This study explored the perceptions of twenty managers in the City of Cape Town regarding the challenges facing talent management. The study revealed a number of challenges facing talent management in the City of Cape Town.
LIST OF APPENDICES
Introduction
This chapter provides a brief background of the study followed by a discussion of the research problems and a justification for the study. An overview of the methodology is provided and the significance and limitations of the study are discussed.
Background to the study
To provide services to the public in an efficient, successful and timely manner, the civil service must effectively manage the talent of its employees. The chapter also provides definitions of key concepts and outlines the structure of the dissertation.
Problem statement
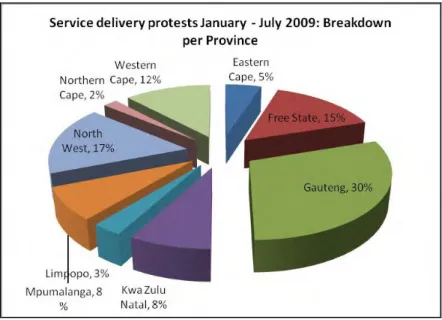
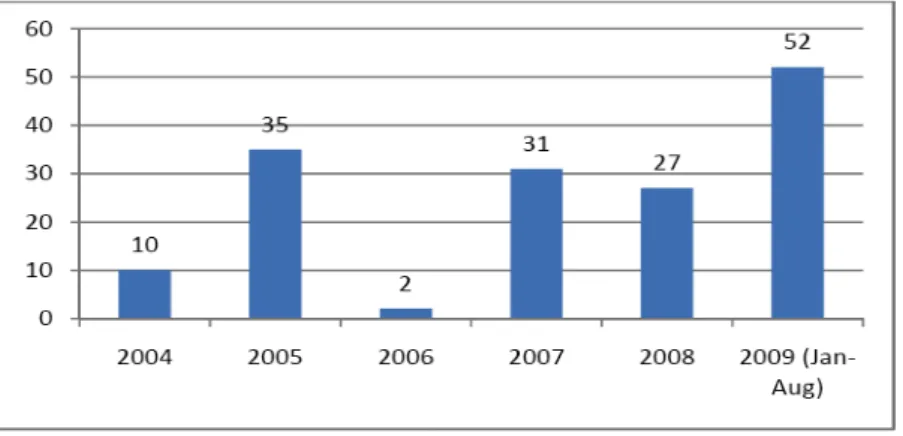
Problems of turnover, turnover intentions, lack of employee recognition and employee disillusionment continue to plague this municipality, slowing the delivery of basic services to the public at a time when service delivery protests are on the rise (the city, like other municipalities in South Africa that affected by the service delivery protests between January and July 2009 (see Figure 2.2 in Chapter 2 of this study) In addition, the city spends significant amounts of money on recruitment and selection processes to replace employees who leave.
Aim of the study
Objectives of the study The objectives of the study were
Research questions
Definition of key terms
Overview of methodology
Robson defines a case study as "a strategy for conducting research that involves the empirical investigation of a particular contemporary phenomenon in its real-life context using multiple sources of evidence". The case study strategy has considerable ability to generate answers to the question "why?", as well as to.
Sampling
For this study, semi-structured interviews and document analysis were the main sources of data.
Ethical considerations
Significance of the study
Demarcation of study
Organisation of the dissertation
The research questions and objectives are discussed in terms of the findings of the study. The chapter will also attempt to link the findings to the literature that was read through in chapter three of the study.
Conclusion
Introduction
South Africa
These challenges, which required reforms, included, among others, the lack, by a significant part of the population, of access to basic services such as water (10.1% of residents in urban areas and 39.2% in rural areas). and lack of proper sanitation (25.8% unavailability in urban areas and 75.8% in rural areas). The issue of the capacity of the Public Service to improve as well as to accelerate the pace at which it is providing services to the citizens of the country has been put in the center of attention in recent years.
Local government legislative framework
Below is a brief discussion of the three different types of municipalities in South Africa. Areas that fall outside the six metropolitan municipal areas are divided into local municipalities.
The constitution
The Constitution requires that the public service must be broadly representative of the people and that it must use personnel practices that develop the potential of civil servants. Public administration should be broadly representative of the South African people, with recruitment and staffing practices based on competence, objectivity, fairness and the need to redress past imbalances in order to achieve broad representation.
SA public service staff turnover rates
The needs of the people must be addressed and the public must be encouraged to participate in policy making. To maximize human resources, good practices in human resource management and career development should be cultivated.
