Diets with an excess of carbohydrates and fat content have been shown to lead to the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). T2DM has been shown to disturb calcium homeostasis by causing changes to calciotropic hormones and calcium-regulating organs. However, the changes to calcium homeostasis in the pre-diabetic state have not been characterized.
A pre-diabetic rat model that mimics the human condition of pre-diabetes was established using a high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet. This diet-induced pre-diabetic rat model was used to investigate the changes of calciotropic hormones, the association of calciotropic hormones with glucose parameters, as well as to evaluate the changes in the function of calcium-regulatory organs. To the endocrinology group: Thank you for all the time you have invested in helping to improve my project, especially Bongeka, Palesa, Nompumelelo, Reveshni, Dr.
To my family: thank you for believing in me and allowing me to continue my studies. Thank you mom and dad for teaching me to fight for my dreams and never lose hope.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Introduction
Calcium homeostasis
- Calciotropic hormones
- The physiological role of PTH
- The physiological role of calcitonin
- The physiological role of vitamin D
- Calcium-regulating organs
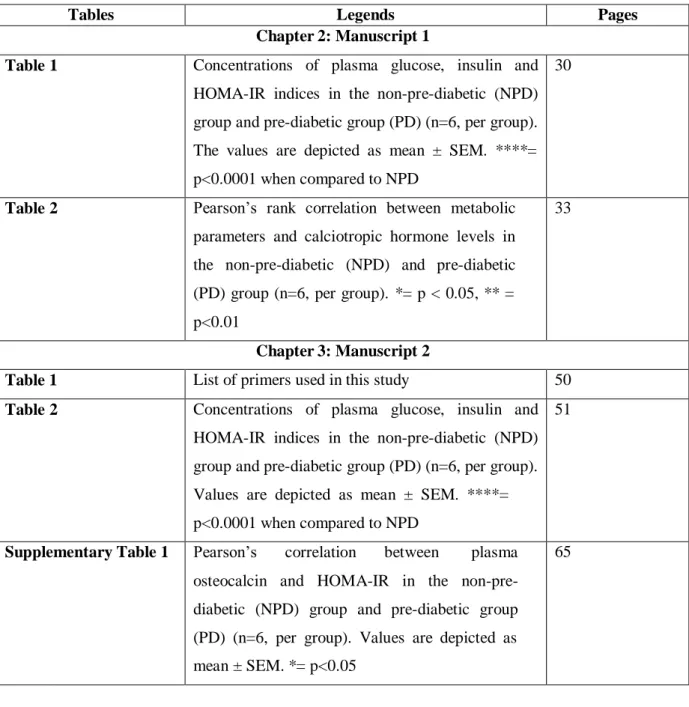
- The role of the intestine in calcium homeostasis
- The role of the kidney in calcium homeostasis
- The role of the bone in calcium homeostasis
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
- Effects of T2DM on calciotropic hormones
- Effects of T2DM on PTH
- Effects of T2DM on calcitonin
- Effects of T2DM on vitamin D
- Effects of T2DM on calcium-regulating organs
- Effects of T2DM on intestinal calcium absorption
- Effects of T2DM on renal calcium reabsorption
- Effects of T2DM on bone turnover
Pre-diabetes
High-fat high-carbohydrate (HFHC) diet-induced model of pre-diabetes
Basis of study
Aim
Objectives
Hypothesis
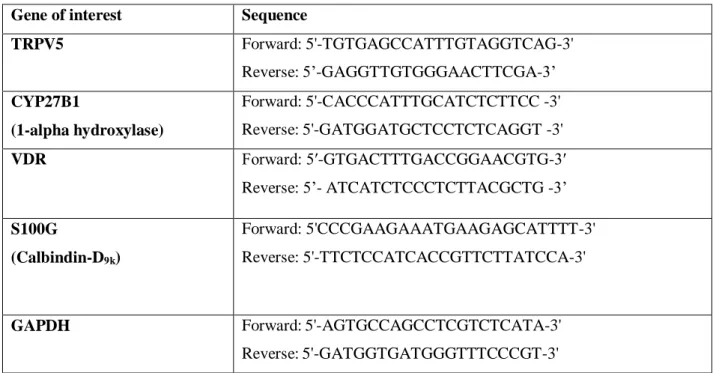
Laboratory methods
MANUSCRIPT 1
MANUSCRIPT 2
Obesity has been shown to be a contributing factor to the development of insulin resistance and prediabetes [6]. The next chapter describes the physiological role of calciotropic hormones in the maintenance of calcium homeostasis. The next chapter describes the role of calcium regulatory organs in maintaining calcium homeostasis.
