This chapter describes the use of mathematics software in the teaching and learning of mathematics. The name of the school is Phuthaditjhaba High School which is in the rural area of KwaZulu Natal, Greytown area. Most of the students at the school are orphans and come from poor homes.
Statement of purpose
Due to certain reasons, the HOD was reassigned so that the educator became responsible for these computers and worked as the HOD. In 2003, the school was equipped with sixteen computers and five of these computers were intended to improve the teaching and learning of mathematics, science and languages.
Critical Questions
Rationale
The overview of the research methodology
Approach
Validity is not a single acid test that can be applied to the research process as a whole. Whereas quantitative researchers try to detach themselves as much as possible from the research process. Due to the evaluative nature of qualitative research, the researcher is a key instrument or tool in the research.
Sampling
According to Winter (2000), for quantitative researchers this involvement would reduce the validity of the test, but for qualitative researchers, denying one's own role in the research also threatens the validity of the research.
Research Instruments
It is easy for the researcher to get answers when she is part of the audience. The interviews were informal and began with the researcher trying to relax the participants and ensure confidentiality and some of their anonymity. A school has its own timetable and it is the researcher's duty to include her accordingly.
Conclusion
CHAPTER TWO
LITERATURE REVIEW, HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVES AND DEFINITIONAL ISSUES
Introduction
A computer can serve as a free-standing workstation that provides instruction to a student and can be structured to accommodate his or her responses. It can serve as a word processor or to support desktop publishing for reporting the work of students. According to Jacobs (2000), System software is software intended to control, support or operate the computer.
An operating system is a group of programs that provide the interface between you (the user) and the hardware (your computer). It translates your commands to the computer so that you can perform tasks such as creating files, running programs and printing documents etc. Utilities are a subcategory of system software designed to extend the operating system by a computer user in a way to control the allocation and usage of hardware resources. Some utilities come with the operating system; they perform tasks such as preparing drives to store data (formatting), providing information about the files on a drive, and copying from one drive to another.
Data communications software can be grouped into the same two categories used to classify all software: application software and system software. Application layer software and protocols provide commonly needed communication tools that support user applications. The most well-known include e-mail packages such as Eudora and web browsers such as Netscape.
Application software refers to programs that end users purchase or develop to solve a specific problem or perform a specific task.
Why curriculum changes?
The vision of mathematics schools in the 21st century is that technology is an essential component of the environment. Loomes and Shafarenko (2001) pointed out that the merging of hypertext and multimedia technology, technology that enables the integration of different media (audio, video, etc.), has resulted in the development of hypermedia that enables differentiation at the level of the individual user. Many researchers in the field of mathematics learning (e.g., Schoenfeld, 1994) believe that learning to solve problems is a fundamental goal of mathematics education.
Using wireless communication in the form of an infrared beam built into each handheld device, students can share their work with each other and the teacher. Beaming has opened up new opportunities in the classroom for collaboration and student assessment. The typology of the problems included in the CD-ROM is varied, ranging from problems of puzzles.
Hypermedia systems in the educational sphere are still in the phase of trials and experiments. We believe that the design and implementation of hypermedia applications can favor individual learning processes, and more so in mathematics, as here with the current CD-ROM (Helier& Underwood, 2002). However, one has to question how useful exercises can be in the new South African in light of the new curriculum's insistence on discovery-based learning (de Lisle, 1997).
There is no attempt to provide students with tools to construct their own concepts, or a way to relate concepts to real-life problems in the students' world (de Lisle, 1997). A theory is a set of related propositions that suggest why events happen the way they do (Hoover, 1984). In this view, knowledge is still a symbolic mental representation in the mind of the individual.
CHAPTER THREE
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY
Introduction
For the why question, the researcher used the semi-structured interviews with both students and teachers as a method for in-depth research. The teacher questionnaire was designed with the intention of first identifying the biographical information of the teachers. Lack of time is one of the biggest problems anyone can face, as you may find that your participants are not available when you are, and vice versa.
~m is to understand phenomena in their natural contexts and to explore the subjective values, beliefs and thoughts of the individual respondent (O'Connell & Layder, 1994). This implies that the actual words of the subjects are thought to be critical to the process of conveying the meaning systems of the participants, which ultimately become the results or findings of the research (Filstead, 1979). Qualitative research allows events to be captured through the subject's words, and the purpose of this research methodology is to "discover and discover, not simply order and predict" (Van Maanen, 1979).