Vacancy rates in the South African public service
It is clear from the above statistics that South Africa's civil service is not exempt from the raging war for talent, which is a global phenomenon. In fact, the war for talent is becoming increasingly intense in South Africa, which is in the midst of a skills crisis.
Talent management landscape in the South African public service
The public service inherited by the new South African government in 1994 was designed to promote and protect the social and economic system of apartheid and was oriented to serve the material needs and interests of the minority. A recent review by the DPSA of the extent to which the HRD Strategy has had an impact on baseline conditions provides a useful indicator of progress made on the key elements of HRM.
Public service reform efforts review
The lack of such actions damages the implementation of the development function entrusted to the public service (PSC 2005:19). Human resources reform should ensure that gender, racial and cultural diversity is fostered in the public service.
Background to the City of Cape Town municipality
The City of Cape Town had 24 352 employees across all departments at the time of the field study (see Appendix E). The following (Figure 2.3) is a diagrammatic representation composed of the images shown in Appendix E of the City of Cape Town Staff Profile.
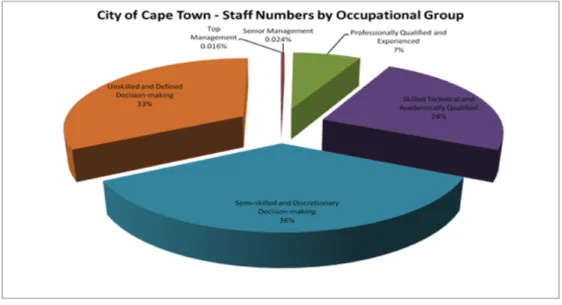
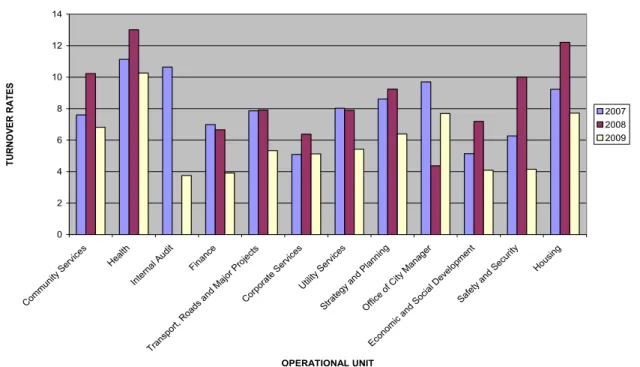
Staff turnover rates at the City of Cape Town
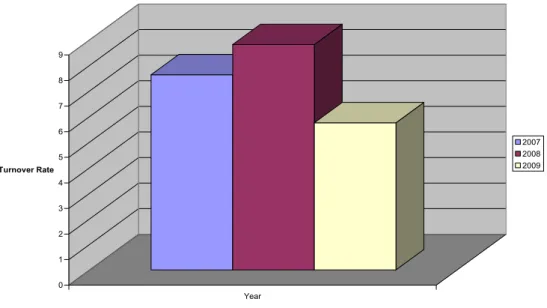
A closer look at these figures suggests a rather bleak picture for the city of Cape Town. It is very clear that the City of Cape Town experienced high rates of staff turnover in 2008.
HR functions and talent management initiatives at City of Cape Town The City of Cape Town has a Training and Development Department, which operates
The study would be so successful if it could gain access to the reasons for this turnover rate. Again, the reasons for this remain to be determined as the study was unable to gain access to the reasons for this departure.
Conclusion
Some of the areas of interest in the document will be highlighted under the document analysis heading in Chapter 4 of this study.
Introduction
Definitions of talent management
The definitions appear to be in three distinctive meanings of talent management (Lewis & Heckman, 2006:140). In the first perspective of talent management definitions; the focus is on the concept of talent pools.
Current state of TM definitions
The basic proposition here is that calling these approaches "talent management" raises the same problems as the first perspective. Lewis and Heckman (2006) argue that the third perspective is perhaps the most problematic.
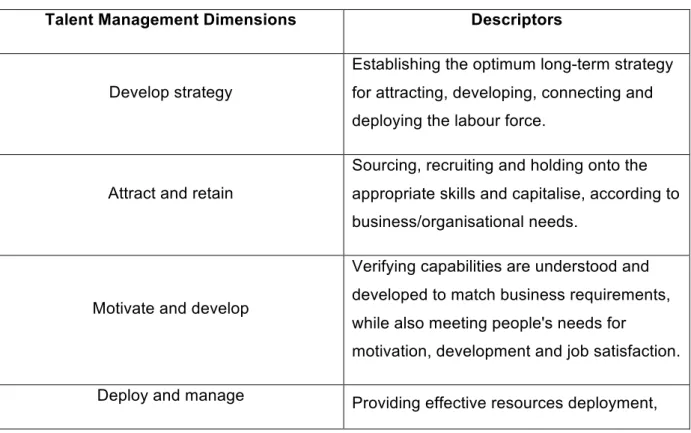
Talent management strategies
The importance of recruitment and selection has never been more necessary than in the realm of talent management. Meyer & Botha (2004) state here that the organization's performance management system should highlight the application of talent management in the workplace.
