The problem is that we do not know the extent of the perceived consequences of techno-stress and it is not clear what the perceived psychological and emotional consequences of techno-stress might have on the academic performance of higher education students. It was recommended that universities of technology like CPUT should design a program to help students manage technostress.
INTRODUCTION
- Introduction
- Overview
- Background to the Research Problem
- Statement of the Research Problem
- Research Questions
- Aim and Objectives
- Rationale
- Research Methodology
- Significance and Contribution of Study
- Delineation of Research
- Thesis Structure
What are the effects and implications of techno-stress as perceived by students on their studies. Determine the potential causes of techno-stress as perceived by students at a technological university.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Introduction
- Understanding the Stress Concept
- Techno-stress
- Assessing Techno-stress
- Elements of Techno-stress
- Techno Overload
- Techno Invasion
- Techno Complexity
- Techno Insecurity
- Techno-uncertainty
- Determinants of Techno-stress
- Environmental Factors
- Social Factors
- Perception
- Recognised Implications of Techno-stress
- The Effects of Techno-stress
- The Impact of Techno-stress
- Physical Implications
- Psychological Implications
- E-environment
- Different Learning Environment Characteristics
- Online and Electronic Learning
- Higher Education and Technology Adoption
- Information Communication Technology (ICT)
- University of Technology context
- Campus-based blended learning
- Techno-stress theory
- Summary
Fuglseth and Sørebø highlight five mechanisms of techno-stress, which have also been identified as techno-stress creators. 26 Figure 1: Creating conditions, outcomes and inhibitory mechanisms of techno-stress (Tarafdar, Tu & Ragu-Nathan, 2011).
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- Introduction
- Interpretive Paradigm
- Qualitative Research
- Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
- Case Study
- Exploratory Case Study
- Population Type
- Sampling
- Data Collection
- The interview processes
- Focus Group Interviews
- Observation
- Data Analysis
- Validity, Reliability and Triangulation
- Limitations
- Ethical Considerations
- Summary
One of the essentials of qualitative studies is the comprehensiveness of perception it gives to the research (Rubin & Babbie, 2010). Anonymity and confidentiality were applied in the research and participant data was protected and used for the purpose of the study.
PRESENTATION OF THE RESEARCH FINDINGS
Introduction
History of the Cape Peninsula University of Technology
- The Cape Technikon
- The Peninsula Technikon
- The Merge: Cape Peninsula University of Technology
However, this changed in 1987 when the institution allowed the removal of a government regulation that allowed students of color to enter the institution. Later, the institution unveiled a new institutional structure that included multiple faculties (six in total), a new mission and vision, and a new institutional identity. Around the 1970s, the status of the organization was changed to Higher Technical Education and later renamed Peninsula College for Advanced Technical Education.
In 1997, the institution underwent a reorganization of its academic program to include engineering, economics and science. The merger of Cape Technikon and Peninsula Technikon took place on 1 January 2005. The two merged institutions became known as Cape Peninsula University of Technology. With more than 30,000 students, the institution is today called the largest technological university in the south of the country.
The name Cape Peninsula University of Technology was approved by the Minister of Higher Education in 2003 (CPUT, 2014). Today, the Cape Peninsula University of Technology's vision is to be "at the heart of technology education and innovation in Africa, with a mission to build" a university that is highly efficient, sustainable and environmentally conscious and will be recognized for the high quality of IT teaching and learning and the relevance of the curriculum; create a vibrant learning environment for students; and promote innovation in aspects of work” (CPUT, 2014:1). The Cape Peninsula University of Technology implemented a major 10-year academic plan called Vision 2020, in which the institution seeks to improve research and put innovation at the forefront.
Part 1: Focus Groups
- Result Analysis
- General themes insights derived from the focus groups
- Summary of themes
- Further responses from the interviewees
- Summary of the Interviews
Most of the participants expressed the same meaning of what techno-stress means to them. The majority of respondents also said they felt feelings of anger as a result of techno-stress. All the respondents in this group believed that slow internet, faulty devices and malfunctioning devices are the causes of techno-stress.
About the influences of techno-stress, all the participants said that it is a bad result; most of the participants from this group also said that the techno-stress they experience when dealing with technology is anger. The group also believes that the impact of technostress is negative for their academic performance due to frustration. From the influences of techno-stress, which they experience on their study, the majority of the participants of this group also said that the kind of techno-stress they experience when dealing with technology is anger.
All participants also believe that techno-stress impact is negative for their academic performance due to frustration. Theme 2: Impacts and negative implications of techno-stress on academic performance (See tables in Appendix I). Respondent GB4 stated “for me, anger is the kind of techno-stress I encounter when dealing with technology.
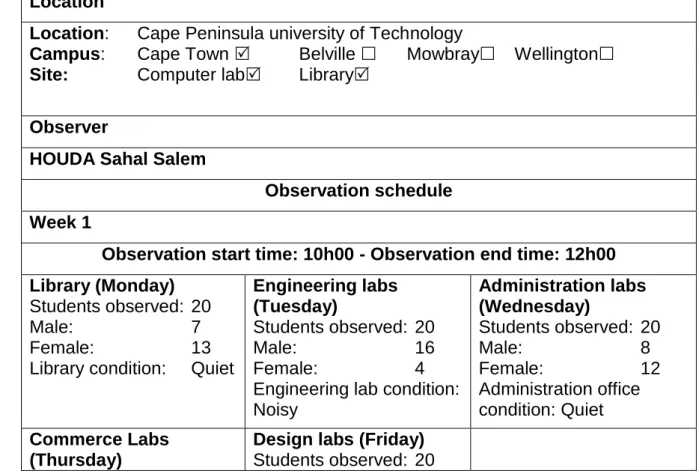
Part 2: Observation
- Schedule of Observation
- Methods
- Site observation form
I can't survive without technology, so techno-stress, I accept it as it is, but don't stay away from technology.” From the respondent data, it is clear that students who encounter problems when using technology are likely to experience techno-stress It is impossible to avoid techno-stress when the technology stops working, resulting in students getting stressed.