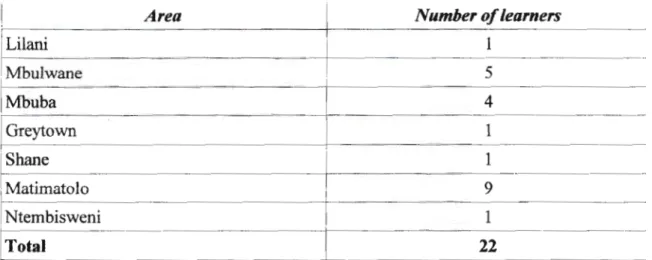
A semi-structured interview is an interview whose purpose is to obtain descriptions of the life world of the interviewee, in relation to the interpretation of the meaning of the described phenomena (Kvale, 1996). During the semi-structured interview, the researcher introduced the topic of the interview, asked relevant questions and followed up with new data depending on the interviewee's answers to her questions. The minority of the class come from Lilani, Greytown, Shane and Ntembisweni, only 1 student from each of these areas.
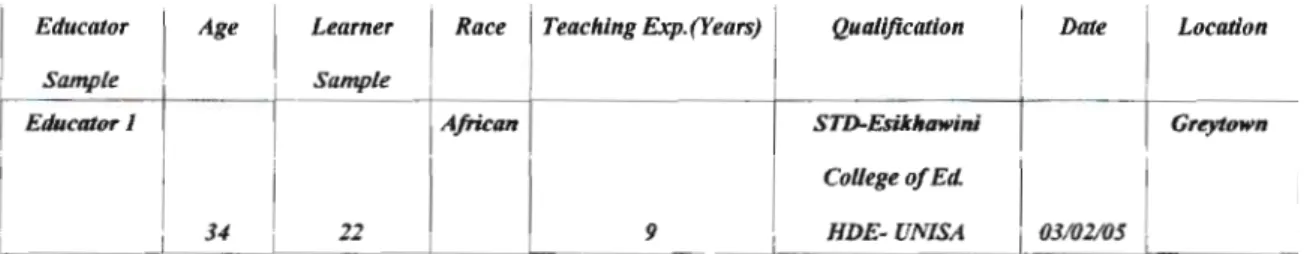
The table above shows information about the educator who participated in this research.
DATA ANALYSIS / FINDINGS & INTERPRETATION
Introduction
- Presentation of section B of the Interview Schedule
The biggest problem faced by the participants (students) of this study was that most of them come from a family background where the parents are completely illiterate and poor. In response to question 3 of the questionnaire, it can be determined that there were 14 males and 8 females, which is representative of the ratio of females to males in the class. Tables, graphs and figures should be used to succinctly present statistical decision-making information.
Visual display of images and graphs that are divided by a combination of row and column dimensions of the table. The respondent said that they are introducing it only for 12th grade students because they don't have enough computers and they are targeting 12th graders because they want high performance at the end of the year. Have there been improvements in the teaching and learning of mathematics since the introduction of this software?
Shelhe said that the time allocated to the use of this software is not sufficient for,. Although there are those few individuals who are good at using the software, almost 70% of the learners need to be given more practice. Does using the software help learners to be more competitive when they are with other learners from neighboring schools.
The students were given time to express themselves and in most cases they were the driving force behind the lesson.
Conclusion
The researcher found that students spent most of the time in dialogue with their teacher. The researcher believes that there is a need to open such educational centers so that students can use them outside office hours. The researcher found that the teacher was viewed as a facilitator, helping students where needed.
The researcher believes that the educator should do what will ultimately be successful. From the findings, the researcher came to the conclusion that students are not given enough time for discussions and group work as time is allocated for the subject. For critical question number two, the researcher found that there is an improvement in the performance of students doing math in grade 12.
The researcher believes that this study could positively change the school based on the findings. The researcher found that the use of math software was uncommon in most rural schools. The researcher believes that every school, from 8th to 12th grade, should use this software.
The researcher says this because you can feel that the computer lab is sometimes closed during school hours.
EDUCATOR QUESTIONNAIRE
Number of years at current school: _. b) The purpose of this section is to establish the learning and teaching of mathematics software: 00, do you think: it is wise to use the software in grade 12, except to introduce it to grade 1 students. Is there any improvement in the teaching and learning of mathematics since the introduction of the use of mathematics software?
10. Do you think the software makes students practice their skills effectively? l1. Should there be more time and emphasis on using the software. Is the teaching and learning of mathematics balanced in terms of theory and the use of new software. c) Competence (perceptions of competency levels. Using the software helps students to be competitive when they are with other students from neighboring schools.
Can the student do RSC after completing 12th with the experience he/she has. Do you think more emphasis should be placed on the theory of mathematics than on using the software itself?