A Critical Investigation of the Potential Impact of Artificial Intelligence Implementation on Health Insurance Claims Processing Performance - The Case of Health Insurance Companies in Harare. The study examined the impact of the use of artificial intelligence on the performance of health insurance claims processing.
INTRODUCTION
STUDY BACKGROUND
Investigating numerous claims manually exposes the health insurance firms to risks of approving erroneous claims that can cost the company large sums of money. These health insurance companies have the responsibility to ensure that the claims that go through their strict screening.
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
There is a need to automate the processing of multiple claims that are submitted by multiple service providers such as public and private hospitals as well as private surgeries. Some claims will contain errors, while some may be misleading, so they will need to be examined carefully and on an ongoing basis so that the company can save money by not processing false or erroneous claims.
RESEARCH AIM AND RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
Major Research Questions
Hypothesis
SCOPE OF THE STUDY
LIMITATION OF THE STUDY
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE RESEARCH
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
DISSERTATION OUTLINE
Chapter four provides a systematic approach to the research findings and an analysis of the study findings, guided by the research questions. Last but not least, chapter five will contain a research conclusion and provide recommendations for the research problem.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
The third chapter will address the research methodology, it covers the design of the research, the philosophy and research approach used by the researcher.
INTRODUCTION
THE RESEARCH STRATEGY
DEFINITION OF THE PHENOMENON
Artificial Intelligence
AI is the part of computer science that focuses on machine learning and enables software to solve problems in a manner similar to human intelligence (Loh, 2018). Artificial intelligence is associated with terms such as expert systems, cognitive science, machine learning, artificial neural networks, systems theory, heuristics and algorithms.
Expert Systems
AI is basically the ability of machines to mimic the functions of the human mind. Artificial intelligence encompasses a wide range of methods and technologies that make software smart enough to draw on data to autonomously control machines, produce forecasts or derive actions (Müller, 2015).
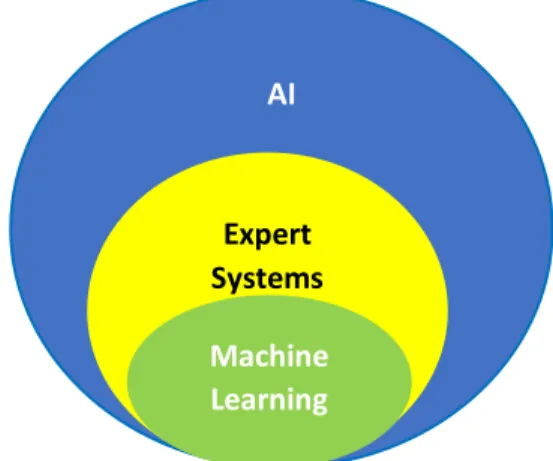
UNDERPINNING THEORY
Cognitive Learning Theory
It seems that artificial intelligence is evident in the healthcare service domain, where smart software and hardware are being used to diagnose chronic diseases like cancer, diabetics, while autonomous vehicle controls in cars are now current and perform many physical tasks that were performed by humans with intelligence is almost a common trait in many business environments. Less well known are the AI applications in the local health insurance industry in a Zimbabwean context and it is the purpose of this research to examine the potential impact that this artificial intelligence and its other associated technologies can have in the health insurance claims processing function. Cognition has a wider application in the medical field to try to understand medication errors and find lasting solutions (Erb, 2016).
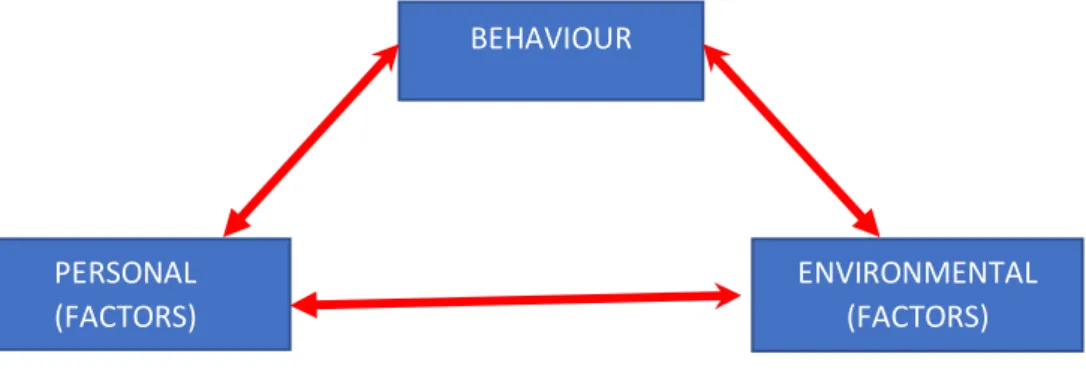
Systems Theory
CLASSIFICATION and TYPES OF AI
The next artificial general intelligence (AGI) also known as hard AI is that type of AI that is as capable as a human being. The emphasis of these classifications or types of AI is to give us a picture of how the technology is developing and where we are with the development currently. Confirming that technology still doesn't have to mimic the human brain, except to do some things that a human being does.