From the students' responses, it is evident that one of the main symptoms of techno stress they experience is irritability. To explore the perceptions and implications of techno-stress among students experiencing techno-stress in a University of Technology, the researcher observed students in four (4) locations (laboratories in engineering, commerce, design and administrative buildings). The study documented undergraduate and postgraduate students to discern the behavior they exhibit related to techno stress.
Factors influencing technostress in academic achievement Types of technostress in dealing with technology The impact of technology on studies: negative or positive. Negative Perception Felt With Problems With Computers Student Reaction When A Problem Occurs While Using Computers Students feel about new updated technology. Factors Influencing Technostress in Academic Achievement Types of technostress in dealing with technology.
Results
Psychologically, the students observed showed a lack of control over their devices as they switched between devices (computers and mobile phones). Physical and facial expressions were observed showing frustration, irritability and anger, with students feeling unhappy with the speed of the internet as they felt that their work would not be done on time and that they were unable to improve the situation . Physically, the students were visibly tired and usually stretch their backs to release pent-up pain.
The insufficient number of computer workstations in the laboratories also caused stress because they had no access to their work. Finally, the corrupt access to the systems for various services also caused stress for the students, as they could not log in to their access point and also could not consult their student board. The participants' observations showed that the students were apparently very happy when their work was submitted to their respective teachers via email and it also seemed time-saving to them as they could complete and submit more than one assignment at a time.
They performed physical damaging actions on the computer while trying to shake it like a human and also looked at the computer from corner to corner as if it would tell them what the problem is. Most of the students observed were not very computer literate, as they were constantly looking around to see if anyone could help them. 77 students while constantly and enthusiastically sharing their knowledge about the new and updated features of the application with their peers.
Summary of the Observations
DISCUSSION
- General Insights
- Discussion of Results from Interviews
- Comparisons with existing Research and Theory
- Adapted diagram for the present study
It can be argued that the influence of techno-stress is directly linked to a user's loss of concentration as they are stressed about technology. The results of techno-stress can be both positive and negative and can have an impact on students' academic performance. It can be argued that the common perception of techno-stress usually negatively affects a user's academic performance.
This analysis yielded key themes that were pertinent to the participants' understanding of techno-stress. The themes of techno-stress were previously studied in the field of education by Yuvaraj and Singh (2015). Techno-stress sufferers can also experience poor health, negative self-esteem and even depression (Erasmus, 2014).
Educational technologist should encourage an understanding of techno-stress to help increase meaningful use of technology. Therefore, they end up experiencing loss of concentration on their studies due to the techno-stress. The research findings resonate with the techno-stress theories of Tarafdar, Tu and Ragu-Nathan (2011).

CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Introduction
Summary of the Research
The results and findings of interviews conducted at Cape Peninsula University of Technology were presented in this section. Information collected from the participants was clustered and provided the choruses that appeared and helped develop and integrate the results of the surveys. This section attempts to answer the main and sub-questions of the study mentioned earlier in this chapter.
Addressing the Research Questions
When technology does not meet students' needs or expectations, the situation causes them to be exposed to several types of techno-stress. It is clear that students in electronic environments or in universities face patterns of anger when exposed to technical stress. Students also experience techno-stress, especially developing nervousness after facing uncertainty with technology.
The potential cause behind techno-stress on students stems from the malfunctioning of the technology devices that students constantly use at school. It was found that broken computers, disruption of the Internet, the insufficient number of computer workstations in laboratories, the corrupt access system to different services, and complications of access points, are the primary reasons behind techno-stress experienced and perceived by students from their study activities. Furthermore, students expressed their negative view about techno-stress as they usually perform under conditions that demoralized them.
Technostress brings nervousness and frustration, which automatically jeopardizes their ability to work and, above all, their final result. Students were able to manage their techno-stress largely by seeking help from their respective friends with more knowledge about the problem and from help desk staff where necessary. On the other hand, students physically face various problems associated with technostress, such as headache, back pain, faster heart rate, dizziness, sweaty palms, faster blood circulation, body weakness.
Limitations of the Research
Recommendations
Conclusion and Further Research
Examine the impact of basic techno-stress training on university of technology students to overcome academic performance. The impact of technical stress and organizational support on user satisfaction in government organizations: A proposed model and literature review. A Comparison of Teachers' Perceptions of Techno-Stress Experienced Against Technology Used by Teachers in Primary Education in a South.
Illustrating the holistic effects of neuroscience and self-reported data in the context of techno-stress research. The perceptions and implications of technostress in an e-learning environment: an exploratory case study. 141 APPENDIX J: ACCUMULATIVE TYPES AND CAUSES OF TECHNOSTRESS AT HIGH INSTITUTION OF TECHNOLOGY FOR THEME 3.
