment can negatively impact organizational performance and cause inflexibility.
Conclusions of literature review
H2: There is a positive relationship between PPM strategic alignment and the organization achieving its strategic goals. H4: PPM strategic alignment and PPM agility have a positive relationship with an organization achieving its strategic goals.
Introduction
Research design and methodology
Population
To ensure that the correct respondents were selected for the sample, a screening question was included as part of the demographic section of the questionnaire. This question was researched as follows: "Does your organization manage a collection of projects or programs to achieve its strategic goals?".
Unit of analysis
The population included multiple respondents who did not have homogenous roles (i.e. executive), as this minimizes the possibility of a common method bias (Brusset, 2016; Lu & Ramamurthy, 2011).
Sampling method and size
Data collection
Research instrument
- Workforce agility
- PPM strategic alignment
- Strategic goals
- Control variables
- Instrument pre-test
Section D: Strategic goals – this section is divided into two parts: the first part asks respondents to list their top three organizational strategic goals (with a minimum of one goal required), part 2 measures the level of achievement of the goals strategic of the organization. . The first part of the strategic goals section of the instrument allowed respondents to identify their organization's strategic goals. The second part of the strategic goals section of the instrument measured the level of achievement of strategic goals by the organization.
Data analysis process
- Data cleaning and coding
- Testing for construct validity
- Testing for instrument reliability
- Descriptive Statistics of items and constructs
- Mean scores comparison
- Test for constructs relationships
- Hypothesis testing
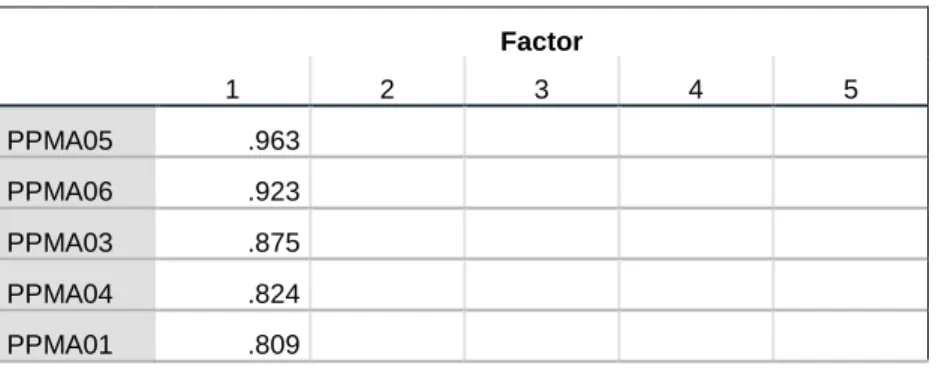
Similarly, the rest of the questions were coded by their respective codes according to Chapter 2 and the codebook in Appendix B. Factor loadings greater than 0.70 on an item are considered good factor identifiers. The reliability of the entire scale was tested using Cronbach's Alpha, with a generally accepted lower limit of 0.6 (Sardana et al., 2016).
Conclusion
Unstandardized Coefficients Sig.: Determined if each of the independent variables were significant predictors of the dependent variable in the linear equation at the 95% level. B (Slope/Gradient): These were the numbers for the linear regression model equation that was: Dependent Variable = B*Independent Variable + Constant. The chapter will close by presenting the results of hypothesis tests through hierarchical linear regression.
Sample description
The results of the statistical tests that were performed through SPSS are described in this chapter with limited discussion.
Respondents demographics
The results of the three top strategic goals of the organizations in Appendix C indicate that the top strategic goal for most organizations is operational excellence (39.16% of respondents as SG1).

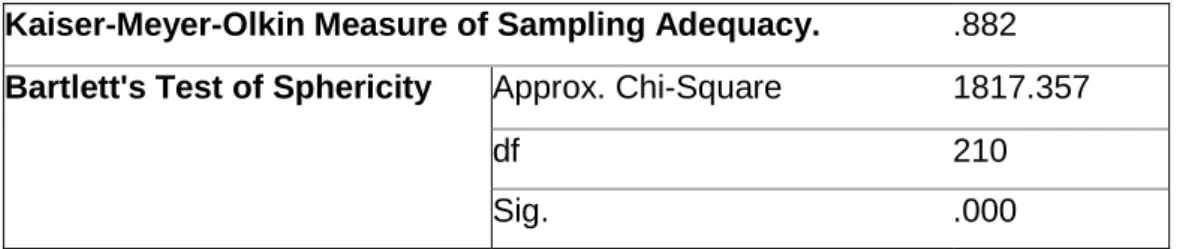
Construct validity results
The Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity and the Kaiser-MeyerOlkin Test of
Exploratory factor analysis
After making the changes to the model as outlined above in step one, the EFA was up and running again. RES01_r had a high cross-loading (r >.400), therefore this item was removed for step three of the EFA. However, all items of Resiliency (RES), which is a dimension of resilience, have been removed from the model as EFA found them invalid.

Instrument reliability results
- Project portfolio management strategic alignment reliability results
- Adaptability reliability results
- Proactivity reliability results
- Strategic goals achieved reliability results
From the EFA results, all six PPM strategic alignment (PPMA) items loaded highly on the construct. From the EFA results, all three Strategic Objectives Achieving (SGA) items loaded highly on the construct. Therefore, the three SGA items and PAC01 were loaded for the Cronbach's alpha reliability test of SGA.