IMPORTANCE OF THE SUBJECT
By continuously reading this data, the system learns and has more knowledge about a beneficiary (Bennett and Hauser, 2013). The ASI is AI, where the system has surpassed humans in almost everything, according to (Akman & Backburn, 2000). Erb (2016) goes on to say that at the same time it has become clear that the complexity of human cognition cannot easily be captured in its entirety in programming logic.
PRESENTATION AND DISCUSSION OF MODELS & MAJOR THEORETICAL
- Anomaly detection model (ADM)
- The Theory of Mind
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
Data mining methods are the core of the integrated information technology software packages sometimes called Business Intelligence (BI)” (Nasiri and Arab, 2015). In this connection, health insurance companies should invest in the collection and storage of data in their electronic form. In the early 21st century, existing AI research was aided by the concepts of processing large-scale datasets using statistical methods called data mining and machine learning (Erb, 2016).
DISCUSSION OF CONTRADICTIONS IN THE RESEARCH AREA
Supervised and unsupervised Methods
They argue that unsupervised learning methods are applied when no prior information about the dependent variable is available for use (Nasiri and Arab, 2015). Nasiri and Arab (2015) say that supervised methods are mostly used for classification and prediction purposes, including traditional statistical methods such as regression analysis and neural networks. While unsupervised methods are mostly used for description, including association rule extraction, such as the Apriori algorithm, and segmentation methods such as clustering and anomaly detection.
DISCUSSION OF KEY VARIABLES/DIMENSIONS
- The role of Executives
- Artificial Intelligence Implementation & Adoption
- Computing power & Infrastructure
- Data formats & Readiness
- Barriers, Skills & Talent pool
- AI in Health insurance
- AI & Business Strategy Alignment
Lauterbach and Bonim (2016) cite the need for companies to understand the competitive landscape, evaluate risk, identify controls, and build organizational talent and resilience to deploy the right strategy and governance around this technology. Healthcare fraud and losses from misuse represent tens of billions of dollars annually in many countries. They emphasize the need to understand how AI integrates or could integrate with current overall business strategy through research and development (R&D).
LITERATURE SYNTHESIS & CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Literature Synthesis
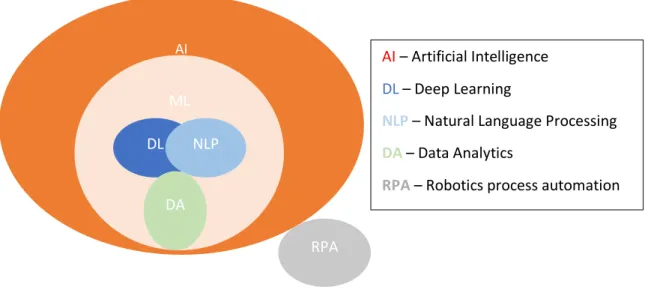
According to Ortega, Ruz and Figueroa, (2006), fraud and corruption in the healthcare industry can be grouped into illegal activities related to affiliates, medical professionals, staff and managers and suppliers. Most agree that AI as a system consists of ES components and within it, ML components and also deep learning technologies as depicted in Figure 2.3. Agile decision making is the rule of the game in this volatile environment; therefore, it requires business management, executives and information systems leaders to be on the lookout for tools that can enable dual and faster decision-making.