Furthermore, insufficient research has been carried out in the prediabetic state, especially with regard to changes in calcium homeostasis. The results may therefore reveal whether changes in calcium homeostasis begin in the prediabetic state. However, there are no scientific results showing the changes of calciotropic hormones in the prediabetic state.
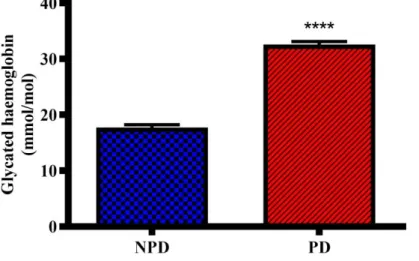
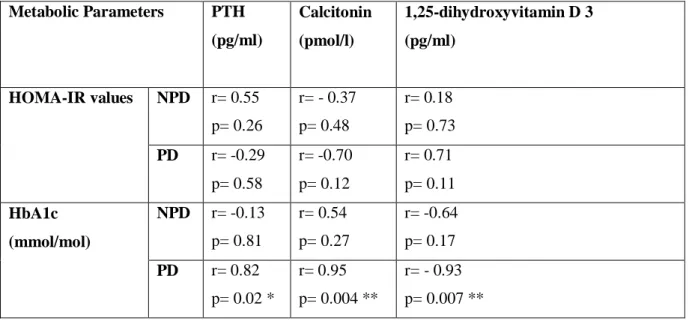
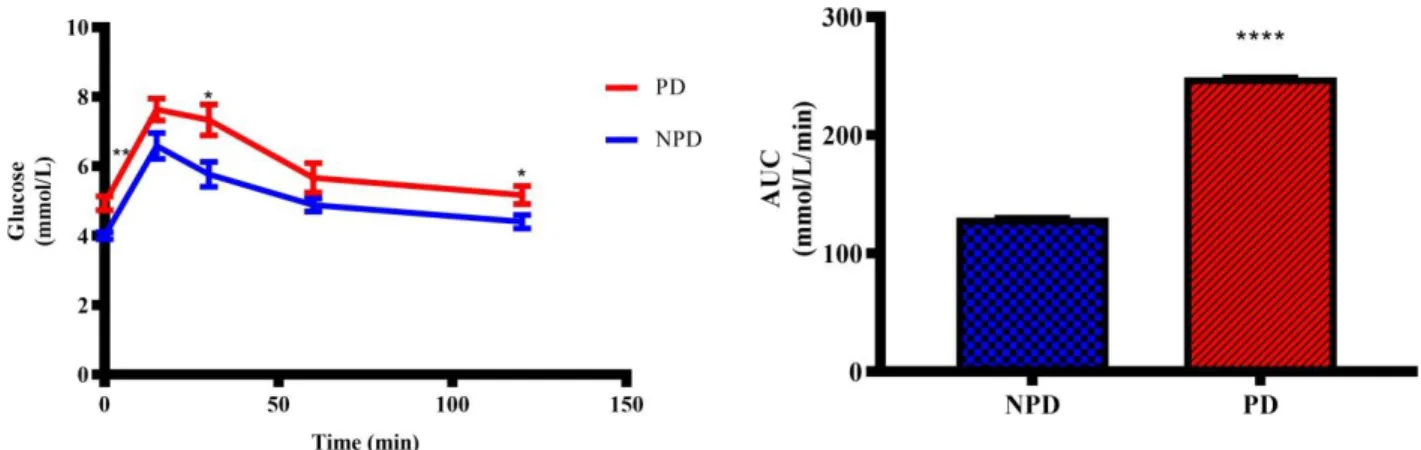
However, the changes of calciotropic hormones in the prediabetic state are not yet known. Moreover, studies have shown that disturbances of calciotropic hormone levels can worsen insulin resistance in the diabetic state [6, 7]. Glycated hemoglobin concentrations were measured in the non-pre-diabetic (NPD) group (n=6) and the pre-diabetic (PD) group (n=6) after the experimental period.