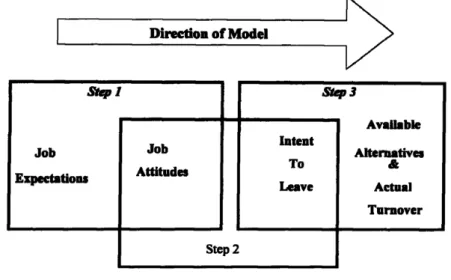
Turnover
- Factors contributing to turnover
- Intention to turnover
This section discusses turnover intention (which is an attitude), which has been found to be a precursor to actual turnover (which is behavior). Therefore, an employee's turnover intention is his/her individual thoughts to leave the organization.
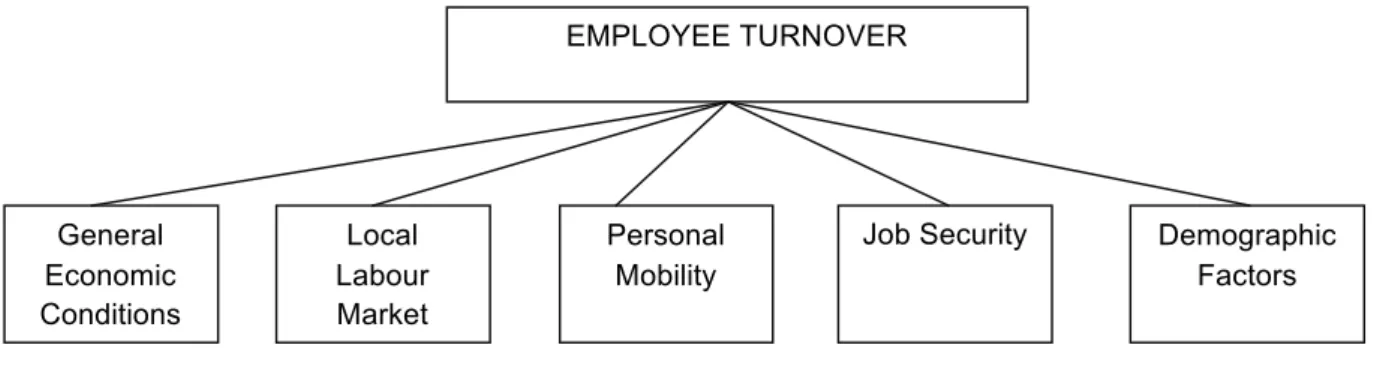
Theories of turnover
- Psychological theories
- Economic theories
- Sociological theories
Violations of the psychological contract can have dire consequences, such as employees leaving their organizations. Economists explain the desire of employees to leave or stay in terms of the ratio of benefits to costs of staying versus leaving the organization.
Pay satisfaction
Discrepancy theorists, on the other hand, believe that pay satisfaction is a function of the employees' comparison between what exists at work and what they seek in the job (Locke, 1969; Porter, 1961). In conclusion, wage satisfaction occurs when current wages are equal to or higher than what one expects to be paid.
Motivation
- The concept of motivation
The concept of motivation is certainly one of the most used in the world today. The human resources approach continues the concepts of the economic man and the social man to introduce the concept of the whole person.
Effective management and motivation
It is important for managers to fully understand the concept of motivation in the management of talent in their organizations, especially in public sector organizations where the turnover rate is always high. These motivation researchers believe that it is imperative for managers and supervisors to understand how to motivate their employees because high levels of motivation are very important contributors to high performance.
Job satisfaction
Job satisfaction is defined more specifically in the literature and various theorists have developed their own workable definitions. Research on job satisfaction continues to emerge and the results are often valued for both humanistic and financial benefits.
Organisational commitment
Involvement, which refers to a willingness to make significant efforts on behalf of the organization; and. Many researchers have considered organizational commitment as a factor that promotes an individual's attachment to the organization.
Employee engagement
The distinction between employee engagement and other related constructs is the predictive nature of engagement. Research by the Corporate Leadership Council shows that there is a strong relationship between employee engagement and employee performance and retention.