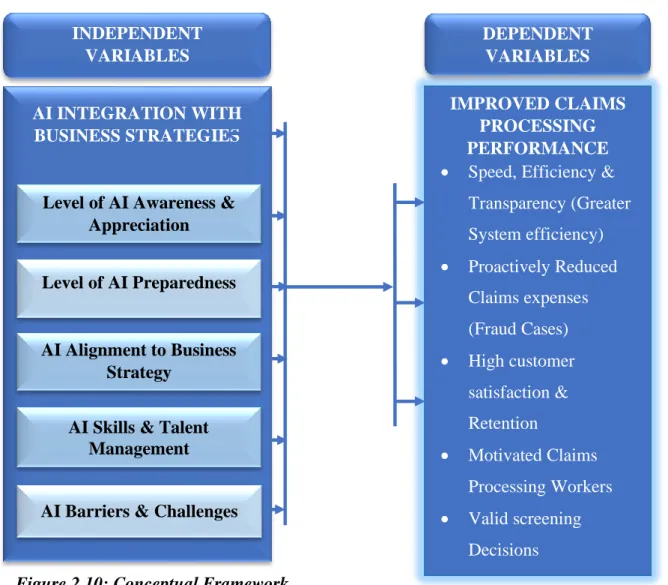
Conceptual Framework
CONCLUSIONS
INTRODUCTION
RESEARCH PURPOSE
RESEARCH DESIGN
RESEARCH PHILOSOPHIES
RESEARCH PARADIGMS
METHODOLOGY
APPROACHES
The main reason for adopting the deductive approach was that it is ideal for larger samples and supports quantitative data. An impartial methodology was used as the researcher used a hypothesis to assess the role/impact of AI on health insurance claim processing.
RESEARCH STRATEGIES
DATA COLLECTION INSTRUMENT
INSTRUMENT DEVELOPMENT
New Instrument – This option requires the researcher to develop a new instrument that would not have been used before. This study used an adaptive approach, the researcher designed a questionnaire but borrowed the layout that had already been tested. To improve the validation of this instrument, the researcher had to pilot test it on a group of first-year MBA students.
POPULATION AND SAMPLING
Adapt – This option involves borrowing and adapting an instrument previously used by another researcher to fit your context. A researcher can borrow from more than one instrument and adapt it to his context. However, choosing this option requires the researcher to conduct a pilot test to validate the instrument.
CREDIBILITY ISSUES
ETHICAL ISSUES
CHAPTER SUMMARY
The study explains the meaning of the answers given by the participants according to the instrument used. Some statistical analyzes of the processed data were done using various tests such as normality tests, correlation and regression tests. Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS) software was used to process and present the collected data.
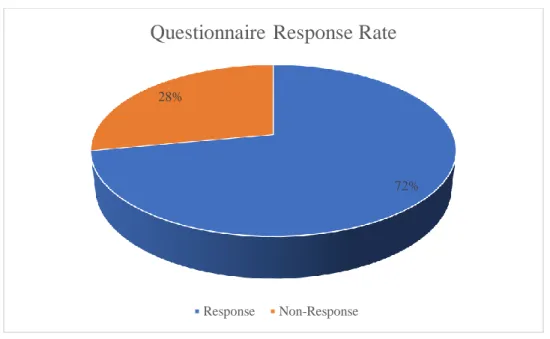
THE RESPONSE RATE
This chapter presents the questionnaire response rate, reliability and validity tests, and normality tests. The chapter provides a discussion of the study's findings related to each objective as described in the first chapter.