However, it is not known whether the function of calcium regulatory organs is disturbed in the prediabetic state.
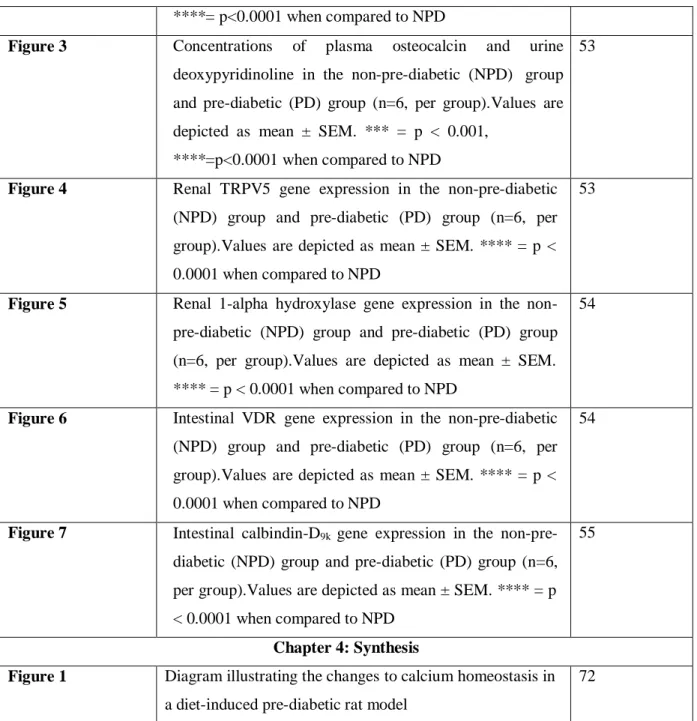
SYNTHESIS AND CONCLUSION
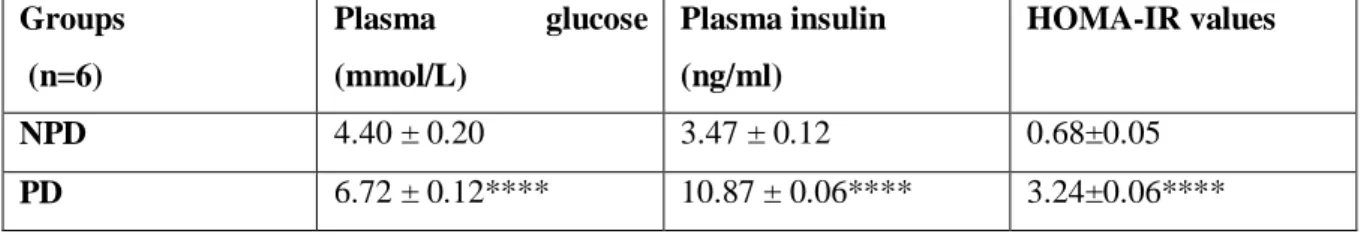
Therefore, this study sought to investigate changes in calciotropic hormones and calcium regulatory organs in the prediabetic state using a diet-induced prediabetic rat. To investigate the effects of diet-induced prediabetes on calciotropic hormones and the functioning of calcium regulatory organs in a prediabetic rat model, in an attempt to elucidate changes in calcium homeostasis in the prediabetic state. In the diabetic state, changes in calcium homeostasis and the association of calciotropic hormones with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and insulin resistance are well documented [ 9 , 10 ].