Measurement items and descriptive statistics
Project portfolio management strategic alignment descriptive statistics
Overall item statistics indicated that this is the best model fit as no higher Cronbach's alpha can be achieved with an item deleted.
Adaptability (Agility) descriptive statistics
Strategic goals achieved descriptive statistics
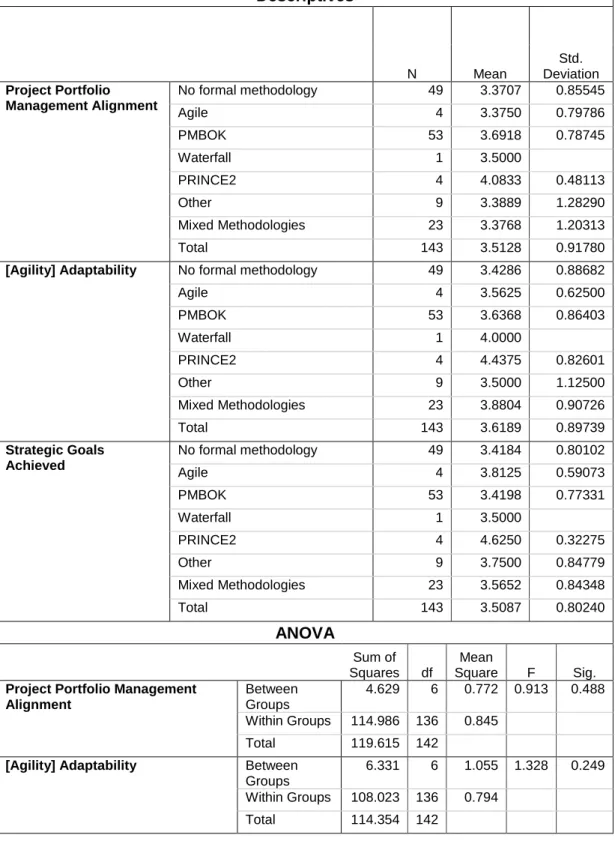
Mean scores comparison between demographics results
The results shown in Table 17 show that there is no statistically significant difference at the 95% confidence level (p < 0.05) between the different project management methodologies used by the organizations in this sample group. "Other" types of organizations had the lowest average scores, but only one organization was measured, which was not sufficient to draw conclusions.
Constructs relationships results
Research hypotheses tests results
- Hypothesis 1 (H1)
- Hypothesis 2 (H2)
- Hypothesis 3 (H3)
- Hypothesis 4 (H4)
H0 (null hypothesis 2): There is no relationship between PPM strategic alignment and an organization achieving its strategic goals. Therefore, when combined, strategic PPM alignment and control variables are statistically significant predictors of achieving an organization's strategic goals. Therefore, when taken together, agility, strategic PPM alignment, and control variables are statistically significant predictors of achieving an organization's strategic goals.

Conclusion on results
Introduction
Discussion of results for sample demographics
Discussion of results for research hypothesis 1
Conclusive findings for research hypothesis 1
The results of this study show that there is a significant positive relationship between agility and PPM strategic alignment. These findings add to the existing body of knowledge, as described in Chapter Two, by confirming the positive impact of strategic alignment agility in the broader context of PPM.
Discussion of results for research hypothesis 2
The relationship between PPM strategic alignment and an organization
In addition, although the size of the organization had a low beta weight, it should still be considered a contributor to PPMA in this model as it has a statistically significant beta weight. However, Equation 2 shows that the beta weight of PPMA (B = .501) contributes the most to achieving an organization's strategic goals.
Conclusive findings for research hypothesis 2
Discussion of results for research hypothesis 3
The relationship between PPM agility and an organization achieving its
Conclusive findings for research hypothesis 3
Discussion of results for research hypothesis 4
The relationship between agility and PPM strategic alignment with an
Additionally, the results showed that organization type and organization size generated a negative beta that showed a negative correlation with strategic goals in this study. Moreover, comparing the average results by industry of an organization showed that there is a statistically significant difference for strategic PPM alignment in different industries. Therefore, PPMA and agility are the strongest predictors of achieving an organization's strategic goals over the control variables.
Conclusive findings for research hypothesis 4
Conclusion
The discussions in this chapter will be used to develop the general conclusions and recommendations of this study in the next chapter (Chapter Seven).
Introduction
Principal findings
- The importance of agility
- The weakness of organization history
- Organization size matters
- The challenge for government entities and state owned enterprises
These results indicate that, in addition to PPMA and all control variables, agility is an important factor in an organization's ability to achieve strategic goals. In all tests of the hierarchical regression hypotheses, the history of the organization did not have a statistically significant effect on the achievement of the strategic goals of the organization or on the strategic coordination of PPM. Therefore, it can be concluded from this sample that the age of the organization has no influence on the achievement of the strategic goals of the organization.
Theoretical implications
State-owned and state-owned entities were the worst rated in achieving strategic goals for the second half. These results show that state-owned and government-owned entities usually fail to achieve their strategic goals. Therefore, there is a partial indication (although not statistically significant) that the government and SOEs are strategically aligned but not agile.
Implications for management
From the mean score statistics paragraph 5.6, the results indicate that these entities received the highest mean scores for PPMA, however they received a low mean score for agility.
Limitations of the study
This can affect the quality of the results and the correlation of the answers between different organizations. These variables further limited the study's conclusions in eliciting causality between construct relationships. This therefore limits the possibility of generalizing the results of this study to other equally relevant populations.
Recommendations for future research
The literature review in the second chapter showed that the construct of agility still needs clarification and further studies to strengthen its theoretical foundations. This study found evidence for this claim, as the agility dimensions “proactivity” and “resilience” failed validity and reliability tests. Therefore, more work needs to be done on building a theory of agility and its dimensions across multiple industries and contexts.
Concluding remarks
I am conducting research on the impact of PPM strategic alignment and agility on strategic goals. This will help us better understand how agility and strategic alignment affect the achievement of strategic goals. What are the three main strategic goals of your organization? entering new markets, developing new products, increasing market share, etc.).