DEMOGRSPHICS
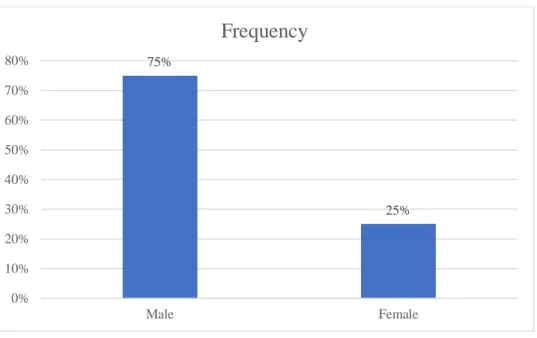
- Gender of Respondents
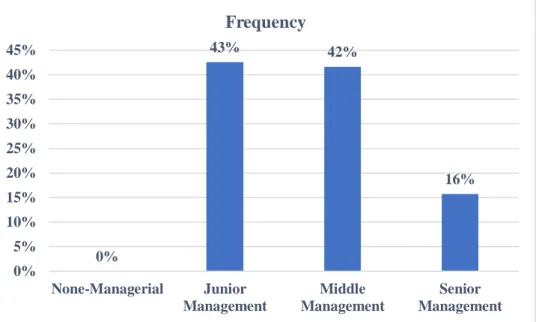
- Position of Respondents in the Organisation
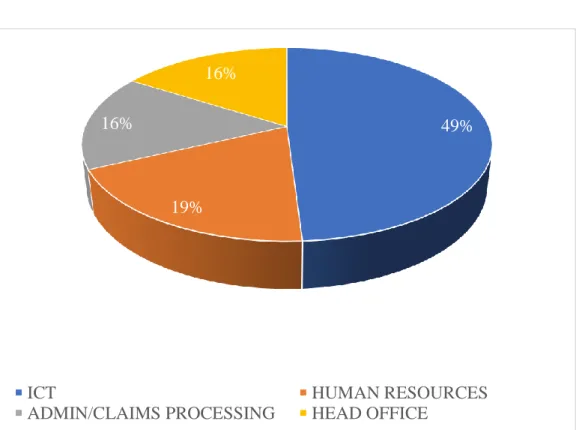
- Departments of Respondents
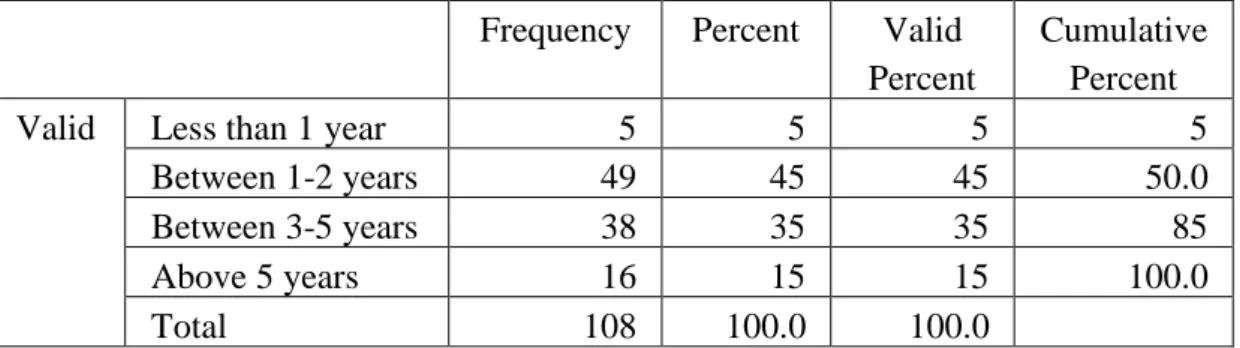
- Length of Service of Respondents in the Organisation
The table above shows that 45% of the participants have spent between 1-2 years in the organization, while 35% have spent 3-5 years in the organization, which means that these respondents at least value the operation of the organization. Only 5% were employed in the organization for less than 1 year, while 15% have been in the organization for more than 5 years. The respondents' service level distribution shows that the respondents have a good knowledge of the organization.
RELIABILITY TESTS
The figure above shows that most respondents came from the ICT department at 49%, followed by Human Resources at 19%, 16% from administration/claims processing and 16% from head office. All variables were greater than 0.7, meaning that the variables were valid and reliable to conduct the study. In addition to the Cronbach Alpha values, the investigator conducted a pilot study to test the instrument before using it for the actual data collection of the study.
NORMALITY TESTS
CORRELATIONS ANALYSIS
The table above shows that the level of AI readiness has a statistically significant correlation that is moderate and positive with the effects of AI on claim processing performance given by Sig. This variable shows a statistically significant correlation that is strong and positive between this variable and the effects of artificial intelligence on claim processing performance given by 0.849; p=0.000. The results show that removing potential barriers to the introduction of artificial intelligence can have a positive impact on the performance of claims processing.