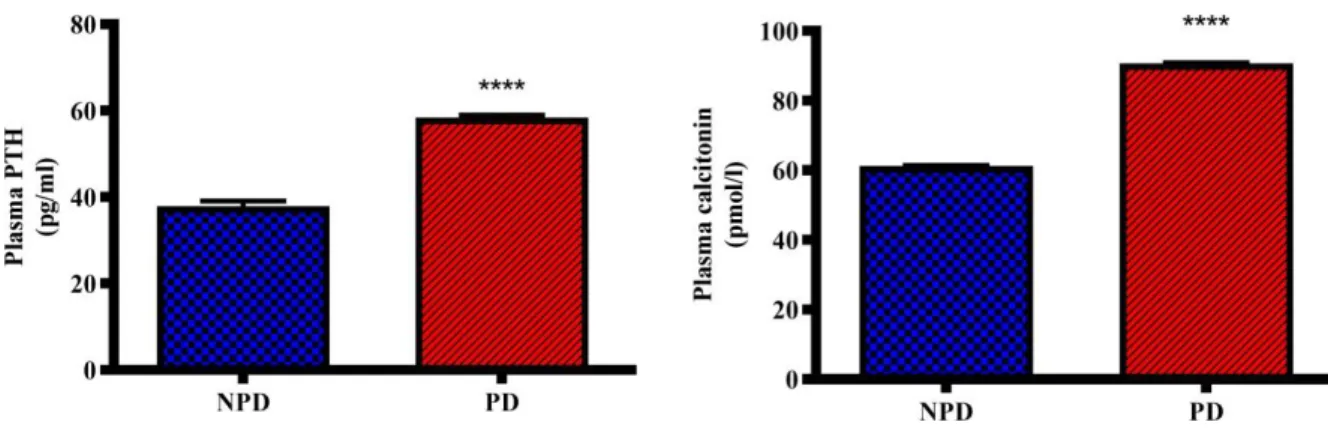
In this study, urinary calcium levels in the PD group were significantly higher compared to NPD. Together, these observations may suggest that calcium homeostasis is disturbed in the PD state, but calciotropic hormones compensate for changes in plasma calcium levels. Furthermore, altered levels of calciotropic hormones in the PD state may contribute to the development of hyperglycemia rather than insulin resistance in T2DM.
In addition, renal TRPV5 expression was significantly higher in the PD group compared to the NPD group. Collectively, these observations may suggest that calcium regulatory organs compensate for the changes in calcium homeostasis in the PD state. The unchanged plasma calcium concentrations of the PD group can be attributed to calciotropic hormones that maintain calcium homeostasis.