Tenure
The Corporate Leadership Council (2004) considers employee engagement as the extent to which employees commit to something or someone in the organization and how hard they work and how long they stay because of that commitment. Management characteristics are strongly represented among the main drivers of both improved performance and intention to stay (ibid).
Talent management challenges
Current approaches to talent management
Succession planning and management (SP&M)
- Reasons for succession planning & management systems
- Succession planning implementation
This scholar argues that the first excellent step towards adopting a succession planning process, and a method that will truly reveal the organization's situation regarding the aging workforce, is to collect data as illustrated in the Figure 3.7 below. A comprehensive strategy for implementing succession planning involves a series of strategies and tactics that together form an overall project plan, Figure 3.8 below.
Assess future service needs
Identify critical positions and high-potential employees
Identify competencies
Do a complete gap analysis
Select training and development activities
Conduct management training
As contributors to the succession plan, managers must work in collaboration with others in the organization to do the following: identify key replacement needs and the high-potential people and critical positions to include in the succession plan; clarify current and future work activities and work results; compare current individual performance and future individual potential; and establish individual development plans (IDPs) to prepare replacements and develop high-potential employees.
Implement development strategies and tactics
Monitor and evaluate
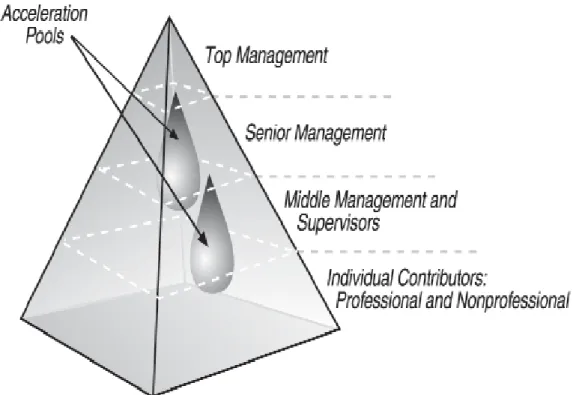
- Acceleration Pools
- Coaching and mentoring
- Conclusion
- Introduction
- Research design and methodology
- Research strategy and design
- Sampling
- Document analysis
- Content analysis
- Access and ethics
- Profiles of participants
- Limitations to study
- Conclusion
- Introduction
- Attraction of talent
- Talent loss
- Reasons for job turnover
- Career management
- Talent retention
- Talent identification
- Challenges to talent management in the public service
- Consolidation of the perceived challenges with the literature
- Chapter summary
In total, 60% of the survey participants cited frustration as the main reason for the loss of talented employees at the City of Cape Town. The size of the city of Cape Town makes it difficult to effectively implement talent management.
6 Chapter 6 – Conclusions and recommendations
Conclusions
The small municipality has the challenges that the larger municipality has because, like the city of Cape Town for example, it is so big, it has 23,000 people, we have so many depots and workstations, you have a huge structure. so the integration and interaction at the various levels is very bureaucratic...". What emerges from the above answers is the fact that bureaucracy in the City of Cape Town is exacerbated by the size of the organization and this makes the implementation of talent management prone to problems.
Recommendations
Within the talent management domain, City of Cape Town HR professionals must be active in the management of this process. The study also recommends that the City of Cape Town be divided into multi-talent pools as it has been observed that its size hampers the leadership of the talent management domain.
7 Chapter 7 - Study summary
The study was also handicapped by the researcher's inability to access causes of turnover in Cape Town City. The study looked at the perceived challenges for talent management in the City of Cape Town Municipality.
APPENDICES
APPENDIX A: INTRODUCTORY LETTER
APPENDIX B – INTERVIEW GUIDE
In your opinion, what are the pull factors that other potential employees would consider before joining your organization. In your opinion, what are the challenges facing talent management in the public service, particularly in your organization.
APPENDIX C – CITY OF CAPE TOWN APPROVAL LETTER
APPENDIX D – CITY OF CAPE TOWN RESEARCH PARTICIPANTS LETTER
APPENDIX E – CITY OF CAPE TOWN STAFF TURNOVER RATES
APPENDIX E CONTINUED
APPENDIX E CONTINUED
APPENDIX F – CPUT RESEARCH ETHICS COMMITTEE FORMS
Registration of Topic for Dissertation / Thesis
Will you tell participants that they can withdraw from the research at any time and for any reason. Will you debrief participants at the end of their participation (ie give them a brief explanation of the study).
APPENDIX G – CITY OF CAPE TOWN STAFF PROFILE