REGRESSION ANALYSIS
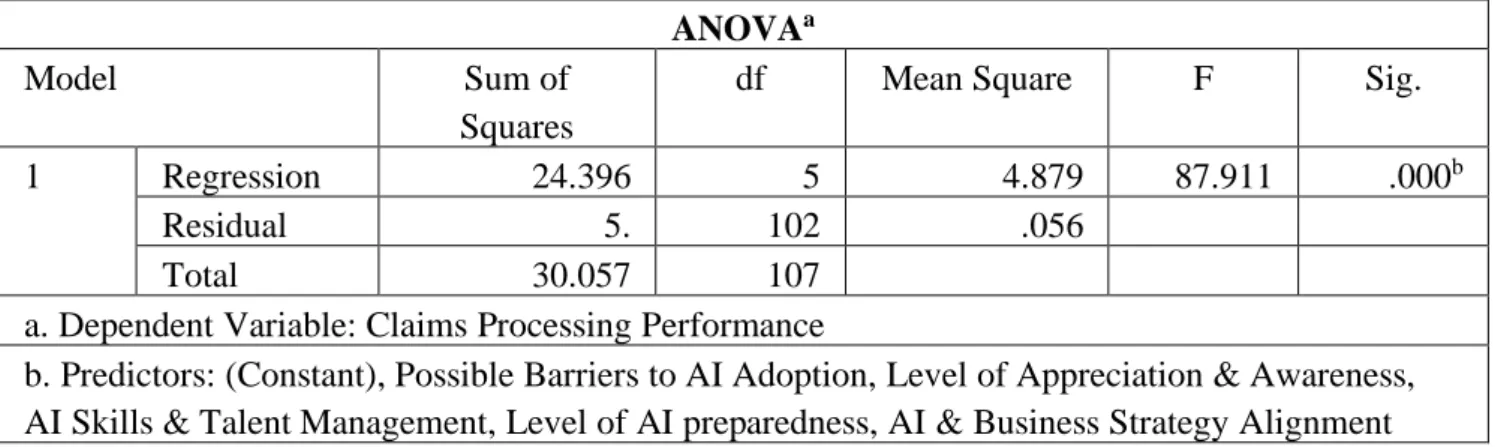
The fit of the model shows that the potential barriers to AI adoption, the level of respect and awareness of AI, the skills and management of AI talent, and the level of readiness and alignment of AI and business strategy are sufficiently suitable to predict the effects of AI on claims processing performance, such as given by ( F = 87.911; p = 0.000). This means that the AI adoption variables used in this study statistically and significantly predict the impact on health insurance claim processing performance. The beta coefficients show that potential barriers to AI adoption have the largest contribution and statistical significance in explaining the contribution of factors to the effectiveness of AI in health insurance claims processing performance as given by (β=0.476: p<0.01).
HYPOTHESIS TESTING
Hypothesis Testing
CHAPTER CONCLUSION
INTRODUCTION
ACHIEVEMENT OF RESEARCH AIM & OBJECTIVES
- Level of AI Appreciation & Awareness
- Level of AI Preparedness
- AI Skills & Talent Management
- AI & Business Strategy Alignment
- Potential Barriers to AI adoption
Because of this, we can claim that the research has achieved the second objective. Findings on the alignment variable of AI and business strategy showed that the variable has a strong and positive statistically significant correlation between it and the effects of AI on claim processing performance. The fifth objective showed the inferential statistical results that the identified potential barriers to the adoption of artificial intelligence have a statistically significant correlation, which is strong and positive on the potential barriers to the adoption of artificial intelligence and the effects of artificial intelligence on claims processing performance given by 0.849; p=0.000.
CONCLUSION
- Level of appreciation and awareness
- Level of AI preparedness
- AI skills & talent management
- AI & business strategy alignment
- Potential barriers to AI adoption
Therefore, we can claim that the goal of the research was successfully achieved, as it was possible to establish that the introduction of artificial intelligence has a positive effect on the success of processing health insurance claims. The study concluded that the level of AI readiness is an important factor and is likely to have a positive impact on the performance of health insurance claims processing. The study also found that the Zimbabwean health insurance industry has adequate ICT infrastructure to some extent to positively impact claims processing performance in the industry.
CONTRIBUTION
- Theoretical Contribution
- Methodological Contribution
- Policy Recommendations
- Managerial Recommendations
These seminars will provide the decision makers with an understanding of the benefits and costs of AI technologies associated with the technology. This will help raise AI awareness among the management and executives who are the decision makers.
GENERALISATIONS OF FINDINGS
RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
AREAS OF FURTHER RESEARCH
2019) “Artificial Intelligence as a Growth Driver for Healthcare Startups:” pp. 2018) “Artificial intelligence in medical practice: the question for the answer?”, American Journal of Medicine. Machine Learning – this is an application of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn and improve by using algorithms and other AI components such as data mining. I am an MBA student at the University of Zimbabwe and am currently doing a dissertation on “A Critical Examination of the Potential Impact of Artificial Intelligence Adoption on Health Insurance Claims Processing – The Case of Health Insurance Companies in Harare.”