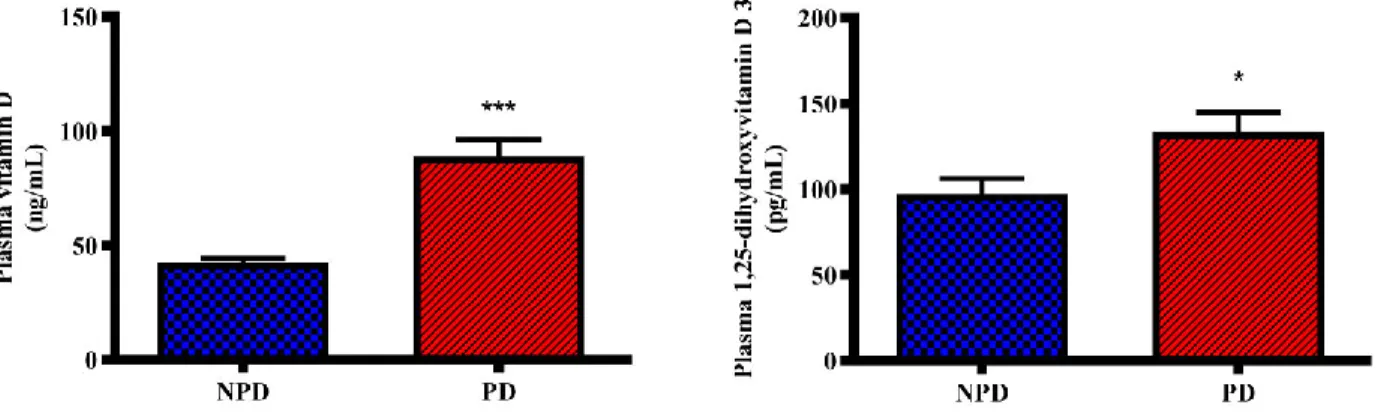
The increased plasma calcitriol levels in the PD group may have been a compensatory mechanism for low plasma calcium. Therefore, the second study aimed to investigate the effects of diet-induced pre-diabetes on the function of calcium-regulating organs in the PD state. In this study, the unchanged plasma calcium levels in the PD group compared with the NPD group suggested that calcium-regulating organs may have compensated for the changes.
Calcium homeostasis is disturbed in the prediabetic state, which was evidenced by changes in calciotropic hormones and calcium regulatory organs. Taken together, these observations suggested that calciotropic hormones and calcium regulatory organs compensate for changes in plasma calcium in the PD state. However, changes in calciotropic hormones in the prediabetic state may promote the progression of hyperglycemia to T2DM.
In the prediabetic state, calcium homeostasis is disturbed, yet calciotropic hormones and calcium regulatory organs maintain normoglycemia. The hypothesis of this study is accepted due to the presence of changes in calciotropic hormones and calcium regulating organs in the prediabetic state. Moreover, the altered levels of calciotropic hormones in the PD state were positively associated with glycated hemoglobin.
In this study, we investigated calcium homeostasis by looking at the changes in calciotropic hormones and calcium regulatory organs.
Ethical clearance
Journal guidelines
Cite the source in the text, in a table footnote, or at the end of the figure caption. Footnotes to the title or authors of the article do not get reference symbols. Identify previously published material by citing the original source as a reference at the end of the table caption.
Identify previously published material by crediting the original source in the form of a reference citation at the end of the figure title. Upon request, authors must be prepared to send relevant documentation or data to verify the validity of the presented results. A notice of alleged violation of ethical standards in the peer review system may be included as part of the bibliographic record of the author and article.
A decision on how to correct the literature will depend on the nature of the error. The retraction note must provide transparency as to which parts of the article are affected by the error. The decision whether to include such information depends not only on the scope of the journal, but also on the scope of the article.
Approval of the change under review is at the editor-in-chief's discretion. Please note that in addition to the above requirements, funding information (given that funding is a potential competing interest (as mentioned above)) must be disclosed when submitting the manuscript to the peer review system. Non-financial interests: Author A sits on the board of Y and receives no compensation as a board member.
For example www.clinicaltrials.gov or any of the major registries participating in the WHO International Clinical Trials Registration Platform. The trial registration number (TRN) and registration date should be included as the last line of the manuscript abstract. The procedures used in this study adhere to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
The questionnaire and methodology for this study were approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of the University of D (Ethics approval number. Letters are published at the discretion of the Editor and those presenting original material are subject to peer review.

Diet compositions
Turnitin report
![Figure 1: Mechanism of calcium absorption in the small intestine mediated by calcitriol adapted from Corbeels et al., 2018 [38]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/pubpdfnet/10327767.0/22.893.111.659.351.625/figure-mechanism-calcium-absorption-intestine-mediated-calcitriol-corbeels.webp)